Abstract
Autophagy may have protective effects in renal ischemia–reperfusion (I/R) injury, although the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. Augmenter of liver regeneration (ALR), a widely distributed multifunctional protein that is originally identified as a hepatic growth factor, may participate in the process of autophagy. To investigate the role of ALR in autophagy, ALR expression is knocked-down in human kidney 2 (HK-2) cells with short hairpin RNA lentivirals. Then, the level of autophagy is measured in the shRNA/ALR group and the shRNA/control group in an in vitro model of ischemia–reperfusion (I/R). The results indicate that the level of autophagy in two groups increase, accompanied by increased reactive oxygen species production, especially in the shRNA/ALR group. The AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway is hyperactive in the shRNA/ALR group. Inhibition of autophagy with the AMPK inhibitor compound C induce apoptosis, especially in the shRNA/ALR group. These findings collectively indicate that ALR negatively regulates the autophagy process through an association with the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Autophagy inhibit apoptosis and play a protective role under conditions of oxidative stress.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basile DP, Yoder MC (2014) Renal endothelial dysfunction in acute kidney ischemia reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets 14(1):3–14
Yeh CH, Hsu SP, Yang CC, Chien CT, Wang NP (2010) Hypoxic preconditioning reinforces HIF-alpha-dependent HSP70 signaling to reduce ischemic renal failure-induced renal tubular apoptosis and autophagy. Life Sci 86(3–4):115–123. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2009.11.022
Nakagawa S, Nishihara K, Inui K, Masuda S (2012) Involvement of autophagy in the pharmacological effects of the mTOR inhibitor everolimus in acute kidney injury. Eur J Pharmacol 696(1–3):143–154. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.09.010
Turkmen K, Martin J, Akcay A, Nguyen Q, Ravichandran K, Faubel S, Pacic A, Ljubanovic D, Edelstein CL, Jani A (2011) Apoptosis and autophagy in cold preservation ischemia. Transplantation 91(11):1192–1197. doi:10.1097/TP.0b013e31821ab9c8
Kimura T, Takabatake Y, Takahashi A, Kaimori JY, Matsui I, Namba T, Kitamura H, Niimura F, Matsusaka T, Soga T, Rakugi H, Isaka Y (2011) Autophagy protects the proximal tubule from degeneration and acute ischemic injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 22(5):902–913. doi:10.1681/ASN.2010070705
Liu S, Hartleben B, Kretz O, Wiech T, Igarashi P, Mizushima N, Walz G, Huber TB (2012) Autophagy plays a critical role in kidney tubule maintenance, aging and ischemia-reperfusion injury. Autophagy 8(5):826–837. doi:10.4161/auto.19419
Jiang M, Wei Q, Dong G, Komatsu M, Su Y, Dong Z (2012) Autophagy in proximal tubules protects against acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 82(12):1271–1283. doi:10.1038/ki.2012.261
Morselli E, Maiuri MC, Markaki M, Megalou E, Pasparaki A, Palikaras K, Criollo A, Galluzzi L, Malik SA, Vitale I, Michaud M, Madeo F, Tavernarakis N, Kroemer G (2010) Caloric restriction and resveratrol promote longevity through the Sirtuin-1-dependent induction of autophagy. Cell Death Dis 1:e10. doi:10.1038/cddis.2009.8
Lieberthal W, Fuhro R, Andry CC, Rennke H, Abernathy VE, Koh JS, Valeri R, Levine JS (2001) Rapamycin impairs recovery from acute renal failure: role of cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis of tubular cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 281(4):F693–F706
