Abstract
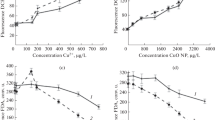
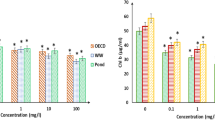
The properties of nanomaterials such as perlite nanoparticles and their increased application have raised concerns about their probable toxic impacts on the aquatic ecosystems and algae. Here, a novel biochemical synthesis and immobilization of CuO is reported on perlite nanoparticles (CuO/Per-NPs) and its toxic effect on alga has been compared with nanoperlites. This biosynthesis of CuO/Per-NPs performed using phytochemicals of Haematococcus pluvialis, Sargassum angustifolium, and walnut leaves in the aqueous extract. The structural, morphological, and colloidal properties of the as-synthesized nanoparticles have been confirmed by various methods. According to the obtained results, the morphology of the synthesized CuO/Per-NPs was spherical with sizes ranging from about 13 to 24 nm. Besides, the effects of Per-NPs and CuO/Per-NPs on unicellular algae H. pluvialis were studied. The changes in the amount of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and Carotenoids in the presence of different concentrations of Per-NPs (25, 50, 100 mg/L) were more than CuO/Per-NPs. Also, decreased growth rate and efficiency of photosystem II confirmed the toxic effects of Per-NPs. However, the toxicity of CuO/Per-NPs appears to be lower than that of Per-NPs, which can be due to the changes in the surface and cationic charge of modified nanoperlit. These changes lead to a decrease in the interaction of nanoparticles with H. pluvilalis and a reduction in ROS production. Finally, the results of GC-MS used to evaluate volatile compounds, indicated an increase in the number of phenolic compounds in comparison to the control samples in 25, 50, and 100 mg/L treatments of nano-perlite.

Highlights
-
The toxicity of biosynthesized CuO/Per-NPs appears to be lower than that of Per-NPs which are used as superabsorbent of heavy metals in water environment.
-
Decreasing growth rate and photosystem II efficiency confirmed the toxic effects of Per-NPs on Alga Haematococcus pluvialis.
-
Lower toxicity effect of CuO/Per-NPs than Per-NPs can be due to the changes in the surface and cationic charge of modified nanoperlit.
-
The changes in the surface of modified nanoperlit (CuO/Per-NPs) may lead to a decrease in the interaction of nanoparticles with H. pluvilalis and a reduction in ROS production.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available by contacting JR (jafar_razeghi@tabrizu.ac.ir) and SJ (jafarirad@tabrizu.ac.ir)
References
Baek S, Joo SH, Su C, Toborek M (2020) Toxicity of ZnO/TiO2‐conjugated carbon‐based nanohybrids on the coastal marine alga Thalassiosira pseudonana. Environ Toxicol 35(1):87–96
Bellinger EG, Sigee DC (2015) Freshwater algae: identification and use as bioindicators. John Wiley & Sons
Boominathan R, Doran PM (2002) Ni‐induced oxidative stress in roots of the Ni hyperaccumulator, Alyssum bertolonii. New phytol 156(2):205–215
Borowitzka MA (2013) High-value products from microalgae—their development and commercialisation. J appl phycol 25(3):743–756
Chen L, Zhou L, Liu Y, Deng S, Wu H, Wang G (2012) Toxicological effects of nanometer titanium dioxide (nano-TiO2) on Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 84:155–162
Chen X, Zhang C, Tan L, Wang J (2018) Toxicity of Co nanoparticles on three species of marine microalgae. Environ Pollut 236:454–461
Costa CHD, Perreault F, Oukarroum A, Melegari SP, Popovic R, Matias WG (2016) Effect of chromium oxide (III) nanoparticles on the production of reactive oxygen species and photosystem II activity in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Sci Total Environ 565:951–960
Czygan F (1970) Blood-rain and blood-snow: nitrogen-deficient cells of H. pluvialis and Chlamydomonas nivalis. Archiv fur Mikrobiologie 74(1):69–76
Dong Q, Zhao X, Xing X, Hu J, Gong JNH (2007) Secretion during astaxanthin synthesis in H. pluvialis under high irradiance and nitrogen defi-cient conditions. Chin J Chem Eng 15(2):162–166
