Abstract
Purpose
The effects of augmenter of liver regeneration (ALR) on the acute kidney injury (AKI) rats were investigated by measuring the inflammatory response associated with transcription factor nuclear factory (NF-κB) pathway.
Methods
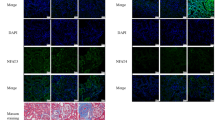
The model of AKI rats was established by occluded the renal pedicles for 60 min and then released. After that, animals were treated with ALR (100 or 200 μg/kg). All rats were killed at different time points (24, 48, 72 h). Renal function and kidney histological changes were measured. The apoptosis of tubular cells was evaluated by TdT-mediated dUTP nick end labeling assay. Cytokines and chemokines were assessed by immunohistochemistry, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). The NF-κB p65 protein was analyzed by immunohistochemistry and RT-PCR, respectively.
Results
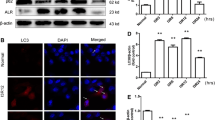
Ischemia reperfusion induced tubular cells necrosis and apoptosis, and ALR can significantly reduce this damages. The productions of MCP-1, IL-1β and IL-6 were lower in the group of ALR treatment, especially in the high-dose group. The inflammatory infiltrates were lower in the rats with administration of ALR. ALR mediated the level of cytokines and chemokines through inhibited the activation of NF-κB.
Conclusion
ALR can improve renal function and inhibit the expression of inflammatory factors. This protects against renal ischemia reperfusion injury, which may be associated with preventing NF-κB activation in rats.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonventre JV, Zuk A (2004) Ischemic acute renal failure: an inflammatory disease? Kidney Int 66:480–485
Kinsey GR, Li L, Okusa MD (2008) Inflammation in acute kidney injury. Exp Nephrol 109:102–107
Dorweiler B, Pruefer D, Andrasi TB, Maksan SM, Schmiedt W et al (2007) Ischemia-reperfusion injury. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 33:600–612
Kato A, Gabay C, Okaya T, Lentsch AB (2002) Specific role of interleukin-1 in hepatic neutrophil recruitment after ischemia/reperfusion. Am J Pathol 161:1797–1803
Maekawa N, Wada H, Kanda T, Niwa T, Yamada Y et al (2002) Improved myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice lacking tumor necrosis factor-α. J Am Coll Cardiol 39:1229–1235
Baldwin AS Jr (1996) The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol 14:649–683
Gandhi CR (2012) Augmenter of liver regeneration. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 5:10–21
Liao X-H, Zhang L, Tang X-P, Liu Q, Sun H (2009) Expression of augmenter of liver regeneration in rats with gentamicin-induced acute renal failure and its protective effect on kidney. Ren Fail 31:946–955
Liao Xh, Zhang L, Liu Q, Sun H, Cm Peng et al (2010) Augmenter of liver regeneration protects kidneys from ischaemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25:2921–2929
Kasagi N et al (1994) Apoptotic cell death in human gastric carcinoma: analysis by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling. Jpn J Cancer Res 85:939–945
Lameire NH, Bagga A, Cruz D, De Maeseneer J, Endre Z et al (2013) Acute kidney injury: an increasing global concern. Lancet 382:170–179
Munshi R, Hsu C, Himmelfarb J (2011) Advances in understanding ischemic acute kidney injury. BMC Med 9:5–11
Grigoryev DN, Liu M, Hassoun HT, Cheadle C, Barnes KC et al (2008) The local and systemic inflammatory transcriptome after acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:547–558
Gerlach UA, Atanasov G, Wallenta L, Polenz D, Reutzel-Selke A et al (2014) Short-term TNF-alpha inhibition reduces short-term and long-term inflammatory changes post-ischemia/reperfusion in rat intestinal transplantation. Transplantation 97:732–739
Long D, Hsu Y-H, Li H-H, Sung J-M, Chen W-T et al (2013) Interleukin-19 mediates tissue damage in murine ischemic acute kidney injury. PLoS One 8:e56028. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0056028
Dong X, Swaminathan S, Bachman LA, Croatt AJ, Nath KA et al (2007) Resident dendritic cells are the predominant TNF-secreting cell in early renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Kidney Int 71:619–628
Hagiya M, Francavilla A, Polimeno L et al (1994) Cloning and sequence analysis of the rat augmenter of liver regeneration (ALR) gene: expression of biologically active recombinant ALR and demonstration of tissue distribution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:8142–8146
Khandoga A, Mende K, Iskandarov E, Rosentreter D, Schelcher C et al (2014) Augmenter of liver regeneration attenuates inflammatory response in the postischemic mouse liver in vivo. J Surg Res 10:1016
Wang N, Wang Z, Sun H, Shi X, Zhang Y et al (2013) Augmenter of liver regeneration improves therapeutic effect of hepatocyte homotransplantation in acute liver failure rats. Int Immunopharmacol 15:325–332
Li Y, Zhang L, Liu Q, Chen GT, Sun H (2014) Exogenous augmenter of liver regeneration (ALR) attenuates inflammatory response in renal hypoxia re-oxygenation injury. Ren Fail 36:432–436
Lawrence T (2009) The nuclear factor NF- B pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 1. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a001651
Sung FL, Zhu TY, Au-Yeung KK, Siow YL, Karmin O (2002) Enhanced MCP-1 expression during ischemia/reperfusion injury is mediated by oxidative stress and NF-kappa B. Kidney Int 62:1160–1170
Gasparini C, Feldmann M (2012) NF-kappa B as a target for modulating inflammatory responses. Curr Pharm Des 18:5735–5745
Luo JG, Zhao XL, Xu WC, Zhao XJ, Wang JN et al (2014) Spinal nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappa B) p65 activation contributes to peripheral inflammation and hyperalgesia in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 66:896–906
Gandhi CR, Murase N, Starzl TE (2010) Cholera toxin-sensitive GTP-binding protein-coupled activation of augmenter of liver regeneration (ALR) receptor and its function in rat kupffer cells. J Cell Physiol 222:365–373
Yang K, Du C, Cheng Y, Li Y, Gong J et al (2013) Augmenter of liver regeneration promotes hepatic regeneration depending on the integrity of Kupffer cell in rat small-for-size liver transplantation. J Surg Res 183:922–928
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by grants from the National Natural Scientific Foundation of China (No. 30971364) and the Applied Basic Research Program of the Public Health Bureau Foundation of Chongqing Province (Nos. 2010-2-126).
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, R., Li, Y., Zhang, L. et al. Augmenter of liver regeneration attenuates inflammation of renal ischemia/reperfusion injury through the NF-kappa B pathway in rats. Int Urol Nephrol 47, 861–868 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-015-0954-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-015-0954-8