Lieberthal W, Fuhro R, Andry C, Patel V, Levine JS (2006) Rapamycin delays but does not prevent recovery from acute renal failure: role of acquired tubular resistance. Transplantation 82(1):17–22
Mordas A, Tokatlidis K (2015) The MIA pathway: a key regulator of mitochondrial oxidative protein folding and biogenesis. Acc Chem Res 48(8):2191–2199. doi:10.1021/acs.accounts.5b00150
Gandhi CR (2012) Augmenter of liver regeneration. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 5(1):10. doi:10.1186/1755-1536-5-10
Polimeno L, Pesetti B, De Santis F, Resta L, Rossi R, De Palma A, Girardi B, Amoruso A, Francavilla A (2012) Decreased expression of the augmenter of liver regeneration results in increased apoptosis and oxidative damage in human-derived glioma cells. Cell Death Dis 3:e289. doi:10.1038/cddis.2012.25
Liao XH, Zhang L, Tang XP, Liu Q, Sun H (2009) Expression of augmenter of liver regeneration in rats with gentamicin-induced acute renal failure and its protective effect on kidney. Ren Fail 31(10):946–955. doi:10.3109/08860220903216154
Liao XH, Zhang L, Liu Q, Sun H, Peng CM, Guo H (2010) Augmenter of liver regeneration protects kidneys from ischaemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Nephrology Dial Transpl Off Publ Eur Dial Transpl Assoc Eur Renal Assoc 25(9):2921–2929. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfq151
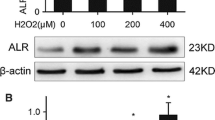
Xia N, Yan RY, Liu Q, Liao XH, Sun H, Guo H, Zhang L (2015) Augmenter of liver regeneration plays a protective role against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in renal proximal tubule cells. Apoptosis 20(4):423–432. doi:10.1007/s10495-015-1096-2
Rambold AS, Lippincott-Schwartz J (2011) Mechanisms of mitochondria and autophagy crosstalk. Cell Cycle 10(23):4032–4038. doi:10.4161/cc.10.23.18384
Todd LR, Gomathinayagam R, Sankar U (2010) A novel Gfer-Drp1 link in preserving mitochondrial dynamics and function in pluripotent stem cells. Autophagy 6(6):821–822. doi:10.1091/mbc.E09-11-0937
Shi HB, Sun HQ, Shi HL, Ren F, Chen Y, Chen DX, Lou JL, Duan ZP (2015) Autophagy in anti-apoptotic effect of augmenter of liver regeneration in HepG2 cells. World J Gastroenterol 21(17):5250–5258. doi:10.3748/wjg.v21.i17.5250
Chien CT, Shyue SK, Lai MK (2007) Bcl-xL augmentation potentially reduces ischemia/reperfusion induced proximal and distal tubular apoptosis and autophagy. Transplantation 84(9):1183–1190. doi:10.1097/01.tp.0000287334.38933.e3
Isaka Y, Suzuki C, Abe T, Okumi M, Ichimaru N, Imamura R, Kakuta Y, Matsui I, Takabatake Y, Rakugi H, Shimizu S, Takahara S (2009) Bcl-2 protects tubular epithelial cells from ischemia/reperfusion injury by dual mechanisms. Transplant Proc 41(1):52–54. doi:10.1016/j.transproceed.2008.10.026
Wu HH, Hsiao TY, Chien CT, Lai MK (2009) Ischemic conditioning by short periods of reperfusion attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion induced apoptosis and autophagy in the rat. J Biomed Sci 16:19. doi:10.1186/1423-0127-16-19
Sciarretta S, Hariharan N, Monden Y, Zablocki D, Sadoshima J (2011) Is autophagy in response to ischemia and reperfusion protective or detrimental for the heart? Pediatr Cardiol 32(3):275–281. doi:10.1007/s00246-010-9855-x
Liao XH, Chen GT, Li Y, Zhang L, Liu Q, Sun H, Guo H (2012) Augmenter of liver regeneration attenuates tubular cell apoptosis in acute kidney injury in rats: the possible mechanisms. Ren Fail 34(5):590–599. doi:10.3109/0886022x.2012.664470
Yan R, Li Y, Zhang L, Xia N, Liu Q, Sun H, Guo H (2015) Augmenter of liver regeneration attenuates inflammation of renal ischemia/reperfusion injury through the NF-kappa B pathway in rats. Int Urol Nephrol 47(5):861–868. doi:10.1007/s11255-015-0954-8
