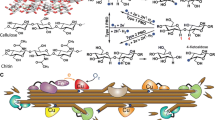
Abstract
Glucoamylases (GAs) are one of the principal groups of enzymes involved in starch hydrolysis and belong to the glycosylhydrolase family. They are classified as exo-amylases due to their ability to hydrolyze α-1,4 glycosidic bonds from the non-reducing end of starch, maltooligosaccharides, and related substrates, releasing β-D-glucose. Structurally, GAs possess a characteristic catalytic domain (CD) with an (α/α)6 fold and exhibit five conserved regions within this domain. The CD may or may not be linked to a non-catalytic domain with variable functions depending on its origin. GAs are versatile enzymes with diverse applications in food, biofuel, bioplastic and other chemical industries. Although fungal GAs are commonly employed for these purposes, they have limitations such as their low thermostability and an acidic pH requirement. Alternatively, GAs derived from prokaryotic organisms are a good option to save costs as they exhibit greater thermostability compared to fungal GAs. Moreover, a group of cold-adapted GAs from psychrophilic organisms demonstrates intriguing properties that make them suitable for application in various industries. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the structural and sequential properties as well as biotechnological applications of GAs in different industrial processes.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article. We have used the following.
References
Abbott DW, van Bueren AL (2014) Using structure to inform carbohydrate binding module function. Curr Opin Struct Biol 28:32–40
Adam AC, Latorre-Garcia L, Polaina J (2004) Structural analysis of glucoamylase encoded by the STA1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae (var. diastaticus). Yeast 21:379–388
Aleshin A, Golubev A, Firsov LM, Honzatko RB (1992) Crystal structure of glucoamylase from Aspergillus awamori var. X100 to 2.2-A resolution. J Biol Chem 267:19291–19298
Aleshin AE, Feng PH, Honzatko RB, Reilly PJ (2003) Crystal structure and evolution of a prokaryotic glucoamylase. J Mol Biol 327:61–73
Ali S, Hossain Z, Mahmood S, Alam R (1990) Purification of glucoamylase from Aspergillus terreus. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 6:431–433
Amaro FX, Kim D, Agarussi MCN, Silva VP, Fernandes T, Arriola KG, Jiang Y, Cervantes AP, Adesogan AT, Ferraretto LF, Yu S, Li W, Vyas D (2021) Effects of exogenous alpha-amylases, glucoamylases, and proteases on ruminal in vitro dry matter and starch digestibility, gas production, and volatile fatty acids of mature dent corn grain. Transl Anim Sci 5:txaa222
Bagheri A, Khodarahmi R, Mostafaie A (2014) Purification and biochemical characterisation of glucoamylase from a newly isolated Aspergillus niger: relation to starch processing. Food Chem 161:270–278
Barrera GN, Tadini CC, Leon AE, Ribotta PD (2016) Use of alpha-amylase and amyloglucosidase combinations to minimize the bread quality problems caused by high levels of damaged starch. J Food Sci Technol 53:3675–3684
Bender H (1981) A bacterial glucoamylase degrading cyclodextrins. Partial purification and properties of the enzyme from a Flavobacterium species. Eur J Biochem 115:287–291
Blanco CA, Caballero I, Barrios R, Rojas A (2014) Innovations in the brewing industry: light beer. Int J Food Sci Nutr 65:655–660
Bott R, Saldajeno M, Cuevas W, Ward D, Scheffers M, Aehle W, Karkehabadi S, Sandgren M, Hansson H (2008) Three-dimensional structure of an intact glycoside hydrolase family 15 glucoamylase from Hypocrea jecorina. Biochemistry 47:5746–5754
Brojanigo S, Gronchi N, Cazzorla T, Wong TS, Basaglia M, Favaro L, Casella S (2022) Engineering Cupriavidus necator DSM 545 for the one-step conversion of starchy waste into polyhydroxyalkanoates. Bioresour Technol 347:126383
Burhan H, Ravinder SR, Deepak C, Poonam S, Fayaz AM, Sanjay S, Ishfaq A (2014) Psychrophilic yeasts and their biotechnological applications. Afr J Biotechnol 13:2188–2197
