Abstract
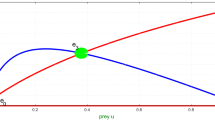
An appropriate mathematical structure to describe the population dynamics is given by the partial differential equations of reaction–diffusion type. The spatiotemporal dynamics and bifurcations of a ratio-dependent Holling type II predator–prey model system with both the effect of linear prey harvesting and constant proportion of prey refuge are investigated. The existence of all ecologically feasible equilibria for the non-spatial model is determined, and the dynamical classifications of these equilibria are developed. The model system representing initial boundary value problem under study is subjected to zero flux boundary conditions. The conditions of diffusion-driven instability and the Turing bifurcation region in two parameter space are explored. The consequences of spatial pattern analysis in two-dimensional domain by means of numerical simulations reveal that the typical dynamics of population density variation is the formation of isolated groups, i.e. spotted or stripe-like patterns or coexistence of both the patterns or labyrinthine patterns and so on. The results around the unique interior feasible equilibrium solution indicate that the effect of refuge and harvesting plays a significant role on the control of spatial pattern formation of the species. Finally, the paper ends with a comprehensive discussion of biological implications of our findings.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akçakaya, H.R., Arditi, R., Ginzburg, L.R.: Ratio-dependent predation: an abstraction that works. Ecology 76(3), 995–1004 (1995)
Arditi, R., Ginzburg, L.R.: Coupling in predator–prey dynamics: ratio-dependence. J. Theor. Biol. 139(3), 311–326 (1989)
Arditi, R., Perrin, N., Saïah, H.: Functional responses and heterogeneities: an experimental test with cladocerans. Oikos 60(1), 69–75 (1991)
Brauer, F., Soudack, A.: Stability regions in predator–prey systems with constant-rate prey harvesting. J. Math. Biol. 8(1), 55–71 (1979)
Clark, C.W.: Mathematical Bioeconomics: The Optimal Management of Renewable Resources. Wiley, New York (1990)
Cosner, C., DeAngelis, D.L., Ault, J.S., Olson, D.B.: Effects of spatial grouping on the functional response of predators. Theor. Popul. Biol. 56(1), 65–75 (1999)
Dai, G., Tang, M.: Coexistence region and global dynamics of a harvested predator–prey system. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 58(1), 193–210 (1998)
Dubey, B., Das, B., Hussain, J.: A predator–prey interaction model with self and cross-diffusion. Ecol. Model. 141(1), 67–76 (2001)
Freedman, H.: Deterministic Mathematical Method in Population Ecology. Dekker, New York (1980)
Garvie, M.R.: Finite-difference schemes for reaction–diffusion equations modeling predator–prey interactions in MATLAB. Bull. Math. Biol. 69(3), 931–956 (2007)
Gatto, M.: Some remarks on models of plankton densities in lakes. Am. Nat. 137(2), 264–267 (1991)
Guin, L.N.: Existence of spatial patterns in a predator–prey model with self- and cross-diffusion. Appl. Math. Comput. 226, 320–335 (2014)
Guin, L.N., Haque, M., Mandal, P.K.: The spatial patterns through diffusion-driven instability in a predator–prey model. Appl. Math. Model. 36(5), 1825–1841 (2012)
Guin, L.N., Mandal, P.K.: Effect of prey refuge on spatiotemporal dynamics of reaction–diffusion system. Comput. Math. Appl. 68(10), 1325–1340 (2014)
Gutierrez, A.: Physiological basis of ratio-dependent predator–prey theory: the metabolic pool model as a paradigm. Ecology 73(5), 1552–1563 (1992)
Hale, J.K.: Theory of Functional Differential Equations. Springer, New York (1971)
Hanski, I.: The functional response of predators: worries about scale. Trends Ecol. Evol. 6(5), 141–142 (1991)
