Abstract
It is generally accepted that the world's reliance on fossil fuels had negative implications, such as a decline in crude oil supply, a drop in air quality, an increase in global temperature, unpredictable weather change, etc. Biofuel production is one of the best options for minimizing the quantity of conventional fuel used. This article presents theoretical and practical methods for process improvement, as well as a brief review of the characteristics of bioethanol production and limitations by using various pre-treatment techniques with wastes such as fruit and lignocellulose biomass to ethanol production using various microbe species. Bioethanol has a variety of applications, including petrol blending, solvent use, and distillery sectors. The pH (4–4.3), temperature (32 °C), and kind of microorganisms all have a significant impact on bioethanol production. Many significant phenolic chemicals and bioactive substances have been extracted from waste during bioethanol manufacturing. The approaches discussed in this study, such as pre-treatment, extraction, and distillation, can enhance the yield of bio-ethanol, which can be beneficial in many ways in the future.
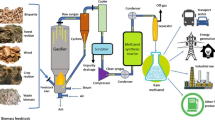
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
Change history
08 March 2024
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-024-02780-8
Abbreviations
- GHG:
-
Greenhouse gases
- SSF:
-
Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation
- CBP:
-
Consolidated bioprocessing
- SHF:
-
Separate hydrolysis and fermentation
- SSCF:
-
Simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation
- GE:
-
Genetic engineering
- TS:
-
Total sugar
- YPD:
-
Yeast extract, peptone, and dextrose media
- LCBs:
-
Lignocellulosic biomass
- GC-FID:
-
Gas chromatography-flame ionization detection
- FTIR:
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- GC:
-
Gas chromatography
- NIR:
-
Near-infrared spectroscopy
- ASTM:
-
American society for testing and materials
- EBP:
-
Ethanol blended Program
References
Abbi M, Kuhad RC, Singh A (1996) Bioconversion of pentose sugars to ethanol by free and immobilized cells of Candida shehatae (NCL-3501): fermentation behavior. Process Biochem 31(6):555–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(95)00104-2
Abo BO, Gao M, Wang Y, Wu C, Ma H, Wang Q (2011) Lignocellulosic biomass for bioethanol: an overview on pretreatment, hydrolysis and fermentation processes. Rev Environ Health 34:229–250. https://doi.org/10.1515/reveh-2018-0054/html
Abo BO, Gao M, Wang Y, Chuanfu Wu, Ma H, Wang Q (2019) Lignocellulosic biomass for bioethanol: an overview on pretreatment, hydrolysis and fermentation processes. Rev Environ Health 34(1):57–68. https://doi.org/10.1515/reveh-2018-0054
Adeniyi OM, Azimov U, Burlika A (2018) Algae biofuel: current status and future applications. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 90:316–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.03.067
Agbor VB, Cicek N, Sparling R, Berlin A, Levin DB (2011) Biomass pretreatment: fundamentals towasrd application. Biotechnol Adv 29(6):675–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.05.005
Ahmed MA, Rehman MSU, Hilares RT, Khalid S, Han J-I (2017) Optimization of twin gear-based pretreatment of rice straw for bioethanol production. Energy Convers Manag 141:120–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.06.022
Akhtar N, Goyal D, Goyal A (2017) Characterization of microwave-alkali-acid pre-treated rice straw for optimization of ethanol production via simultaneous saccharification and fermentation (SSF). Energy Convers Manag 141:133–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.06.081
Alexandropoulou M, Antonopoulou G, Fragkou E, Ntaikou I, Lyberatos G (2017) Fungal pretreatment of willow sawdust and its combination with alkaline treatment for enhancing biogas production. J Environ Manag 203(2):704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.04.006
Alvarez AL, Diaz-Perez AL, Sosa-Aguirre C, Rodriguez LM, Garcia JC (2012) Ethanol yield and volatile compound content in fermentation of agave must Kluyveromyces marxianus UMPe-1 comparing with Saccharomyces cerevisiae baker’s yeast used in tequila production. J Biosci Bioeng 113:614–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2011.12.015
Arni SA (2018) Extraction and isolation methods for lignin separation from sugarcane bagasse: a review. Ind Crops Prod 115:330–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.02.012