Busi MV, Barchiesi J, Martin M, Gomez-Casati DF (2013) Starch metabolism in green algae. Starch/stärke 66:28–40
Busic A, Mardetko N, Kundas S, Morzak G, Belskaya H, Ivancic Santek M, Komes D, Novak S, Santek B (2018) Bioethanol production from renewable raw materials and its separation and purification: a review. Food Technol Biotechnol 56:289–311
Carrasco M, Alcaino J, Cifuentes V, Baeza M (2017) Purification and characterization of a novel cold adapted fungal glucoamylase. Microb Cell Fact 16:75
Chen Z, Wang L, Shen Y, Hu D, Zhou L, Lu F, Li M (2022) Improving thermostability of chimeric enzymes generated by domain shuffling between two different original glucoamylases. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 10:881421
Christiansen C, Abou Hachem M, Janecek S, Vikso-Nielsen A, Blennow A, Svensson B (2009) The carbohydrate-binding module family 20–diversity, structure, and function. FEBS J 276:5006–5029
Coutinho PM, Reilly PJ (1994) Structure-function relationships in the catalytic and starch binding domains of glucoamylase. Protein Eng 7:393–400
Coutinho PM, Reilly PJ (1997) Glucoamylase structural, functional, and evolutionary relationships. Proteins 29:334–347
Crabb WD, Mitchinson C (1997) Enzymes involved in the processing of starch to sugars. Trends Biotechnol 15:349–352
Del Pozo-Insfran D, Urias-Lugo D, Hernandez-Brenes C, Saldivar SO (2004) Effect of amyloglucosidase on wort composition and fermentable carbohydrate depletion in sorghum lager beers. J Inst Brew 110:124–132
Devant M, Yu S, Genis S, Larsen T, Wenting L (2020) Effects of exogenous glucoamylase enzymes alone or in combination with a neutral protease on apparent total tract digestibility and feces d-lactate in crossbred angus bulls fed a ration rich in rolled corn. Animals (basel) 10:1077
Diler G, Rannou C, Guyon C, Prost C, Le-Bail A (2021) Use of amyloglucosidase in a soft wheat dough: impact of process and formulation on glucose production. Appl Food Res 1:100007
Dilshad E, Waheed H, Ali U, Amin A, Ahmed I (2021) General structure and classification of bioplastics and biodegradable plastics. In: Kuddus RM (ed) Bioplastics for sustainable development. Springer, Berlin, pp 61–82
Drula E, Garron ML, Dogan S, Lombard V, Henrissat B, Terrapon N (2022) The carbohydrate-active enzyme database: functions and literature. Nucleic Acids Res 50:D571–D577
Dock C, Hess M, Antranikian G (2008) A thermoactive glucoamylase with biotechnological relevance from the thermoacidophilic Euryarchaeon Thermoplasma acidophilum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:105–114
Else AJ, Tronsmo KM, Niemann L-A, Moonen JHE (2013) Use of an anti-staling enzyme mixture in the preparation of baked bread. In: World Intellectual Property Organization, Vol Patent WO2013028071A1
Fagerstrom R (1994) Purification and specificity of recombinant Hormoconis resinae glucoamylase P and endogenous glucoamylase from Trichoderma reesei. Enzyme Microb Technol 16:36–42
Fredi G, Dorigato A (2021) Recycling of bioplastic waste: a review. Polym Res 4:159–177
Ge Y, Wang Y, Zhou H, Wang S, Tong Y, Li W (1999) Coimmobilization of glucoamylase and glucose isomerase by molecular deposition technique for one-step conversion of dextrin to fructose. J Biotechnol 67:33–40
Gregory DA, Taylor CS, Fricker ATR, Asare E, Tetali SSV, Haycock JW, Roy I (2022) Polyhydroxyalkanoates and their advances for biomedical applications. Trends Mol Med 28:331–342
Gupta K, Jana AK, Kumar S, Maiti M (2013) Immobilization of alpha-amylase and amyloglucosidase onto ion-exchange resin beads and hydrolysis of natural starch at high concentration. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 36:1715–1724
Hasunuma T, Ishii J, Kondo A (2015) Rational design and evolutional fine tuning of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for biomass breakdown. Curr Opin Chem Biol 29:1–9
Hebeda RE, Zobel HF (1996) Baked goods freshness: technology, evaluation and inhibition of staling. In: Hebeda HS (ed) REZ. CRC Press, New York