Ebadollahi R, Jafarirad S, Kosari-Nasab M, Mahjouri S (2019) Effect of explant source, perlite nanoparticles and TiO 2/perlite nanocomposites on phytochemical composition of metabolites in callus cultures of Hypericum perforatum. Sci Rep 9(1):1–15
Fink P (2007) Ecological functions of volatile organic compounds in aquatic systems. Mar Freshw Behav Physiol 40(3):155–168
Jafarirad S, Kordi M, Kosari-Nasab M (2017) Extracellular one-pot synthesis of nanosilver using Hyssopus officinalis L.: a biophysical approach on bioconstituent-Ag+ interactions. Inorg Nano-Met Chem 47:632–638
Jafarirad S, Rasoulpour I, Divband B, Hammami Torghabe I, Kosari-Nasab M (2018) Innovative biocapped CuO nano-photocatalysts: a rapid and green method for photocatalytic degradation of 4-nitrophenol. Mater Res Innov 22(7):415–421
Jafarirad S, Salmasi M, Divband B, Sarabchi M (2019) Systematic study of Nd3+ on structural properties of ZnO nanocomposite for biomedical applications; in-vitro biocompatibility, bioactivity, photoluminescence and antioxidant properties. J Rare Earths 37:508–514
Jafarirad S, Taghizadeh PM, Divband B (2020) Biosynthesis, characterization and structural properties of a novel kind of Ag/ZnO nanocomposites in order to increase its biocompatibility across human A549 cell line. Bionanoscience 10:42–53
Hu C, Wang Q, Zhao H, Wang L, Guo S, Li X (2015) Ecotoxicological effects of graphene oxide on the protozoan Euglena gracilis. Chemosphere 128:184–190
Le Faucheur S, Behra R, Sigg L (2005) Phytochelatin induction, cadmium accumulation, and algal sensitivity to free cadmium ion in Scenedesmus vacuolatus. Environ Toxicol Chem 24(7):1731–1737
Lei C, Zhang L, Yang K, Zhu L, Lin D (2016) Toxicity of iron-based nanoparticles to green algae: effects of particle size, crystal phase, oxidation state and environmental aging. Environ Pollut 218:505–512
Lorenz RT(1999) A technical review of Haematococcus algae NatuRoseTM Tech Bull 60:1–12
Manzo S, Buono S, Rametta G, Miglietta M, Schiavo S, Di, Francia G (2015) The diverse toxic effect of SiO2 and TiO2 nanoparticles toward the marine microalgae Dunaliella tertiolecta. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(20):15941–15951
Maxwell K, Johnson GN (2000) Chlorophyll fluorescence—a practical guide. J Exp Bot 51(345):659–668
Miki W (1991) Biological functions and activities of animal carotenoids. Pure Appl Chem 63(1):141–146
Morelli E, Gabellieri E, Bonomini A, Tognotti D, Grassi G, Corsi I (2018) TiO2 nanoparticles in seawater: aggregation and interactions with the green alga Dunaliella tertiolecta. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:184–193
Nguyen NH, Von Moos NR, Slaveykova VI, Mackenzie K, Meckenstock RU, Thűmmler S, Bosch J, Ševců A (2018) Biological effects of four iron-containing nanoremediation materials on the green alga Chlamydomonas sp. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 154:36–44
Nogueira P, Nakabayashi D, Zucolotto V (2015) The effects of graphene oxide on green algae Raphidocelis subcapitata. Aquat Toxicol 166:29–35
Nolte TM, Hartmann NB, Kleijn JM, Garnæs J, Van De Meent D, Hendriks AJ, Baun A (2017) The toxicity of plastic nanoparticles to green algae as influenced by surface modification, medium hardness and cellular adsorption. Aquat Toxicol 183:11–20
Parr AJ, Bolwell GP (2000) Phenols in the plant and in man. The potential for possible nutritional enhancement of the diet by modifying the phenols content or profile. J Sci Food Agric 80(7):985–1012
Rasoulpour I, Jafarirad S (2017) Synthesis of biocapped CuO nanoparticles: an investigation on biorganic-Cu2+ interactions, in vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial aspects. Inorg Nano-Met Chem 47(11):1599–1604
Rezaei Z, Jafarirad S, Kosari-Nasab M (2019) Modulation of secondary metabolite profiles by biologically synthesized MgO/perlite nanocomposites inMelissa officinalis plant organ cultures J Hazard Mater 3800:120878–12089
Rippka R, Deruelles J, Waterbury JB, Herdman M, Stanier RY (1979) Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. Microbiology 111(1):1–61
Safafar H, Wagenen JV, Møller P, Jacobsen C (2015) Carotenoids, phenolic compounds and tocopherols contribute to the antioxidative properties of some microalgae species grown on industrial wastewater. Mar Drugs 13(12):7339–7356
