Abstract
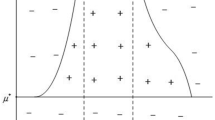
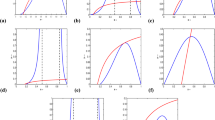
In this paper, spatial patterns of a Holling–Tanner predator-prey model subject to cross diffusion, which means the prey species exercise a self-defense mechanism to protect themselves from the attack of the predator are investigated. By using the bifurcation theory, the conditions of Hopf and Turing bifurcation critical line in a spatial domain are obtained. A series of numerical simulations reveal that the typical dynamics of population density variation is the formation of isolated groups, such as spotted, stripe-like, or labyrinth patterns. Our results confirm that cross diffusion can create stationary patterns, which enrich the finding of pattern formation in an ecosystem.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tanner, J.T.: The stability and the intrinsic growth rates of prey and predator populations. Ecology 56, 855–867 (1975)
Wollkind, D.J., Collings, J.B., Logan, J.A.: Metastability in a temperature-dependent model system for predator-prey mite outbreak interactions on fruit flies. Bull. Math. Biol. 50, 379–409 (1988)
Saez, E., Gonzalez-Olivares, E.: Dynamics of a predator-prey model. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 59, 1867–1878 (1999)
Hsu, S.-B., Huang, T.-W.: Global stability for a class of predator-prey systems. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 55, 763–783 (1995)
Sun, G.-Q., Jin, Z., Liu, Q.-X., Li, L.: Spatial pattern in an epidemic system with cross-diffusion of the susceptible. J. Biol. Syst. 17, 141–152 (2009)
Hanski, I., Gilpin, M.E.: Metapopulation Biology. Academic Press, San Diego (1997)
Sun, G.-Q., Zhang, G., Jin, Z., Li, L.: Predator cannibalism can give rise to regular spatial pattern in a predator-prey system. Nonlinear Dyn. 58, 75–84 (2009)
Okubo, A.: Diffusion and Ecological Problems: Mathematical Models. Springer, Berlin (1980)
Sun, G.-Q., Jin, Z., Li, L., Li, B.-L.: Self-organized wave pattern in a predator-prey model. Nonlinear Dyn. 60, 265–275 (2010)
Lou, Y., Ni, W.M.: Diffusion vs cross-diffusion: an elliptic approach. J. Differ. Equ. 154, 157–190 (1999)
Dubey, B., Das, B., Hussain, J.: A predator-prey interaction model with self and cross-diffusion. Ecol. Model. 141, 67–76 (2001)
Sun, X.-K., Huo, H.-F., Xiang, H.: Bifurcation and stability analysis in predator-prey model with a stage-structure for predator. Nonlinear Dyn. 58, 497–513 (2009)
Murray, J.D.: Mathematical Biology, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin; New York (1993)
Chung, J.M., Peacock-López, E.: Bifurcation diagrams and Turing patterns in a chemical self-replicating reaction-diffusion system with cross diffusion. J. Chem. Phys. 127, 174903 (2007)
Li, L., Jin, Z., Sun, G.-Q.: Spatial pattern of an epidemic model with cross-diffusion. Chin. Phys. Lett. 25, 3500–3503 (2008)
Sun, G.-Q., Jin, Z., Liu, Q.-X., Li, L.: Pattern formation induced by cross-diffusion in a predator-prey system. Chin. Phys. B 17, 3936–3941 (2008)
Sun, G.-Q., Jin, Z., Zhao, Y.-G., Liu, Q.-X., Li, L.: Spatial pattern in a predator-prey system with both self- and cross-diffusion. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 20, 71–84 (2009)
Ipsen, M., Hynne, F., Soensen, P.: Amplitude equations for reaction-diffusion systems with a Hopf bifurcation and slow real modes. Physica D 136, 66–92 (2000)
Pena, B., Perez-Garcia, C.: Stability of Turing patterns in the Brusselator model. Phys. Rev. E 64, 056213 (2001)
Sun, G.-Q., Li, L., Jin, Z., Li, B.-L.: Effect of noise on the pattern formation in an epidemic model. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 1168–1179 (2010)
Sun, G.-Q., Jin, Z., Liu, Q.-X., Li, B.-L.: Rich dynamics in a predator-prey model with both noise and periodic force. Biosystems 100, 14–22 (2010)
Sun, G.-Q., Jin, Z., Li, L., Liu, Q.-X.: The role of noise in a predator-prey model with Allee effect, J. Biol. Phys. 35, 185–196 (2009)
Li, L., Jin, Z.: Pattern dynamics of a spatial predator-prey model with noise. Nonlinear Dyn. 67, 1737–1744 (2012)
Sun, G.-Q., Jin, Z., Liu, Q.-X., Li, L.: Dynamical complexity of a spatial predator-prey model with migration. Ecol. Model. 219, 248–255 (2008)
Acknowledgements
The research was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants (11171314, 10901145, and 11147015), Program for Basic Research (2010011007), and International and Technical Cooperation Project (2010081005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, GQ., Jin, Z., Li, L. et al. Spatial patterns of a predator-prey model with cross diffusion. Nonlinear Dyn 69, 1631–1638 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-012-0374-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-012-0374-6