Hooper SD, Bassett A, Sadohara R, Cichy KA (2021) Elucidation of the low resistant starch phenotype in Phaseolus vulgaris exhibited in the yellow bean Cebo Cela. J Food Sci 86:3975–3986
Hua H, Luo H, Bai Y, Wang K, Niu C, Huang H, Shi P, Wang C, Yang P, Yao B (2014) A thermostable glucoamylase from Bispora sp. MEY-1 with stability over a broad pH range and significant starch hydrolysis capacity. PLoS ONE 9:e113581
Janecek S, Marecek F, MacGregor EA, Svensson B (2019) Starch-binding domains as CBM families-history, occurrence, structure, function and evolution. Biotechnol Adv 37:107451
Jia DX, Wang T, Liu ZJ, Jin LQ, Li JJ, Liao CJ, Chen DS, Zheng YG (2018) Whole cell immobilization of refractory glucose isomerase using tris(hydroxymethyl)phosphine as crosslinker for preparation of high fructose corn syrup at elevated temperature. J Biosci Bioeng 126:176–182
Jin LQ, Chen XX, Jin YT, Shentu JK, Liu ZQ, Zheng YG (2021) Immobilization of recombinant Escherichia coli cells expressing glucose isomerase using modified diatomite as a carrier for effective production of high fructose corn syrup in packed bed reactor. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 44:1781–1792
Jin LQ, Xu Q, Liu ZQ, Jia DX, Liao CJ, Chen DS, Zheng YG (2017) Immobilization of recombinant glucose isomerase for efficient production of high fructose corn syrup. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 183:293–306
Kawaguchi H, Hasunuma T, Ogino C, Kondo A (2016) Bioprocessing of bio-based chemicals produced from lignocellulosic feedstocks. Curr Opin Biotechnol 42:30–39
Kim MS, Park JT, Kim YW, Lee HS, Nyawira R, Shin HS, Park CS, Yoo SH, Kim YR, Moon TW, Park KH (2004) Properties of a novel thermostable glucoamylase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus in relation to starch processing. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:3933–3940
Kognou AL, Shrestha S, Jiang Z, Xu C, Sun F, Qin W (2022) High-fructose corn syrup production and its new applications for 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and value-added furan derivatives: promises and challenges. J Biores Bioprod 7:148–160
Kumar D, Singh V (2016) Dry-grind processing using amylase corn and superior yeast to reduce the exogenous enzyme requirements in bioethanol production. Biotechnol Biofuels 9:228
Kumar P, Satyanarayana T (2007) Optimization of culture variables for improving glucoamylase production by alginate-entrapped Thermomucor indicae-seudaticae using statistical methods. Bioresour Technol 98:1252–1259
Kumar P, Satyanarayana T (2009) Microbial glucoamylases: characteristics and applications. Crit Rev Biotechnol 29:225–255
Kumar S, Satyanarayana T (2003) Purification and kinetics of a raw starch-hydrolyzing, thermostable, and neutral glucoamylase of the thermophilic mold Thermomucor indicae-seudaticae. Biotechnol Prog 19:936–944
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874
Lago MC, Dos Santos FC, Bueno PSA, de Oliveira MAS, Barbosa-Tessmann IP (2021) The glucoamylase from Aspergillus wentii: purification and characterization. J Basic Microbiol 61:443–458
Lam WC, Pleissner D, Lin CS (2013) Production of fungal glucoamylase for glucose production from food waste. Biomolecules 3:651–661
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Lebenthal E, Khin Maung U, Zheng BY, Lu RB, Lerner A (1994) Small intestinal glucoamylase deficiency and starch malabsorption: a newly recognized alpha-glucosidase deficiency in children. J Pediatr 124:541–546
Lebenthal E, Lee PC (1980a) Development of functional responses in human exocrine pancreas. Pediatrics 66:556–560
Lebenthal E, Lee PC (1980b) Glucoamylase and disaccharidase activities in normal subjects and in patients with mucosal injury of the small intestine. J Pediatr 97:389–393
Lee PC, Werlin S, Trost B, Struve M (2004) Glucoamylase activity in infants and children: normal values and relationship to symptoms and histological findings. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 39:161–165