Jiang M, Liu K, Luo J, Dong Z (2010) Autophagy is a renoprotective mechanism during in vitro hypoxia and in vivo ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Pathol 176(3):1181–1192. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2010.090594
Dong W, Wang H, Shahzad K, Bock F, Al-Dabet MM, Ranjan S, Wolter J, Kohli S, Hoffmann J, Dhople VM, Zhu C, Lindquist JA, Esmon CT, Grone E, Grone HJ, Madhusudhan T, Mertens PR, Schluter D, Isermann B (2015) Activated protein C ameliorates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by restricting Y-box binding protein-1 ubiquitination. J Am Soc Nephrol 26(11):2789–2799. doi:10.1681/ASN.2014080846
Zhang ZS, Yang DY, Fu YB, Zhang L, Zhao QP, Li G (2015) Knockdown of CkrL by shRNA deteriorates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced H9C2 cardiomyocyte apoptosis and survival inhibition Via Bax and downregulation of P-Erk1/2. Cell Biochem Funct 33(2):80–88. doi:10.1002/cbf.3093
Wang LT, Chen BL, Wu CT, Huang KH, Chiang CK, Hwa Liu S (2013) Protective role of AMP-activated protein kinase-evoked autophagy on an in vitro model of ischemia/reperfusion-induced renal tubular cell injury. PloS One 8(11):e79814. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0079814
Dayoub R, Vogel A, Schuett J, Lupke M, Spieker SM, Kettern N, Hildt E, Melter M, Weiss TS (2013) Nrf2 activates augmenter of liver regeneration (ALR) via antioxidant response element and links oxidative stress to liver regeneration. Mol Med 19:237–244. doi:10.2119/molmed.2013.00027
Liu M, Grigoryev DN, Crow MT, Haas M, Yamamoto M, Reddy SP, Rabb H (2009) Transcription factor Nrf2 is protective during ischemic and nephrotoxic acute kidney injury in mice. Kidney Int 76(3):277–285. doi:10.1038/ki.2009.157
Cao Y, Fu YL, Yu M, Yue PB, Ge CH, Xu WX, Zhan YQ, Li CY, Li W, Wang XH, Wang ZD, Li YH, Yang XM (2009) Human augmenter of liver regeneration is important for hepatoma cell viability and resistance to radiation-induced oxidative stress. Free Rad Biol Med 47(7):1057–1066. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.07.017
Sun GY, Dong LY, An W (2014) Involvement of hepatic stimulator substance in the regulation of hepatoblast maturation into hepatocytes in vitro. Stem Cells Dev 23(14):1675–1687. doi:10.1089/scd.2013.0468
Li Y, Farooq M, Sheng D, Chandramouli C, Lan T, Mahajan NK, Kini RM, Hong Y, Lisowsky T, Ge R (2012) Augmenter of liver regeneration (alr) promotes liver outgrowth during zebrafish hepatogenesis. PloS One 7(1):e30835. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030835
Grahammer F, Haenisch N, Steinhardt F, Sandner L, Roerden M, Arnold F, Cordts T, Wanner N, Reichardt W, Kerjaschki D, Ruegg MA, Hall MN, Moulin P, Busch H, Boerries M, Walz G, Artunc F, Huber TB (2014) mTORC1 maintains renal tubular homeostasis and is essential in response to ischemic stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(27):E2817–E2826. doi:10.1073/pnas.1402352111
Hardie DG (2011) AMP-activated protein kinase: an energy sensor that regulates all aspects of cell function. Genes Dev 25(18):1895–1908. doi:10.1101/gad.17420111
Kim TW, Kim YJ, Kim HT, Park SR, Lee MY, Park YD, Lee CH, Jung JY (2016) NQO1 deficiency leads enhanced autophagy in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury through the AMPK/TSC2/mTOR signaling pathway. Antioxid Redox Signal 24(15):867–883. doi:10.1089/ars.2015.6386
Duan P, Hu C, Quan C, Yu T, Zhou W, Yuan M, Shi Y, Yang K (2016) 4-Nonylphenol induces apoptosis, autophagy and necrosis in Sertoli cells: involvement of ROS-mediated AMPK/AKT-mTOR and JNK pathways. Toxicology 341–343:28–40. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2016.01.004
