Abstract
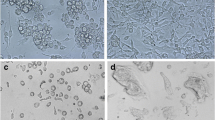
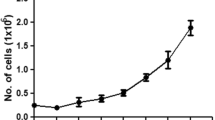
Three cell lines (QAU-Se-E-1, -2 and -3, or Se-1, -2 and -3 for short) were established from eggs of beet armyworm (Spodoptera exigua) that have been passaged stably for more than 60 times in TNM-FH medium supplemented with 10 % fetal bovine serum. The cell lines consisted of round and spindle-shaped cells. The round cells accounted for 96.82, 84.34 and 83.16 % of the cells in the three cell lines, respectively, with cell diameters of 16.21 ± 0.72, 15.63 ± 0.58 and 13.06 ± 0.44 μm. Random amplified polymorphic DNA and analysis of the CO I gene showed that the three cell lines were all derived from S. exigua. Growth curves at passage 30 were determined and the results showed that the cell population doubling times were 59.03, 49.08 and 49.91 h, respectively. The three cell lines can be infected by S. exigua multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus (SeMNPV). Se-3 was extremely susceptible to the virus with an infection rate of 97.52 % 4 days after the inoculation and produced 2.02 × 106 OBs per mL of culture. Flow cytometry analysis showed that some of Se-1 and Se-2 cells had apoptosis after infection, whereas Se-3 cells did not. Bioassays showed that the virulence of the SeMNPV proliferated from Se-3 was similar to that from the insect with LC50 of 5.55 × 105 and 2.64 × 105 OBs/mL. Therefore, the cell lines can be used to study the SeMNPV-host interactions and mechanisms underlying the interactions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bianchi FJ, Vlak JM, Werf WD (2002) Evaluation of the control of beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua, with baculoviruses in greenhouses using a process-based simulation model. Biol Control 24:277–284
Decombel L, Tirry L, Smagghe G (2005) Action of 24-epibrassinolide on a cell line of the beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 58:145–156
Ding WF, Feng Y, Zhang X, Li X, Wang CY (2013) Establishment and characterization of a cell line developed from the neonate larvae of Papilio demoleus Linnaeus (Lepidoptera: Papilionidae). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 49:108–113
Eide PE, Caldwell JM, Marks EP (1975) Establishment of two cell lines from embryonic tissue of the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta (L.). In Vitro 11:395–399
Folmer O, Black M, Hoeh W, Lutz R, Vrijenhoek R (1994) DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome coxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol Mar Biol 3:294–299
Goblirsch MJ, Spivak MS, Kurtti TJ (2013) A cell line resource derived from honey bee (Apis mellifera) embryonic tissues. PLoS One 8:e69831
Goodman CL, El Sayed GN, McIntosh AH, Grasela JJ, Stiles B (2001a) Establishment and characterization of insect cell lines from 10 lepidopteran species. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 37:367–373
Goodman CL, McIntosh AH, El Sayed GN, Grasela JJ, Stiles B (2001b) Production of selected baculoviruses in newly established lepidopteran cell lines. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 37:374–379
Hakim R, Caccia S, Loeb M, Smagghe G (2009) Primary culture of insect midgut cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 45:106–110
Hara K, Funakoshi M, Tsuda K, Kawarabata T (1993) New Spodoptera exigua cell lines susceptible to Spodoptera exigua nuclear polyhedrosis virus. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 29:904–907
Hara K, Funakoshi M, Kawarabata T (1995) A cloned cell line of Spodoptera exigua has a highly increased susceptibility to the Spodoptera exigua nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Can J Microbiol 41:1111–1116
Hebert PDN, Cywinska A, Ball SL, deWaard JR (2003) Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc Bio Sci 270:313–321
Hink WF, Thomsen DR, Davidson DJ, Meyer AL, Castellino FJ (1991) Expression of three recombinant proteins using baculovirus vectors in 23 insect cell lines. Biotechnol Prog 7:9–14
Ishikawa H, Ikeda M, Yanagimoto K, Alves CAF, Katou Y, Lavina-Caoili BA, Kobayashi M (2003) Induction of apoptosis in an insect cell line, IPLB-Ld652Y, infected with nucleopolyhedroviruses. J Gen Virol 84:705–714
Kawai Y, Mitsuhshi J (1997) An insect cell line discrimination method by RAPD-PCR. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 33:512–515
Li GX, Hashimoto Y, Granados RR (2003) Growth characteristics and expression of recombinant protein by new cell clones derived from Trichoplusia ni (BTI Tn5B1-4) High Five cells. Bioprocessing 2:35–38
Li MM, Zheng GL, Li CY (2011) Establishment and characterization of a new cell line Bm-Em-1 from Bombyx mori embryos. Acta Entomol Sin 54:1341–1347