Haque, M.: Existence of complex patterns in the Beddington-DeAngelis predator–prey model. Math. Biosci. 239(2), 179–190 (2012)
Hassell, M.P., May, R.M.: Stability in insect host-parasite models. J. Anim. Ecol. 42, 693–726 (1973)
Hsu, S.B., Hwang, T.W., Kuang, Y.: Global analysis of the Michaelis–Menten-type ratio-dependent predator–prey system. J. Math. Biol. 42(6), 489–506 (2001)
Hsu, S.B., Hwang, T.W., Kuang, Y.: A ratio-dependent food chain model and its applications to biological control. Math. Biosci. 181(1), 55–83 (2003)
Hu, J.H., Xue, Y.K., Sun, G.Q., Jin, Z., Zhang, J.: Global dynamics of a predator–prey system modeling by metaphysiological approach. Appl. Math. Comput. 283, 369–384 (2016)
Kot, M.: Elements of Mathematical Ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2001)
Kuang, Y., Beretta, E.: Global qualitative analysis of a ratio-dependent predator–prey system. J. Math. Biol. 36(4), 389–406 (1998)
Li, L., Jin, Z., Li, J.: Periodic solutions in a herbivore-plant system with time delay and spatial diffusion. Appl. Math. Model. 40(7), 4765–4777 (2016)
Liu, C., Zhang, Q., Zhang, X., Duan, X.: Dynamical behavior in a stage-structured differential-algebraic prey–predator model with discrete time delay and harvesting. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 231(2), 612–625 (2009)
Liu, C., Zhang, Q., Zhang, Y., Duan, X.: Bifurcation and control in a differential-algebraic harvested prey–predator model with stage structure for predator. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 18(10), 3159–3168 (2008)
Lotka, A.J.: Elements of Mathematical Biology. Dover Publications, Mineola (1956)
Lv, Y., Yuan, R., Pei, Y.: Effect of harvesting, delay and diffusion in a generalist predator–prey model. Appl. Math. Comput. 226, 348–366 (2014)
Ma, J., Qin, H., Song, X., Chu, R.: Pattern selection in neuronal network driven by electric autapses with diversity in time delays. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 29(1), 1450239 (2015)
Ma, J., Tang, J.: A review for dynamics of collective behaviors of network of neurons. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 58(12), 2038–2045 (2015)
Ma, J., Xu, Y., Ren, G., Wang, C.: Prediction for breakup of spiral wave in a regular neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 84(2), 497–509 (2016)
May, R.M.: Stability and Complexity in Model Ecosystems, vol. 6. Princeton University Press, Princeton (1973)
Medvinsky, A.B., Petrovskii, S.V., Tikhonova, I.A., Malchow, H., Li, B.L.: Spatiotemporal complexity of plankton and fish dynamics. SIAM Rev. 44(3), 311–370 (2002)
Meyer, J.J., Byers, J.E.: As good as dead? Sublethal predation facilitates lethal predation on an intertidal clam. Ecol. Lett. 8(2), 160–166 (2005)
Murray, J.D.: Mathematical Biology II. Springer, Heidelberg (2002)
Myerscough, M., Gray, B., Hogarth, W., Norbury, J.: An analysis of an ordinary differential equation model for a two-species predator–prey system with harvesting and stocking. J. Math. Biol. 30(4), 389–411 (1992)
Ruxton, G.: Short term refuge use and stability of predator–prey models. Theor. Popul. Biol. 47(1), 1–17 (1995)
Sambath, M., Balachandran, K.: Spatiotemporal dynamics of a predator–prey model incorporating a prey refuge. J. Appl. Anal. Comput. 3(1), 71–80 (2013)
Schreiber, S.J.: Generalist and specialist predators that mediate permanence in ecological communities. J. Math. Biol. 36(2), 133–148 (1997)
Sotomayor, J.: Generic bifurcations of dynamical systems. In: Peixoto, M.M. (ed.) Dynamical Systems, Proceedings of a Symposium at the University of Bahia, Salvador, pp. 549–560. Academic Press, New York (1973)
Sun, G.Q.: Mathematical modeling of population dynamics with Allee effect. Nonlinear Dyn. 85, 1–12 (2016)
