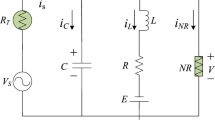
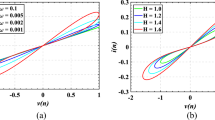
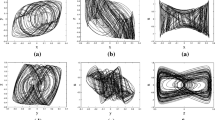
Abstract
This paper proposes a fractional-order memristor-coupled Hindmarsh–Rose neurons model, which the number and stability of equilibrium points are related to the coupling strength. By Lyapunov exponent spectrum, local attraction basins, spectral entropy and so on, firing pattern transition of the system is revealed. In order to deeply expose information transmission in neural networks, the bifurcation behavior of different neuronal orders is studied by three dimensional two-parameter bifurcation diagram. Furthermore, when external stimulus is applied to a neuron, the system produces anti-monotonicity and bursting behavior. A microcontroller based on ARM is used to implement the system and verify various firing activities. Finally, we use the properties of the chaotic system to design a medical image encryption algorithm based on the region of interest. Numerical simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm can improve the security of medical image transmission and resource utilization. It provides strong resistance against attacks to ensure privacy.




























Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
Wang, G.W., Yu, D., Ding, Q.M., Li, T.Y., Jia, Y.: Effects of electric field on multiple vibrational resonances in Hindmarsh–Rose neuronal systems. Chaos Solitons Fractals 150, 111210 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2021.111210
Xu, Q., Chen, X.J., Chen, B., Wu, H.G., Li, Z., Bao, H.: Dynamical analysis of an improved FitzHugh–Nagumo neuron model with multiplier-free implementation. Nonlinear Dyn. 111(9), 8737–8749 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08274-4
Kusbeyzi Aybar, I.: Memristor-based oscillatory behavior in the FitzHugh–Nagumo and Hindmarsh–Rose models. Nonlinear Dyn. 103(3), 2917–2929 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06231-7
Joshi, S.K.: Synchronization of coupled Hindmarsh–Rose neuronal dynamics: analysis and experiments. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 69(3), 1737–1741 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsii.2021.3106400
Bao, H., Zhu, D., Liu, W., Xu, Q., Bao, B.: Memristor synapse-based Morris–Lecar model: Bifurcation analyses and FPGA-based validations for periodic and chaotic bursting/spiking firings. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 30(3), 2050045 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218127420500455
Rajagopal, K., Karthikeyan, A., Srinivasan, A.: Dynamical analysis and FPGA implementation of a chaotic oscillator with fractional-order memristor components. Nonlinear Dyn. 91(3), 1491–1512 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3960-9
Chen, L., Zhou, W.H., Li, C.D., Huang, J.J.: Forgetting memristors and memristor bridge synapses with long- and short-term memories. Neurocomputing 456, 126–135 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.05.062
Li, C.L., Wang, X., Du, J.R., Li, Z.J.: Electrical activity and synchronization of HR-Tabu neuron network coupled by Chua Corsage Memristor. Nonlinear Dyn. 111(22), 21333–21350 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08998-3
Ge, M.Y., Jia, Y., Xu, Y., Yang, L.J.: Mode transition in electrical activities of neuron driven by high and low frequency stimulus in the presence of electromagnetic induction and radiation. Nonlinear Dyn. 91(1), 515–523 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3886-2
Li, Z.J., Zhou, H.Y., Wang, M.J., Ma, M.L.: Coexisting firing patterns and phase synchronization in locally active memristor coupled neurons with HR and FN models. Nonlinear Dyn. 104(2), 1455–1473 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06315-4
Hua, M.J., Zhang, Y.Z., Chen, M., Xu, Q., Bao, B.C.: Memristive single-neuron model and its memristor-coupled network: homogenously coexisting attractors and parallel-offset synchronization. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 32(15), 2250225 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1142/S021812742250225X
Bao, B.C., Yang, Q.F., Zhu, D., Zhang, Y.Z., Xu, Q., Chen, M.: Initial-induced coexisting and synchronous firing activities in memristor synapse-coupled Morris–Lecar bi-neuron network. Nonlinear Dyn. 99, 2339–2354 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-05395-7
Ding, D.W., Chen, X.Y., Yang, Z.L., Hu, Y.B., Wang, M.Y., Niu, Y.: Dynamics of stimuli-based fractional-order memristor-coupled Tabu learning two-neuron model and its engineering applications. Nonlinear Dyn. 111(2), 1791–1817 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07886-6
