Abstract
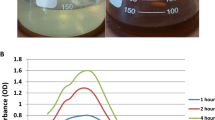
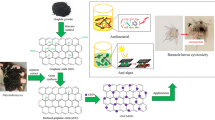
The growing demands for nanotechnology in the recent years have resulted in environmental release of nanomaterials. In the current study, reduced graphene oxide-silver nanocomposites (Ag-rGO) were synthesized by an easy method and their characteristics were determined using X-ray diffraction (XRD), ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-Vis), energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) techniques. Subsequently, toxicity of Ag-rGO was examined on the marine microalga Chlorella vulgaris. After treatment of algal cells with different concentrations of Ag-rGO for 24 h, growth parameters have been significantly decreased. In addition, a considerable reduction in viability of the treated cells was designated. Further considerable effects of Ag-rGO treatments have been revealed by increments in the activities of a number of antioxidant enzymes and reductions in the photosynthetic pigment contents. Our results showed that the main toxic effects of Ag-rGO are associated with the presence of Ag nanoparticles in the structure of these nanocomposites.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu, X., & Zhou, Q. (2013). Health and ecosystem risks of graphene. Chemical Reviews, 113(5), 3815–3835.
Jastrzebska, A. M., Kurtycz, P., & Olszyna, A. R. (2012). Recent advances in graphene family materials toxicity investigations. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 14(12), 1–21.
Hu, C., Wang, Q., Zhao, H., Wang, L., Guo, S., & Li, X. (2015). Ecotoxicological effects of graphene oxide on the protozoan Euglena gracilis. Chemosphere, 128, 184–190.
Shao, W., Liu, X., Min, H., Dong, G., Feng, Q., & Zuo, S. (2015). Preparation, characterization, and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticle-decorated graphene oxide nanocomposite. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 7(12), 6966–6973.
Zhao, S., Wang, Q., Zhao, Y., Rui, Q., & Wang, D. (2015). Toxicity and translocation of graphene oxide in Arabidopsis thaliana. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 39(1), 145–156.
Thu, T. V., Ko, P. J., Phuc, N. H. H., & Sandhu, A. (2013). Room-temperature synthesis and enhanced catalytic performance of silver-reduced graphene oxide nanohybrids. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 15(10), 1–13.
Qian, H., Li, J., Sun, L., Chen, W., Sheng, G. D., Liu, W., & Fu, Z. (2009). Combined effect of copper and cadmium on Chlorella vulgaris growth and photosynthesis-related gene transcription. Aquatic Toxicology, 94(1), 56–61.
Chen, X., Zhu, X., Li, R., Yao, H., Lu, Z., & Yang, X. (2012). Photosynthetic toxicity and oxidative damage induced by nano-Fe3O4 on Chlorella vulgaris in aquatic environment. Open Journal of Ecology, 2(01), 21–28.
Hu, X., Lu, K., Mu, L., Kang, J., & Zhou, Q. (2014). Interactions between graphene oxide and plant cells: regulation of cell morphology, uptake, organelle damage, oxidative effects and metabolic disorders. Carbon, 80, 665–676.
Chen, T.-H., Lin, C.-Y., & Tseng, M.-C. (2011). Behavioral effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on larval zebrafish (Danio rerio). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 63(5), 303–308.
Khataee, A., Movafeghi, A., Nazari, F., Vafaei, F., Dadpour, M. R., Hanifehpour, Y., & Joo, S. W. (2014). The toxic effects of L-cysteine-capped cadmium sulfide nanoparticles on the aquatic plant Spirodela polyrrhiza. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 16(12), 1–10.
Cherchi, C., & Gu, A. Z. (2010). Impact of titanium dioxide nanomaterials on nitrogen fixation rate and intracellular nitrogen storage in Anabaena variabilis. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(21), 8302–8307.
Sadiq, I. M., Dalai, S., Chandrasekaran, N., & Mukherjee, A. (2011). Ecotoxicity study of titania (TiO2) NPs on two microalgae species: Scenedesmus sp. and Chlorella sp. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 74(5), 1180–1187.
Sun, X., Liu, Z., Welsher, K., Robinson, J. T., Goodwin, A., Zaric, S., & Dai, H. (2008). Nano-graphene oxide for cellular imaging and drug delivery. Nano Research, 1(3), 203–212.
Jafarirad, S., Kordi, M., & Kosari-Nasab, M. (2017). Extracellular one-pot synthesis of nanosilver using Hyssopus officinalis L.: a biophysical approach on bioconstituent-Ag+ interactions. Inorganic and Nano-Metal Chemistry, 47(4), 632–638.
Suman, T., Rajasree, S. R., & Kirubagaran, R. (2015). Evaluation of zinc oxide nanoparticles toxicity on marine algae Chlorella vulgaris through flow cytometric, cytotoxicity and oxidative stress analysis. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 113, 23–30.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72(1–2), 248–254.
Obinger, C., Maj, M., Nicholls, P., & Loewen, P. (1997). Activity, peroxide compound formation, and heme d synthesis in Escherichia coli HPII catalase. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 342(1), 58–67.
Boominathan, R., & Doran, P. M. (2002). Ni-induced oxidative stress in roots of the Ni hyperaccumulator, Alyssum bertolonii. New Phytologist, 156(2), 205–215.
Winterbourn, C. C., McGrath, B. M., & Carrell, R. W. (1976). Reactions involving superoxide and normal and unstable haemoglobins. Biochemical Journal, 155(3), 493–502.
Sukran, D., GUNES, T., & Sivaci, R. (1998). Spectrophotometric determination of chlorophyll-a, B and total carotenoid contents of some algae species using different solvents. Turkish Journal of Botany, 22(1), 13–18.