Li Z, Wei P, Cheng H, He P, Wang Q, Jiang N (2014) Functional role of β-domain in the Thermoanaerobacter tengcongensis glucoamylase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:2091–2099
Li X, Mettu S, Martin GJO, Ashokkumar M, Sze C, Lin K (2019) Ultrasonic pretreatment of food waste to accelerate enzymatic hydrolysis for glucose production. Ultrason Sonochem 53:77–82
Li Z, Ji K, Dong W, Ye X, Wu J, Zhou J, Wang F, Chen Q, Fu L, Li S, Huang Y, Cui Z (2017) Cloning, heterologous expression, and enzymatic characterization of a novel glucoamylase GlucaM from Corallococcus sp. strain EGB. Protein Expr Purif 129:122–127
Lincoln L, More VS, More SS (2019) Purification and biochemical characterization of extracellular glucoamylase from Paenibacillus amylolyticus strain. J Basic Microbiol 59:375–384
Liu HL, Wang WC (2003) Protein engineering to improve the thermostability of glucoamylase from Aspergillus awamori based on molecular dynamics simulations. Protein Eng 16:19–25
Liu YN, Lai YT, Chou WI, Chang MD, Lyu PC (2007) Solution structure of family 21 carbohydrate-binding module from Rhizopus oryzae glucoamylase. Biochem J 403:21–30
Liu ZQ, Zheng W, Huang JF, Jin LQ, Jia DX, Zhou HY, Xu JM, Liao CJ, Cheng XP, Mao BX, Zheng YG (2015) Improvement and characterization of a hyperthermophilic glucose isomerase from Thermoanaerobacter ethanolicus and its application in production of high fructose corn syrup. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 42:1091–1103
Lopez C, Torrado A, Guerra NP, Pastrana L (2005) Optimization of solid-state enzymatic hydrolysis of chestnut using mixtures of alpha-amylase and glucoamylase. J Agric Food Chem 53:989–995
Marin-Navarro J, Polaina J (2011) Glucoamylases: structural and biotechnological aspects. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89:1267–1273
Marshall CJ (1997) Cold-adapted enzymes. Trends Biotechnol 15:359–364
Mirdita M, Schutze K, Moriwaki Y, Heo L, Ovchinnikov S, Steinegger M (2022) ColabFold: making protein folding accessible to all. Nat Methods 19:679–682
Mertens JA, Braker JD, Jordan DB (2010) Catalytic properties of two Rhizopus oryzae 99–880 glucoamylase enzymes without starch binding domains expressed in Pichia pastoris. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 162:2197–2213
Mishra A, Debnath Das M (2002) Effect of pH on simultaneous saccharification and isomerization by glucoamylase and glucose isomerase. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 102–103:193–199
Mohamed L, Zakaria M, Ali A, el Youssfi K, Mohamed E, Mohamed O, El Hassan B, Mohamed J (2007) Optimization of composition of media for the production of extracellular glucoamylase by Candida guilliermendii. Pak J Biol Sci 10:3322–3329
Morimoto NHT, Isono N, Tochihara T, Watanabe K, Ito HMH (2004) Cloning, sequencing and heterologous expression of the gene encoding glucoamylase from Clostridium thermoamylolyticum and biochemical characterization of the recombinant enzyme. J Appl Glycosci 51:33–36
Nevoigt E (2008) Progress in metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 72:379–412
Nisha M, Satyanarayana T (2014) Characterization and multiple applications of a highly thermostable and Ca(2)(+)-independent amylopullulanase of the extreme thermophile Geobacillus thermoleovorans. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 174:2594–2615
O’Rourke T, Godfrey T, West S (1996) In industrial enzymology, 2nd edn. MacMillan, London
Obulisamy PK, Mehariya S (2021) Polyhydroxyalkanoates from extremophiles: a review. Bioresour Technol 325:124653
Ogunsona E, Ojogbo E, Mekonnen T (2018) Advanced material applications of starch and its derivatives. Eur Polym J 108:570–581
Ohnishi H, Sakai H, Ohta T (1991) Purification and some properties of a glucoamylase from Clostridium sp. G0005. Agric Biol Chem 55:1901–1902
Parashar D, Satyanarayana T (2017) Engineering a chimeric acid-stable alpha-amylase-glucoamylase (Amy-Glu) for one step starch saccharification. Int J Biol Macromol 99:274–281
