Abstract
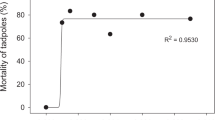
Among the measures used to manage mosquito populations and prevent human diseases, the application of pesticides is the global strategy mostly employed. To investigate the lethal and sublethal effects of insecticides used to control mosquitoes on amphibians (Rhinella arenarum, Rhinella fernandezae, and Physalaemus albonotatus), tadpoles were exposed to commercial formulations of temephos (Abate®), Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis (Introban®), and permethrin (Depe®). Their acute toxicity in terms of median lethal concentration (LC50) and no- (NOEC) and lowest-observed-effect concentrations (LOEC) was evaluated. To assess the sublethal effects on behavioral endpoints, tadpoles were exposed to the NOEC-24-h value of each insecticide. After that, tadpoles were recorded and video-streaming data were processed by Smart® software. Based on LC50, permethrin was the most toxic insecticide, followed by temephos and B. thuringiensis var. israelensis. Also, intraspecific and interspecific susceptibilities of tadpoles to insecticides were observed. Regarding behavior, the exposure of R. arenarum to the three insecticides had a significant effect on all behavioral endpoints. Two of the three swimming parameters evaluated for R. fernandezae were affected by permethrin, and in the end, only one behavioral pattern was altered in P. albonotatus after exposure to temephos. These results showed that tadpoles’ species were affected differently depending on the chemical properties of the pesticide and on a dose-response effect of the insecticides. Overall, our study suggests that further research is needed to quantify the potential damage of pyrethroid insecticides used for mosquito control on non-target aquatic organisms, mainly due to etho-toxic effects.



Similar content being viewed by others

References
Agnelli, P., Bellucci, V., Bianco, P. M., Jacomini, C., Modonesi, C. M., Panizza, C., & Tamino, G. (2015). Impatto sugli ecosistemi e sugli esseri viventi delle sostanze sintetiche utilizzate nella profilassi antizanzara. In: D. Mazzella (Ed.). Roma: Istituto Superiore per la Protezione e la Ricerca Ambientale Via-Ambiente e Societá.
ASIH: American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists. (2004). Guidelines for use of live amphibians and reptiles in field and laboratory research, 2nd edn. Washington, D.C.: Herpetological Animal Care and Use Committee (HACC) of the American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists.
ASTM: American Society for Testing and Materials (2007). Standard guide for conducting whole sediment toxicity tests with amphibians, E. 2591-07. In: ASTM book of standards, biological effects and environmental fate; biotechnology, vol. 11.06, pp. 776–791.
Attademo, A. M., Peltzer, P. M., Lajmanovich, R. C., Cabagna-Zenklusen, M. C., Junges, C. M., & Basso, A. (2014). Biological endpoints, enzyme activities, and blood cell parameters in two anuran tadpole species in rice agroecosystems of mid-eastern Argentina. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(1), 635–649.
Biber, P. A., Dueñas, J. R., Almeida, F. L., Gardenal, C. N., & Almirón, W. R. (2006). Laboratory evaluation of susceptibility of natural subpopulations of Aedes aegypti larvae to temephos. Journal of the American Mosquito Control Association, 22(3), 408–411.
Boisvert, M., & Boisvert, J. (2000). Effects of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis on target and nontarget organisms: a review of laboratory and field experiments. Biocontrol Science and Technology, 10(5), 517–561.
Bowatte, G., Perera, P., Senevirathne, G., Meegaskumbura, S., & Meegaskumbura, M. (2013). Tadpoles as dengue mosquito (Aedes aegypti) egg predators. Biological Control, 67(3), 469–474.
Brunelli, E., Bernabó, I., Berg, C., Lundstedt-Enkel, K., Bonacci, A., & Tripepi, S. (2009). Environmentally relevant concentrations of endosulfan impair development, metamorphosis and behaviour in Bufo bufo tadpoles. Aquatic Toxicology, 91, 135–142.
