Abstract
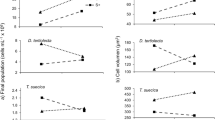
To understand the tolerance mechanisms of dark septate endophytes (DSE), Exophiala salmonis, to CuO nanoparticles (CuO-NPs) with different sizes (40 and 150 nm), we investigated the morphology, antioxidant response, Cu subcellular distribution, and the melanin gene expression in the mycelia of E. salmonis. E. salmonis was cultured in liquid and solid media under the stress of increasing CuO-NP concentrations (0, 50, 100, 150, and 250 mg/L). Results showed that (1) E. salmonis showed good CuO-NP tolerance, and the tolerance to CuO-NPs at 150 nm was stronger than that at 40 nm. A large number of agglomeration structures were observed on the mycelia surface with the exception of 50 mg/L CuO-NPs with a diameter of 150 nm. (2) CuO-NP stress significantly stimulated the production of antioxidant enzymes, particularly the CuO-NPs with small particle size (40 nm). (3) Cu uptaken by E. salmonis increased proportionally with the increase of CuO-NP concentration in the medium. More than 80% Cu was absorbed in cell wall of mycelia treated with a small particle size (40 nm). (4) FTIR analysis revealed that hydroxyl, amine, carboxyl, and phosphate groups were associated with CuO-NP binding regardless of particle size. (5) Fungal melanin content increased with the addition of CuO-NPs; the increase of melanin induced by CuO-NPs with small particle size (40 nm) was more significant. (6) The expression of 1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxynaphthalene reductase (Arp2) in the melanin synthesis pathway increased under the stress of CuO-NPs, and CuO-NPs with a small particle size (40 nm) caused a significant change in the expression level of Arp2 gene than those with a large particle size (150 nm). In conclusion, E. salmonis had a strong tolerance to CuO-NPs and mitigated the toxic effects of CuO-NPs through the antioxidant system, the expression of genes related to melanin synthesis, and the synthesis of melanin.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abdel-Kareem MM, Zohri AA (2018) Extracellular mycosynthesis of gold nan-oparticles using Trichoderma hamatum, optimization, characterization and antimicrobial activity. Lett Appl Microbiol 67:465–475. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.13055
Babele PK, Thakre PK, Kumawat R, Tomar RS (2018) Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce toxicity by affecting cell wall integrity pathway, mitochondrial function and lipid homeostasis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Chemosphere 213:65–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.09.028
Bakshi MS (2020) Impact of nanomaterials on ecosystems, mechanistic aspects in vivo. Environ Res 182:109099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.109099
Ban YH, Xiao Z, Wu C, Lv YC, Meng FK, Wang JY, Xu ZY (2021) The positive effects of inoculation using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and/or dark septate endophytes on the purification efficiency of CuO-nanoparticles-polluted wastewater in constructed wetland. J Hazard Mater 416:126095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126095
Berthelot C, Perrin Y, Leyval C, Blaudez D (2017) Melanization and ageing are not drawbacks for successful agro-transformation of dark septate endophytes. Fungal Biol 121:652–663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funbio.2017.04.004
Berthelot C, Zegeye A, Gaber DA, Chalot M, Franken P, Kovács GM, Blaudez D (2020) Unravelling the role of melanin in Cd and Zn tolerance and accumulation of three dark septate endophytic species. Microorganisms 8:537. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040537
Borgohain K, Singh JB, Rao MR, Shripathi T, Mahamuni S (2000) Quantum size effects in CuO nanoparticles. Phys Rev B 61:11093. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.61.11093
Cao GH, He S, Chen D, Li T, Zhao ZW (2019) EpABC genes in the adaptive responses of Exophiala pisciphila to metal stress, functional importance and relation to metal tolerance. Appl Environ Microbiol 85:e01844-e1919. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01844-19
Cervantes-Avilés P, Díaz Barriga-Castro E, Palma-Tirado L, Cuevas-Rodríguez G (2017) Interactions and effects of metal oxide nanoparticles on microorganisms involved in biological wastewater treatment. Microsc Res Tech 80:1103–1112. https://doi.org/10.1002/jemt.22907
Cordero RJ, Casadevall A (2017) Functions of fungal melanin beyond virulence. Fungal Biol Rev 31:99–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbr.2016.12.003
Cronholm P, Karlsson HL, Hedberg J, Lowe TA, Winnberg L, Elihn K, Möller L (2013) Intracellular uptake and toxicity of Ag and CuO nanoparticles, a comparison between nanoparticles and their corresponding metal ions. Small 9:970–982. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201201069
Dang C, Yang Z, Liu W, Du P, Cui F, He K (2018) Role of extracellular polymeric substances in biosorption of Pb2+ by a high metal ion tolerant fungal strain Aspergillus niger PTN31. J Environ Chem Eng 6:2733–2742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.04.005
