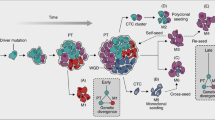
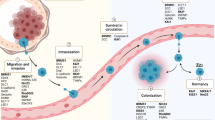
Abstract
Since the identification of NM23 (now called NME1) as the first metastasis suppressor gene (MSG), a small number of other gene products and non-coding RNAs have been identified that suppress specific parameters of the metastatic cascade, yet which have little or no ability to regulate primary tumor initiation or maintenance. MSG can regulate various pathways or cell biological functions such as those controlling mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway mediators, cell–cell and cell-extracellular matrix protein adhesion, cytoskeletal architecture, G-protein-coupled receptors, apoptosis, and transcriptional complexes. One defining facet of this gene class is that their expression is typically downregulated, not mutated, in metastasis, such that any effective therapeutic intervention would involve their re-expression. This review will address the therapeutic targeting of MSG, once thought to be a daunting task only facilitated by ectopically re-expressing MSG in metastatic cells in vivo. Examples will be cited of attempts to identify actionable oncogenic pathways that might suppress the formation or progression of metastases through the re-expression of specific metastasis suppressors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Khan, I., & Steeg, P. S. (2018). Metastasis suppressors: Functional pathways. Lab Investigations, 98, 198–210.
Shevde, L. A., & Welch, D. R. (2003). Metastasis suppressor pathways–An evolving paradigm. Cancer Letters, 198, 1–20.
Hurst, D. R., & Welch, D. R. (2011). Metastasis suppressor genes at the interface between the environment and tumor cell growth. International Review Cell and Molecular Biology, 286, 107–180.
Smith, S. C., & Theodorescu, D. (2009). Learning therapeutic lessons from metastasis suppressor proteins. Nature Reviews Cancer, 9, 253–264.
Sasaki, K., Kurahara, H., Young, E. D., Natsugoe, S., Ijichi, A., Iwakuma, T., & Welch, D. R. (2017). Genome-wide in vivo RNAi screen identifies ITIH5 as a metastasis suppressor in pancreatic cancer. Clinical Experimental Metastasis, 34, 229–239.
Gao, H., Chakraborty, G., Lee-Lim, A. P., Mavrakis, K. J., Wendel, H. G., & Giancotti, F. G. (2014). Forward genetic screens in mice uncover mediators and suppressors of metastatic reactivation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science U. S. A., 111, 16532–16537.
Su, B., Gao, L., Baranowski, C., Gillard, B., Wang, J., Ransom, R., Ko, H. K., & Gelman, I. H. (2014). A genome-wide RNAi screen identifies FOXO4 as a metastasis-suppressor through counteracting PI3K/AKT signal pathway in prostate cancer. PLoS ONE, 9, e101411.
Zhou, X., Li, R., Jing, R., Zuo, B., & Zheng, Q. (2020). Genome-wide CRISPR knockout screens identify ADAMTSL3 and PTEN genes as suppressors of HCC proliferation and metastasis, respectively. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology, 146, 1509–1521.
Li, C., Jiang, W., Hu, Q., Li, L. C., Dong, L., Chen, R., Zhang, Y., Tang, Y., Thrasher, J. B., Liu, C. B., & Li, B. (2016). Enhancing DPYSL3 gene expression via a promoter-targeted small activating RNA approach suppresses cancer cell motility and metastasis. Oncotarget, 7, 22893–22910.
Li, K., Pang, J., Cheng, H., Liu, W. P., Di, J. M., Xiao, H. J., Luo, Y., Zhang, H., Huang, W. T., Chen, M. K., Li, L. Y., Shao, C. K., Feng, Y. H., & Gao, X. (2015). Manipulation of prostate cancer metastasis by locus-specific modification of the CRMP4 promoter region using chimeric TALE DNA methyltransferase and demethylase. Oncotarget, 6, 10030–10044.
Biggs, J., Hersperger, E., Steeg, P. S., Liotta, L. A., & Shearn, A. (1990). A Drosophila gene that is homologous to a mammalian gene associated with tumor metastasis codes for a nucleoside diphosphate kinase. Cell, 63, 933–940.
Lambert, A. W., Pattabiraman, D. R., & Weinberg, R. A. (2017). Emerging biological principles of metastasis. Cell, 168, 670–691.
Boissan, M., & Lacombe, M. L. (2011). Learning about the functions of NME/NM23: Lessons from knockout mice to silencing strategies. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Archives in Pharmacology, 384, 421–431.
Theroux, S., Pereira, M., Casten, K. S., Burwell, R. D., Yeung, K. C., Sedivy, J. M., & Klysik, J. (2007). Raf kinase inhibitory protein knockout mice: Expression in the brain and olfaction deficit. Brain Research Bulletin, 71, 559–567.
Akakura, S., Huang, C., Nelson, P. J., Foster, B., & Gelman, I. H. (2008). Loss of the SSeCKS/Gravin/AKAP12 gene results in prostatic hyperplasia. Cancer Research, 68, 5096–5103.
Lee, J. W., Hur, J., Kwon, Y. W., Chae, C. W., Choi, J. I., Hwang, I., Yun, J. Y., Kang, J. A., Choi, Y. E., Kim, Y. H., Lee, S. E., Lee, C., Jo, D. H., Seok, H., Cho, B. S., Baek, S. H., & Kim, H. S. (2021). KAI1(CD82) is a key molecule to control angiogenesis and switch angiogenic milieu to quiescent state. Journal of Hematological Oncology, 14, 148.
Liu, W. M., & Zhang, X. A. (2006). KAI1/CD82, a tumor metastasis suppressor. Cancer Letters, 240, 183–194.
Asaoka, Y., & Nishina, H. (2010). Diverse physiological functions of MKK4 and MKK7 during early embryogenesis. Journal of Biochemistry, 148, 393–401.
Varfolomeev, E. E., Schuchmann, M., Luria, V., Chiannilkulchai, N., Beckmann, J. S., Mett, I. L., Rebrikov, D., Brodianski, V. M., Kemper, O. C., Kollet, O., Lapidot, T., Soffer, D., Sobe, T., Avraham, K. B., Goncharov, T., Holtmann, H., Lonai, P., & Wallach, D. (1998). Targeted disruption of the mouse Caspase 8 gene ablates cell death induction by the TNF receptors, Fas/Apo1, and DR3 and is lethal prenatally. Immunity, 9, 267–276.
Prabhu, V. V., Siddikuzzaman Grace, V. M., & Guruvayoorappan, C. (2012). Targeting tumor metastasis by regulating Nm23 gene expression. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer PReviews, 13, 3539–3548.
Robinson, V. L., Hickson, J. A., Vander Griend, D. J., Dubauskas, Z., & Rinker-Schaeffer, C. W. (2003). MKK4 and metastasis suppression: A marriage of signal transduction and metastasis research. Clinical Experimental Metastasis, 20, 25–30.
Yesilkanal, A. E., & Rosner, M. R. (2018). Targeting Raf kinase inhibitory protein regulation and function. Cancers (Basel), 10, 306.
Lacombe, M. L., Lamarche, F., De, W. O., Padilla-Benavides, T., Carlson, A., Khan, I., Huna, A., Vacher, S., Calmel, C., Desbourdes, C., Cottet-Rousselle, C., Hininger-Favier, I., Attia, S., Nawrocki-Raby, B., Raingeaud, J., Machon, C., Guitton, J., Le, G. M., Clary, G., … Boissan, M. (2021). The mitochondrially-localized nucleoside diphosphate kinase D (NME4) is a novel metastasis suppressor. BMC Biology, 19, 228–01155.
Guo, H., & Xia, B. (2016). Collapsin response mediator protein 4 isoforms (CRMP4a and CRMP4b) have opposite effects on cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in gastric cancer. BMC Cancer, 16, 565.
Cetkovic, H., Harcet, M., Roller, M., & Bosnar, M. H. (2018). A survey of metastasis suppressors in Metazoa. Lab Investigations, 98, 554–570.
Wertheim, G. B., Yang, T. W., Pan, T. C., Ramne, A., Liu, Z., Gardner, H. P., Dugan, K. D., Kristel, P., Kreike, B., van de Vijver, M. J., Cardiff, R. D., Reynolds, C., & Chodosh, L. A. (2009). The Snf1-related kinase, Hunk, is essential for mammary tumor metastasis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science. U. S. A., 106, 15855–15860.
Allen, M., Svensson, L., Roach, M., Hambor, J., McNeish, J., & Gabel, C. A. (2000). Deficiency of the stress kinase p38alpha results in embryonic lethality: Characterization of the kinase dependence of stress responses of enzyme-deficient embryonic stem cells. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 191, 859–870.
Hiratsuka, S., Duda, D. G., Huang, Y., Goel, S., Sugiyama, T., Nagasawa, T., Fukumura, D., & Jain, R. K. (2011). C-X-C receptor type 4 promotes metastasis by activating p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in myeloid differentiation antigen (Gr-1)-positive cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science. U. S. A, 108, 302–307.
Suarez-Cuervo, C., Merrell, M. A., Watson, L., Harris, K. W., Rosenthal, E. L., Vaananen, H. K., & Selander, K. S. (2004). Breast cancer cells with inhibition of p38alpha have decreased MMP-9 activity and exhibit decreased bone metastasis in mice. Clinical Experimental Metastasis, 21, 525–533.
Grave, N., Scheffel, T. B., Cruz, F. F., Rockenbach, L., Goettert, M. I., Laufer, S., & Morrone, F. B. (2022). The functional role of p38 MAPK pathway in malignant brain tumors. Front Pharmacology, 13, 975197.
Zou, X., & Blank, M. (2017). Targeting p38 MAP kinase signaling in cancer through post-translational modifications. Cancer Letters, 384, 19–26.
Igea, A., & Nebreda, A. R. (2015). The stress kinase p38α as a target for cancer therapy. Cancer Research, 75, 3997–4002.
Koul, H. K., Pal, M., & Koul, S. (2013). Role of p38 MAP kinase signal transduction in solid tumors. Genes & Cancer, 4, 342–359.
Del Barco Barrantes, I., & Nebreda, A. R. (2012). Roles of p38 MAPKs in invasion and metastasis. Biochemistry Society Transactions, 40, 79–84.