Caquet, T., Roucaute, M., Le Goff, P., & Lagadic, L. (2011). Effects of repeated field applications of two formulations of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis on non-target saltmarsh invertebrates in Atlantic coastal wetlands. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 74(5), 1122–1130.
Crivelenti, L. Z., Guilherme, L. C., Morelli, S., & Borin, S. (2010). Toxicidade do inseticida organofosforado Abate® em alevinos de Poecilia reticulata. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Ecotoxicology, 5(2–3), 1–4.
Davies, T. G. E., Field, L. M., Usherwood, P. N. R., & Williamson, M. S. (2007). DDT, pyrethrins, pyrethroids and insect sodium channels. IUBMB Life, 59(3), 151–162.
Denoël, M., Bichot, M., Ficetola, G. F., Delcourt, J., Ylieff, M., Kestemont, P., & Poncin, P. (2010). Cumulative effects of road de-icing salt on amphibian behavior. Aquatic Toxicology, 99(2), 275–280.
Denoël, M., D’Hooghe, B., Ficetola, G. F., Brasseur, C., De Pauw, E., Thomé, J.-P., & Kestemont, P. (2012). Using sets of behavioral biomarkers to assess short-term effects of pesticide: a study case with endosulfan on frog tadpoles. Ecotoxicology, 21(4), 1240–1250.
Denoël, M., Libon, S., Kestemont, P., Brasseur, C., Focant, J.-F., & De Pauw, E. (2013). Effects of a sublethal pesticide exposure on locomotor behavior: a video-tracking analysis in larval amphibians. Chemosphere, 90(3), 945–951.
Fort, D. J., Propst, T. L., Stover, E. L., Helgen, J. C., Levey, R. B., Gallagher, K., & Burkhart, J. G. (1999). Effects of pond water, sediment, and sediment extracts from Minnesota and Vermont, USA, on early development and metamorphosis of Xenopus. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 18(10), 2305–2315.
Gosner, K. L. (1960). A simplified table for staging anuran embryos and larvae with notes on identification. Herpetologica, 16(3), 183–190.
Hagman, M., & Shine, R. (2007). Effects of invasive cane toads on Australian mosquitoes: does the dark cloud have a silver lining? Biological Invasions, 9(4), 445–452.
Hamilton, M. A., Russo, R. C., & Thurston, R. V. (1977). Trimmed Spearman-Karber method for estimating median lethal concentrations in toxicity bioassays. Environmental Science & Technology, 11, 714–719.
Harischandra, H. K. S. P., Karunaratne, S. H. P. P., & Rajakaruna, R. S. (2011). Effect of mosquito larvicide Abate® on the developmental stages of the Asian common toad, Bufo melanostictus. Ceylon Journal of Science, 40(2), 133–140.
Hilbert, J. (2016). Argentina battles major outbreak of dengue as mosquito population swells–the New York Times. New York: New York Times http://www.nytimes.com/2016/02/18/world/americas/argentina-battles-major-outbreak-of-dengue-as-mosquito-population-swells.html?_r=0. Accessed 22 July 2016.
IUCN (2015). An analysis of amphibians on the 2015. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2015-4. >. Accessed 11 June 2015.
Jager, T. (2012). Bad habits die hard: the NOEC’s persistence reflects poorly on ecotoxicology. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 31(2), 228–229.
Johansson, M., Piha, H., Kylin, H., & Merilä, J. (2006). Toxicity of six pesticides to common frog (Rana temporaria) tadpoles. Environmental Toxicology, 25(12), 3164–3170.
Lagadic, L., Roucaute, M., & Caquet, T. (2014). Bti sprays do not adversely affect non-target aquatic invertebrates in French Atlantic coastal wetlands. Journal of Applied Ecology, 51, 102–113.
Lajmanovich, R. C., Peltzer, P. M., Junges, C. M., Attademo, A. M., Sanchez, L. C., & Bassó, A. (2010). Activity levels of B-esterases in the tadpoles of 11 species of frogs in the middle Paraná River floodplain: Implication for ecological risk assessment of soybean crops. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 73(7), 1517–1524.