Dimapilis EAS, Hsu CS, Mendoza RMO, Lu MC (2018) Zinc oxide nanoparti-cles for water disinfection. Sustain Environ Res 28:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.serj.2017.10.001
Długosz O, Szostak K, Staroń A, Pulit-Prociak J, Banach M (2020) Methods for reducing the toxicity of metal and metal oxide NPs as biomedicine. Materials 13:279. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13020279
Doyama K, Yamaji K, Haruma T, Ishida A, Mori S, Kurosawa Y (2021) Zn tolerance in the evergreen shrub, Aucuba japonica, naturally growing at a mine site, cell wall immobilization, aucubin production, and Zn adsorption on fungal mycelia. PLoS ONE 16:e0257690. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0257690
El-Argawy E, Rahhal MMH, El-Korany A, Elshabrawy EM, Eltahan RM (2017) Efficacy of some nanoparticles to control damping-off and root rot of sugar beet in El-Behiera Governorate. Asian J Plant Pathol 11:35–47
El Bialy BE, Hamouda RA, Abd Eldaim MA, El Ballal SS, Heikal HS, Khalifa HK, Hozzein WN (2020) Comparative toxicological effects of biologically and chemically synthesized copper oxide nanoparticles on mice. Int J Nanomedicine 15:3827. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S241922
El-Gendy MMAA, Ten NM, Ibrahim HAEH, Abd El-Baky DH (2017) Heavy metals biosorption from aqueous solution by endophytic Drechslera hawaiiensis of Morus alba L. derived from heavy metals habitats. Mycobiology 45:73–83. https://doi.org/10.5941/MYCO.2017.45.2.73
El-Mahdy OM, Mohamed HI, Mogazy AM (2021) Biosorption effect of Aspergillus niger and Penicillium chrysosporium for Cd-and Pb-contaminated soil and their physiological effects on Vicia faba L. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:67608–67631. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15382-4
Eisenman HC, Casadevall A (2012) Synthesis and assembly of fungal melanin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:931–940. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3777-2
El-Naggar NEA, Saber WI (2022) Natural melanin: Current trends, and future approaches, with especial reference to microbial source. Polymers 14:1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14071339
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.1985.tb00420.x
Gadd GM, de Rome L (1998) Biosorption of copper by fungal melanin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 29:610–617. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00260993
Gadd GM, Ramsay L, Crawford JW, Ritz K (2001) Nutritional influence on f-ungal colony growth and biomass distribution in response to toxic metals.FEMS Microbiol. Lett 204:311–316. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2001.tb10903.x
Gadd GM (2016) Fungi and industrial pollutants. Appl Environ Microbiol 99-125.https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-29532-9_5
Galindo TPS, Pereira R, Freitas AC, Santos-Rocha TAP, Rasteiro MG, AntunesF LI (2013) Toxicity of organic and inorganic nanoparticles to four species of white-rot fungi. Sci Total Environ 458:290–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.04.019
Galván Márquez I, Ghiyasvand M, Massarsky A, Babu M, Samanfar B, OmidiK GA (2018) Zinc oxide and silver nanoparticles toxicity in the baker’s yeast Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Plos One 13:e0193111. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0193111
García-Gómez C, Fernández MD, García S, Obrador AF, Letón M, Babín M (2018) Soil pH effects on the toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles to soil microbial community. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:28140–28152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2833-1
Gonzalez Mateu M, Baldwin AH, Maul JE, Yarwood SA (2020) Dark septate endophyte improves salt tolerance of native and invasive lineages of Phr-agmites australis. ISME J 14:1943–1954. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-02-0654-y
Hayat R, Din G, Farooqi A, Haleem A, Hasan F, Badshah M, Shah AA (2022) Characterization of melanin pigment from Aspergillus terreus LCM8 and its role in cadmium remediation. Int J Environ Sci Technol 1-10.https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04165-0
He C, Wang W, Hou J, Li X (2021) Dark septate endophytes isolated from wild licorice roots grown in the desert regions of northwest China enhance the growth of host plants under water deficit stress. Front Microbiol 12:522449. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.522449
Hou W, Ma Z, Sun L, Han M, Lu J, Li Z, Wei G (2013) Extracellular poly-meric substances from copper-tolerance Sinorhizobium meliloti immobilize Cu2+. J Hazard Mater 261:614–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.06.043
Hou L, Yu J, Zhao L, He X (2020) Dark septate endophytes improve the gro-wth and the tolerance of Medicago sativa and Ammopiptanthus mongolic-us under cadmium stress. Front Microbiol 10:3061. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.03061