Sun, G.Q., Chakraborty, A., Liu, Q.X., Jin, Z., Anderson, K.E., Li, B.L.: Influence of time delay and nonlinear diffusion on herbivore outbreak. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 19(5), 1507–1518 (2014)
Sun, G.Q., Jin, Z., Li, L., Haque, M., Li, B.L.: Spatial patterns of a predator–prey model with cross diffusion. Nonlinear Dyn. 69(4), 1631–1638 (2012)
Sun, G.Q., Jin, Z., Liu, Q.X., Li, L.: Pattern formation induced by cross-diffusion in a predator–prey system. Chin. Phys. B 17(11), 3936–3941 (2008)
Sun, G.Q., Jin, Z., Zhao, Y.G., Liu, Q.X., Li, L.: Spatial pattern in a predator–prey system with both self-and cross-diffusion. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 20(01), 71–84 (2009)
Sun, G.Q., Li, L., Zhang, Z.K.: Spatial dynamics of a vegetation model in an arid flat environment. Nonlinear Dyn. 73(4), 2207–2219 (2013)
Sun, G.Q., Wang, S.L., Ren, Q., Jin, Z., Wu, Y.P.: Effects of time delay and space on herbivore dynamics: linking inducible defenses of plants to herbivore outbreak. Sci. Rep. 5(11), 246 (2015)
Sun, G.Q., Wu, Z.Y., Wang, Z., Jin, Z.: Influence of isolation degree of spatial patterns on persistence of populations. Nonlinear Dyn. 83(1–2), 811–819 (2016)
Sun, G.Q., Zhang, J., Song, L.P., Jin, Z., Li, B.L.: Pattern formation of a spatial predator–prey system. Appl. Math. Comput. 218(22), 11151–11162 (2012)
Tripathi, J.P., Abbas, S., Thakur, M.: Dynamical analysis of a prey–predator model with beddington-deangelis type function response incorporating a prey refuge. Nonlinear Dyn. 80(1–2), 177–196 (2015)
Turing, A.M.: The chemical basis of morphogenesis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 237(641), 37–72 (1952)
Wang, W., Liu, Q.X., Jin, Z.: Spatiotemporal complexity of a ratio-dependent predator–prey system. Phys. Rev. E 75(5), 051913 (2007)
Xiao, D., Jennings, L.S.: Bifurcations of a ratio-dependent predator–prey system with constant rate harvesting. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 65(3), 737–753 (2005)
Xiao, D., Ruan, S.: Global dynamics of a ratio-dependent predator–prey system. J. Math. Biol. 43(3), 268–290 (2001)
Xiao, M., Cao, J.: Hopf bifurcation and non-hyperbolic equilibrium in a ratio-dependent predator–prey model with linear harvesting rate: analysis and computation. Math. Comput. Model. 50(3), 360–379 (2009)
Xiao, Y., Chen, L.: A ratio-dependent predator–prey model with disease in the prey. Appl. Math. Comput. 131(2), 397–414 (2002)
Yodzis, P.: Predator–prey theory and management of multispecies fisheries. Ecol. Appl. 4(1), 51–58 (1994)
Zhang, X., Zhang, Ql, Zhang, X.: Bifurcations of a class of singular biological economic models. Chaos Solitons Fractals 40(3), 1309–1318 (2009)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the anonymous referees and the editors for their suggestions and constructive comments which greatly improved the presentation of this manuscript. Also, the authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support in part from Special Assistance Programme (SAP-III) sponsored by the University Grants Commission (UGC), New Delhi, India (Grant No. F.510 / 3 / DRS-III / 2015 (SAP-I)).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guin, L.N., Acharya, S. Dynamic behaviour of a reaction–diffusion predator–prey model with both refuge and harvesting. Nonlinear Dyn 88, 1501–1533 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-3326-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-3326-8
Keywords
- Interacting populations
- Prey refuge
- Prey harvesting
- Stability and instability
- Self- and cross-diffusion
- Reaction–diffusion predator–prey model
- Spatiotemporal pattern formation