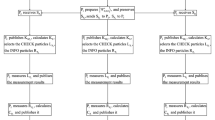
Abstract
The study of hierarchical quantum communication is of great importance in resolving practical scenarios involving multiple agents with varying permissions to access information. Inspired by the work (Shukla et al. Quantum Inf Process 16(8):1–32, 2017), we reinvestigated probabilistic hierarchical protocols and presented an alternative deterministic hierarchical joint remote state preparation scheme via a non-maximally entangled channel, in which the successful probability of remote state preparation reaches 1 with appropriate operations or measurements. And this scheme is also applicable to many different quantum communication scenarios. For example, we described a scenario where senders are unknown to information. In this scenario, the information can also be deterministically transferred to recipients by our program. This protocol solves the problem of inefficient communication due to entanglement degradation and contributes to realizing practical quantum communication.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shannon, C.E.: A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 27(3), 379–423 (1948)
Benioff, P.: The computer as a physical system: A microscopic quantum mechanical Hamiltonian model of computers as represented by Turing machines. J. Stat. Phys. 22, 563–591 (1980)
Lloyd, S.: Almost any quantum logic gate is universal. Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 346–349 (1995)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. Theor. Comput. Sci. 560, 7–11 (2014)
Xu, H., Song, X.-K., Wang, D., Ye, L.: Quantum sensing of control errors in three-level systems by coherent control techniques. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 66(4), 240314 (2023)
Deutsch, D.: Quantum theory, the Church–Turing principle and the universal quantum computer. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 400(1818), 97–117 (1985)
Deutsch, D.E.: Quantum computational networks. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 425(1868), 73–90 (1989)
Shor, P.W.: Algorithms for quantum computation: discrete logarithms and factoring. In: Proceedings 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, pp. 124–134 (1994)
Shor, P.W.: Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. SIAM Rev. 41(2), 303–332 (1999)
Duan, L.-M., Lukin, M.D., Cirac, J.I., Zoller, P.: Long-distance quantum communication with atomic ensembles and linear optics. Nature 414(6862), 413–418 (2001)
Gisin, N., Thew, R.: Quantum communication. Nat. Photonics 1(3), 165–171 (2007)
Ekert, A.K.: Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 661–663 (1991)
Shor, P.W., Preskill, J.: Simple proof of security of the bb84 quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 441–444 (2000)
Kwek, L.-C., Cao, L., Luo, W., Wang, Y., Sun, S., Wang, X., Liu, A.Q.: Chip-based quantum key distribution. AAPPS Bull. 31(1), 15 (2021)
Liu, B., Xia, S., Xiao, D., Huang, W., Xu, B., Li, Y.: Decoy-state method for quantum-key-distribution-based quantum private query. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 65(4), 66 (2022)
Li, Z., Wei, K.: Improving parameter optimization in decoy-state quantum key distribution. Quantum Eng. 2022, 9717591 (2022)
Sheng, Y.-B., Zhou, L.: Accessible technology enables practical quantum secret sharing. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 66(6), 260331 (2023)
Shenoy-Hejamadi, A., Pathak, A., Radhakrishna, S.: Quantum cryptography: key distribution and beyond. Quanta 6(1), 1–47 (2017)
Chen, M.-F., Zhou, P., Lan, Q., Lu, X.-Q.: Hyper-parallel nonlocal cnot operation assisted by quantum-dot spin in a double-sided optical microcavity. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 40(12), 3291–3300 (2023)
Bennett, C.H., Wiesner, S.J.: Communication via one- and two-particle operators on Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 69, 2881–2884 (1992)
Mattle, K., Weinfurter, H., Kwiat, P.G., Zeilinger, A.: Dense coding in experimental quantum communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 4656–4659 (1996)
Bruß, D., D’Ariano, G.M., Lewenstein, M., Macchiavello, C., Sen, A., Sen, U.: Distributed quantum dense coding. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 210–501 (2004)
Guo, Y., Liu, B.-H., Li, C.-F., Guo, G.-C.: Advances in quantum dense coding. Adv. Quantum Technol. 2(5–6), 1900011 (2019)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Crépeau, C., Jozsa, R., Peres, A., Wootters, W.K.: Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1895–1899 (1993)
Karlsson, A., Bourennane, M.: Quantum teleportation using three-particle entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 58, 4394–4400 (1998)
Stenholm, S., Bardroff, P.J.: Teleportation of n-dimensional states. Phys. Rev. A 58, 4373–4376 (1998)
Sisodia, M., Shukla, A., Thapliyal, K., Pathak, A.: Design and experimental realization of an optimal scheme for teleportation of an n-qubit quantum state. Quantum Inf. Process. 16, 1–19 (2017)
Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65, 032302 (2002)
