Abstract
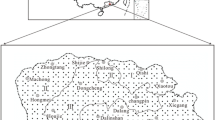
Concentrations of ten heavy elements (Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Hg, Mn, Ni, Pb, and Zn), as well as the pH values, organic matter contents, and electrical conductivities were measured in the surface soil samples collected from 21 sites of urban areas in the city of Novi Sad, the second largest city in Serbia, its suburban settlement and the nearby villages. Range of the heavy element concentrations was from 0.16 mg/kg (for Hg) to 18,994 mg/kg (for Fe). Significantly higher Hg and Mn concentrations were observed in subgroups with rural and market garden samples in comparison to the subgroups with urban and grassland samples, respectively, while the contents of Pb found in the grasslands subgroup were significantly higher than in the subgroup with market garden soils. Only one sample of urban soil exceeded the maximum permissible value for Zn set by the relevant Serbian legislation. According to the Dutch soil quality standard, the Cd and Co concentrations in majority of the examined soils were higher than the target values for unpolluted soil. The content of Hg was above the target value in 52% of the samples, most of them belonging to the subgroup of market garden soils. The results for the Novi Sad city area were compared to the relevant data available for other cities in the Western Balkan Countries. Principal component analysis of data revealed seven outlying samples, while the rest of the analyzed samples were grouped together indicating similar heavy element patterns most probably due to mixed emission sources.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
MΩcm (Mega ohm centimeter)
mS/m (milli Siemens per meter)
References
Bojinova, P., Georgiev, B., Kabakchiev, I., Krasteva, V., Stanislavova, L., Tchuldjian, H., Welp, G., & Brummer, G. (1996). Harmonization of the methods for the investigation of heavy metal pollution of soils and the standardization of the assessment criteria for soil protection. In: Terytze, K. N. (Ed.), Report No. UBA-FB 96-071, Poushkarov Institute of Soil Science and Agroecology, Sofia and Institut fur Bodenkunde, Bonn, Umweltbundesamt, Berlin.
Bretzel, F., & Calderisi, M. (2006). Metal contamination in urban soils of Coastal Tuscany (Italy). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 118, 319–335.
Cal-Prieto, M. J., Carlosena, A., Andrade, J. M., Martinez, M. L., Muniatequi, S., Lopez-Mahia, P., et al. (2001). Antimony as tracer of the anthropogenic influence on soils and estuarine sediments. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 129, 248–333.
Cannon, W. F., & Horton, J. D. (2009). Soil geochemical signature of urbanization and industrialization Chicago, Illinois, USA. Applied Geochemistry, 24, 1590–1601.
Christoforidis, A., & Stamatis, N. (2009). Heavy metal contamination in street dust and roadside soils along the major national road in Kavala's region, Greece. Geoderma, 151, 257–263.
Crnković, D., Ristić, M., & Antonović, D. (2006). Distribution of heavy metals and arsenic in soils of Belgrade (Serbia and Montenegro). Soil and Sediment Contamination, 15, 581–589.
Davidson, C. M., Urquhart, G. J., Ajmone-Marsan, F., Biasioli, M., Duarte, A. C., Dıaz-Barrientos, E., et al. (2006). Fractionation of potentially toxic elements in urban soils from five European cities by means of a harmonised sequential extraction procedure. Analytica Chimica Acta, 565, 63–72.
Davis, A. P., Shokouhian, M., & Shubei, N. (2001). Loading estimates of lead, copper, cadmium, and zinc in urban runoff from specific sources. Chemosphere, 44, 997–1009.
Gimeno-García, E., Andreu, V., & Boluda, R. (1996). Heavy metals incidence in the application of inorganic fertilizers and pesticides to rice farming soil. Environmental Pollution, 92, 19–25.
Golobočanin, D., Škrbić, B., & Miljević, N. (2004). Principal component analysis for soil contamination with PAHs. Chemometrics and Intellingent Laboratory Systems, 72, 219–223.