La Rocca N, Andreoli C, Giacometti GÁ, Rascio N, Moro I (2009) Responses of the Antarctic microalga Koliella antarctica (Trebouxiophyceae, Chloro-phyta) to cadmium contamination. Photosynthetica 47:471–479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-009-0071-y
Mani D, Kumar C (2014) Biotechnological advances in bioremediation of heav-y metals contaminated ecosystems: an overview with special reference to phytoremediation. Int J Environ Sci Technol (tehran) 11:843–872. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0299-8
Jaiswal A, Verma A, Jaiswal P (2018) Detrimental effects of heavy metals in soil, plants, and aquatic ecosystems and in humans. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 37:183–197. https://doi.org/10.1615/jenvironpatholtoxicoloncol.2018025348
Juárez-Maldonado A, Tortella G, Rubilar O, Fincheira P, Benavides-Mendoza A (2021) Biostimulation and toxicity, The magnitude of the impact of nano-materials in microorganisms and plants. J Adv Res 31:113–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2020.12.011
Kahlon SK, Sharma G, Julka JM, Kumar A, Sharma S, Stadler FJ (2018) Impact of heavy metals and nanoparticles on aquatic biota. Environ Chem Lett 16:919–946. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0737-4
Karlsson HL, Gustafsson J, Cronholm P, Möller L (2009) Size-dependent toxicity of metal oxide particles—a comparison between nano-and micrometer size. Toxicol Lett 188:112–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2009.03.014
Karuppannan SK, Ramalingam R, Khalith SM, Dowlath MJH, Raiyaan GD, Arunachalam KD (2021) Characterization, antibacterial and photocatalytic evaluation of green synthesized copper oxide nanoparticles. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 31:101904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101904
Kasemets K, Ivask A, Dubourguier HC, Kahru A (2009) Toxicity of nanoparticles of ZnO, CuO and TiO2 to yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Toxicol in Vitro 23:1116–1122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2009.05.015
Khanna K, Kohli SK, Handa N, Kaur H, Ohri P, Bhardwaj R, Ahmad P (2021) Enthralling the impact of engineered nanoparticles on soil microbiome, a concentric approach towards environmental risks and cogitation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 222:112459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112459
Leitner J, Sedmidubský D, Jankovský O (2019) Size and shape-dependent solu-bility of CuO nanostructures. Materials 12:3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12203355
Li XQ, Guo BL, Cai WY, Zhang JM, Huang HQ, Zhan P, De Hoog GS (2016) The role of melanin pathways in extremotolerance and virulence of F-onsecaea revealed by de novo assembly transcriptomics using illumina p-aired-end sequencing. Stud Mycol 83:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.simyco.2016.02.001
Li N, Zhang X, Wang D, Cheng Y, Wu L, Fu L (2017) Contribution characteristics of the in situ extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in Phanerochaete chrysosporium to Pb immobilization. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 40:1447–1452. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-017-1802-2
Li X, Lan X, Feng X, Luan X, Cao X, Cui Z (2021) Biosorption capacity of Mucor circinelloides bioaugmented with Solanum nigrum L. for the clean-up of lead, cadmium and arsenic. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 212:112014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112014
Liu S, Youngchim S, Zamith-Miranda D, Nosanchuk JD (2021) Fungal melanin and the mammalian immune system. J Fungi 7:264. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7040264
Lu H, Wei T, Lou H, Shu X, Chen Q (2021) A critical review on communication mechanism within plant-endophytic fungi interactions to cope with biotic and abiotic stresses. J Fungi 7:719. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7090719
Majumder R, Sheikh L, Naskar A, Mukherjee M, Tripathy S (2017) Depletion of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution by heat dried biomass of a newly isol-ated fungus Arthrinium malaysianum, a mechanistic approach. Sci Rep 7:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10160-0
Oh JJ, Kim JY, Kim YJ, Kim S, Kim GH (2021) Utilization of extracellular fungal melanin as an eco-friendly biosorbent for treatment of metal con-taminated effluents. Chemosphere 272:129884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129884
Oprica L, Ungureanu E (2015) The impact of CoFeO4 nanoparticles on soluble protein content at white rot fungus phanerochaete chrysosporium. J Exp Biol 16:161
Pavithra NS, Manukumar KN, Viswanatha R, Nagaraju G (2021) Combustion- derived CuO nanoparticles: Application studies on lithium-ion battery and photocatalytic activities. Inorg Chem Commun 130:108689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2021.108689