Deng, F.-G., Long, G.L., Liu, X.-S.: Two-step quantum direct communication protocol using the Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen pair block. Phys. Rev. A 68, 042317 (2003)
Deng, F.-G., Long, G.L.: Secure direct communication with a quantum one-time pad. Phys. Rev. A 69, 052319 (2004)
Banerjee, A., Pathak, A.: Maximally efficient protocols for direct secure quantum communication. Phys. Lett. A 376(45), 2944–2950 (2012)
Zhang, W., Ding, D.-S., Sheng, Y.-B., Zhou, L., Shi, B.-S., Guo, G.-C.: Quantum secure direct communication with quantum memory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 220501 (2017)
Liu, X., Luo, D., Lin, G., Chen, Z., Huang, C., Li, S., Zhang, C., Zhang, Z., Wei, K.: Fiber-based quantum secure direct communication without active polarization compensation. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 65(12), 120311 (2022)
Zhou, L., Xu, B.-W., Zhong, W., Sheng, Y.-B.: Device-independent quantum secure direct communication with single-photon sources. Phys. Rev. Appl. 19, 014036 (2023)
Zeng, H., Du, M.-M., Zhong, W., Zhou, L., Sheng, Y.-B.: High-capacity device-independent quantum secure direct communication based on hyper-encoding. Fundamental Research (2023)
Lo, H.-K.: Classical-communication cost in distributed quantum-information processing: a generalization of quantum-communication complexity. Phys. Rev. A 62, 012313 (2000)
Pati, A.K.: Minimum classical bit for remote preparation and measurement of a qubit. Phys. Rev. A 63, 014302 (2000)
Bennett, C.H., DiVincenzo, D.P., Shor, P.W., Smolin, J.A., Terhal, B.M., Wootters, W.K.: Remote state preparation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 077902 (2001)
Nguyen, B.A., Cao, T.B., Nung, V.D., Kim, J.: Remote state preparation with unit success probability. Adv. Nat. Sci. 2(3), 035009 (2011)
Dakić, B., Lipp, Y.O., Ma, X., Ringbauer, M., Kropatschek, S., Barz, S., Paterek, T., Vedral, V., Zeilinger, A., Brukner, Č, Walther, P.: Quantum discord as resource for remote state preparation. Nat. Phys. 8(9), 666–670 (2012)
Sharma, V., Shukla, C., Banerjee, S., Pathak, A.: Controlled bidirectional remote state preparation in noisy environment: a generalized view. Quantum Inf. Process. 14, 3441–3464 (2015)
Li, X., Ghose, S.: Optimal joint remote state preparation of equatorial states. Quantum Inf. Process. 14(12), 4585–4592 (2015)
Nguyen, B.A., Kim, J.: Joint remote state preparation. J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 41(9), 095501 (2008)
Peng, J.-Y., Luo, M.-X., Mo, Z.-W.: Joint remote state preparation of arbitrary two-particle states via ghz-type states. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 2325–2342 (2013)
An, N.B., Dat, L.T., Kim, J.: Nonstandard protocols for joint remote preparation of a general quantum state and hybrid entanglement of any dimension. Phys. Rev. A 98, 042329 (2018)
Du, Z., Li, X.: Deterministic joint remote state preparation of four-qubit cluster type with tripartite involvement. Quantum Inf. Process. 19(1), 39 (2019)
Gottesman, D.: Theory of quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 61, 042311 (2000)
Wang, X.-W., Xia, L.-X., Wang, Z.-Y., Zhang, D.-Y.: Hierarchical quantum-information splitting. Opt. Commun. 283(6), 1196–1199 (2010)
Shukla, C., Pathak, A.: Hierarchical quantum communication. Phys. Lett. A 377(19), 1337–1344 (2013)
Wang, X.-W., Zhang, D.-Y., Tang, S.-Q., Xie, L.-J.: Multiparty hierarchical quantum-information splitting. J. Phys. B: At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 44(3), 035505 (2011)
Bich, C.T., An, N.B.: Hierarchically controlling quantum teleportations. Quantum Inf. Process. 18, 1–14 (2019)
Ma, S., Wang, N.: Hierarchical remote preparation of an arbitrary two-qubit state with multiparty. Quantum Inf. Process. 20(8), 276 (2021)
Shukla, C., Thapliyal, K., Pathak, A.: Hierarchical joint remote state preparation in noisy environment. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(8), 1–32 (2017)
Chen, N., Yan, B., Chen, G., Zhang, M.-J., Pei, C.-X.: Deterministic hierarchical joint remote state preparation with six-particle partially entangled state. Chin. Phys. B 27(9), 090304 (2018)
Jing, R.-H., Huang, Y.-B., Bi, A.-A., Luo, W.-W., Zhou, P., Lan, Q.: Mentor initialed multiparty hierarchical joint remote preparation of an arbitrary n-qudit state via generalized bell states. Phys. Scr. 99(2), 025103 (2024)
Mohanty, P., Jariwala, E.M.Q., Webb, R.A.: Intrinsic decoherence in mesoscopic systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 3366–3369 (1997)
Braun, D., Haake, F., Strunz, W.T.: Universality of decoherence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 2913–2917 (2001)
Carvalho, A.R.R., Mintert, F., Buchleitner, A.: Decoherence and multipartite entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 230501 (2004)
Lindner, B., Garcia-Ojalvo, J., Neiman, A., Schimansky-Geier, L.: Effects of noise in excitable systems. Phys. Rep. 392(6), 321–424 (2004)
Tyloo, M., Coletta, T., Jacquod, P.: Robustness of synchrony in complex networks and generalized Kirchhoff indices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 084101 (2018)