Hartsough, M. T., Morrison, D. K., Salerno, M., Palmieri, D., Ouatas, T., Mair, M., Patrick, J., & Steeg, P. S. (2002). Nm23-H1 metastasis suppressor phosphorylation of kinase suppressor of Ras via a histidine protein kinase pathway. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277, 32389–32399.
Salerno, M., Palmieri, D., Bouadis, A., Halverson, D., & Steeg, P. S. (2005). Nm23-H1 metastasis suppressor expression level influences the binding properties, stability, and function of the kinase suppressor of Ras1 (KSR1) Erk scaffold in breast carcinoma cells. Molecular Cell Biology, 25, 1379–1388.
Yu, L., Wang, X., Zhang, W., Khan, E., Lin, C., & Guo, C. (2021). The multiple regulation of metastasis suppressor NM23-H1 in cancer. Life Sciences, 268, 118995.
Lee, H. Y., & Lee, H. (1999). Inhibitory activity of nm23-H1 on invasion and colonization of human prostate carcinoma cells is not mediated by its NDP kinase activity. Cancer Letters, 145, 93–99.
Khan, I., & Steeg, P. S. (2017). The relationship of NM23 (NME) metastasis suppressor histidine phosphorylation to its nucleoside diphosphate kinase, histidine protein kinase and motility suppression activities. Oncotarget, 9, 10185–10202.
Zhang, Q., McCorkle, J. R., Novak, M., Yang, M., & Kaetzel, D. M. (2011). Metastasis suppressor function of NM23-H1 requires its 3’-5’ exonuclease activity. International Journal of Cancer, 128, 40–50.
Khan, I., Gril, B., Hoshino, A., Yang, H. H., Lee, M. P., Difilippantonio, S., Lyden, D. C., & Steeg, P. S. (2022). Metastasis suppressor NME1 in exosomes or liposomes conveys motility and migration inhibition in breast cancer model systems. Clinical Experimental Metastasis., 39, 815–831.
Mátyási, B., Farkas, Z., Kopper, L., Sebestyén, A., Boissan, M., Mehta, A., & Takács-Vellai, K. (2020). The function of NM23-H1/NME1 and its homologs in major processes linked to metastasis. Pathology & Oncology Research, 26, 49–61.
Pamidimukkala, N., Puts, G. S., Kathryn, L. M., Snyder, D., Dabernat, S., De Fabo, E. C., Noonan, F. P., Slominski, A., Merlino, G., & Kaetzel, D. M. (2021). Nme1 and Nme2 genes exert metastasis-suppressor activities in a genetically engineered mouse model of UV-induced melanoma. British Journal of Cancer, 124, 161–165.
Trakul, N., Menard, R. E., Schade, G. R., Qian, Z., & Rosner, M. R. (2005). Raf kinase inhibitory protein regulates Raf-1 but not B-Raf kinase activation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 24931–24940.
Figy, C., Guo, A., Fernando, V. R., Furuta, S., Al-Mulla, F., & Yeung, K. C. (2023). Changes in expression of tumor suppressor gene RKIP impact how cancers interact with their complex environment. Cancers (Basel), 15, 958.
Ahmed, M., Lai, T. H., Kim, W., & Kim, D. R. (2021). A functional network model of the metastasis suppressor PEBP1/RKIP and its regulators in breast cancer cells. Cancers (Basel), 13, 6098.
Aguirre-Ghiso, J. A. (2018). How dormant cancer persists and reawakens. Science, 361, 1314–1315.
Remy, G., Risco, A. M., Iñesta-Vaquera, F. A., González-Terán, B., Sabio, G., Davis, R. J., & Cuenda, A. (2010). Differential activation of p38MAPK isoforms by MKK6 and MKK3. Cell Signaling, 22, 660–667.
Hickson, J. A., Huo, D., Vander Griend, D. J., Lin, A., Rinker-Schaeffer, C. W., & Yamada, S. D. (2006). The p38 kinases MKK4 and MKK6 suppress metastatic colonization in human ovarian carcinoma. Cancer Research, 66, 2264–2270.
Vander Griend, D. J., Kocherginsky, M., Hickson, J. A., Stadler, W. M., Lin, A., & Rinker-Schaeffer, C. W. (2005). Suppression of metastatic colonization by the context-dependent activation of the c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase kinases JNKK1/MKK4 and MKK7. Cancer Research, 65, 10984–10991.
Dong, Y. Q., Lu, C. W., Zhang, L., Yang, J., Hameed, W., & Chen, W. (2015). Toll-like receptor 4 signaling promotes invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through MKK4/JNK pathway. Molecular Immunology, 68, 671–683.
Wang, P. N., Huang, J., Duan, Y. H., Zhou, J. M., Huang, P. Z., Fan, X. J., Huang, Y., Wang, L., Liu, H. L., Wang, J. P., & Huang, M. J. (2017). Downregulation of phosphorylated MKK4 is associated with a poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients. Oncotarget, 8, 34352–34361.
Odintsova, E., Sugiura, T., & Berditchevski, F. (2000). Attenuation of EGF receptor signaling by a metastasis suppressor, the tetraspanin CD82/KAI-1. Current Biology, 10, 1009–1012.
Bienstock, R. J., & Barrett, J. C. (2001). KAI1, a prostate metastasis suppressor: Prediction of solvated structure and interactions with binding partners; integrins, cadherins, and cell-surface receptor proteins. Molecular Carcinogenesis, 32, 139–153.
Ordas, L., Costa, L., Lozano, A., Chevillard, C., Calovoulos, A., Kantar, D., Fernandez, L., Chauvin, L., Dosset, P., Doucet, C., Heron-Milhavet, L., Odintsova, E., Berditchevski, F., Milhiet, P. E., & Bénistant, C. (2021). Mechanical control of cell migration by the metastasis suppressor tetraspanin CD82/KAI1. Cells, 10, 1545.
Prabhu, V. V., & Devaraj, S. N. (2017). KAI1/CD82, Metastasis suppressor gene as a therapeutic target for non-small-cell lung carcinoma. Journal of Environmental Pathology, Toxicology and Oncology, 36, 269–275.
Jeanes, A., Gottardi, C. J., & Yap, A. S. (2008). Cadherins and cancer: How does cadherin dysfunction promote tumor progression? Oncogene, 27, 6920–6929.
Hu, Y., Dai, M., Zheng, Y., Wu, J., Yu, B., Zhang, H., Kong, W., Wu, H., & Yu, X. (2018). Epigenetic suppression of E-cadherin expression by Snail2 during the metastasis of colorectal cancer. Clinical Epigenetics, 10, 154.
Hazan, R. B., Phillips, G. R., Qiao, R. F., Norton, L., & Aaronson, S. A. (2000). Exogenous expression of N-cadherin in breast cancer cells induces cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. Journal of Cell Biology, 148, 779–790.
Hulit, J., Suyama, K., Chung, S., Keren, R., Agiostratidou, G., Shan, W., Dong, X., Williams, T. M., Lisanti, M. P., Knudsen, K., & Hazan, R. B. (2007). N-cadherin signaling potentiates mammary tumor metastasis via enhanced extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Cancer Research, 67, 3106–3116.
Chung, S., Yao, J., Suyama, K., Bajaj, S., Qian, X., Loudig, O. D., Eugenin, E. A., Phillips, G. R., & Hazan, R. B. (2013). N-cadherin regulates mammary tumor cell migration through Akt3 suppression. Oncogene, 32, 422–430.
Qian, X., Anzovino, A., Kim, S., Suyama, K., Yao, J., Hulit, J., Agiostratidou, G., Chandiramani, N., McDaid, H. M., Nagi, C., Cohen, H. W., Phillips, G. R., Norton, L., & Hazan, R. B. (2014). N-cadherin/FGFR promotes metastasis through epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stem/progenitor cell-like properties. Oncogene, 33, 3411–3421.
Kashima, T., Nakamura, K., Kawaguchi, J., Takanashi, M., Ishida, T., Aburatani, H., Kudo, A., Fukayama, M., & Grigoriadis, A. E. (2003). Overexpression of cadherins suppresses pulmonary metastasis of osteosarcoma in vivo. International Journal of Cancer, 104, 147–154.
Li, Y., Chao, F., Huang, B., Liu, D., Kim, J., & Huang, S. (2014). HOXC8 promotes breast tumorigenesis by transcriptionally facilitating cadherin-11 expression. Oncotarget, 5, 2596–2607.
Von, B. C., Oliveira-Ferrer, L., Lüning, T., Trillsch, F., Mahner, S., & Milde-Langosch, K. (2015). Cadherin-11 mRNA and protein expression in ovarian tumors of different malignancy: No evidence of oncogenic or tumor-suppressive function. Molecular Clinical Oncology, 3, 1067–1072.
Satriyo, P. B., Bamodu, O. A., Chen, J. H., Aryandono, T., Haryana, S. M., Yeh, C. T., & Chao, T. Y. (2019). Cadherin 11 Inhibition downregulates b-catenin, deactivates the canonical WNT signalling pathway and suppresses the cancer stem cell-like phenotype of triple negative breast cancer. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8, 148.
Chen, J. H., Huang, W. C., Bamodu, O. A., Chang, P. M., Chao, T. Y., & Huang, T. H. (2019). Monospecific antibody targeting of CDH11 inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and represses cancer stem cell-like phenotype by up-regulating miR-335 in metastatic breast cancer, in vitro and in vivo. BMC Cancer, 19, 634–5811.
Ablain, J., Al, M. A., Rothschild, H., Prasad, M., Aires, S., Yang, S., Dokukin, M. E., Xu, S., Dang, M., Sokolov, I., Lian, C. G., & Zon, L. I. (2022). Loss of NECTIN1 triggers melanoma dissemination upon local IGF1 depletion. Nature Genetics, 54, 1839–1852.
Martin, T. A., Lane, J., Harrison, G. M., & Jiang, W. G. (2013). The expression of the Nectin complex in human breast cancer and the role of Nectin-3 in the control of tight junctions during metastasis. PLoS ONE, 8, e82696.
Kallakury, B. V., Yang, F., Figge, J., Smith, K. E., Kausik, S. J., Tacy, N. J., Fisher, H. A., Kaufman, R., Figge, H., & Ross, J. S. (1996). Decreased levels of CD44 protein and mRNA in prostate carcinoma. Correlation with tumor grade and ploidy, Cancer, 78, 1461–1469.