Fossi, J.T., Edima, H.C., Njitacke, Z.T., Kemwoue, F.F., Mendimi, J.M., Atangana, J.: Coexistence of attractors and its control with selection of a desired attractor in a model of extended Hindmarsh–Rose neuron with nonlinear smooth fitting function: microcontroller implementation. J. Vib. Eng. Technol. 10(7), 2751–2764 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42417-022-00518-8
Lin, H.R., Wang, C.H., Sun, Y.C., Yao, W.: Firing multistability in a locally active memristive neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn. 100(4), 3667–3683 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05687-3
Njitacke, Z.T., Takembo, C.N., Koumetio, B.N., Awrejcewicz, J.: Complex dynamics and autapse-modulated information patterns in memristive Wilson neurons. Nonlinear Dyn. 110(3), 2793–2804 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07738-3
Semenov, D.M., Fradkov, A.L.: Adaptive synchronization in the complex heterogeneous networks of Hindmarsh–Rose neurons. Chaos Solitons Fractals 150, 111170 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2021.111170
Wang, W.Y., Wang, G.Y., Ying, J.J., Liu, G.Z., Liang, Y.: Dynamics of a fractional-order voltage-controlled locally active memristor. Pramana 96(2), 109 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-022-02354-7
Yang, X.J., Li, C.D., Huang, T.W., Song, Q.K., Huang, J.J.: Synchronization of fractional-order memristor-based complex-valued neural networks with uncertain parameters and time delays. Chaos Solitons Fractals 110, 105–123 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2018.03.016
Drapaca, C.S., Sivaloganathan, S.: A fractional model of continuum mechanics. J. Elast. 107(2), 105–123 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10659-011-9346-1
Ni, J.K., Liu, L., Liu, C.X., Hu, X.Y.: Fractional order fixed-time nonsingular terminal sliding mode synchronization and control of fractional order chaotic systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 89(3), 2065–2083 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3570-6
Qiao, Z.J., Elhattab, A., Shu, X.D., He, C.B.: A second-order stochastic resonance method enhanced by fractional-order derivative for mechanical fault detection. Nonlinear Dyn. 106(1), 707–723 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06857-7
Rajagopal, K., Hasanzadeh, N., Parastesh, F., Hamarash, I.I., Jafari, S., Hussain, I.: A fractional-order model for the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak. Nonlinear Dyn. 101(1), 711–718 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05757-6
Yu, Y.J., Shi, M., Kang, H.Y., Chen, M., Bao, B.C.: Hidden dynamics in a fractional-order memristive Hindmarsh–Rose model. Nonlinear Dyn. 100, 891–906 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05495-9
Xu, S.C., Wang, X.Y., Ye, X.L.: A new fractional-order chaos system of Hopfield neural network and its application in image encryption. Chaos Solitons Fractals 157, 111889 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2022.111889
Lu, Y.M., Wang, C.H., Deng, Q.L., Xu, C.: The dynamics of a memristor-based Rulkov neuron with fractional-order difference. Chin. Phys. B 31(6), 60502 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/ac539a
Huang, X., Jia, J., Li, Y.X., Wang, Z.: Complex nonlinear dynamics in fractional and integer order memristor-based systems. Neurocomputing 218, 296–306 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.08.078
Rani, N., Sharma, S.R., Mishra, V.: Grayscale and colored image encryption model using a novel fused magic cube. Nonlinear Dyn. 108(2), 1773–1796 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07276-y
Ding, Y., Wu, G.Z., Chen, D.J., Zhang, N., Gong, L.P., Cao, M.S., Qin, Z.G.: DeepEDN: a deep-learning-based image encryption and decryption network for internet of medical things. IEEE Internet Things J. 8(3), 1504–1518 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2020.3012452
Gao, X.Y., Sun, B., Cao, Y.H., Banerjee, S., Mou, J.: A color image encryption algorithm based on hyperchaotic map and DNA mutation. Chin. Phys. B 32(3), 030501 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/ac8cdf
Kayani, M., Mohsin Riaz, M., Ghafoor, A.: Efficient region of interest encryption based on a new chaotic map. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 32(12), 2250175 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1142/s0218127422501759
