Abstract
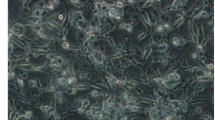
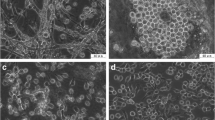
The first continuous cell line from the embryo of Gampsocleis gratiosa (Orthoptera: Tettigoniidae), designated as RIRI-GG1, was established. This cell line was serially subcultured in modified Grace medium. The cells were grown adherent to a culture flask and had spindle-like and polygonal shapes. The chromosome number ranged from 26 to 79 at the 50th passage, and 68% of cells had a diploid chromosome number. The growth rate was determined at the 53rd passage, and the population doubling time was calculated to be 122.1 h. The rDNA internal transcribed spacer and the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I gene sequence analysis indicated that the RIRI-GG1 cell line was derived from G. gratiosa. This cell line had no apparent susceptibility to Autographa californica nucleopolyhedrovirus and Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyapalle S.; Pal N.; Miller W. A.; Bonning B. A glassy-winged sharpshooter cell line supports replication of Rhopalosiphum padi virus (Dicistroviridae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 67: 199–204; 2007.
Chen Y. R.; Solter L. F.; Chien T. Y.; Jiang M. H.; Lin H. F.; Fan H. S.; Lo C. F.; Wang C. H. Characterization of a new insect cell line (NTU-YB) derived from the common grass yellow butterfly, Eurema hecabe (Linnaeus) (Pieridae: Lepidoptera) and its susceptibility to microsporidia. J. Invertebr. Pathol 102: 256–262; 2009.
Cui S-y. Research progress of trehalose metabolism in insects. J. Anhui Agri. Sci. 36(23): 9998–9999; 2008.
Folmer O.; Black M.; Hoeh W.; Lutz R.; Vrijenhoek R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 3(5): 294–299; 1994.
Gelernter W. D.; Federici B. A. Continuous cell line from Spodopera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) that supports replication of nuclear polyhedrosis viruses from Spodoptera exigua and Autographa californica. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 48: 199–207; 1986.
Goodwin R. H.; Topkins G. J.; McCawley P. Gypsy moth cell lines divergent in viral susceptibility. In Vitro. 14(6): 485–494; 1978.
Grace T. D. C. Establishment of four strains of cells from insect tissues grown in vitro. Nature 195: 788–789; 1962.
Hayflick L. Subculturing human diploid fibroblast cultures. In: Kurse P. F.; Patterson Jr. M. K. (eds) Tissue culture: methods and applications. Academic, New York, pp 220–223; 1973.
Hernández-Crespo P.; Bergoin M.; Lopez-Blachere C.; Quiot J. M. Letter to the Editor: establishemnt of two new orthopteran cell lines. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Animal 36: 559–562; 2000.
Hernández-Crespo P.; Lopez-Blachere C.; Bergoin M.; Quiot J. M. Establishment of new cell lines from embryos of Schistocerca gregaria Forsk and Anacridium aegyptium L. (Orthoptera: Acrididae). 7th European Meeting in the IOBC/WPRS. Vienna, Austria; 1999.
Hink W. F.; Thomsen D. R.; Davidson D. J.; Meyer A. L.; Castellino F. J. Expression of three recombinant proteins using baculovirus vectors in 23 insect cell lines. Biotechnol. Prog. 7: 9–14; 1991.
Hoshino K.; Hirose M.; Iwabuchi K. A new insect cell line from the longicorn beetle Plagionotus christophi (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim 45: 19–22; 2009.
Iwanaga M.; Arai R.; Shibano Y.; Kawasaki H.; Imanishi S. Establishment and characterization of the Bombyx mandarina cell line. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 101: 124–129; 2009.
Levin D. B.; Huang J. Spodoptera littoralis type B nucleopolyhedrovirus infection of a grasshopper cell line. J. Invertebr. Pathol 74: 184–192; 1999.
Lynn D. E. Effects of long- and short-term passage of insect cells in different culture media on baculovirus replication. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 76: 164–168; 2000.
Lynn D. E. Novel techniques to establish new insect cell lines. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim 37: 319–321; 2001.