Ross, J. S., del Rosario, A. D., Bui, H. X., Kallakury, B. V., Okby, N. T., & Figge, J. (1996). Expression of the CD44 cell adhesion molecule in urinary bladder transitional cell carcinoma. Modern Pathology, 9, 854–860.
Gvozdenovic, A., Arlt, M. J., Campanile, C., Brennecke, P., Husmann, K., Born, W., Muff, R., & Fuchs, B. (2013). Silencing of CD44 gene expression in human 143-B osteosarcoma cells promotes metastasis of intratibial tumors in SCID mice. PLoS ONE, 8, e60329.
Rudy, W., Hofmann, M., Schwartz-Albiez, R., Zöller, M., Heider, K. H., Ponta, H., & Herrlich, P. (1993). The two major CD44 proteins expressed on a metastatic rat tumor cell line are derived from different splice variants: each one individually suffices to confer metastatic behavior. Cancer Research, 53, 1262–1268.
Hassn, M. M., Syafruddin, S. E., Mohtar, M. A., & Syahir, A. (2021). CD44: A multifunctional mediator of cancer progression. Biomolecules, 11, 1850.
Ma, L., Dong, L., & Chang, P. (2019). CD44v6 engages in colorectal cancer progression. Cell Death & Disease, 10, 30.
Gao, A. C., Lou, W., Sleeman, J. P., & Isaacs, J. T. (1998). Metastasis suppression by the standard CD44 isoform does not require the binding of prostate cancer cells to hyaluronate. Cancer Research, 58, 2350–2352.
Ahmed, M., Sottnik, J. L., Dancik, G. M., Sahu, D., Hansel, D. E., Theodorescu, D., & Schwartz, M. A. (2016). An osteopontin/CD44 axis in RhoGDI2-mediated metastasis suppression. Cancer Cell, 30, 432–443.
Prochazka, L., Tesarik, R., & Turanek, J. (2014). Regulation of alternative splicing of CD44 in cancer. Cell Signaling, 26, 2234–2239.
Sakuma, K., Sasaki, E., Kimura, K., Komori, K., Shimizu, Y., Yatabe, Y., & Aoki, M. (2018). HNRNPLL, a newly identified colorectal cancer metastasis suppressor, modulates alternative splicing of CD44 during epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Gut, 67, 1103–1111.
Sun, J., Zhang, D., Bae, D. H., Sahni, S., Jansson, P., Zheng, Y., Zhao, Q., Yue, F., Zheng, M., Kovacevic, Z., & Richardson, D. R. (2013). Metastasis suppressor, NDRG1, mediates its activity through signaling pathways and molecular motors. Carcinogenesis, 34, 1943–1954.
Park, K. C., Paluncic, J., Kovacevic, Z., & Richardson, D. R. (2020). Pharmacological targeting and the diverse functions of the metastasis suppressor, NDRG1, in cancer. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 157, 154–175.
Wangpu, X., Yang, X., Zhao, J., Lu, J., Guan, S., Lu, J., Kovacevic, Z., Liu, W., Mi, L., Jin, R., Sun, J., Yue, F., Ma, J., Lu, A., Richardson, D. R., Wang, L., & Zheng, M. (2015). The metastasis suppressor, NDRG1, inhibits “stemness” of colorectal cancer via down-regulation of nuclear b-catenin and CD44. Oncotarget, 6, 33893–33911.
Ohtaki, T., Shintani, Y., Honda, S., Matsumoto, H., Hori, A., Kanehashi, K., Terao, Y., Kumano, S., Takatsu, Y., Masuda, Y., Ishibashi, Y., Watanabe, T., Asada, M., Yamada, T., Suenaga, M., Kitada, C., Usuki, S., Kurokawa, T., Onda, H., … Fujino, M. (2001). Metastasis suppressor gene KiSS-1 encodes peptide ligand of a G-protein-coupled receptor. Nature, 411, 613–617.
McNally, L. R., Welch, D. R., Beck, B. H., Stafford, L. J., Long, J. W., Sellers, J. C., Huang, Z. Q., Grizzle, W. E., Stockard, C. R., Nash, K. T., & Buchsbaum, D. J. (2010). KISS1 over-expression suppresses metastasis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma in a xenograft mouse model. Clinical Experimental Metastasis, 27, 591–600.
Harihar, S., & Welch, D. R. (2023). KISS1 metastasis suppressor in tumor dormancy: A potential therapeutic target for metastatic cancers? Cancer Metastasis Review, 42, 183–196.
Nash, K. T., Phadke, P. A., Navenot, J. M., Hurst, D. R., Accavitti-Loper, M. A., Sztul, E., Vaidya, K. S., Frost, A. R., Kappes, J. C., Peiper, S. C., & Welch, D. R. (2007). Requirement of KISS1 secretion for multiple organ metastasis suppression and maintenance of tumor dormancy. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 99, 309–321.
Navenot, J. M., Fujii, N., & Peiper, S. C. (2009). Activation of Rho and Rho-associated kinase by GPR54 and KiSS1 metastasis suppressor gene product induces changes of cell morphology and contributes to apoptosis. Molecular Pharmacology, 75, 1300–1306.
Kaverina, N., Borovjagin, A. V., Kadagidze, Z., Baryshnikov, A., Baryshnikova, M., Malin, D., Ghosh, D., Shah, N., Welch, D. R., Gabikian, P., Karseladze, A., Cobbs, C., & Ulasov, I. V. (2017). Astrocytes promote progression of breast cancer metastases to the brain via a KISS1-mediated autophagy. Autophagy, 13, 1905–1923.
Ly, T., Harihar, S., & Welch, D. R. (2020). KISS1 in metastatic cancer research and treatment: Potential and paradoxes. Cancer Metastasis Review, 39, 739–754.
Simon, C., Soga, T., & Parhar, I. (2023). Kisspeptin-10 mitigates a-synuclein-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis in SH-SY5Y-derived neurons via a kisspeptin receptor-independent manner. International Journal of Molecular Science, 24, 6056.
LaTulippe, E., Satagopan, J., Smith, A., Scher, H., Scardino, P., Reuter, V., & Gerald, W. L. (2002). Comprehensive gene expression analysis of prostate cancer reveals distinct transcriptional programs associated with metastatic disease. Cancer Research, 62, 4499–4506.
Singh, L. S., Berk, M., Oates, R., Zhao, Z., Tan, H., Jiang, Y., Zhou, A., Kirmani, K., Steinmetz, R., Lindner, D., & Xu, Y. (2007). Ovarian cancer G protein-coupled receptor 1, a new metastasis suppressor gene in prostate cancer. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 99, 1313–1327.
Li, H., Wang, D., Singh, L. S., Berk, M., Tan, H., Zhao, Z., Steinmetz, R., Kirmani, K., Wei, G., & Xu, Y. (2009). Abnormalities in osteoclastogenesis and decreased tumorigenesis in mice deficient for ovarian cancer G protein-coupled receptor 1. PLoS ONE, 4, e5705.
Yan, L., Singh, L. S., Zhang, L., & Xu, Y. (2014). Role of OGR1 in myeloid-derived cells in prostate cancer. Oncogene, 33, 157–164.
Ingber, D. E. (1997). Tensegrity: The architectural basis of cellular mechanotransduction. Annual Reviews in Physiology, 59, 575–599.
Orgaz, J. L., Herraiz, C., & Sanz-Moreno, V. (2014). Rho GTPases modulate malignant transformation of tumor cells. Small GTPases, 5, e29019.
Jansen, S., Gosens, R., Wieland, T., & Schmidt, M. (2017). Paving the Rho in cancer metastasis: Rho GTPases and beyond. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 183, 1–21.
Reiner, D. J., & Lundquist, E. A. (2018). Small GTPases. WormBook, 2018, 1–65.
Moissoglu, K., McRoberts, K. S., Meier, J. A., Theodorescu, D., & Schwartz, M. A. (2009). Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor 2 suppresses metastasis via unconventional regulation of RhoGTPases. Cancer Research, 69, 2838–2844.
Huang, W., Liu, J., Feng, X., Chen, H., Zeng, L., Huang, G., Liu, W., Wang, L., Jia, W., Chen, J., & Ren, C. (2015). DLC-1 induces mitochondrial apoptosis and epithelial mesenchymal transition arrest in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting EGFR/Akt/NF-kB pathway. Medical Oncology, 32, 115–0564.
Liao, Y. C., Shih, Y. P., & Lo, S. H. (2008). Mutations in the focal adhesion targeting region of deleted in liver cancer-1 attenuate their expression and function. Cancer Research, 68, 7718–7722.
Popescu, N. C., & Goodison, S. (2014). Deleted in liver cancer-1 (DLC1): An emerging metastasis suppressor gene. Molecular Diagnostics and Therapeutics, 18, 293–302.
Zhou, X., Thorgeirsson, S. S., & Popescu, N. C. (2004). Restoration of DLC-1 gene expression induces apoptosis and inhibits both cell growth and tumorigenicity in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncogene, 23, 1308–1313.
Yuan, B. Z., Zhou, X., Durkin, M. E., Zimonjic, D. B., Gumundsdottir, K., Eyfjord, J. E., Thorgeirsson, S. S., & Popescu, N. C. (2003). DLC-1 gene inhibits human breast cancer cell growth and in vivo tumorigenicity. Oncogene, 22, 445–450.
Yuan, B. Z., Jefferson, A. M., Baldwin, K. T., Thorgeirsson, S. S., Popescu, N. C., & Reynolds, S. H. (2004). DLC-1 operates as a tumor suppressor gene in human non-small cell lung carcinomas. Oncogene, 23, 1405–1411.
Liao, Y. C., & Lo, S. H. (2008). Deleted in liver cancer-1 (DLC-1): A tumor suppressor not just for liver. International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 40, 843–847.
Harding, M. A., & Theodorescu, D. (2007). RhoGDI2: A new metastasis suppressor gene: Discovery and clinical translation. Urologic Oncology, 25, 401–406.
Papadas, A., Arauz, G., Cicala, A., Wiesner, J., & Asimakopoulos, F. (2020). Versican and versican-matrikines in cancer progression, inflammation, and immunity. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry, 68, 871–885.