Pedersen S (1993) Industrial aspects of immobilized glucose isomerase. Bioprocess Technol 16:185–208
Pomeranz Y, Rubenthaler GL, Finney KF (1964) Use of amyloglucosidase in bread making. Food Technol 18:138–140
Rajendran N, Han J (2023) Techno-economic analysis and life cycle assessment of poly (butylene succinate) production using food waste. Waste Manag 156:168–176
Reilly PJ (1999) Protein engineering of glucoamylase to improve industrial performance—a review. Starch-Stärke 51:269–274
Roth C, Moroz OV, Ariza A, Skov LK, Ayabe K, Davies GJ, Wilson KS (2018) Structural insight into industrially relevant glucoamylases: flexible positions of starch-binding domains. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 74:463–470
Sakaguchi M, Matsushima Y, Nankumo T, Seino J, Miyakawa S, Honda S, Sugahara Y, Oyama F, Kawakita M (2014) Glucoamylase of Caulobacter crescentus CB15: cloning and expression in Escherichia coli and functional identification. AMB Express 4:5
Sato K, Mizuno A, Mukai N, Amano H (2006) Method of manufacturing fermented malt beverages. In: Vol patent Us7, 115, 289 B2
Sauer J, Sigurskjold BW, Christensen U, Frandsen TP, Mirgorodskaya E, Harrison M, Roepstorff P, Svensson B (2000) Glucoamylase: structure/function relationships, and protein engineering. Biochim Biophys Acta 1543:275–293
Serour E, Antranikian G (2002) Novel thermoactive glucoamylases from the thermoacidophilic Archaea Thermoplasma acidophilum, Picrophilus torridus and Picrophilus oshimae. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 81:73–83
Sevcik J, Hostinova E, Solovicova A, Gasperik J, Dauter Z, Wilson KS (2006) Structure of the complex of a yeast glucoamylase with acarbose reveals the presence of a raw starch binding site on the catalytic domain. FEBS J 273:2161–2171
Sevcik J, Solovicova A, Hostinova E, Gasperik J, Wilson KS, Dauter Z (1998) Structure of glucoamylase from Saccharomycopsis fibuligera at 1.7 A resolution. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 54:854–866
Siddiqui KS, Cavicchioli R (2006) Cold-adapted enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem 75:403–433
Siguenza-Andres T, Pando V, Gomez M, Rodriguez-Nogales JM (2022) Optimization of a simultaneous enzymatic hydrolysis to obtain a high-glucose slurry from bread waste. Foods 11:1793
Silveira ST, Oliveira MS, Costa JA, Kalil SJ (2006) Optimization of glucoamylase production by Aspergillus niger in solid-state fermentation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 128:131–140
Smith AM (2008) Prospects for increasing starch and sucrose yields for bioethanol production. Plant J 54:546–558
Sorimachi K, Jacks AJ, Le Gal-Coeffet MF, Williamson G, Archer DB, Williamson MP (1996) Solution structure of the granular starch binding domain of glucoamylase from Aspergillus niger by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Mol Biol 259:970–987
Specka U, Mayer F, Antranikian G (1991) Purification and properties of a thermoactive glucoamylase from clostridium thermosaccharolyticum. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:2317–2323
Struyf N, Verspreet J, Verstrepen KJ, Courtin CM (2017) Investigating the impact of α-amylase, α-glucosidase and glucoamylase action on yeast-mediated bread dough fermentation and bread sugar levels. J Cereal Sci 75:35–44
Svensson B, Larsen K, Gunnarsson A (1986) Characterization of a glucoamylase G2 from Aspergillus niger. Eur J Biochem 154:497–502
Swain MR, Natarajan V, Krishnan C (2017) Marine enzymes and microorganisms for bioethanol production. Adv Food Nutr Res 80:181–197
Tanaka Y, Tao W, Blanchard JS, Hehre EJ (1994) Transition state structures for the hydrolysis of alpha-d-glucopyranosyl fluoride by retaining and inverting reactions of glycosylases. J Biol Chem 269:32306–32312
Tang G, Zhong L, Yang K, Zheng Y, Cao X (1996) Construction of a brewing yeast having glucoamylase activity and its fermentation characteristics. Chin J Biotechnol 12:263–267
