Abstract
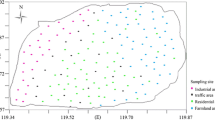
Soils from different land use areas in Lahore City, Pakistan, were analyzed for concentrations of heavy metals—cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr), nickel (Ni), and lead (Pb). One hundred one samples were randomly collected from six land use areas categorized as park, commercial, agricultural, residential, urban, and industrial. Each sample was analyzed in the laboratory with the tri-acid digestion method. Metal concentrations in each sample were obtained with the use of an atomic absorption spectrophotometer. The statistical techniques of analysis of variance, correlation analysis, and cluster analysis were used to analyze all data. In addition, kriging, a geostatistical procedure supported by ArcGIS, was used to model and predict the spatial concentrations of the four heavy metals—Cd, Cr, Ni, and Pb. The results demonstrated significant correlation among the heavy metals in the urban and industrial areas. The dendogram, and the results associated with the cluster analysis, indicated that the agricultural, commercial, and park areas had high concentrations of Cr, Ni, and Pb. High concentrations of Cd and Ni were also observed in the residential and industrial areas, respectively. The maximum concentrations of both Cd and Pb exceeded world toxic limit values. The kriging method demonstrated increasing spatial diffusion of both Cd and Pb concentrations throughout and beyond the Lahore City area.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriano, D. C. (2003). Trace elements in terrestrial environments: biogeochemistry, bioavailability and risks of metals (2nd ed.). New York: Springer.
Ali, Z., Kazi, A. G., Malik, R. N., Naz, M., Khan, T., Hayat, Z., & Kazi, A. M. (2015). Heavy metal built-up in agricultural soils of Pakistan: sources, ecological consequences, and possible remediation measures. In I. Sherameti & A. Varma (Eds.), Heavy metal contamination of soils (pp. 23–42). Switzerland: Springer International. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-14526-6-2.
Alloway, B. J. (1995). Heavy metals in soils. Glasgow: Blackie Academic and Professional. 368p.
Campbell, P. G. C. (2006). Cadmium-A priority pollutant. Environmental Chemistry, 3(6), 387–388.
CEM Corporation. (2012). Microwave accelerated reaction system. North Carolina: Matthews.
Cheng, J., Shi, Z., & Zhu, Y. (2007). Assessment and mapping of environmental quality in agricultural soils of Zhejiang Province, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 19, 50–54.
De Vries, W., Romkens, P. F., & Schutze, G. (2007). Critical soil concentrations of cadmium, lead, and mercury in view of health effects on humans and animals. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 191, 91–130.
ESRI. (2002). ArcView 3.1 software. Redlands: Environmental Systems Research Institute (ESRI).
ESRI. (2005). ArcGIS 9.1 software. Redlands: Environmental Systems Research Institute (ESRI).
Ghauri, B., Lodhi, A., & Mansha, M. (2007). Development of baseline (air quality) data in Pakistan. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 127, 237–252.
Gjoka, F., Henningsen, P. F., Wegener, H. R., Salillari, I., & Beqiraj, A. (2011). Heavy metals in soils from Tirana (Albania). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 172(1–4), 517–527.
Godt, J., Scheidig, F., & Grosse-Siestrup, et al. (2006). The toxicity of cadmium and resulting hazards for human health. Journal of Occupational Medicine and Toxicology, 1, article 22.
GWRTAC. (1997). Remediation of metals-contaminated soils and groundwater. Technical Report TE-97-01. GWRTAC-E-Series. Pittsburgh: GWRTAC.
Hani, A., & Pazira, E. (2011). Heavy metals assessment and identification of their sources in agricultural soils of Southern Tehran, Iran. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 176(1–4), 677–691.
IARC (2006). IARC Monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. Vol. 87. Inorganic and organic lead compounds. International Agency for Research on Cancer.
IARC (2012). A review of human carcinogens: metals, arsenic, fibres and dusts. Vol. 100C. International Agency for Research on Cancer: Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans.
Ikenaka, Y., Nakayama, S. M. M., Muzandu, K., Choongo, K., Teraoka, H., Mizuno, N., & Ishizuka, M. (2010). Heavy metal contamination of soil and sediment in Zambia. African Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 4(11), 729–739.
Iram, S., Ahmad, I., Javed, B., Yaqoob, S., Akhtar, K., Kazmi, M., & Rand Zaman, B. (2009). Fungal tolerance to heavy metals. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 41(5), 2583–2594.
Kabata-Pendias, A., & Pendias, H. (2001). Trace metals in soils and plants (2nd ed.). Boca Raton: CRC.
Khan, A., Javid, S., Muhmood, A., Mjeed, T., Niaz, A., Majeed, A., et al. (2013). Heavy metal status of soil and vegetables grown on peri-urban area of Lahore district. Soil and Environment, 32(1), 49–54.