Xie, F., Ye, L., Ta, M., Zhang, L., & Jiang, W. G. (2011). MTSS1: A multifunctional protein and its role in cancer invasion and metastasis. Frontiers in Biosciences (Scholars Ed), 3, 621–631.
Liu, K., Wang, G., Ding, H., Chen, Y., Yu, G., & Wang, J. (2010). Downregulation of metastasis suppressor 1(MTSS1) is associated with nodal metastasis and poor outcome in Chinese patients with gastric cancer. BMC Cancer, 10, 428.
Shi, W., Hasimu, G., Wang, Y., Li, N., Chen, M., & Zhang, H. (2015). MTSS1 is an independent prognostic biomarker for survival in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma patients. American Journal of Translational Research, 7, 1974–1983.
Zeleniak, A. E., Huang, W., Brinkman, M. K., Fishel, M. L., & Hill, R. (2017). Loss of MTSS1 results in increased metastatic potential in pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget, 8, 16473–16487.
Du, P., Ye, L., Ruge, F., Yang, Y., & Jiang, W. G. (2011). Metastasis suppressor-1, MTSS1, acts as a putative tumour suppressor in human bladder cancer. Anticancer Research, 31, 3205–3212.
Kayser, G., Csanadi, A., Kakanou, S., Prasse, A., Kassem, A., Stickeler, E., Passlick, B., & Zur, H. A. (2015). Downregulation of MTSS1 expression is an independent prognosticator in squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. British Journal of Cancer, 112, 866–873.
Schemionek, M., Kharabi, M. B., Klaile, Y., Krug, U., Hebestreit, K., Schubert, C., Dugas, M., Büchner, T., Wörmann, B., Hiddemann, W., Berdel, W. E., Brümmendorf, T. H., Müller-Tidow, C., & Koschmieder, S. (2015). Identification of the adapter molecule mtss1 as a potential oncogene-specific tumor suppressor in acute myeloid leukemia. PLoS ONE, 10, e0125783.
Mertz, K. D., Pathria, G., Wagner, C., Saarikangas, J., Sboner, A., Romanov, J., Gschaider, M., Lenz, F., Neumann, F., Schreiner, W., Nemethova, M., Glassmann, A., Lappalainen, P., Stingl, G., Small, J. V., Fink, D., Chin, L., & Wagner, S. N. (2014). MTSS1 is a metastasis driver in a subset of human melanomas. Nature Communications, 5, 3465.
Gelman, I. H. (2012). Suppression of tumor and metastasis progression through the scaffolding functions of SSeCKS/Gravin/AKAP12. Cancer Metastasis Review, 31, 493–500.
Su, B., Gao, L., Meng, F., Guo, L. W., Rothschild, J., & Gelman, I. H. (2013). Adhesion-mediated cytoskeletal remodeling is controlled by the direct scaffolding of Src from FAK complexes to lipid rafts by SSeCKS/AKAP12. Oncogene, 32, 2016–2026.
Gelman, I. H., & Gao, L. (2006). The SSeCKS/Gravin/AKAP12 metastasis suppressor inhibits podosome formation via RhoA- and Cdc42-dependent pathways. Molecular Cancer Research, 4, 151–158.
Guo, L. W., Gao, L., Rothschild, J., Su, B., & Gelman, I. H. (2011). Control of protein kinase C activity, phorbol ester-induced cytoskeletal remodeling, and cell survival signals by the scaffolding protein SSeCKS/GRAVIN/AKAP12. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 286, 38356–38366.
Ko, H. K., Guo, L. W., Su, B., Gao, L., & Gelman, I. H. (2014). Suppression of chemotaxis by SSeCKS via scaffolding of phosphoinositol phosphates and the recruitment of the Cdc42 GEF, Frabin, to the leading edge. PLoS ONE, 9, e111534.
Drake, J. M., Graham, N. A., Stoyanova, T., Sedghi, A., Goldstein, A. S., Cai, H., Smith, D. A., Zhang, H., Komisopoulou, E., Huang, J., Graeber, T. G., & Witte, O. N. (2012). Oncogene-specific activation of tyrosine kinase networks during prostate cancer progression. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science. U. S. A., 109, 1643–1648.
Xia, W., Unger, P., Miller, L., Nelson, J., & Gelman, I. H. (2001). The Src-suppressed C kinase substrate, SSeCKS, is a potential metastasis inhibitor in prostate cancer. Cancer Research, 61, 5644–5651.
Su, B., Zheng, Q., Vaughan, M. M., Bu, Y., & Gelman, I. H. (2006). SSeCKS metastasis-suppressing activity in MatLyLu prostate cancer cells correlates with VEGF inhibition. Cancer Research, 66, 5599–5607.
Akakura, S., Bouchard, R., Bshara, W., Morrison, C., & Gelman, I. H. (2010). Carcinogen-induced squamous papillomas and oncogenic progression in the absence of the SSeCKS/AKAP12 metastasis suppressor correlates with FAK upregulation. International Journal of Cancer, 129, 2025–2031.
Muramatsu, M., Gao, L., Peresie, J., Balderman, B., Akakura, S., & Gelman, I. H. (2017). SSeCKS/Akap12 scaffolding functions suppress B16F10-induced peritoneal metastasis by attenuating Cxcl9/10 secretion by resident myofibroblasts. Oncotarget, 8, 70281–70298.
Muramatsu, M., Akakura, S., Gao, L., Peresie, J., Balderman, B., & Gelman, I. H. (2018). SSeCKS/Akap12 suppresses metastatic melanoma lung colonization by attenuating Src-mediated pre-metastatic niche crosstalk. Oncotarget, 9, 33515–33527.
Kimura, K., Markowski, M., Bowen, C., & Gelmann, E. P. (2001). Androgen blocks apoptosis of hormone-dependent prostate cancer cells. Cancer Research, 61, 5611–5618.
Schoenfeld, N., Bauer, M. K., & Grimm, S. (2004). The metastasis suppressor gene C33/CD82/KAI1 induces apoptosis through reactive oxygen intermediates. FASEB Journal, 18, 158–160.
Yin, Y., Tang, L., & Shi, L. (2017). The metastasis suppressor gene KISS-1 regulates osteosarcoma apoptosis and autophagy processes. Molecular Medicine Reports, 15, 1286–1290.
Guo, Z., Wang, Y., Yang, J., Zhong, J., Liu, X., & Xu, M. (2017). KAI1 overexpression promotes apoptosis and inhibits proliferation, cell cycle, migration, and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. American Journal of Otolaryngology, 38, 511–517.
Li, L., Wang, Z., Lu, T., Li, Y., Pan, M., Yu, D., & Hu, G. (2021). Expression and functional relevance of ANXA1 in hypopharyngeal carcinoma with lymph node metastasis. Oncogy Targets & Therapeutics, 14, 1387–1399.
Zhang, H. M., Qiao, Q. D., Xie, H. F., & Wei, J. X. (2017). Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 (BRMS1) suppresses prostate cancer progression by inducing apoptosis and regulating invasion. European Review of Medical and Pharmacological Science, 21, 68–75.
You, J., He, X., Ding, H., & Zhang, T. (2015). BRMS1 regulates apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cell Biochemistry & Biophysics, 71, 465–472.
Navenot, J. M., Fujii, N., & Peiper, S. C. (2009). KiSS1 metastasis suppressor gene product induces suppression of tyrosine kinase receptor signaling to Akt, tumor necrosis factor family ligand expression, and apoptosis. Molecular Pharmacology, 75, 1074–1083.
Ozturk, S., Papageorgis, P., Wong, C. K., Lambert, A. W., Abdolmaleky, H. M., Thiagalingam, A., Cohen, H. T., & Thiagalingam, S. (2016). SDPR functions as a metastasis suppressor in breast cancer by promoting apoptosis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science. U. S. A., 113, 638–643.
Zimmermann, R. C., & Welch, D. R. (2020). BRMS1: A multifunctional signaling molecule in metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Review, 39, 755–768.
Lewis, M. J., Liu, J., Libby, E. F., Lee, M., Crawford, N. P., & Hurst, D. R. (2016). SIN3A and SIN3B differentially regulate breast cancer metastasis. Oncotarget, 7, 78713–78725.
Liu, Y., Mayo, M. W., Nagji, A. S., Hall, E. H., Shock, L. S., Xiao, A., Stelow, E. B., & Jones, D. R. (2013). BRMS1 suppresses lung cancer metastases through an E3 ligase function on histone acetyltransferase p300. Cancer Research, 73, 1308–1317.
Hurst, D. R., Xie, Y., Thomas, J. W., Liu, J., Edmonds, M. D., Stewart, M. D., & Welch, D. R. (2013). The C-terminal putative nuclear localization sequence of breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1, BRMS1, is necessary for metastasis suppression. PLoS ONE, 8, e55966.
Gong, C., Qu, S., Lv, X. B., Liu, B., Tan, W., Nie, Y., Su, F., Liu, Q., Yao, H., & Song, E. (2014). BRMS1L suppresses breast cancer metastasis by inducing epigenetic silence of FZD10. Nature Communications, 5, 5406.
Koyama, R., Tamura, M., Nakagaki, T., Ohashi, T., Idogawa, M., Suzuki, H., Tokino, T., & Sasaki, Y. (2017). Identification and characterization of a metastatic suppressor BRMS1L as a target gene of p53. Cancer Sciences, 108, 2413–2421.
Cao, P., Zhao, S., Sun, Z., Jiang, N., Shang, Y., Wang, Y., Gu, J., & Li, S. (2018). BRMS1L suppresses ovarian cancer metastasis via inhibition of the b-catenin-wnt pathway. Experimental Cell Research, 371, 214–221.
Lv, J., Yang, H., Wang, X., He, R., Ding, L., & Sun, X. (2018). Decreased BRMS1L expression is correlated with glioma grade and predicts poor survival in glioblastoma via an invasive phenotype. Cancer Biomarkers, 22, 311–316.
Phadke, P. A., Vaidya, K. S., Nash, K. T., Hurst, D. R., & Welch, D. R. (2008). BRMS1 suppresses breast cancer experimental metastasis to multiple organs by inhibiting several steps of the metastatic process. American Journal of Pathology, 172, 809–817.