Lajmanovich, R. C., Junges, C. M., Cabagna-Zenklusen, M. C., Attademo, A. M., Peltzer, P. M., Maglianese, M., et al. (2015). Toxicity of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis in aqueous suspension on the South American common frog Leptodactylus latrans (Anura: Leptodactylidae) tadpoles. Environmental Research, 136, 205–212.
Lavorato, M., Bernabò, I., Crescente, A., Denoël, M., Tripepi, S., & Brunelli, E. (2013). Endosulfan effects on Rana dalmatina tadpoles: Quantitative developmental and behavioural analysis. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 64(2), 253–262.
Maletz, S., Wollenweber, M., Kubiak, K., Müller, A., Schmitz, S., Maier, D., et al. (2015). Investigation of potential endocrine disrupting effects of mosquito larvicidal Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis (Bti) formulations. Science of the Total Environment Journal, 536, 729–738.
Mandrillon, A., & Saglio, P. (2007). Waterborne amitrole affects the predator–prey relationship between common frog tadpoles (Rana temporaria) and larval spotted salamander (Salamandra salamandra). Environmental Toxicology, 53, 233–240.
McDiarmid, R. W., & Altig, R. (1999). Tadpoles: the biology of anuran larvae. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Ministerio de Salud de la Nación (2011). Directrices para la prevención y control de Aedes aegypti. Dirección de Enfermedades Transmisibles por Vectores-Cdad. Autónoma de Bs. As., República Argentina.Web: www.msal.gov.ar
Miyamoto, M., Saito, S., Fujisawa, T., & Katagi, T. (2015). Bioconcentration and metabolism of trans-tetramethrin in fish. Journal of Pesticide Science, 40(3), 1–8.
Moore, L. J., Fuentes, L., Rodgers, J. H., Bowerman, W. W., Yarrow, G. K., Chao, W. Y., & Bridges, W. C. (2012). Relative toxicity of the components of the original formulation of Roundup® to five North American anurans. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 78, 128–133.
Nkya, T. E., Akhouayri, I., Kisinza, W., & David, J.-P. (2013). Impact of environment on mosquito response to pyrethroid insecticides: facts, evidences and prospects. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 43(4), 407–416.
Peltzer, P. M., Lajmanovich, R. C., Attademo, A. M., & Beltzer, A. H. (2006). Diversity of anurans across agricultural ponds in Argentina. Biodiversity and Conservation, 15, 3499–3513.
Peltzer, P. M., Junges, C. M., Attademo, A. M., Bassó, A., Grenón, P., & Lajmanovich, R. C. (2013). Cholinesterase activities and behavioral changes in Hypsiboas pulchellus (Anura: Hylidae) tadpoles exposed to glufosinate ammonium herbicide. Ecotoxicology, 22(7), 1165–1173.
Preud’homme, V., Milla, S., Gillardin, V., De Pauw, E., Denoël, M., & Kestemont, P. (2015). Effects of low dose endosulfan exposure on brain neurotransmitter levels in the African clawed frog Xenopus laevis. Chemosphere, 120, 357–364.
Relyea, R. A., & Jones, D. K. (2009). The toxicity of roundup original max to 13 species of larval amphibians. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 28(9), 2004–2008.
Rubbo, M. J., Lanterman, J. L., Falco, R. C., & Daniels, T. J. (2011). The influence of amphibians on mosquitoes in seasonal pools: Can wetlands protection help to minimize disease risk? Wetlands, 31(4), 799–804.
Sarwar, M. (2015). Controlling dengue spreading Aedes mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) using ecological services by frogs, toads and tadpoles (Anura) as predators. American Journal of Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery, 1(1), 18–24.
Schleier, J. J., & Peterson, R. K. D. (2010). Toxicity and risk of permethrin and naled to non-target insects after adult mosquito management. Ecotoxicology, 19(6), 1140–1146.
