Abstract
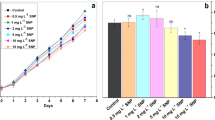
Although doping of various rare earth elements such as samarium on zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) can noticeably improve their photocatalytic performance, it may enhance their toxicity to living organisms. Thus, the toxic impacts of samarium-doped ZnO NPs (Sm/ZnO NPs) on different organisms should be carefully evaluated. In this study, an eco-toxicological experimentation system using the green microalga Chlorella vulgaris was established to determine the potential toxicity of ZnO and Sm/ZnO NPs synthesized by polymer pyrolysis method. Accordingly, growth parameters, oxidative stress biomarkers, and morphological features of the algal cells were analyzed. Both ZnO and Sm/ZnO NPs induced a concentration-dependent cytotoxicity by reducing the cell growth, decreasing photosynthetic pigment contents, and causing deformation in the cellular morphology. Moreover, generation of excessive H2O2, increased activity of superoxide dismutase and ascorbate peroxidase, and reduction in total phenolic and flavonoid contents were observed. Catalase activity was inversely influenced by the NPs in a way that its activity significantly increased at the concentrations of 20 and 25 mg L−1 of ZnO NPs, but was lessened by all supplemented dosages (5–25 mg L−1) of Sm/ZnO NPs. Altogether, the obtained results revealed that Sm-doping can play a significant role in ZnO NP-induced toxicity on C. vulgaris cells.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in the manuscript file.
References
Ahmad HR, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Sohail MI, ulHaq MA, Khalid H, Ayub MA, Ishaq G (2018) Effects of rare earth oxide nanoparticles on plants. In: Tripathi DK, Ahmad P, Sharma S, Chauhan DK, Dubey NK (eds) Nanomaterials in plants, algae, and microorganisms: Concepts and Controversies. Elsevier, pp 239–275
Bhuvaneshwari M, Iswarya V, Archanaa S, Madhu G, Kumar GS, Nagarajan R, Chandrasekaran N, Mukherjee A (2015) Cytotoxicity of ZnO NPs towards fresh water algae Scenedesmus obliquus at low exposure concentrations in UV-C, visible and dark conditions. Aquat Toxicol 162:29–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.03.004
Boominathan R, Doran PM (2002) Ni-induced oxidative stress in roots of the Ni hyperaccumulator, Alyssum bertolonii. New Phytol 156:205–215. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.2002.00506.x
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Carofiglio M, Barui S, Cauda V, Laurenti M (2020) Doped zinc oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and potential use in nanomedicine. Appl Sci 10:5194. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10155194
Chang C-C, Yang M-H, Wen H-M, Chern J-C (2002) Estimation of total flavonoid content in propolis by two complementary colorimetric methods. J Food Drug Anal 10:178–182
Cheloni G, Marti E, Slaveykova VI (2016) Interactive effects of copper oxide nanoparticles and light to green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Aquat Toxicol 170:120–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.11.018
Chen P, Powell BA, Mortimer M, Ke PC (2012) Adaptive interactions between zinc oxide nanoparticles and Chlorella sp. Environ Sci Technol 46:12178–12185. https://doi.org/10.1021/es303303g
Djearamane S, Lim YM, Wong LS, Lee PF (2019) Cellular accumulation and cytotoxic effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles in microalga Haematococcus pluvialis. PeerJ 7:e7582. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.7582
Farooqi MMH, Srivastava RK (2016) Enhanced UV–vis photoconductivity and photoluminescence by doping of samarium in ZnO nanostructures synthesized by solid state reaction method. Optik 127:3991–3998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2016.01.074
Fazelian N, Movafeghi A, Yousefzadi M, Rahimzadeh M (2019) Cytotoxic impacts of CuO nanoparticles on the marine microalga Nannochloropsis oculata. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:17499–17511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05130-0
Goecke F, Zachleder V, Vítová M (2015) Rare earth elements and algae: physiological effects, biorefinery and recycling. In: Prokop A, Bajpai R, Zappi M (eds) Algal Biorefineries. Springer, Cham, pp 339–363
Gong N, Shao K, Feng W, Lin Z, Liang C, Sun Y (2011) Biotoxicity of nickel oxide nanoparticles and bio-remediation by microalgae Chlorella vulgaris. Chemosphere 83:510–516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.12.059
Hoecke KV, Quik JT, Mankiewicz-Boczek J, Schamphelaere KAD, Elsaesser A, Meeren PVd, Barnes C, McKerr G, Howard CV, Meent DVD (2009) Fate and effects of CeO2 nanoparticles in aquatic ecotoxicity tests. Environ Sci Technol 43:4537–4546. https://doi.org/10.1021/es9002444
Kaliamurthi S, Selvaraj G, Cakmak ZE, Korkmaz AD, Cakmak T (2019) The relationship between Chlorella sp. and zinc oxide nanoparticles: changes in biochemical, oxygen evolution, and lipid production ability. Process Biochem 85:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2019.06.005