Savicka M, Škute N (2010) Effects of high temperature on MDA content, superoxide production and growth changes in wheat seedlings (Triticum aestivum L.). Ekologija 56(1):26–33
Seaton A, Tran L, Aitken R, Donaldson K (2009) Nanoparticles, human health hazard and regulation. J R Soc Interface 7(Suppl_1):S119–S129
Shabani KS, Ardejani FD, Badii K, Olya ME (2017) Preparation and characterization of novel nano-mineral for the removal of several heavy metals from aqueous solution: batch and continuous systems. Arab J Chem 10:S3108–S3127
Shah MMR, Liang Y, Cheng JJ, Daroch M (2016) Astaxanthin-Producing Green Microalga H. pluvialis: From Single Cell to High Value Commercial Products. Front Plant Sci; https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00531
Solovchenko A, Solovchenko O, Khozin-Goldberg I, Didi-Cohen S, Pal D, Cohen Z et al. (2013) Probing the effects of high-light stress on pigment and lipid metabolism in nitrogen-starving microalgae by measuring chlorophyll fluorescence transients: studies with a Δ5 desaturase mutant of Parietochloris incisa (Chlorophyta, Trebouxiophyceae). Algal Res 2(3):175–182
Solovchenko AE (2015) Recent breakthroughs in the biology of astaxanthin accumulation by microalgal cell. Photosynth Res 125(3):437–449
Sousa CA, Soares HM, Soares EV (2018) Toxic effects of nickel oxide (NiO) nanoparticles on the freshwater alga Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. Aquat Toxicol 204:80–90
Sørensen SN, Engelbrekt C, Lützhøft HCH, Jiménez-Lamana J, Noori JS, Alatraktchi FA, Delgado CG, Slaveykova VI, Baun A (2016) A multimethod approach for investigating algal toxicity of platinum nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 50(19):10635–10643
Tayemeh MB, Esmailbeigi M, Shirdel I, Joo HS, Johari SA, Banan A, Nourani H, Mashhadi H, Jami MJ, Tabarrok M (2020) Perturbation of fatty acid composition, pigments, and growth indices of Chlorella vulgaris in response to silver ions and nanoparticles: a new holistic understanding of hidden ecotoxicological aspect of pollutants. Chemosphere 238:124576
Thomas NV, Kim S-K (2013) Beneficial effects of marine algal compounds in cosmeceuticals. Mar Drugs 11(1):146–164
Wang G, Hao Z, Huang Z, Chen L, Li X, Hu C et al. (2010) Raman spectroscopic analysis of a desert cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. in response to UVB radiation. Astrobiology 10(8):783–788
Wang F, Guan W, Xu L, Ding Z, Ma H, Ma A, Terry N (2019) Effects of nanoparticles on algae: adsorption, distribution, ecotoxicity and fate. Appl Sci 9(8):1534
Wang Z, Li J, Zhao J, Xing B (2011) Toxicity and internalization of CuO nanoparticles to prokaryotic alga microcystis aeruginosa as affected by dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 45(14):6032–6040
Wellburn AR (1994) The spectral determination of chlorophylls a and b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution. J Plant Physiol 144(3):307–313
Zuo Z-J, Zhu Y-R, Bai Y-L, Wang Y (2012) Volatile communication between Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cells under salt stress. Biochem Syst Ecol 40:19–24
Author contributions
All authors listed in the current study contributed to the experimental design and conduct, data analysis and interpretation of results, as well as authoring the paper.
Funding
This study was supported entirely by funds internal to the university (University of Tabriz).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent to publish
All authors have approved the paper and agree with its publication.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals, Clinical Trials Registration or Plant Reproducibility performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali Babazadeh, B., Razeghi, J., Jafarirad, S. et al. Are biosynthesized nanomaterials toxic for the environment? Effects of perlite and CuO/perlite nanoparticles on unicellular algae Haematococcus pluvialis. Ecotoxicology 30, 899–913 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-021-02406-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-021-02406-5