Chang, R.Y., Feng, X.F., Zhang, H., Yan, P.F.: A robust privacy protection scheme for stereoscopic medical images based on fractal chaos. Nonlinear Dyn. 111(20), 19425–19445 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08900-1
Chen, R., Li, X.M., Teng, L., Wang, X.Y.: Selective region medical image encryption algorithm based on cascade chaos and two-dimensional Joseph traversal. Phys. Scr. 98(3), 035227 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1088/1402-4896/acbcf8
Meng, X., Li, J.Q., Di, X.Q., Sheng, Y.H., Jiang, D.H.: An encryption algorithm for region of interest in medical DICOM based on one-dimensional e\(\lambda \)-cos-cot map. Entropy 24(7), 901 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/e24070901
Zhang, B., Rahmatullah, B., Wang, S.L., Almutairi, H.M., Xiao, Y., Liu, X.J., Liu, Z.Y.: A variable dimensional chaotic map-based medical image encryption algorithm with multi-mode. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 61(11), 2971–3002 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-023-02874-3
Shen, M., Lei, Z.K.: Optical selective encryption based on the FRFCM algorithm and face biometric for the medical image. Opt. Laser Technol. 138, 106911 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106911
Ding, D.W., Jiang, L., Hu, Y.B., Li, Q., Yang, Z.L., Zhang, Z.X., Wu, Q.J.: Hidden dynamical behaviors, sliding mode control and circuit implementation of fractional-order memristive Hindmarsh–Rose neuron model. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 136(5), 521 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01107-6
Hodgkin, A.L., Huxley, A.F.: A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. 117(4), 500–544 (1952). https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764
Ye, X.L., Mou, J., Luo, C.F., Yang, F.F., Cao, Y.H.: Complexity analysis of a mixed memristive chaotic circuit. Complexity (2018). https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8639470
Ma, C.G., Mou, J., Xiong, L., Banerjee, S., Liu, T.M., Han, X.T.: Dynamical analysis of a new chaotic system: asymmetric multistability, offset boosting control and circuit realization. Nonlinear Dyn. 103(3), 2867–2880 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06276-8
De Sarkar, S.S., Sharma, A.K., Chakraborty, S.: Chaos, antimonotonicity and coexisting attractors in Van der Pol oscillator based electronic circuit. Analog Integr. Circ. Sig. Process 110(2), 211–229 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-021-01934-8
Xie, W.L., Wang, C.H., Lin, H.R.: A fractional-order multistable locally active memristor and its chaotic system with transient transition, state jump. Nonlinear Dyn. 104(4), 4523–4541 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06476-2
Xu, Q., Tan, X., Zhu, D., Bao, H., Hu, Y.H., Bao, B.C.: Bifurcations to bursting and spiking in the Chay neuron and their validation in a digital circuit. Chaos Solitons Fractals 141, 110353 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2020.110353
Sun, J.W., Yan, Y.L., Wang, Y.F., Fang, J.: Dynamical analysis of HR-FN neuron model coupled by locally active hyperbolic memristor and DNA sequence encryption application. Nonlinear Dyn. 111(4), 3811–3829 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-08027-9
Zheng, J.M., Bao, T.Y.: An image encryption algorithm based on cascade chaotic map and DNA coding. IET Image Proc. 17(12), 3510–3523 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1049/ipr2.12882
Hussain, M., Iqbal, N., Bashir, Z.: A chaotic image encryption scheme based on multi-directional confusion and diffusion operations. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 70, 103347 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jisa.2022.103347
Wang, X.Y., Chen, S.N., Zhang, Y.Q.: A chaotic image encryption algorithm based on random dynamic mixing. Opt. Laser Technol. 138, 106837 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106837
Liu, L.D., Lei, Y.H., Wang, D.: A fast chaotic image encryption scheme with simultaneous permutation-diffusion operation. IEEE Access 8, 27361–27374 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.2971759
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, D., Chen, S., Zhang, H. et al. Firing pattern transition of fractional-order memristor-coupled Hindmarsh–Rose neurons model and its medical image encryption for region of interest. Nonlinear Dyn (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-024-09593-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-024-09593-w