Kayani ZN, Sahar M, Riaz S, Naseem S, Saddiqe Z (2020) Enhanced magnetic, antibacterial and optical properties of Sm doped ZnO thin films: role of Sm doping. Opt Mater 108:110457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2020.110457
Khatamian M, Khandar A, Divband B, Haghighi M, Ebrahimiasl S (2012) Heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of 4-nitrophenol in aqueous suspension by Ln (La3+, Nd3+ or Sm3+) doped ZnO nanoparticles. J Mol Catal A Chem 365:120–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2012.08.018
Krzyżewska I, Kyzioł-Komosińska J, Rosik-Dulewska C, Czupioł J, Antoszczyszyn-Szpicka P (2016) Inorganic nanomaterials in the aquatic environment: behavior, toxicity, and interaction with environmental elements. Arch Environ Prot 42. https://doi.org/10.1515/aep-2016-0011
Kurvet I, Juganson K, Vija H, Sihtmäe M, Blinova I, Syvertsen-Wiig G, Kahru A (2017) Toxicity of nine (doped) rare earth metal oxides and respective individual metals to aquatic microorganisms Vibrio fischeri and Tetrahymena thermophila. Materials 10:754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070754
Liu N, Wang Y, Ge F, Liu S, Xiao H (2018) Antagonistic effect of nano-ZnO and cetyltrimethyl ammonium chloride on the growth of Chlorella vulgaris: dissolution and accumulation of nano-ZnO. Chemosphere 196:566–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.184
Ma S, Lin D (2013) The biophysicochemical interactions at the interfaces between nanoparticles and aquatic organisms: adsorption and internalization. Environ Sci Proc Imp 15:145–160. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2EM30637A
Ma S, Zhou K, Yang K, Lin D (2015) Heteroagglomeration of oxide nanoparticles with algal cells: effects of particle type, ionic strength and pH. Environ Sci Technol 49:932–939. https://doi.org/10.1021/es504730k
Mahjouri S, Kosari-Nasab M, Kazemi EM, Divband B, Movafeghi A (2020) Effect of Ag-doping on cytotoxicity of SnO2 nanoparticles in tobacco cell cultures. J Hazard Mater 381:121012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121012
Mahjouri S, Movafeghi A, Divband B, Kosari-Nasab M (2018) Toxicity impacts of chemically and biologically synthesized CuO nanoparticles on cell suspension cultures of Nicotiana tabacum. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 135:223–234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-018-1458-x
Manzo S, Miglietta ML, Rametta G, Buono S, Di Francia G (2013) Toxic effects of ZnO nanoparticles towards marine algae Dunaliella tertiolecta. Sci Total Environ 445:371–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.12.051
Meda A, Lamien CE, Romito M, Millogo J, Nacoulma OG (2005) Determination of the total phenolic, flavonoid and proline contents in Burkina Fasan honey, as well as their radical scavenging activity. Food Chem 91:571–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.10.006
Michalak A (2006) Phenolic compounds and their antioxidant activity in plants growing under heavy metal stress. Pol J Environ Stud 15:523–530
Mishra PK, Mishra H, Ekielski A, Talegaonkar S, Vaidya B (2017) Zinc oxide nanoparticles: a promising nanomaterial for biomedical applications. Drug Discov Today 22:1825–1834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2017.08.006
Navarro E, Piccapietra F, Wagner B, Marconi F, Kaegi R, Odzak N, Sigg L, Behra R (2008) Toxicity of silver nanoparticles to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Environ Sci Technol 42:8959–8964. https://doi.org/10.1021/es801785m
Nazari F, Movafeghi A, Jafarirad S, Kosari-Nasab M, Divband B (2018) Synthesis of reduced graphene oxide-silver nanocomposites and assessing their toxicity on the green microalga Chlorella vulgaris. Bionanoscience 8:997–1007. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-018-0561-0
Obinger C, Maj M, Nicholls P, Loewen P (1997) Activity, peroxide compound formation, and heme d synthesis in Escherichia coli HPII catalase. Arch Biochem Biophys 342:58–67. https://doi.org/10.1006/abbi.1997.9988
Peng C, Zhang W, Gao H, Li Y, Tong X, Li K, Zhu X, Wang Y, Chen Y (2017) Behavior and potential impacts of metal-based engineered nanoparticles in aquatic environments. Nanomaterials 7:21. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7010021
Poborilova Z, Opatrilova R, Babula P (2013) Toxicity of aluminium oxide nanoparticles demonstrated using a BY-2 plant cell suspension culture model. Environ Exp Bot 91:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2013.03.002
Qureshi M, Abdin M, Qadir S, Iqbal M (2007) Lead-induced oxidative stress and metabolic alterations in Cassia angustifolia Vahl. Biol Plant 51:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-007-0024-x
Ravichandran A, Karthick R, Xavier AR, Chandramohan R, Mantha S (2017) Influence of Sm doped ZnO nanoparticles with enhanced photoluminescence and antibacterial efficiency. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28:6643–6648. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6355-2