Potisek M, Likar M, Vogel-Mikuš K, Arčon I, Grdadolnik J, Regvar M (2021) 1,8-dihydroxy naphthalene (DHN)-melanin confers tolerance to cadmium in isolates of melanised dark septate endophytes. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 222:112493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112493
Priyadarshini E, Priyadarshini SS, Cousins BG, Pradhan N (2021) Metal-Fungusinteraction, review on cellular processes underlying heavy metal detoxific-ation and synthesis of metal nanoparticles. Chemosphere 274:129976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129976
Rajput VD, Minkina T, Suskova S, Mandzhieva S, Tsitsuashvili V, Chapligin V, Fedorenko A (2018) Effects of copper nanoparticles (CuO NPs) on crop plants, a mini review. Bionanoscience 8:36–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-017-0466-3
Rehman K, Fatima F, Waheed I, Akash MSH (2018) Prevalence of exposure of heavy metals and their impact on health consequences. J Cell Biochem 119:157–184. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26234
Reuveni R, Shimoni M, Karchi Z, Kuc J (1992) Peroxidase activity as a biochemical marker for resistance of muskmelon (Cucumis melo) to Pseudoperonospora cubensis. Phytopathology 82:749–753. https://doi.org/10.1094/phyto-82-749
Romsdahl J, Schultzhaus Z, Cuomo CA, Dong H, Abeyratne-Perera H, Hervey WJ, Wang Z (2021) Phenotypic characterization and comparative genomics of the melanin-producing yeast Exophiala lecanii-corni reveals a distinct stress tolerance profile and reduced ribosomal genetic content. J Fungi 7:1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7121078
Shadmani L, Jamali S, Fatemi A (2021) Isolation, identification, and characterization of cadmium-tolerant endophytic fungi isolated from barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) roots and their role in enhancing phytoremediation. Braz J Microbiol 52:1097–1106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-021-00493-4
Shakya M, Sharma P, Meryem SS, Mahmood Q, Kumar A (2016) Heavy metalremoval from industrial wastewater using fungi, uptake mechanism and b-iochemical aspects. J Environ Eng 142:C6015001. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0000983
Sharma KR, Giri R, Sharma RK (2022) Efficient bioremediation of metal containing industrial wastewater using white rot fungi. Int J Environ Sci Technol 1-8.https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-03914-5
Siegel SM, Galun M, Siegel BZ (1990) Filamentous fungi as metal biosorbents, a review. Water Air Soil Pollut 53:335–344. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00170747
Singh J, Kaur G, Rawat M (2016) A brief review on synthesis and characterization of copper oxide nanoparticles and its applications. J Bioelectron Nanotechnol 1:9. https://doi.org/10.13188/2475-224X.1000003
Singh S, Nimse SB, Mathew DE, Dhimmar A, Sahastrabudhe H, Gajjar A, Shinde PB (2021) Microbial melanin: Recent advances in biosynthesis, extraction, characterization, and applications. Biotechnol Adv 53:107773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2021.107773
Smith SE, Read DJ (2010) Mycorrhizal symbiosis, 3rd edn. Academic Press
Soni D, Naoghare PK, Saravanadevi S, Pandey RA (2015) Release, transport and toxicity of engineered nanoparticles. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 234:1–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10638-0_1
Staroń A, Długosz O, Pulit-Prociak J, Banach M (2020) Analysis of the expos-ure of organisms to the action of nanomaterials. Materials 13:349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13020349
Su Y, Wu D, Xia H, Zhang C, Shi J, Wilkinson KJ, Xie B (2019) Metallic n-anoparticles induced antibiotic resistance genes attenuation of leachate cul-turable microbiota, the combined roles of growth inhibition, ion dissoluti-on and oxidative stress. Environ Int 128:407–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.05.007
Su ZZ, Dai MD, Zhu JN, Liu XH, Li L, Zhu XM, Lin FC (2021) Dark septate endophyte Falciphora oryzae-assisted alleviation of cadmium in rice. J Hazard Mater 419:126435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126435
Sun M, Yu Q, Hu M, Hao Z, Zhang C, Li M (2014) Lead sulfide nanoparticl-es increase cell wall chitin content and induce apoptosis in Saccharomyc-es cerevisiae. J Hazard Mater 273:7–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.03.008
Tamura K, Stecher G, Kumar S (2021) MEGA11: molecular evolutionary gene-tics analysis version 11. Mol Biol Evol 38:3022–3027. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst197
Teng Y, Du X, Wang T, Mi C, Yu H, Zou L (2018) Isolation of a fungus Pencicillium sp. with zinc tolerance and its mechanism of resistance. Arch Microbiol 200:159–169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-017-1430-x
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/22.22.4673
Tran-Ly AN, Ribera J, Schwarze FW, Brunelli M, Fortunato G (2020) Fungal melanin-based electrospun membranes for heavy metal detoxification of water. Sustainable Mater Technol 23:e00146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2019.e00146