Wang, S., Zhang, Y., Ma, H. L., Zhang, Q., Xu, W., Peng, J., Li, J., Yu, Z. Z., & Zhai, M. (2013). Ionic-liquid-assisted facile synthesis of silver nanoparticle-reduced graphene oxide hybrids by gamma irradiation. Carbon, 55, 245–252.
Fu, L., Zheng, Y., Fu, Z., Wang, A., & Cai, W. (2015). Dissolved oxygen detection by galvanic displacement-induced graphene/silver nanocomposite. Bulletin of Materials Science, 38(3), 611–616.
Gong, N., Shao, K., Feng, W., Lin, Z., Liang, C., & Sun, Y. (2011). Biotoxicity of nickel oxide nanoparticles and bio-remediation by microalgae Chlorella vulgaris. Chemosphere, 83(4), 510–516.
Zhou, H., Wang, X., Zhou, Y., Yao, H., & Ahmad, F. (2014). Evaluation of the toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles to Chlorella vulgaris by use of the chiral perturbation approach. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 406(15), 3689–3695.
Oukarroum, A., Bras, S., Perreault, F., & Popovic, R. (2012). Inhibitory effects of silver nanoparticles in two green algae, Chlorella vulgaris and Dunaliella tertiolecta. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 78, 80–85.
Ji, J., Long, Z., & Lin, D. (2011). Toxicity of oxide nanoparticles to the green algae Chlorella sp. Chemical Engineering Journal, 170(2), 525–530.
Qian, H., Li, J., Pan, X., Sun, L., Lu, T., Ran, H., & Fu, Z. (2011). Combined effect of copper and cadmium on heavy metal ion bioaccumulation and antioxidant enzymes induction in Chlorella vulgaris. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 87(5), 512–516.
Rai, U., Singh, N., Upadhyay, A., & Verma, S. (2013). Chromate tolerance and accumulation in Chlorella vulgaris L.: role of antioxidant enzymes and biochemical changes in detoxification of metals. Bioresource Technology, 136, 604–609.
Wang, H. Y., Zeng, X. B., Guo, S. Y., & Li, Z. T. (2008). Effects of magnetic field on the antioxidant defense system of recirculation-cultured Chlorella vulgaris. Bioelectromagnetics, 29(1), 39–46.
Mallick, N. (2004). Copper-induced oxidative stress in the chlorophycean microalga Chlorella vulgaris: response of the antioxidant system. Journal of Plant Physiology, 161(5), 591–597.
Chongpraditnun, P., Mori, S., & Chino, M. (1992). Excess copper induces a cytosolic Cu, Zn-superoxide dismutase in soybean root. Plant and Cell Physiology, 33(3), 239–244.
Gupta, D., Nicoloso, F., Schetinger, M., Rossato, L., Pereira, L., Castro, G., Srivastava, S., & Tripathi, R. (2009). Antioxidant defense mechanism in hydroponically grown Zea mays seedlings under moderate lead stress. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 172(1), 479–484.
Dazy, M., Masfaraud, J.-F., & Ferard, J.-F. (2009). Induction of oxidative stress biomarkers associated with heavy metal stress in Fontinalis antipyretica Hedw. Chemosphere, 75(3), 297–302.
Qian, H., Chen, W., Li, J., Wang, J., Zhou, Z., Liu, W., & Fu, Z. (2009). The effect of exogenous nitric oxide on alleviating herbicide damage in Chlorella vulgaris. Aquatic Toxicology, 92(4), 250–257.
Gao, Q., & Tam, N. (2011). Growth, photosynthesis and antioxidant responses of two microalgal species, Chlorella vulgaris and Selenastrum capricornutum, to nonylphenol stress. Chemosphere, 82(3), 346–354.
di Toppi, L. S., Musetti, R., Marabottini, R., Corradi, M. G., Vattuone, Z., Favali, M. A., & Badiani, M. (2004). Responses of Xanthoria parietina thalli to environmentally relevant concentrations of hexavalent chromium. Functional Plant Biology, 31(4), 329–338.
Assche, F. V., & Clijsters, H. (1990). Effects of metals on enzyme activity in plants. Plant, Cell & Environment, 13(3), 195–206.
Frueh, J., Gai, M., Yang, Z., & He, Q. (2014). Influence of polyelectrolyte multilayer coating on the degree and type of biofouling in freshwater environment. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 14(6), 4341–4350.
Cooper, S. P., Finlay, J. A., Cone, G., Callow, M. E., Callow, J. A., & Brennan, A. B. (2011). Engineered antifouling microtopographies: kinetic analysis of the attachment of zoospores of the green alga Ulva to silicone elastomers. Biofouling, 27(8), 881–892.
Voulvoulis, N., Scrimshaw, M., & Lester, J. (1999). Alternative antifouling biocides. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 13(3), 135–143.
Chaudhury, M. K., Finlay, J. A., Chung, J. Y., Callow, M. E., & Callow, J. A. (2005). The influence of elastic modulus and thickness on the release of the soft-fouling green alga Ulva linza (syn. Enteromorpha linza) from poly (dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) model networks. Biofouling, 21(1), 41–48.
Xiao, L., Thompson, S. E., Rohrig, M., Callow, M. E., Callow, J. A., Grunze, M., & Rosenhahn, A. (2013). Hot embossed microtopographic gradients reveal morphological cues that guide the settlement of zoospores. Langmuir, 29(4), 1093–1099.
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to R. Tarrahi for critically reading the manuscript. The authors thank the University of Tabriz, Iran, for all the support provided.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nazari, F., Movafeghi, A., Jafarirad, S. et al. Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide-Silver Nanocomposites and Assessing Their Toxicity on the Green Microalga Chlorella vulgaris. BioNanoSci. 8, 997–1007 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-018-0561-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-018-0561-0