Khan, S., Cao, Q., Zheng, Y. M., Huang, Y. Z., & Zhu, Y. G. (2008). Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing, China. Environmental Pollution, 152(3), 686–692.
Khan, S., Rehman, S., Khan, A. Z., Khan, M. A., & Shah, M. T. (2010). Soil and vegetables enrichment with heavy metals from geological sources in Gilgit, northern Pakistan. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 73(7), 1820–1827.
Kuang, C., Neumann, T., Norra, S., & Stüben, D. (2004). Land use-related chemical composition of street sediments in Beijing. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 11(2), 73–83.
Lacatusu, R. (2000). Appraising levels of soil contamination and pollution with heavy metals. European Soil Bureau Research Report Number 4, Section 5(7): 393–403. The European Soil Bureau, Joint Research Centre.
Lakhan, V. C., Cabana, K., & LaValle, P. D. (2002). Heavy metal concentrations in surficial sediments from accreting and eroding areas along the coast of Guyana. Environmental Geology, 42, 73–80.
Lee, C. S., Li, X., Shi, W., Cheung, S. C., & Thornton, I. (2006). Metal contamination in urban, suburban, and country park soils of Hong Kong: a study based on GIS and multivariate statistics. Science of the Total Environment, 356, 45–61.
Liu, X., Wu, J., & Xu, J. (2006). Characterizing the risk assessment of heavy metals and sampling uncertainty analysis in paddy field by geostatistics and GIS. Environmental Pollution, 141, 257–264.
Malik, R. N., Jadoon, W. A., & Husain, S. (2010). Metal contamination of surface soils of industrial city Sialkot, Pakistan: a multivariate and GIS approach. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 32(3), 179–191.
Manahan, S. E. (2003). Toxicological chemistry and biochemistry (3rd ed.). London: CRC Press.
Manta, D. S., Angelone, M., Bellanca, A., Neri, R., & Sprovieri, M. (2002). Heavy metals in urban soils: a case study from the city of Palermo (Sicily), Italy. Science of the Total Environment, 300, 229–243.
Markus, J. A., & Mcbratney, A. B. (1996). An urban soil study: heavy metals in Glebe, Australia. Soil Research, 34, 453–465.
McGrath, S. P. (1995). Chromium and nickel. In B. J. Alloway (Ed.), Heavy metals in soils (2nd ed., pp. 152–178). London: Blackie Academic & Professional.
Micó, C., Recatalá, L., Peris, M., & Sánchez, J. (2006). Assessing heavy metal sources in agricultural soils of a European Mediterranean area by multivariate analysis. Chemosphere, 65, 863–872.
Miguel, E., Llamas, J. F., Chacón, E., Berg, T., Larssen, S., Røyset, O., & Vadset, M. (1997). Origin and patterns of distribution of trace elements in street dust: unleaded petrol and urban lead. Atmospheric Environment, 31(17), 2733–2740.
Mudgal, V., Madaan, N., Mudgal, A., Singh, R., & Mishra, S. (2010). Effect of toxic metals on human health. Open Nutraceuticals Journal, 3, 94–99.
NSC. (2009). Lead poisoning. Itasca: National Safety Council. http://www.nsc.org/news_resources/Resources/Documents/Lead_Poisoning.pdf.
Parizanganeh, A., Lakhan, V. C., Jalalian, H., & Ahmad, S. R. (2008). Contamination of nearshore surficial sediments from the Iranian coast of the Caspian Sea. Soil and Sediment Contamination: An International Journal, 17(1), 19–28.
Peris, M., Recatalá, L., Micó, C., Sánchez, R., & Sánchez, J. (2008). Increasing the knowledge of heavy metal contents and sources in agricultural soils of the European Mediterranean Region. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 192(1–4), 25–37.
Perveen, S., Samad, A., Nazif, W., & Shah, S. (2012). Impact of sewage water on vegetables quality with respect to heavy metals in Peshawar, Pakistan. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 44(6), 1923–1931.
Qiao, M., Cai, C., Huang, Y., Liu, Y., Lin, A., & Zheng, Y. (2011). Characterization of soil heavy metal contamination and potential health risk in metropolitan region of northern China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 172(1–4), 353–365.
Rattigan, O. V., Mirza, M. I., Ghauri, B. M., Khan, A. R., Swami, K., Yang, K., et al. (2002). Aerosol sulfate and trace elements in urban fog. Energy and Fuels, 16, 640–646.
Saif, M. S., Midrar-Ul-Haq, & Memon, K. S. (2005). Heavy metals contamination through industrial effluent to irrigation water and soil in Korangi area of Karachi (Pakistan). International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 7, 646–648.