Wang X, Liu Y, Zeng G, Chai L, Song X, Min Z, Xiao X (2008) Subcellulardistribution and chemical forms of cadmium in Bechmeria nivea (L.) Ga-ud. Environ Exp Bot 62:389–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2007.10.014
Xiao Y, Dai MX, Zhang GQ, Yang ZX, He YM, Zhan FD (2021) Effects of the dark septate endophyte (DSE) Exophiala pisciphila on the growth of root cell wall polysaccharides and the cadmium content of Zea mays L. under cadmium stress. J Fungi 7:1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7121035
Xu H, Hao RX, Xu XY, Ding Y, Lu AH, Li YH (2021) Removal of hexavalent chromium by Aspergillus niger through reduction and accumulation. Geomicrobiol J 38:20–28. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2020.1807659
Yang ZZ, Xiao YF, Jiao TT, Zhang Y, Chen J, Gao Y (2020) Effects of copper oxide nanoparticles on the growth of rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings and the relevant physiological responses. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17:1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17041260
Ye S, Zeng G, Wu H, Zhang C, Liang J, Dai J, Cheng M (2017) Co-occurre-nce and interactions of pollutants, and their impacts on soil remediation—a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 47:1528–1553. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2017.1386951
Yin L, Cheng Y, Espinasse B, Colman BP, Auffan M, Wiesner M, Bernhardt ES (2011) More than the ions, the effects of silver nanoparticles on Lolium multiflorum. Environ Sci Technol 45:2360–2367. https://doi.org/10.1021/es103995x
Yin K, Wang Q, Lv M, Chen L (2019) Microorganism remediation strategies t-owards heavy metals. Chem Eng J 360:1553–1563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.226
Zhan F, He Y, Zu Y, Li T, Zhao Z (2011) Characterization of melanin isolated from a dark septate endophyte (DSE) Exophiala Pisciphila. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27:2483–2489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0712-8
Zhan F, He Y, Li Y, Li T, Yang YY, Toor GS, Zhao Z (2015) Subcellular dis-tribution and chemical forms of cadmium in a dark septate endophyte (DSE), Exophiala pisciphila. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:17897–17905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5012-7
Zhan F, He Y, Yang Y, Li Y, Li T, Zhao Z (2016) Effects of tricyclazole on cadmium tolerance and accumulation characteristics of a dark septate endophyte (DSE), Exophiala pisciphila. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 96:235–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1676-4
Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Liu M, Shi X, Zhao Z (2008) Dark septate endophyte (DSE) fungi isolated from metal polluted soils, their taxonomic position, tolerance, and accumulation of heavy metals in vitro. J Microbiol 46:624–632. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-008-0163-6
Zhang C, Liu F, Kong W, He Y (2015) Application of visible and near-infrared hyperspectral imaging to determine soluble protein content in oilseed rape leaves. Sensors 15:16576–16588. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150716576
Zhao D, Li T, Wang J, Zhao Z (2015) Diverse strategies conferring extreme cadmium (Cd) tolerance in the dark septate endophyte (DSE), Exophiala pisciphila, evidence from RNA-seq data. Microbiol Res 170:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2014.09.005
Funding
This research was supported by “National Natural Science Foundation of China (31800420),” “National Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for Undergraduate (S202110497082),” “Independent Innovation Research Fund for Undergraduate (2021-HS-B1-07),” and “the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (WUT: 2020IB029)”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yihui Ban: Conducting most of the experiment. Jiayuan Tan: Writing—review and editing. Yang Xiong: Searching for references. Xiantong Mo: Searching for references. Wenxuan Li: Searching for references. Chenyue jia: Searching for references. Yiwen Ding: Searching for references. Zhouying Xu: Review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable. This manuscript does not involve researching about humans or animals.
Consent to participate
All of the authors consented to participate in the drafting of this manuscript.
Consent for publication
All of the authors consented to publish this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Diane Purchase
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ban, Y., Tan, J., Xiong, Y. et al. The responses and detoxification mechanisms of dark septate endophytes (DSE), Exophiala salmonis, to CuO nanoparticles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 13773–13787 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23099-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23099-1