Teigiserova DA, Hamelin L, Thomsen M (2020) Towards transparent valorization of food surplus, waste and loss: clarifying definitions, food waste hierarchy, and role in the circular economy. Sci Total Environ 706:136033
Tong L, Zheng J, Wang X, Wang X, Huang H, Yang H, Tu T, Wang Y, Bai Y, Yao B, Luo H, Qin X (2021) Improvement of thermostability and catalytic efficiency of glucoamylase from Talaromyces leycettanus JCM12802 via site-directed mutagenesis to enhance industrial saccharification applications. Biotechnol Biofuels 14:202
Tse TJ, Wiens DJ, Reaney MJ (2021) Production of bioethanol—a review of factors affecting ethanol yield. Fermentation 7:268
Valjakka TT, Ponte JG, Kulp K (1994) Studies on a raw-starch digesting enzyme. II. Replacement of sucrose in white pan bread. Cereal Chem 71:145–149
Vallat I, Monsan P, Riba JP (1985) Influence of glucose on the kinetics of maltodextrin hydrolysis using free and immobilized glucoamylase. Biotechnol Bioeng 27:1274–1275
Wang JB, Kong B, Wang H, Cai LY, Zhang RJ, Cai FJ, Zhu ZJ, Cao JH, Xu J (2021a) Production of butanol from distillers’ grain waste by a new aerotolerant strain of Clostridium beijerinckii LY-5. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 44:2167–2179
Wang X, Liao B, Li Z, Liu G, Diao L, Qian F, Yang J, Jiang Y, Zhao S, Li Y, Yang S (2021b) Reducing glucoamylase usage for commercial-scale ethanol production from starch using glucoamylase expressing Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biores Bioprod 8:20
Wang XQ, Wang QH, Hong ZM, Yin W (2009) Lactic acid fermentation of food waste using integrated glucoamylase production. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 84:139–143
Wayllace NM, Hedin N, Busi MV, Gomez-Casati DF (2021) Characterization of SdGA, a cold-adapted glucoamylase from Saccharophagus degradans. Biotechnol Rep (amst) 30:e00625
Wayllace NM, Hedin N, Busi MV, Gomez-Casati DF (2022) Identification, molecular and biochemical characterization of a novel thermoactive and thermostable glucoamylase from Thermoanaerobacter ethanolicus. Biotechnol Lett 44:1201–1216
Xian L, Feng JX (2018) Purification and biochemical characterization of a novel mesophilic glucoamylase from Aspergillus tritici WZ99. Int J Biol Macromol 107:1122–1130
Yadav AR, Guha M, Reddy SY, Tharanathan RN, Ramteke RS (2007) Physical properties of acetylated and enzyme-modified potato and sweet potato flours. J Food Sci 72:E249-253
Yan BX, Sun YQ (1997) Glycine residues provide flexibility for enzyme active sites. J Biol Chem 272:3190–3194
Yang X, Lee JH, Yoo HY, Shin HY, Thapa LP, Park C, Kim SW (2014) Production of bioethanol and biodiesel using instant noodle waste. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 37:1627–1635
Zheng Y, Xue Y, Zhang Y, Zhou C, Schwaneberg U, Ma Y (2010) Cloning, expression, and characterization of a thermostable glucoamylase from Thermoanaerobacter tengcongensis MB4. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:225–233
Zong X, Wen L, Wang Y, Li L (2022) Research progress of glucoamylase with industrial potential. J Food Biochem 46:e14099
Acknowledgements
NMW is a doctoral fellow from CONICET. MM, MVB and DFGC are research scientists from CONICET.
Funding
This work was supported by ANPCyT (PICT 2018 01440), National University of Rosario (VT-2021) and CONICET (PIP 2021–3068).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Writing original draft: NMW; writing, review and editing: DFGC, MVB and MM. We searched databases (Pubmed and Scopus) for keywords such as glucoamylase, glucoside hydrolase, microbial glucoamylases, glucoamylase structure and biotechnological applications of glucoamylases.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wayllace, N.M., Martín, M., Busi, M.V. et al. Microbial glucoamylases: structural and functional properties and biotechnological uses. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 39, 293 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03731-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03731-z