Petri, B. J., & Klinge, C. M. (2020). Regulation of breast cancer metastasis signaling by miRNAs. Cancer Metastasis Review, 39, 837–886.
Jahangiri, L., & Ishola, T. (2022). Dormancy in breast cancer, the role of autophagy, lncRNAs, miRNAs and exosomes. International Journal of Molecular Science, 23, 5271.
Ma, L., & Weinberg, R. A. (2008). MicroRNAs in malignant progression. Cell Cycle, 7, 570–572.
Le, X. F., Merchant, O., Bast, R. C., & Calin, G. A. (2010). The roles of MicroRNAs in the cancer invasion-metastasis cascade. Cancer Microenvironment, 3, 137–147.
Chan, S. H., & Wang, L. H. (2015). Regulation of cancer metastasis by microRNAs. Journal of Biomedical Science, 22, 9.
Zhang, Y., Zhao, L., Bi, Y., Zhao, J., Gao, C., Si, X., Dai, H., Asmamaw, M. D., Zhang, Q., Chen, W., & Liu, H. (2023). The role of lncRNAs and exosomal lncRNAs in cancer metastasis. Biomedical Pharmacotherapeutics, 165, 115207.
Ahmad, M., Weiswald, L. B., Poulain, L., Denoyelle, C., & Meryet-Figuiere, M. (2023). Involvement of lncRNAs in cancer cells migration, invasion and metastasis: Cytoskeleton and ECM crosstalk. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 42, 173.
Li, Y., Fang, Z., Ge, S., Li, J., Qu, L., Shi, X., Zhang, W., Sun, Y., Ren, S., & Wang, L. (2023). Long non-coding RNA ENST00000503625 is a potential prognostic biomarker and metastasis suppressor gene in prostate cancer. Journal of Cancer Research & Clinical Oncology, 149, 7305–7317.
Lu, K., Feng, F., Yang, Y., Liu, K., Duan, J., Liu, H., Yang, J., Wu, M., Liu, C., & Chang, Y. (2020). High-throughput screening identified miR-7-2-3p and miR-29c-3p as metastasis suppressors in gallbladder carcinoma. Journal of Gastroenterology, 55, 51–66.
Yin, X., Chai, Z., Sun, X., Chen, J., Wu, X., Yang, L., Zhou, X., & Liu, F. (2020). Overexpression of microRNA-96 is associated with poor prognosis and promotes proliferation, migration and invasion in cholangiocarcinoma cells via MTSS1. Experimental & Therapeutic Medicine, 19, 2757–2765.
Zhang, S., & Guo, W. (2019). Long non-coding RNA MEG3 suppresses the growth of glioma cells by regulating the miRNA96-5p/MTSS1 signaling pathway. Molecular Medicine Reports, 20, 4215–4225.
Xie, W., Sun, F., Chen, L., & Cao, X. (2018). miR-96 promotes breast cancer metastasis by suppressing MTSS1. Oncology Letters, 15, 3464–3471.
Guo, Z., Li, J., Sun, J., Sun, L., Zhou, Y., & Yu, Z. (2018). miR-346 promotes HCC progression by suppressing breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 expression. Oncology Research, 26, 1073–1081.
Yue, C. F., Li, L. S., Ai, L., Deng, J. K., & Guo, Y. M. (2021). sMicroRNA-28-5p acts as a metastasis suppressor in gastric cancer by targeting Nrf2. Experimental Cell Research, 402, 112553.
Shibuya, N., Kakeji, Y., & Shimono, Y. (2020). MicroRNA-93 targets WASF3 and functions as a metastasis suppressor in breast cancer. Cancer Sciences, 111, 2093–2103.
Wang, M., Wang, M., Wang, Z., Yu, X., Song, Y., Wang, C., Xu, Y., Wei, F., Zhao, Y., & Xu, Y. (2018). Long non-coding RNA-CTD-2108O9.1 represses breast cancer metastasis by influencing leukemia inhibitory factor receptor. Cancer Sciences, 109, 1764–1774.
Rang, Z., Yang, G., Wang, Y. W., & Cui, F. (2016). miR-542-3p suppresses invasion and metastasis by targeting the proto-oncogene serine/threonine protein kinase, PIM1, in melanoma. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 474, 315–320.
Li, C., Yuan, L., Han, S., Xuan, M., Liu, D., Tian, B., & Yu, W. (2020). Reduced Kiss-1 expression is associated with clinical aggressive feature of gastric cancer patients and promotes migration and invasion in gastric cancer cells. Oncology Reports, 44, 1149–1157.
Lu, G., Wang, X., Wang, Y., Cheng, Z., & Zhou, L. (2018). Value of CagA, HER2, ALDH1, and KiSS-1 in predicting metastasis and prognosis for gastric adenocarcinoma. International Journal of Clinical & Experimental Pathology, 11, 3628–3637.
Cao, F., Chen, L., Liu, M., Lin, W., Ji, J., You, J., Qiao, F., & Liu, H. (2016). Expression of preoperative KISS1 gene in tumor tissue with epithelial ovarian cancer and its prognostic value. Medicine (Baltimore), 95, e5296.
Zhu, B., Wang, Y., Wang, X., Wu, S., Zhou, L., Gong, X., Song, W., & Wang, D. (2018). Evaluation of the correlation of MACC1, CD44, Twist1, and KiSS-1 in the metastasis and prognosis for colon carcinoma. Diagnostic Pathology, 13, 45.
Yue, X., Han, Z., Zhang, L., Li, J., & Gong, X. (2018). Aberrant expression of ALDH1, MMP9, Integrin v 3, and KiSS-1 in invasive ductal carcinoma and their clinical significance. International Journal of Clinical & Experimental Pathology, 11, 3511–3522.
Shoushtari, A. N., Szmulewitz, R. Z., & Rinker-Schaeffer, C. W. (2011). Metastasis-suppressor genes in clinical practice: Lost in translation? Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology, 8, 333–342.
Ci, H., & Wu, L. (2022). Expression of KAI1 and AGR2 in lung adenocarcinoma and their clinicopathological significance. Medicine (Baltimore), 101, e32498.
Al-Khater, K. M., Almofty, S., Ravinayagam, V., Alrushaid, N., & Rehman, S. (2021). Role of a metastatic suppressor gene KAI1/CD82 in the diagnosis and prognosis of breast cancer. Saudi Journal of Biological Scienc, 28, 3391–3398.
Xu, J., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Tao, X., Cheng, L., Wu, S., & Tao, Y. (2018). Correlation of KAI1, CD133 and vasculogenic mimicry with the prediction of metastasis and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. International Journal of Clinical & Experimental Pathology, 11, 3638–3646.
Sun, B., Cheng, Z., & Sun, J. (2018). Associations of MACC1, AGR2, and KAI1 expression with the metastasis and prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. International Journal of Clinical & Experimental Pathology, 11, 822–830.
Bucciarelli, P. R., Tan, K. S., Chudgar, N. P., Brandt, W., Montecalvo, J., Eguchi, T., Liu, Y., Aly, R., Travis, W. D., Adusumilli, P. S., & Jones, D. R. (2018). BRMS1 expression in surgically resected lung adenocarcinoma predicts future metastases and is associated with a poor prognosis. Journal of Thoracic Oncology, 13, 73–84.
Wu, Y., Wang, H., Zhi, J., Hu, L., Hou, X., Ruan, X., Zheng, X., Liu, H., & Gao, M. (2019). BRMS1 downregulation is a poor prognostic biomarker in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma patients. Oncology Targets & Therapeutics, 12, 6937–6945.
Lin, L. Z., Cai, M. G., Dai, Y. C., Zheng, Z. B., Jiang, F. F., Shi, L. L., Pan, Y., & Song, H. B. (2017). BRMS1 gene expression may be associated with clinico-pathological features of breast cancer. Bioscience Reports, 37, BSR20170672.
Lin, L., Cai, M., Dai, Y., Zheng, Z., Jiang, F., Shi, L., Pan, Y., & Song, H. B. (2018). Breast cancer metastasis suppressor gene, breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1, may be associated with clinicopathological features of breast cancer. Journal of Cancer Research & Therapeutics, 14, S368–S374.
Han, W., Zhang, C., Cao, F. Y., Cao, F., Jiang, L., & Ding, H. Z. (2017). Prognostic and clinicopathological value of NM23 expression in patients with breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Current Problems in Cancer, 41, 80–93.
Kanat, O., Adim, S., Evrensel, T., Yerci, O., Ediz, B., Kurt, E., Demiray, M., Gonullu, G., Arslan, M., & Manavoglu, O. (2004). Prognostic value of nm23 in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Medical Oncology, 21, 53–58.
van den Oord, J. J., Maes, A., Stas, M., Nuyts, J., De, W., & I, & De Wolf-Peeters, C. (1997). Prognostic significance of nm23 protein expression in malignant melanoma. An immunohistochemical study, Melanoma Research, 7, 121–128.
Snyder, D., Wang, Y., & Kaetzel, D. M. (2020). A rare subpopulation of melanoma cells with low expression of metastasis suppressor NME1 is highly metastatic in vivo. Science Reports, 10, 1971–58996.
Song, L. J., Liu, Q., Meng, X. R., Li, S., Wang, L. X., Fan, Q. X., & Xuan, X. Y. (2016). DLC-1 is an independent prognostic marker and potential therapeutic target in hepatocellular cancer. Diagnostic Pathology, 11, 19.
An, X., Lin, X., Yang, A., Jiang, Q., Geng, B., Huang, M., Lu, J., Xiang, Z., Yuan, Z., Wang, S., Shi, Y., & Zhu, H. (2020). Cavin3 suppresses breast cancer metastasis via inhibiting AKT pathway. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 11, 01228.
Yang, J., Lv, Z., Huang, J., Zhao, Y., & Li, Y. (2017). High expression of NME1 correlates with progression and poor prognosis in patients of hepatocellular carcinoma. International Journal of Clinical & Experimental Pathology, 10, 8561–8568.
Szarcvel, S. K., Op de, B. K., Ratman, D., Wouters, A., Beck, I. M., Declerck, K., Heyninck, K., Fransen, E., Bracke, M., De, B. K., Lardon, F., Van, C. G., & VandenBerghe, W. (2014). Pharmacological levels of Withaferin A (Withania somnifera) trigger clinically relevant anticancer effects specific to triple negative breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE, 9, e87850.