Alers S, Loffler AS, Wesselborg S, Stork B (2012) Role of AMPK-mTOR-Ulk1/2 in the regulation of autophagy: cross talk, shortcuts, and feedbacks. Mol Cell Biol 32(1):2–11. doi:10.1128/MCB.06159-11
Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B, Guan KL (2011) AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol 13(2):132–141. doi:10.1038/ncb2152
Polimeno L, Rossi R, Mastrodonato M, Montagnani M, Piscitelli D, Pesetti B, De Benedictis L, Girardi B, Resta L, Napoli A, Francavilla A (2013) Augmenter of liver regeneration, a protective factor against ROS-induced oxidative damage in muscle tissue of mitochondrial myopathy affected patients. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 45(11):2410–2419. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2013.07.010
Bolisetty S, Traylor AM, Kim J, Joseph R, Ricart K, Landar A, Agarwal A (2010) Heme oxygenase-1 inhibits renal tubular macroautophagy in acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 21(10):1702–1712. doi:10.1681/ASN.2010030238
Maiuri MC, Zalckvar E, Kimchi A, Kroemer G (2007) Self-eating and self-killing: crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8(9):741–752. doi:10.1038/nrm2239
Yang C, Kaushal V, Shah SV, Kaushal GP (2008) Autophagy is associated with apoptosis in cisplatin injury to renal tubular epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 294(4):F777–F787. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00590.2007
Zeng Y, Li S, Wu J, Chen W, Sun H, Peng W, Yu X, Yang X (2014) Autophagy inhibitors promoted aristolochic acid I induced renal tubular epithelial cell apoptosis via mitochondrial pathway but alleviated nonapoptotic cell death in mouse acute aritolochic acid nephropathy model. Apoptosis Int J Program Cell Death 19(8):1215–1224. doi:10.1007/s10495-014-0996-x
Guan X, Qian Y, Shen Y, Zhang L, Du Y, Dai H, Qian J, Yan Y (2015) Autophagy protects renal tubular cells against ischemia / reperfusion injury in a time-dependent manner. Cell Physiol Biochem 36(1):285–298. doi:10.1159/000374071
Gandhi CR, Chaillet JR, Nalesnik MA, Kumar S, Dangi A, Demetris AJ, Ferrell R, Wu T, Divanovic S, Stankeiwicz T, Shaffer B, Stolz DB, Harvey SA, Wang J, Starzl TE (2015) Liver-specific deletion of augmenter of liver regeneration accelerates development of steatohepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. Gastroenterology 148(2):379–391 e374. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2014.10.008
Ilowski M, Kleespies A, de Toni EN, Donabauer B, Jauch KW, Hengstler JG, Thasler WE (2011) Augmenter of liver regeneration (ALR) protects human hepatocytes against apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 404(1):148–152. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.11.083
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81000299, 30971364), clinical medicine research special funds of the Chinese medical association (14050370574), Natural Science Foundation Project of CQ CSTC (cstc2015jcyjA10069), Grants from medical scientific research Projects of Chongqing health and family planning commission (20142031), the found for fostering talents in scientific research of chongqing medical university (201404), and a Grant from the science and technology department of Guizhou province, NO.LKZ(2012)27.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pu, T., Liao, Xh., Sun, H. et al. Augmenter of liver regeneration regulates autophagy in renal ischemia–reperfusion injury via the AMPK/mTOR pathway. Apoptosis 22, 955–969 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-017-1370-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-017-1370-6