Rippka R, Deruelles J, Waterbury JB, Herdman M, Stanier RY (1979) Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. Microbiology 111:1–61. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-111-1-1
Saxena P, Saharan V, Baroliya PK, Gour VS, Rai MK (2021) Mechanism of nanotoxicity in Chlorella vulgaris exposed to zinc and iron oxide. Toxicol Rep 8:724–731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.03.023
Silva A, Figueiredo SA, Sales MG, Delerue-Matos C (2009) Ecotoxicity tests using the green algae Chlorella vulgaris—a useful tool in hazardous effluents management. J Hazard Mater 167:179–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.12.102
Sin J-C, Lam S-M, Lee K-T, Mohamed AR (2013) Photocatalytic performance of novel samarium-doped spherical-like ZnO hierarchical nanostructures under visible light irradiation for 2, 4-dichlorophenol degradation. J Colloid Interface Sci 401:40–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.03.043
Şükran D, GÜNEŞ T, Sivaci R (1998) Spectrophotometric determination of chlorophyll-A, B and total carotenoid contents of some algae species using different solvents. Turk J Botany 22:13–18
Suman T, Rajasree SR, Kirubagaran R (2015) Evaluation of zinc oxide nanoparticles toxicity on marine algae Chlorella vulgaris through flow cytometric, cytotoxicity and oxidative stress analysis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 113:23–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.11.015
Tang Y, Xin H, Yang S, Guo M, Malkoske T, Yin D, Xia S (2018) Environmental risks of ZnO nanoparticle exposure on Microcystis aeruginosa: toxic effects and environmental feedback. Aquat Toxicol 204:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.08.010
Taylor NS, Merrifield R, Williams TD, Chipman JK, Lead JR, Viant MR (2016) Molecular toxicity of cerium oxide nanoparticles to the freshwater alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is associated with supra-environmental exposure concentrations. Nanotoxicol 10:32–41. https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390.2014.1002868
Velikova V, Yordanov I, Edreva A (2000) Oxidative stress and some antioxidant systems in acid rain-treated bean plants: protective role of exogenous polyamines. Plant Sci 151:59–66
Winterbourn CC, McGrath BM, Carrell RW (1976) Reactions involving superoxide and normal and unstable haemoglobins. Biochem J 155:493–502. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj1550493
Xia B, Liu K, Gong Z, Zheng B, Zhang X, Fan B (2009) Rapid toxicity prediction of organic chemicals to Chlorella vulgaris using quantitative structure–activity relationships methods. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:787–794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2008.09.002
Yingjun W, Hangbiao J, Shihuai D, Yan C, You Y (2011) Effects of neodymium on growth and physiological characteristics of Microcystis aeruginosa. J Rare Earth 29:388–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0721(10)60466-8
Yuan X-Z, Pan G, Chen H, Tian B-H (2009) Phosphorus fixation in lake sediments using LaCl3-modified clays. Ecol Eng 35:1599–1602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2008.08.002
Zhao J, Cao X, Liu X, Wang Z, Zhang C, White JC, Xing B (2016) Interactions of CuO nanoparticles with the algae Chlorella pyrenoidosa: adhesion, uptake, and toxicity. Nanotoxicology 10:1297–1305. https://doi.org/10.1080/17435390.2016.1206149
Zhou H, Wang X, Zhou Y, Yao H, Ahmad F (2014) Evaluation of the toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles to Chlorella vulgaris by use of the chiral perturbation approach. Anal Bioanal Chem 406:3689–3695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-7773-0
Zhu Y, Liu X, Hu Y, Wang R, Chen M, Wu J, Wang Y, Kang S, Sun Y, Zhu M (2019) Behavior, remediation effect and toxicity of nanomaterials in water environments. Environ Res 174:54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.04.014
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the University of Tabriz (Iran) for scientific and financial supports. They are also grateful to Dr. N. Farsad for his help in the statistical data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S. Feizi, M. Kosari-Nasab, and A. Movafeghi designed the experiments. S. Feizi conducted the experiments. B. Divband helped in the synthesis and characterization of nanoparticles. M. Kosari-Nasab and A. Movafeghi controlled the methodology of microalgae culture and bioassays. S. Mahjouri and A. Movafeghi contributed to the data analysis, writing, review, and editing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Bruno Nunes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feizi, S., Kosari-Nasab, M., Divband, B. et al. Comparison of the toxicity of pure and samarium-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles to the green microalga Chlorella vulgaris. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 32002–32015 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18539-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18539-x