Liu YZ, Wei G, Lu ES, Yuan ZF (2010) The data generating model in toxicity test and estimation for the toxicity indicators. Plant Dis Pests 1:42–45
Meng MJ, Li TL, Li CY, Li GX (2008) A suspended cell line from Trichoplusia ni (Lepidoptera): characterization and expression of recombinant proteins. Insect Sci 15:423–428
Norusis MJ (2012) IBM SPSS statistics 19.0 advanced statistical procedures companion. Prentice Hall press, Upper Saddle River
Palli SR, Caputo GF, Sohi SS, Brownwright AJ, Ladd TR, Cook BJ, Primavera M, Arif BM, Retnakaran A (1996) CfMNPV blocks AcMNPV-induced apoptosis in a continuous midgut cell line. Virology 222:201–213
Saeed S, Sayyed AH, Ahmad I (2010) Effect of host plants on life-history traits of Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Pest Sci 83:165–172
Shao HL, Zheng WW, Liu PC, Wang Q, Wang JX, Zhao XF (2008) Establishment of a new cell line from lepidopteran epiderm is and hormonal regulation on the genes. PLoS One 3:e3127
Si SY, Zhou LL, Wang SL, Jiang XF, Xu ZF, Mu W, Wang DS, Wang XP, Chen HT, Yang YH, Ji XC (2012) Progress in research on prevention and control of beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua in China. Chin J Appl Entomol 49:1432–1438
Smagghe G, Goodman CL, Stanley D (2009) Insect cell culture and applications to research and pest management. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 45:93–105
Sudeep AB, Mourya DT, Shouche YS, Pidiyar V, Pant U (2002) A new cell line from the embryonic tissue of Helicoverpa armigera HBN (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 38:262–264
Sumerford DV (2003) Larval development of Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae on artificial diet and cotton leaves containing a Bacillus thuringiensis toxin: heritable variation to tolerate Cry1Ac. Fla Entomol 86:295–299
Underwood N (2011) Density dependence in insect performance within individual plants: induced resistance to Spodoptera exigua in tomato. Oikos 119:1993–1999
Wang P, Toung R, Granados RR (1999) The establishment of new cell lines from Pseudaletia unipuncta with differential responses to baculovirus infection. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 35:333–338
Weng QB, Yang K, Xiao W, Yuan MJ, Zhang WJ, Pang Y (2009) Establishment of an insect cell clone that harbours a partial baculoviral genome and is resistant to homologous virus infection. J Gen Virol 90:2871–2876
Wu CY, Wang CH (2006) New cell lines from Lymantria xylina (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae): characterization and susceptibility to baculoviruses. J Invertebr Pathol 93:186–191
Wu CY, Chen YW, Lin CC, Hsu CL, Wang CH, Lo CF (2012) A new cell line (NTU-SE) from pupal tissues of the beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), is highly susceptible to S. exigua multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus (SeMNPV) and Autographa californica MNPV (AcMNPV). J Invertebr Pathol 111:143–151
Yasunaga-Aoki C, Imanishi S, Liyama K, Kawarabata T (2004) Establishment of phagocytic cell lines from larval hemocytes of the beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 40:183–186
Zhang H, Zhang YA, Qin QL, Li X, Miao L, Wang YZ, Yang ZQ, Ding C (2006) New cell lines from larval fat bodies of Spodoptera exigua, characterization and susceptibility to baculoviruses (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Invertebr Pathol 91:9–12
Zhang H, Zhang YA, Qin Q, Li X, Miao L, Wang YZ, Qu LJ, Zhang AJ, Yang Q (2009) A cell strain cloned from Spodoptera exigua cell line (IOZCAS-Spex II) highly susceptible to S. exigua nucleopolyhedrovirus infection. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 45:201–204
Zhang X, Feng Y, Ding WF, Chen XM, Wang CY, Ma T (2011) Establishment and characterization of an embryonic cell line from Gampsocleis gratiosa (Orthoptera: Tettigoniidae). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 47:327–332
Zhang A, Li X, Zhang H, Wang H, Miao L, Zhang J, Qin Q (2012) A new cell line from Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and its differentially expressed genes. J Appl Entomol 136:632–637
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31272376), Graduate Innovation Project of Qingdao Agricultural University (QYC201307), and Tai-Shan Scholar Construction Foundation of Shandong Province, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, R., Zheng, GL., Wan, FH. et al. Establishment and characterization of three embryonic cell lines of beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Cytotechnology 68, 1223–1232 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-015-9882-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-015-9882-9