Shandiz, S. A. S., Sharifian, F., Behboodi, S., Ghodratpour, F., & Baghbani-Arani, F. (2021). Evaluation of metastasis suppressor genes expression and in vitro anti-cancer effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles in human breast cancer cell lines MCF-7 and T47D. Avicenna. J. Med. Biotechnol., 13, 9–14.
Badak, B., Aykanat, N. E. B., Kacar, S., Sahinturk, V., Arik, D., & Canaz, F. (2021). Effects of astaxanthin on metastasis suppressors in ductal carcinoma. A preliminary study. Annali Italiani di Chirurgia, 92, 565–574.
Zhu, C., Takasu, C., Morine, Y., Bando, Y., Ikemoto, T., Saito, Y., Yamada, S., Imura, S., Arakawa, Y., & Shimada, M. (2015). KISS1 associates with better outcome via inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-9 in colorectal liver metastasis. Annals of Surgical Oncology, 22, S1516–S1523.
Liang, Q., Peng, J., Xu, Z., Li, Z., Jiang, F., Ouyang, L., Wu, S., Fu, C., Liu, Y., Liu, Y., & Yan, Y. (2022). Pan-cancer analysis of the prognosis and immunological role of AKAP12: A potential biomarker for resistance to anti-VEGF inhibitors. Frontiers in Genetics, 13, 943006.
Bateman, N. W., Jaworski, E., Ao, W., Wang, G., Litzi, T., Dubil, E., Marcus, C., Conrads, K. A., Teng, P. N., Hood, B. L., Phippen, N. T., Vasicek, L. A., McGuire, W. P., Paz, K., Sidransky, D., Hamilton, C. A., Maxwell, G. L., Darcy, K. M., & Conrads, T. P. (2015). Elevated AKAP12 in paclitaxel-resistant serous ovarian cancer cells is prognostic and predictive of poor survival in patients. Journal of Proteome Research, 14, 1900–1910.
Chappell, N. P., Teng, P. N., Hood, B. L., Wang, G., Darcy, K. M., Hamilton, C. A., Maxwell, G. L., & Conrads, T. P. (2012). Mitochondrial proteomic analysis of Cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer. Journal of Proteome Research, 11, 4605–4614.
Lopez-Ayllon, B. D., Moncho-Amor, V., Abarrategi, A., de Caceres, I. I., Castro-Carpeno, J., Belda-Iniesta, C., Perona, R., & Sastre, L. (2014). Cancer stem cells and cisplatin-resistant cells isolated from non-small-lung cancer cell lines constitute related cell populations. Cancer Medicine, 3, 1099–1111.
Iacobuzio-Donahue, C. A. (2009). Epigenetic changes in cancer. Annual Review of Pathology: Mechanisms of Disease, 4, 229–249.
Kong, B., Lv, Z. D., Wang, Y., Jin, L. Y., Ding, L., & Yang, Z. C. (2015). Down-regulation of BRMS1 by DNA hypermethylation and its association with metastatic progression in triple-negative breast cancer. International Journal of Clinical & Experimental Pathology, 8, 11076–11083.
Verkaik, N. S., van Steenbrugge, G. J., van Weerden, W. M., Bussemakers, M. J., & van der Kwast, T. H. (2000). Silencing of CD44 expression in prostate cancer by hypermethylation of the CD44 promoter region. Lab Investigation, 80, 1291–1298.
Lee, J., Lee, M. S., Jeoung, D. I., Kim, Y. M., & Lee, H. (2017). Promoter CpG-site methylation of the KAI1 metastasis suppressor gene contributes to its epigenetic repression in prostate cancer. Prostate, 77, 350–360.
Chen, S. Q., Chen, Z. H., Lin, S. Y., Dai, Q. B., Fu, L. X., & Chen, R. Q. (2014). KISS1 methylation and expression as predictors of disease progression in colorectal cancer patients. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 20, 10071–10081.
Mardin, W. A., Haier, J., & Mees, S. T. (2013). Epigenetic regulation and role of metastasis suppressor genes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer, 13, 264.
Stubendorff, B., Wilhelm, K., Posselt, K., Catto, J., Hartmann, A., Bertz, S., Füssel, S., Ovotny, V., Oma, M., Ajda, M., Ehmann, J., Underlich, H., Rimm, M. O., Töckle, M., & Unker, K. (2019). A three-gene methylation marker panel for the nodal metastatic risk assessment of muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Journal of Cancer Research Clinical Oncology, 145, 811–820.
Spillman, M. A., Lacy, J., Murphy, S. K., Whitaker, R. S., Grace, L., Teaberry, V., Marks, J. R., & Berchuck, A. (2007). Regulation of the metastasis suppressor gene MKK4 in ovarian cancer. Gynecologic Oncology, 105, 312–320.
Hartsough, M. T., Clare, S. E., Mair, M., Elkahloun, A. G., Sgroi, D., Osborne, C. K., Clark, G., & Steeg, P. S. (2001). Elevation of breast carcinoma Nm23-H1 metastasis suppressor gene expression and reduced motility by DNA methylation inhibition. Cancer Research, 61, 2320–2327.
Wei, H., Liu, Z., She, H., Liu, B., Gu, J., Wei, D., Zhang, X., Wang, J., Qi, S., & Ping, F. (2017). Promoter methylation and expression of Raf kinase inhibitory protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncology Letters, 13, 1866–1872.
Li, D. X., Cai, H. Y., Wang, X., Feng, Y. L., & Cai, S. W. (2014). Promoter methylation of Raf kinase inhibitory protein: A significant prognostic indicator for patients with gastric adenocarcinoma. Experimental & Therapeutic Medicine, 8, 844–850.
Guo, W., Dong, Z., Lin, X., Zhang, M., Kuang, G., & Zhu, T. (2012). Decreased expression and aberrant methylation of Raf kinase inhibitory protein gene in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Investigation, 30, 703–711.
Guo, W., Dong, Z., Guo, Y., Lin, X., Chen, Z., Kuang, G., & Yang, Z. (2013). Aberrant methylation and loss expression of RKIP is associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis in gastric cardia adenocarcinoma. Clinical and Experimental Metastasis, 30, 265–275.
Jo, U., Whang, Y. M., Kim, H. K., & Kim, Y. H. (2009). AKAP12alpha is associated with promoter methylation in lung cancer. Cancer Research and Treatment, 38, 144–151.
Bonazzi, V. F., Irwin, D., & Hayward, N. K. (2009). Identification of candidate tumor suppressor genes inactivated by promoter methylation in melanoma. Genes Chromosomes & Cancer, 48, 10–21.
Liu, W., Guan, M., Su, B., Ye, C., Li, J., Zhang, X., Liu, C., Li, M., Lin, Y., & Lu, Y. (2010). Quantitative assessment of AKAP12 promoter methylation in colorectal cancer using methylation-sensitive high resolution melting: Correlation with dukes’ stage. Cancer Biology and Therapy, 9, 862–871.
Mardin, W., Petrov, K., Enns, A., Senninger, N., Haier, J., & Mees, S. (2010). SERPINB5 and AKAP12 – Expression and promoter methylation of metastasis suppressor genes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer, 10, 549.
Wu, W., Zhang, J., Yang, H., Shao, Y., & Yu, B. (2010). Examination of AKAP12 promoter methylation in skin cancer using methylation-sensitive high-resolution melting analysis. Clinical and Experimental Dermatology, 36, 381–385.
Goeppert, B., Schmezer, P., Dutruel, C., Oakes, C., Renner, M., Breinig, M., Warth, A., Vogel, M. N., Mittelbronn, M., Mehrabi, A., Gdynia, G., Penzel, R., Longerich, T., Breuhahn, K., Popanda, O., Plass, C., Schirmacher, P., & Kern, M. A. (2010). Down-regulation of tumor suppressor A kinase anchor protein 12 in human hepatocarcinogenesis by epigenetic mechanisms. Hepatology, 52, 2023–2033.
Wilhelm, T., Lipka, D. B., Witte, T., Wierzbinska, J. A., Fluhr, S., Helf, M., Mucke, O., Claus, R., Konermann, C., Nollke, P., Niemeyer, C. M., Flotho, C., & Plass, C. (2016). Epigenetic silencing of AKAP12 in juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia. Epigenetics, 11, 110–119.
Wang, Z., Kambhampati, S., Cheng, Y., Ma, K., Simsek, C., Tieu, A. H., Abraham, J. M., Liu, X., Prasath, V., Duncan, M. D., Stark, A., Trick, A., Tsai, H. L., Wang, H., He, Y., Khashab, M. A., Ngamruengphong, S., Shin, E. J., Wang, T. H., & Meltzer, S. J. (2019). Methylation biomarker panel performance in EsophaCap cytology samples for diagnosing Barrett’s esophagus: A prospective validation study. Clinical Cancer Research, 25, 2127–2135.
Li, Q., & Chen, H. (2011). Epigenetic modifications of metastasis suppressor genes in colon cancer metastasis. Epigenetics, 6, 849–852.
Gelman, I. H. (2010). Emerging roles for SSeCKS/Gravin/AKAP12 in the control of cell proliferation, cancer malignancy, and barriergenesis. Genes & Cancer, 1, 1147–1156.
Lin, X., Tombler, E., Nelson, P. J., Ross, M., & Gelman, I. H. (1996). A novel src- and ras-suppressed protein kinase C substrate associated with cytoskeletal architecture. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 271, 28430–28438.
Esposito, S., Russo, M. V., Airoldi, I., Tupone, M. G., Sorrentino, C., Barbarito, G., Di, M. S., & Di, C. E. (2015). SNAI2/Slug gene is silenced in prostate cancer and regulates neuroendocrine differentiation, metastasis-suppressor and pluripotency gene expression. Oncotarget, 6, 17121–17134.
Bu, Y., & Gelman, I. H. (2007). v-Src-mediated down-regulation of SSeCKS metastasis suppressor gene promoter by the recruitment of HDAC1 into a USF1-Sp1-Sp3 complex. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 282, 26725–26739.
Bu, Y., Gao, L., & Gelman, I. H. (2010). Role for transcription factor TFII-I in the suppression Of SSeCKS/Gravin/Akap12 transcription by Src. International Journal of Cancer, 128, 1836–1842.