Imperato, M., Adamo, P., Naimo, D., Arienzo, M., Stanzione, D., & Violante, P. (2003). Spatial distribution of heavy metals in urban soils of Naples city (Italy). Environment Pollution, 124, 247–256.
Ip, C. C. M., Li, X. D., Zhang, G., Wong, C. S. C., & Zhang, W. L. (2005). Heavy metal and Pb isotopic compositions of aquatic organisms in the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Environmental Pollution, 138, 494–504.
Jiries, A. G., Al Nasir, F. M., & Beese, F. (2002). Pesticide and heavy metals residue in wastewater, soil and plants in wastewater disposal site near Al-Lajoun valley, Karak/Jordan. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 133, 97–107.
Kabata-Pendias, A., & Pendias, H. (2001). Trace elements in soils and plants (p. 432). Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Kaiser, H. F., & Rice, J. (1974). Little jiffy, mark IV. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 34, 111–117.
Kummer, U., Pacyna, J., Pacyna, E., & Friedrich, R. (2009). Assessment of heavy metal releases from the use phase of road transport in Europe. Atmospheric Environment, 43, 640–647.
Lee, C. S., Li, X., Shi, W., Cheung, S. C., & Thornton, I. (2006). Metal contamination in urban, suburban, and country park soils of Hong Kong: a study based on GIS and multivariate statistics. Science of the Total Environment, 356, 45–61.
Luo, W., Wang, T., Lu, Y., Giesy, J. P., Shi, Y., Zheng, Y., et al. (2007). Landscape ecology of the Guanting Reservoir, Beijing, China: multivariate and geostatistical analyses of metals in soils. Environmental Pollution, 146, 567–576.
Maas, S., Scheifler, R., Benslama, M., Crini, N., Lucot, E., Brahmis, Z., et al. (2010). Spatial distribution of heavy metal concentrations in urban, suburban and agricultural soils in a Mediterranean city of Algeria. Environmental Pollution, 158, 2294–2301.
Madrid, L., Diaz-Barrientos, E., Reinoso, R., & Madrid, F. (2004). Metals in urban soils of Sevilla: seasonal changes and relations with other soil components and plant contents. European Journal of Soil Science, 55, 209–217.
Manta, D. S., Angelone, M., Bellanca, A., Neri, R., & Sprovieri, M. (2002). Heavy metals in urban soils: a case study from the city of Palermo (Sicily), Italy. Science of the Total Environment, 300, 229–243.
Marjanović, M. D., Vukčević, M. M., Antonović, D. G., Dimitrijević, S. I., Jovanović, Đ. M., Matavulj, M. N., et al. (2009). Heavy metals concentration in soils from parks and green areas in Belgrade. Journal of Serbian Chemical Society, 74, 697–706.
Morton-Bermea, O., Hernández-Álvarez, E., González-Hernández, G., Romero, F., Lozano, R., & Beramendi-Orosco, L. E. (2009). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in urban topsoils from the metropolitan area of Mexico City. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 101, 218–224.
Official Bulletin of the Republic of Serbia. (1994). Regulations about allowed quantities of dangerous and harmful substances in soil and irrigating waters and methods about their analysis. No. 23/94 [in Serbian].
Reimann, C., & de Caritat, P. (1998). Chemical elements in the environment. Springer Verlag, Berlin.
Šajn, R. (2001). Geochemical research of soil and attic dust in Celje area (Slovenia). Geologija, 44, 351–362.
Salminen, R., Batista, M. J., Bidovec, M., Demetriades, A., De Vivo, B., De Vos, W., et al. (2005). Geochemical Atlas of Europe. Part 1, Background information, methodology and maps, Geological Survey of Finland, Espoo, Finland.
Škrbić, B., & Čupić, S. (2004). Trace metal distribution in surface soils of Novi Sad and bank sediment of the Danube river. Journal of Environmental Science and Health: A, 39, 1547–1558.