Ronellenfitsch, H., Dunkel, J., Wilczek, M.: Optimal noise-canceling networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 208301 (2018)
Banaszek, K.: Optimal quantum teleportation with an arbitrary pure state. Phys. Rev. A 62, 024301 (2000)
Li, W.-L., Li, C.-F., Guo, G.-C.: Probabilistic teleportation and entanglement matching. Phys. Rev. A 61, 034301 (2000)
Roa, L., Delgado, A., Fuentes-Guridi, I.: Optimal conclusive teleportation of quantum states. Phys. Rev. A 68, 022310 (2003)
Roa, L., Groiseau, C.: Probabilistic teleportation without loss of information. Phys. Rev. A 91, 012344 (2015)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Popescu, S., Schumacher, B., Smolin, J.A., Wootters, W.K.: Purification of noisy entanglement and faithful teleportation via noisy channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 722–725 (1996)
Pan, J.-W., Gasparoni, S., Ursin, R., Weihs, G., Zeilinger, A.: Experimental entanglement purification of arbitrary unknown states. Nature 423(6938), 417–422 (2003)
Bombin, H., Martin-Delgado, M.A.: Topological quantum distillation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 180501 (2006)
Sheng, Y.-B., Zhou, L., Zhao, S.-M., Zheng, B.-Y.: Efficient single-photon-assisted entanglement concentration for partially entangled photon pairs. Phys. Rev. A 85, 012307 (2012)
Zwerger, M., Briegel, H.J., Dür, W.: Universal and optimal error thresholds for measurement-based entanglement purification. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 260503 (2013)
Riera-Sàbat, F., Sekatski, P., Pirker, A., Dür, W.: Entanglement-assisted entanglement purification. Phys. Rev. Lett. 127, 040502 (2021)
Luo, C.-C., Zhou, L., Zhong, W., Sheng, Y.-B.: Purification for hybrid logical qubit entanglement. Quantum Inf. Process. 21(8), 300 (2022)
Yan, P.-S., Zhou, L., Zhong, W., Sheng, Y.-B.: Advances in quantum entanglement purification. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 66(5), 250301 (2023)
Yan, P.-S., Zhou, L., Sheng, Y.-B.: Single-copy entanglement purification for Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger states. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 40(8), 2050–2057 (2023)
Jonathan, D., Plenio, M.B.: Entanglement-assisted local manipulation of pure quantum states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83(17), 3566 (1999)
Daftuar, S., Klimesh, M.: Mathematical structure of entanglement catalysis. Phys. Rev. A 64, 042314 (2001)
Dam, W., Hayden, P.: Universal entanglement transformations without communication. Phys. Rev. A 67, 060302 (2003)
Sanders, Y.R., Gour, G.: Necessary conditions for entanglement catalysts. Phys. Rev. A 79, 054302 (2009)
Popescu, S.: Bell’s inequalities and density matrices: revealing “hidden’’ nonlocality. Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 2619–2622 (1995)
Peres, A.: Collective tests for quantum nonlocality. Phys. Rev. A 54, 2685–2689 (1996)
Masanes, L.: All bipartite entangled states are useful for information processing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 150501 (2006)
Masanes, L., Liang, Y.-C., Doherty, A.C.: All bipartite entangled states display some hidden nonlocality. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 090403 (2008)
Liang, Y.-C., Masanes, L., Rosset, D.: All entangled states display some hidden nonlocality. Phys. Rev. A 86, 052115 (2012)
Ma, P.-C., Chen, G.-B., Li, X.-W., Zhan, Y.-B.: Hierarchically controlled remote preparation of an arbitrary single-qubit state by using a four-qubit entangled state. Quantum Inf. Process. 17(5), 1–10 (2018)
Choudhury, B.S., Samanta, S.: An optional remote state preparation protocol for a four-qubit entangled state. Quantum Inf. Process. 18(4), 1–10 (2019)
Zhou, P., Lv, L.: Joint remote preparation of single-photon three-qubit state with hyperentangled state via linear-optical elements. Quantum Inf. Process. 19, 1–21 (2020)
Jin, R.-H., Wei, W.-S., Zhou, P.: Hierarchical controlled remote preparation of an arbitrary m-qudit state with four-qudit cluster states. Quantum Inf. Process. 22(2), 113 (2023)
Peng, J., Yang, Z., Tang, L., Peng, J.: Multicast-based multiparty remote state preparation of complex coefficient two-qubit states. Quantum Inf. Process. 22(3), 141 (2023)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grant No. 12274053.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization was performed by X.X. and C.L.; methodology by X.X. and C.L.; software by X.X.; writing—original draft preparation—by X.X.; writing—-review and editing—by X.X., S.H., and C.L.; discussion and suggestion by X.X., S.H., and C.L. All authors have read and agreed to the submitted version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xin, X., He, S. & Li, C. Deterministic hierarchical joint remote state preparation via a non-maximally entangled state. Quantum Inf Process 23, 121 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-024-04329-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-024-04329-6