Li, B., & Li, C. (2017). Suppression of prostate cancer metastasis by DPYSL3-targeted saRNA. Advances in Experimental Medicine & Biology, 983, 207–216.
Li, L. C., Okino, S. T., Zhao, H., Pookot, D., Place, R. F., Urakami, S., Enokida, H., & Dahiya, R. (2006). Small dsRNAs induce transcriptional activation in human cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, U. S. A., 103, 17337–17342.
Gilbert, L. A., Horlbeck, M. A., Adamson, B., Villalta, J. E., Chen, Y., Whitehead, E. H., Guimaraes, C., Panning, B., Ploegh, H. L., Bassik, M. C., Qi, L. S., Kampmann, M., & Weissman, J. S. (2014). Genome-scale CRISPR-mediated control of gene repression and activation. Cell, 159, 647–661.
Wong, K. M., Song, J., Saini, V., & Wong, Y. H. (2019). Small molecules as drugs to upregulate metastasis suppressors in cancer cells. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 26, 5876–5899.
Sahu, A., Verma, S., Varma, M., & Yadav, M. K. (2022). Impact of ErbB receptors and anticancer drugs against breast cancer: A review. Current Pharmocology and Biotechnology, 23, 787–802.
Pan, Q., Lu, Y., Xie, L., Wu, D., Liu, R., Gao, W., Luo, K., He, B., & Pu, Y. (2023). Recent advances in boosting EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors-based cancer therapy. Molecular Pharmacology, 20, 829–852.
Ramani, S., Samant, S., & Manohar, S. M. (2022). The story of EGFR: From signaling pathways to a potent anticancer target, Future. Future Medicinal Chemistry, 14, 1267–1288.
Hantschel, O., Rix, U., & Superti-Furga, G. (2008). Target spectrum of the BCR-ABL inhibitors imatinib, nilotinib and dasatinib. Leukemia and Lymphoma, 49, 615–619.
Shandiz, S. A. S., Khosravani, M., Mohammadi, S., Noorbazargan, H., Mirzaie, A., Inanlou, D. N., Jalali, M. D., Jouzaghkar, H., Baghbani-Arani, F., & Keshavarz-Pakseresht, B. (2016). Evaluation of imatinib mesylate (Gleevec) on KAI1/CD82 gene expression in breast cancer MCF-7 cells using quantitative real-time PCR. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, 6, 159–163.
Song, K., Yuan, Y., Lin, Y., Wang, Y. X., Zhou, J., Gai, Q. J., Zhang, L., Mao, M., Yao, X. X., Qin, Y., Lu, H. M., Zhang, X., Cui, Y. H., Bian, X. W., Zhang, X., & Wang, Y. (2018). ERBB3, IGF1R, and TGFBR2 expression correlate with PDGFR expression in glioblastoma and participate in PDGFR inhibitor resistance of glioblastoma cells. American Journal of Cancer Research, 8, 792–809.
Keshavarz-Pakseresht, B., Shandiz, S. A., & Baghbani-Arani, F. (2017). Imatinib induces up-regulation of NM23, a metastasis suppressor gene, in human hepatocarcinoma (HepG2) cell line. Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Bedside to Bench, 10, 29–33.
Zhang, Y., Xia, M., Jin, K., Wang, S., Wei, H., Fan, C., Wu, Y., Li, X., Li, X., Li, G., Zeng, Z., & Xiong, W. (2018). Function of the c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase in carcinogenesis and associated therapeutic opportunities. Molecular Cancer, 17, 45.
Titus, B., Frierson, H. F., Jr., Conaway, M., Ching, K., Guise, T., Chirgwin, J., Hampton, G., & Theodorescu, D. (2005). Endothelin axis is a target of the lung metastasis suppressor gene RhoGDI2. Cancer Research, 65, 7320–7327.
Palmieri, D., Halverson, D. O., Ouatas, T., Horak, C. E., Salerno, M., Johnson, J., Figg, W. D., Hollingshead, M., Hursting, S., Berrigan, D., Steinberg, S. M., Merino, M. J., & Steeg, P. S. (2005). Medroxyprogesterone acetate elevation of Nm23-H1 metastasis suppressor expression in hormone receptor-negative breast cancer. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 97, 632–642.
Mashimo, T., Watabe, M., Hirota, S., Hosobe, S., Miura, K., Tegtmeyer, P. J., Rinker-Shaeffer, C. W., & Watabe, K. (1998). The expression of the KAI1 gene, a tumor metastasis suppressor, is directly activated by p53. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science. U. S. A., 95, 11307–11311.
Labbozzetta, M., Poma, P., Vivona, N., Gulino, A., D’Alessandro, N., & Notarbartolo, M. (2015). Epigenetic changes and nuclear factor-kB activation, but not microRNA-224, downregulate Raf-1 kinase inhibitor protein in triple-negative breast cancer SUM 159 cells. Oncology Letters, 10, 3807–3815.
Beach, S., Tang, H., Park, S., Dhillon, A. S., Keller, E. T., Kolch, W., & Yeung, K. C. (2008). Snail is a repressor of RKIP transcription in metastatic prostate cancer cells. Oncogene, 27, 2243–2248.
Sun, M., Song, C. X., Huang, H., Frankenberger, C. A., Sankarasharma, D., Gomes, S., Chen, P., Chen, J., Chada, K. K., He, C., & Rosner, M. R. (2013). HMGA2/TET1/HOXA9 signaling pathway regulates breast cancer growth and metastasis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, U.S.A, 110, 9920–9925.
Lee, J. E., & Kim, J. H. (2015). Valproic acid inhibits the invasion of PC3 prostate cancer cells by upregulating the metastasis suppressor protein NDRG1. Genetics and Molecular Biology, 38, 527–533.
Meadows, G. G. (2012). Diet, nutrients, phytochemicals, and cancer metastasis suppressor genes. Cancer Metastasis Review, 31, 441–454.
Wijesinghe, T. P., Dharmasivam, M., Dai, C. C., & Richardson, D. R. (2021). Innovative therapies for neuroblastoma: The surprisingly potent role of iron chelation in up-regulating metastasis and tumor suppressors and down-regulating the key oncogene, N-myc. Pharmacology Research, 173, 105889.
Le, N. T., & Richardson, D. R. (2004). Iron chelators with high antiproliferative activity up-regulate the expression of a growth inhibitory and metastasis suppressor gene: A link between iron metabolism and proliferation. Blood, 104, 2967–2975.
He, X., Ma, X., Wang, C., Luan, M., Li, Y., Huang, X., & Ma, K. (2021). The peptide mimicking small extracellular ring domain of CD82 inhibits tumor cell migration in vitro and metastasis in vivo. Journal of Cancer Research Clinical Oncology, 147, 1927–1934.
He, X., Huang, X., Wang, C., Luan, M., Li, Y., Ma, X., & Ma, K. (2020). The peptide mimicking small extracellular ring domain of CD82 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition by downregulating Wnt pathway and upregulating hippo pathway. Biochemical Biophysical Research Communications, 533, 338–345.
Cheng, S., Castillo, V., Eliaz, I., & Sliva, D. (2015). Honokiol suppresses metastasis of renal cell carcinoma by targeting KISS1/KISS1R signaling. International Journal of Oncology, 46, 2293–2298.
MacLean, D. B., Matsui, H., Suri, A., Neuwirth, R., & Colombel, M. (2014). Sustained exposure to the investigational Kisspeptin analog, TAK-448, down-regulates testosterone into the castration range in healthy males and in patients with prostate cancer: Results from two phase 1 studies. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 99, E1445–E1453.
Tsoutsouki, J., Abbara, A., & Dhillo, W. (2022). Novel therapeutic avenues for kisspeptin. Current Opinions in Pharmacology, 67, 102319.
Moritz, M. N. O., Casali, B. C., Stotzer, S., dos Santos, P. K., & Selistre-de-Araujo, H. S. (2022). Alternagin-C, an alpha2beta1 integrin ligand, attenuates collagen-based adhesion, stimulating the metastasis suppressor 1 expression in triple-negative breast tumor cells. Toxicon, 210, 1–10.
Myers, R. B., & Grizzle, W. E. (1997). Changes in biomarker expression in the development of prostatic adenocarcinoma. Biotechnic and Histochemistry, 72, 86–95.
Bozdogan, O., Yulug, I. G., Vargel, I., Cavusoglu, T., Karabulut, A. A., Karahan, G., & Sayar, N. (2015). Differential expression patterns of metastasis suppressor proteins in basal cell carcinoma. International Journal of Dermatology, 54, 905–915.
Bozdogan, O., Vargel, I., Cavusoglu, T., Karabulut, A. A., Karahan, G., Sayar, N., Atasoy, P., & Yulug, I. G. (2016). Metastasis suppressor proteins in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Pathology Research & Practice, 212, 608–615.
Kim, H. L., Vander, G., Yang, X. M., Benson, D. A., Dubauskas, Z., Yoshida, B. A., Chekmareva, M. A., Ichikawa, Y., Sokoloff, M. H., Zhan, P., Karrison, T., Lin, A. N., Stadler, W. M., Ichikawa, T., Rubin, M. A., & Rinker-Schaeffer, C. W. (2001). Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 metastasis suppressor gene expression is inversely related to histological pattern in advancing human prostatic cancers. Cancer Research, 61, 2833–2837.
Khamis, Z. I., Iczkowski, K. A., & Sang, Q. X. A. (2011). Metastasis suppressors in human benign prostate, intraepithelial neoplasia, and invasive cancer: Their prospects as therapeutic agents. Medicinal Research Reviews, 32, 1026–1077.
Zhong, Y., Naito, Y., Cope, L., Naranjo-Suarez, S., Saunders, T., Hong, S. M., Goggins, M. G., Herman, J. M., Wolfgang, C. L., & Iacobuzio-Donahue, C. A. (2014). Functional p38 MAPK identified by biomarker profiling of pancreatic cancer restrains growth through JNK inhibition and correlates with improved survival. Clinical Cancer Research, 20, 6200–6211.