Škrbić, B., & Đurišić-Mladenović, N. (2007a). Principal component analysis for soil contamination with organochlorine compounds. Chemosphere, 68, 2144–2152.
Škrbić, B., & Đurišić-Mladenović, N. (2007b). Distribution of chlorinated organic pollutants in a wide variety of soils from Europe and Asia: a multivariate statistical approach. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 52, 466–474.
Škrbić, B., & Đurišić-Mladenović, N. (2010). Chemometric interpretation of heavy metal patterns in soils worldwide. Chemosphere, 80, 1360–1369.
Škrbić, B., & Miljević, N. (2002). An evaluation of residues at an oil refinery sites following fires. Jounal of Environmental Science Health A, 37, 1029–1039.
Škrbić, B., Szyrwinska, K., Đurišić-Mladenović, N., Nowicki, P., & Lulek, J. (2010). Principal component analysis of indicator PCB profiles in breast milk from Poland. Environmental International, 36, 862–872.
Sollito, D., Romic, M., Castrignano, S., Romic, D., & Bakic, H. (2010). Assessing heavy metal contamination in soils of the Zagreb region (Northwest Croatia) using multivariate geostatistics. Catena, 80, 182–194.
Stafilov, T., Šajn, R., Pančevski, Z., Boev, B., Frontasyeva, M. V., & Strelkova, L. P. (2010). Heavy metal contamination of topsoil around a lead and zinc smelter in the Republic of Macedonia. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 175, 896–914.
Stafilov, T., Škrbić, B., Klanova, J., Čupr, P., Holoubek, I., Kočov, M., et al. (2011). Chemometric assessment of the semivolatile organic contaminants contents in the atmosphere of the selected sites in the Republic of Macedonia. Journal of Chemometrics, 25, 262–274.
The Netherlands Government Gazette. (2000). Dutch Ministry of Housing, Spatial Planning and Environment. Circular on target values and intervention values for soil remediation.
Ubavić, M., Bogdanović, D., & Hadžić, V. (1993). Basic chemical properties of soil of the Vojvodina province and possibilities of their contamination with heavy metals. Contempoary Agriculture, 1, 47–51 [in Serbian].
Varmuza, K., & Filzmoser, P. (2009). Introduction to multivariate statistical analysis in chemometrics (p. 336). Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Vinodhini, R., & Narayanan, M. (2008). Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in organs of fresh water fish Cyprinus carpio (common carp). International Journal of Environmental Science and Techology, 5, 179–182.
Wedepohl, K. H. (1995). The composition of the continental crust. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59, 1217–1232.
Wilcke, W., Kretzschmar, S., Bundt, M., Saborío, G., & Zech, W. (1998). Aluminum and heavy metal partitioning in A horizons of soils in Costa Rican coffee plantations. Soil Science, 163, 463–471.
Wong, C. S. C., Li, X., & Thornton, I. (2006). Urban environmental geochemistry of trace metals. Environmental Pollution, 142, 1–16.
Yay, O. D., Alagha, O., & Tuncel, G. (2008). Multivariate statistics to investigate metal contamination in surface soils. Journal of Environmental Management, 86, 581–594.
Zyadah, M. A., & Abdel-Baky, T. E. (2000). Toxicity and bioaccumulation of copper, zinc, and cadmium in some aquatic organisms. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 64, 740–747.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Serbian Ministry of Education and Science as a part of the Project 172050: Development and application of the advanced chromatographic and separation methods in the analysis of xenobiotics and their degradation pathways in biotic and abiotic matrices, coordinated by prof. B. Škrbić.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 1,193 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Škrbić, B., Đurišić-Mladenović, N. Distribution of heavy elements in urban and rural surface soils: the Novi Sad city and the surrounding settlements, Serbia. Environ Monit Assess 185, 457–471 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2567-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2567-3