Scott, G. R., & Sloman, K. A. (2004). The effects of environmental pollutants on complex fish behaviour: integrating behavioural and physiological indicators of toxicity. Aquatic Toxicology, 68, 369–392.
Seccacini, E., Lucia, A., Zerba, E., Licastro, S., & Masuh, H. (2008). Aedes aegypti resistance to temephos in Argentina. Journal of the American Mosquito Control Association, 24(4), 608–609.
Selvi, M., Sarikaya, R., & Erkoç, F. (2004). Acute behavioral changes in the guppy (Poecilia reticulata) exposed to temephos. Gazi University Journal of Science, 17(4), 15–19.
Shao, Q. (2000). Estimation for hazardous concentrations based on NOEC toxicity data: an alternative approach. Environmetrics, 11(5), 583–595.
Smetanová, S., Bláha, L., Liess, M., Schäfer, R. B., & Beketov, M. A. (2014). Do predictions from species sensitivity distributions match with field data? Environmental Pollution, 189, 126–133.
Sparling, D. W., Lowe, T. P., & Pinkney, A. E. (1997). Toxicity of abate to green frog tadpoles. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 58, 475–481.
Tarragona, S., Monteverde, M., Marchioni, S., Caporale, J., Pereiro, A., & Palacios, J. (2012). Dengue in Argentina: an economic analysis of the impact of the 2009 epidemic. Salud Colectiva (English Edition), 8(2), 151–162.
USEPA (1975). Methods for acute toxicity tests with fish, macroinvertebrates, and amphibians. USEPA660/3-75-009, p. 62.
USEPA (2002). Methods for measuring the acute toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to freshwater and marine organisms. Fifth edition, USEPA 821-R-02-012.
Van Buskirk, J., & McCollum, S. A. (2000). Influence of tail shape on tadpole swimming performance. The Journal Experimental Biology, 203, 2149–2158.
Wagner, C., & Løkke, H. (1991). Estimation of ecotoxicological protection levels from NOEC toxicity data. Water Research, 25(10), 1237–1242.
Wheeler, M. W., Park, R. M., & Bailer, A. J. (2006). Comparing median lethal concentration values using confidence interval overlap or ratio tests. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 25(5), 1441–1444.
WHO. (2008). WHO specifications and evaluations for public health pesticides—temephos. Geneva: World Health Organization Accessed 20 October 2015.
WHO (2009). Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis (Bti) in drinking-water. WHO Guidelines for drinking-water quality. Switzerland. http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/gdwqrevision/RevisedFourthEditionBacillusthuringiensis_Bti_July272009_2.pdf. Accessed 15 Oct 2015.
Winandy, L., & Denoël, M. (2011). The use of visual and automatized behavioral markers to assess methodologies: a study case on PIT-tagging in the Alpine newt. Behavior Research Methods, 43(2), 568–576.
Zambrini, D. A. B. (2011). Neglected lessons from the 2009 dengue epidemic in Argentina. Revista de Saúde Pública, 45(2), 428–431.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by the National Agency for Promotion of Science and Technology (ANPCyT-FONCyT PICT) and the Course of Action for Research and Science Promotion (CAI + D-UNL).
Author Contributions
Celina M. Junges, Mariana I. Maglianese, and Rafael C. Lajmanovich conceived and designed the experiments. Rafael C. Lajmanovich and Andrés M. Attademo collected the amphibian species. Celina M. Junges and Paola M. Peltzer contributed writing and revising the paper. All authors reviewed the manuscript and approved the final version.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in this study involving animals were in accordance with the ASIH (2004) criteria and ethical standards of the animal ethics committee of the Facultad de Bioquímica y Ciencias Biológicas, FBCB Res. CD no. 388/06.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Junges, C.M., Maglianese, M.I., Lajmanovich, R.C. et al. Acute Toxicity and Etho-toxicity of Three Insecticides Used for Mosquito Control on Amphibian Tadpoles. Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 143 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3324-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3324-6