Shah, M. H., & Shaheen, N. (2007). Statistical analysis of atmospheric trace metals and particulate fractions in Islamabad, Pakistan. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 147(3), 759–767.
Shah, M. H., Shaheen, N., Jaffar, M., & Saqib, M. (2004). Distribution of lead in relation to size of airborne particulate matter in Islamabad, Pakistan. Journal of Environmental Management, 70(2), 95–100.
Shi, J. C., Wang, H. Z., Xu, J. M., Wu, J. J., Liu, X. M., Zhu, H. P., & Yu, C. (2007). Spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils: a case study of Changxing, China. Environmental Geology, 52, 1–10.
Shimadzu Corporation. Technical report. Atomic Spectroscopy. Tokyo, Japan: Shimadzu Corporation.
Sial, R. A., Chaudhary, M. F., Abbas, S. T., Latif, M. I., & Khan, A. G. (2006). Quality of effluents from Hattar Industrial Estate. Journal of Zhejiang University. Science. B, 7(12), 974–980.
StataCorp. (2011). Stata statistical software: release 12. College Station: StataCorp. LP.
StatSoft Inc. (2010). Statistica version 10. Tulsa: StatSoft Inc.
Šxkrbić, B., & Đurišić-Mladenović, N. (2013). Distribution of heavy elements in urban and rural surface soils: the Novi Sad city and the surrounding settlements, Serbia. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(1), 457–471.
Tahmasbian, I., Nasrazadani, A., Shoja, H., & Sinegani, A. A. S. (2013). The effects of human activities and different land-use on trace element pollution in urban topsoil of Isfahan (Iran). Environmental Earth Science, 71, 1551–1560.
Tariq, S. R., Shah, M. H., Shaheen, N., Jaffar, M., & Khalique, A. (2008). Statistical source identification of metals in groundwater exposed to industrial contamination. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 138(1–3), 159–165.
Ullah, R., Malik, R. N., & Qadir, A. (2009). Assessment of groundwater contamination in an industrial city, Sialkot, Pakistan. African Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 3, 429–446.
Ullah, Z., Khan, H., Waseem, A., Mahmood, Q., & Farooq, U. (2013). Water quality assessment of the River Kabul at Peshawar, Pakistan: industrial and urban wastewater impacts. Journal of Water Chemistry and Technology, 35, 170–176.
United States Environmental Protection Agency. (1996). Method 3052: Microwave assisted acid digestion of siliceous and organically based matrices. Washington, D.C.: Environmental Protection Agency.
United States Environmental Protection Agency. (2007). Treatment technologies for site cleanup: annual status report. 12th Edition. Technical Report EPA-542-R-07-012. Solid waste and emergency response (5203P). Washington, D.C: Environmental Protection Agency.
von Schneidemesser, E., Stone, E. A., Quraishi, T. A., Shafer, M. M., & Schauer, J. J. (2010). Toxic metals in the atmosphere in Lahore, Pakistan. Science of the Total Environment, 408, 1640–1648.
Wang, X. S., & Qin, Y. (2006). Spatial distribution of metals in urban topsoils of Xuzhou (China): controlling factors and environmental implications. Environmental Geology, 49, 905–914.
Wasseem, A., Arshad, J., Iqbal, F., Sajjad, A., Mehmood, Z., & Murtaza, G. (2014). Pollution status of Pakistan: a retrospective review on heavy metal contamination of water, soil, and vegetables. BioMed Research International. Article ID 813206. doi:10.1155/2014/813206.
Wuana, R.A., & Okieimen, F.E. (2011). Heavy metals in contaminated soils: a review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. International Scholarly Research Network. ISRN Ecology. Article ID 402647. doi:10.5402/2011/402647.
Zhang, C. S. (2006). Using multivariate analyses and GIS to identify pollutants and their spatial patterns in urban soils in Galway, Ireland. Environmental Pollution, 142(3), 501–511.
Zhang, C., Wu, L., Luo, Y., Zhang, H., & Christie, P. (2008). Identifying sources of soil inorganic pollutants on a regional scale using a multivariate statistical approach: role of pollutant migration and soil physicochemical properties. Environmental Pollution, 151, 470–476.
Zhang, M. K., Liu, Z. Y., & Wang, H. (2010). Use of single extraction methods to predict bioavailability of heavy metals in polluted soils to rice. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 41(7), 820–831.
Zheng, Y. M., Chen, T. B., & He, J. Z. (2008). Multivariate geostatistical analysis of heavy metal in topsoils from Beijing, China. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 8(1), 51–58.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alam, N., Ahmad, S.R., Qadir, A. et al. Use of statistical and GIS techniques to assess and predict concentrations of heavy metals in soils of Lahore City, Pakistan. Environ Monit Assess 187, 636 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4855-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4855-1