Mitsuhashi J. Invertebrate tissue culture methods. Springer, Tokyo, pp 118–120; 2002a.
Mitsuhashi J. Invertebrate tissue culture methods. Springer, Tokyo, pp 116–117; 2002b.
Mitsuhashi J. Invertebrate tissue culture methods. Springer, Tokyo, pp 321–324; 2002c.
Mitsuhashi J. Invertebrate tissue culture methods. Springer, Tokyo, pp 73–86; 2002d.
Munderloh U. G.; Kurtti T. J.; Liu Y.; Chunsheng C. Grasshopper cell culture. In: Maramorosch K.; McIntosh A. H. (eds) Arthropod cell culture systems. CRC Press, Florida, pp 51–64; 1994.
Pan M. H.; Cai X. J.; Liu M.; Lv J.; Tang H.; Tan J.; Lu C. Establishment and characterization of an ovarian cell line of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Tissue Cell 617: 5; 2009.
Pant U.; Sudeep A. B.; Athawale S. S.; Vipat V. C. Baculovirus studies in new indigenous lepidopteran cell lines. Indian J. Expt. Biol. 40(1): 63–68; 2002.
Rey G. J.; Ferro C.; Bello F. J. Establishment and characterization of a new continuous cell line from Lutzomyia longipalpis (Diptera: Psychodidae) and its susceptibility to infections with Arboviruses and Leishmania chagasi. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro. 95(1): 103–110; 2000.
Sahara K.; Marec F.; Traut W. TTAGG telomeric repeats in chromosomes of some insects and other arthropods. Chromosome Res. 7(6): 449–460; 1999.
Scheinkonig C.; Kappicht S.; Kolb H. J.; Schleuning M. Adoption of long-term cultures to evaluate the cryoprotective potential of trehalose for freezing hematopoietic stem cells. Bone Marrow Transplant. 34: 31–36; 2004.
Shen C. F.; Kiyota T.; Jardin B.; Konishi Y.; Kamen A. Characterization of yeastolate fractions that promote insect cell growth and recombinant protein production. Cytotechnology 54: 25–34; 2007.
Shih C. J.; Lin R. W.; Wang C. H. Establishment of a cell line from Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and replication of S. litura nuclear polyhedrosisvirus in vitro. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 69: 1–6; 1997.
Summers M. D.; Smith F. E. A manual of methods for baculovirus vectors and insect cell culture procedure. Texas Agricultural Experiment Station, No. 1555, p 57; 1988.
Tsang K. R.; Freeman F. A.; Kurtti T. J.; Brooks M. A. New cell lines from embryos of Melanoplus sanguinipes (Orthoptera: Acrididae). Acrida. 10: 105–111; 1981.
Wang C. H.; Chou C. M.; Liu H. C.; Kau S. L.; Kou G. H.; Lo C. F. Continuous cell line from pupal ovary of Perina nuda (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae) that is permissive to nuclear polyhedrosis virus from P. nuda. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 67: 199–204; 1996.
Wickham T. J.; Davis T.; Granados R. R.; Shuler M. L.; Wood H. A. Screening of insect cell lines for the production of recombinant protein and infectious virus in the baculovirus expression system. Biotechnol. Prog. 8: 391–396; 1992.
Yeh S. C.; Lee S. T.; Wu C. Y.; Wang C. H. A cell line (NTU-MV) established from Maruca vitrata (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae): characterization, viral susceptibility, and polyhedra production. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 96: 138–146; 2007.
Zhang H.; Zhang Y. A.; Qin Q.; Li X.; Miao L.; Wang Y. Z.; Yang Z. Q.; Ding C. New cell lines from larval fat bodies of Spodoptera exigua: characterization and susceptibility to baculoviruses(Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Invertebr. Pathol 91: 9–12; 2006.
Acknowledgment
This work is supported by a grant from the National Ministry of Forestry of China (no. 200704038).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: Tetsuji Okamoto
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Feng, Y., Ding, WF. et al. Establishment and characterization of an embryonic cell line from Gampsocleis gratiosa (Orthoptera: Tettigoniidae). In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 47, 327–332 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-011-9397-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-011-9397-4