Mikami, S., Mizuno, R., Kosaka, T., Saya, H., Oya, M., & Okada, Y. (2015). Expression of TNF-a and CD44 is implicated in poor prognosis, cancer cell invasion, metastasis and resistance to the sunitinib treatment in clear cell renal cell carcinomas. International Journal of Cancer, 136, 1504–1514.
Swarts, D. R., Henfling, M. E., Van, N. L., van Suylen, R. J., Dingemans, A. M., Dinjens, W. N., Haesevoets, A., Rudelius, M., Thunnissen, E., Volante, M., Van, C. W., Van, E. M., Ramaekers, F. C., & Speel, E. J. (2013). CD44 and OTP are strong prognostic markers for pulmonary carcinoids. Clinical Cancer Research, 19, 2197–2207.
Wu, Q., Yang, Y., Wu, S., Li, W., Zhang, N., Dong, X., & Ou, Y. (2015). Evaluation of the correlation of KAI1/CD82, CD44, MMP7 and b-catenin in the prediction of prognosis and metastasis in colorectal carcinoma. Diagnostic Pathology, 10, 176.
Zhang, G., Cheng, Y., Chen, G., Tang, Y., Ardekani, G., Rotte, A., Martinka, M., McElwee, K., Xu, X., Wang, Q., & Zhou, Y. (2015). Loss of tumor suppressors KAI1 and p27 identifies a unique subgroup of primary melanoma patients with poor prognosis. Oncotarget, 6, 23026–23035.
Zhou, L., Yu, L., Wu, S., Feng, Z., Song, W., & Gong, X. (2015). Clinicopathological significance of KAI1 expression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer. World Journal of Surgical Oncology, 13, 234.
Lu, G., Zhou, L., Zhang, X., Zhu, B., Wu, S., Song, W., Gong, X., Wang, D., & Tao, Y. (2016). The expression of metastasis-associated in colon cancer-1 and KAI1 in gastric adenocarcinoma and their clinical significance. World Journal of Surgical Oncology, 14, 276.
Patil, N. N., Wadhwan, V., Chaudhary, M., & Nayyar, A. S. (2016). KAI-1 and p53 expression in oral squamous cell carcinomas: Markers of significance in future diagnostics and possibly therapeutics. Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology, 20, 384–389.
Krishna, L. T., Verma, A., Thakur, G. K., Banerjee, B., Kaur, N., Singh, U. R., & Sharma, S. (2019). Down regulation of KAI1/CD82 in lymph node positive and advanced T-stage group in breast cancer patients. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, 20, 3321–3329.
Ulasov, I. V., Kaverina, N. V., Pytel, P., Thaci, B., Liu, F., Hurst, D. R., Welch, D. R., Sattar, H. A., Olopade, O. I., Baryshnikov, A. Y., Kadagidze, Z. G., & Lesniak, M. S. (2012). Clinical significance of KISS1 protein expression for brain invasion and metastasis. Cancer, 118, 2096–2105.
Chen, Y., Yusenko, M. V., & Kovacs, G. (2011). Lack of KISS1R expression is associated with rapid progression of conventional renal cell carcinomas. Journal of Pathology, 223, 46–53.
Wang, H., Jones, J., Turner, T., He, Q. P., Hardy, S., Grizzle, W. E., Welch, D. R., & Yates, C. (2012). Clinical and biological significance of KISS1 expression in prostate cancer. American Journal of Pathology, 180, 1170–1178.
Theodorescu, D., Sapinoso, L. M., Conaway, M. R., Oxford, G., Hampton, G. M., & Frierson, H. F., Jr. (2004). Reduced expression of metastasis suppressor RhoGDI2 is associated with decreased survival for patients with bladder cancer. Clinical Cancer Research, 10, 3800–3806.
Parr, C., & Jiang, W. G. (2009). Metastasis suppressor 1 (MTSS1) demonstrates prognostic value and anti-metastatic properties in breast cancer. European Journal of Cancer, 45, 1673–1683.
Xu, G., Zhang, M., Zhu, H., & Xu, J. (2017). A 15-gene signature for prediction of colon cancer recurrence and prognosis based on SVM. Gene, 604, 33–40.
Zhang, G. M., Goyal, H., & Song, L. L. (2018). Bioinformatics analysis of differentially expressed miRNA-related mRNAs and their prognostic value in breast carcinoma. Oncology Reports, 39, 2865–2872.
Pan, J., Xiang, Z., Dai, Q., Wang, Z., Liu, B., & Li, C. (2019). Prediction of platinum-resistance patients of gastric cancer using bioinformatics. Journal of Cell Biochemistry, 120, 13478–13486.
Marshall, J. C., Collins, J., Marino, N., & Steeg, P. (2010). The Nm23-H1 metastasis suppressor as a translational target. European Journal of Cancer, 46, 1278–1282.
Natarajan, K., Mori, N., Artemov, D., & Bhujwalla, Z. M. (2002). Exposure of human breast cancer cells to the anti-inflammatory agent indomethacin alters choline phospholipid metabolites and Nm23 expression. Neoplasia, 4, 409–416.
Zhou, X., Jiao, D., Dou, M., Zhang, W., Lv, L., Chen, J., Li, L., Wang, L., & Han, X. (2020). Curcumin inhibits the growth of triple-negative breast cancer cells by silencing EZH2 and restoring DLC1 expression. Journal of Cell & Molecular Medicine, 24, 10648–10662.
Liu, Y., Zhou, J., Hu, Y., Wang, J., & Yuan, C. (2017). Curcumin inhibits growth of human breast cancer cells through demethylation of DLC1 promoter. Molecular Cell Biochemistry, 425, 47–58.
Au, S. L., Wong, C. C., Lee, J. M., Wong, C. M., & Ng, I. O. (2013). EZH2-mediated H3K27me3 is involved in epigenetic repression of deleted in liver cancer 1 in human cancers. PLoS ONE, 8, e68226.
Park, S., Ahn, E. S., Lee, S., Jung, M., Park, J. H., Yi, S. Y., & Yeom, C. H. (2009). Proteomic analysis reveals upregulation of RKIP in S-180 implanted BALB/C mouse after treatment with ascorbic acid. Journal of Cell Biochemistry, 106, 1136–1145.
Huang, Q., Bai, F., Nie, J., Lu, S., Lu, C., Zhu, X., Zhuo, L., & Lin, X. (2017). Didymin ameliorates hepatic injury through inhibition of MAPK and NF-kB pathways by up-regulating RKIP expression. International Immunopharmacology, 42, 130–138.
Wei, J., Huang, Q., Bai, F., Lin, J., Nie, J., Lu, S., Lu, C., Huang, R., Lu, Z., & Lin, X. (2017). Didymin induces apoptosis through mitochondrial dysfunction and up-regulation of RKIP in human hepatoma cells. Chemical & Biological Interactions, 261, 118–126.
Hu, C. J., Zhou, L., & Cai, Y. (2014). Dihydroartemisinin induces apoptosis of cervical cancer cells via upregulation of RKIP and downregulation of bcl-2. Cancer Biology & Therapeutics, 15, 279–288.
Kim, S. O., & Kim, M. R. (2013). (-)-Epigallocatechin 3-gallate inhibits invasion by inducing the expression of Raf kinase inhibitor protein in AsPC‑1 human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells through the modulation of histone deacetylase activity. International Journal of Oncology, 42, 349–358.
Hsu, Y. L., Chen, C. Y., Lin, I. P., Tsai, E. M., Kuo, P. L., & Hou, M. F. (2012). 4-Shogaol, an active constituent of dietary ginger, inhibits metastasis of MDA-MB-231 human breast adenocarcinoma cells by decreasing the repression of NF-ΰB/Snail on RKIP. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry, 60, 852–861.
Eves, E. M., Shapiro, P., Naik, K., Klein, U. R., Trakul, N., & Rosner, M. R. (2006). Raf kinase inhibitory protein regulates aurora B kinase and the spindle checkpoint. Molecular Cell, 23, 561–574.
Ohtsuka, T., Buchsbaum, D., Oliver, P., Makhija, S., Kimberly, R., & Zhou, T. (2003). Synergistic induction of tumor cell apoptosis by death receptor antibody and chemotherapy agent through JNK/p38 and mitochondrial death pathway. Oncogene, 22, 2034–2044.
Ohtsuka, T., & Zhou, T. (2002). Bisindolylmaleimide VIII enhances DR5-mediated apoptosis through the MKK4/JNK/p38 kinase and the mitochondrial pathways. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277, 29294–29303.
Fernandes, B. F., Di, C. S., Neto, B. R., Maloney, S., Martins, C., Castiglione, E., Isenberg, J., Abourbih, D., Antecka, E., & Burnier, M. N., Jr. (2011). Imatinib mesylate alters the expression of genes related to disease progression in an animal model of uveal melanoma. Analytical Cellular Pathology (Amst), 34, 123–130.
Whitnall, M., Howard, J., Ponka, P., & Richardson, D. R. (2006). A class of iron chelators with a wide spectrum of potent antitumor activity that overcomes resistance to chemotherapeutics. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science. U. S. A., 103, 14901–14906.
Zhou, X., Yang, X. Y., & Popescu, N. C. (2010). Synergistic antineoplastic effect of DLC1 tumor suppressor protein and histone deacetylase inhibitor, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA), on prostate and liver cancer cells: Perspectives for therapeutics. International Journal of Oncology, 36, 999–1005.
Zhou, X., Yang, X. Y., & Popescu, N. C. (2012). Preclinical evaluation of combined antineoplastic effect of DLC1 tumor suppressor protein and suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid on prostate cancer cells. Biochemical Biophysical Research Communications, 420, 325–330.
Kim, T. Y., Kim, I. S., Jong, H. S., Lee, J. W., Kim, T. Y., Jung, M., & Bang, Y. J. (2008). Transcriptional induction of DLC-1 gene through Sp1 sites by histone deacetylase inhibitors in gastric cancer cells. Experimental Molecular Medicine, 40, 639–646.
Funding
This work was supported by grants R21-CA235092 (NCI) and W81XWH-20-BCRP-BTA12-2 (DOD) to I.H.G. and by the P30-CA016056 (NCI) Comprehensive Cancer Center grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This manuscript was written and edited by the author.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gelman, I.H. Metastasis suppressor genes in clinical practice: are they druggable?. Cancer Metastasis Rev 42, 1169–1188 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-023-10135-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-023-10135-w