Arora R, Behera S, Sharma NK, Kumar S (2015) A new search for thermotolerant yeasts, its characterization and optimization using response surface methodology for ethanol production. Sec. Microbiotechnol 6:889. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00889
Arora A, Priya S, Sharma P, Sharma S, Nain L (2016) Evaluating biological pretreatment as a feasible methodology for ethanol production from paddy straw. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 8:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2016.08.006
Ask M, Olofsson K, Di Felice T, Ruohonen L, Penttila M, Liden G, Olsson L (2012) Challenges in enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation of pretreated Arundo donax revealed by a comparison between SHF and SSF. Process Biochem 47(10):1452–1459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2012.05.016
Ayodele BV, Alsaffar MA, Mustapa SI (2020) An overview of integration opportunities for sustainable bioethanol production from first- and second-generation sugar-based feedstocks. J Clean Prod 245:118857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118857
Balat M (2011) Production of bioethanol from lignocellulosic materials via the biochemical pathway: a review. Energy Convers Manag 52(2):858–875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2010.08.013
Barua VB, Goud VV, Kalamdhad AS (2018) Microbial pretreatment of water hyacinth for enhanced hydrolysis followed by biogas production. Renew Energy 126:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renen.2018.03.028
Breisha GZ (2010) Production of 16% ethanol from 35% sucrose. Biomass Bioenerg 34(8):1243–1249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2010.03.017
Broda M, Yelle DJ, Serwanska K (2022) Bioethanol production from lignocellulosic biomass—challenges and solutions. Molecules 27(24):8717. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248717
Cabrera E, Munoz MJ, Martin R, Ildefons C, Curbelo C, Diaz AB (2014) Alkaline and alkaline peroxide pretreatments at mild temperature to enhance enzymatic hydrolysis of rice hulls and straw. Biores Technol 167:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.05.103
Campillo M, Diaz NU, Soto O, Barrio E, Rutiaga M, Peaz J (2012) Effect of glucose concentration on the rate of fructose consumption in native strains isolated from the fermentation of Agave duranguensis. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:3387–3391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1143-x
Cantarella M, Cantarella L, Gallifuoco A, Spera A, Alfani F (2004) Comparison of different detoxification methods for steam-exploded poplar wood as a substrate for the bioproduction of ethanol in SHF and SSF. Process Biochem 39(11):1533–1542. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(03)00285-1
Casabar JT, Unpaprom Y, Ramaraj R (2019) Fermentation of pineapple fruit peel wastes for bioethanol production. Biomass Convers Boiorefin 9:761–765.
Chang Y-H, Chang K-S, Chen C-Y, Hsu C-L, Chang T-C, Jang H-D (2018) Enhancement of the efficiency of bioethanol production by saccharomyces cerevisiae via gradually batch-wise and fed-batch increasing the glucose concentration. Fermentation 4(2):45.
Charnnok B, Sakdaronnarong N, Sakdaronnarong C (2019) Hydrothermal pretreatment with sulfonated bentonite catalyst enhances potassium removal and bioconversion of oil palm empty fruit bunch to sugar and biohydrogen. Biomass Convers Biorefin 9:389–399.
Chen JH, Kun JX, Huang P-L, Sun RC (2016) Effect of alkaline pretreatment on the preparation of regenerated lignocellulose fibers from bamboo stem. Cellulose 23:2727–2739. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0983-1
Chitranshi R, Kapoor R (2021) Utilization of over-ripened fruit (waste fruit) for the eco-friendly production of ethanol. Vegetos 34:270–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42535-020-00185-8
Cristele D (2017) Plant cell wall: description, role in transport, and effect of electroporation. Handbook of electroporation. Springer, Cham, Switzerland, pp 489–509
Das N, Jena PK, Padhi D, Mohanty MK, Sahoo G (2023) A comprehensive review of characterization, pretreatment and its applications on different lignocellulosic biomass for bioethanol production. Biomass Convers Biorefin 13:1503–1527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01294-3
De Bhowmick G, Sarmah AK, Sen R (2018) Lignocellulosic biorefinery as a model for sustainable development of biofuels and value added products. Biores Technol 247:1144–1155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.163
de Miranda Rita CM, Neta JV, Ferreira LFR, Junior WAG, do Nascimento CS, Gomes EB, Mattedi S, Soares CMF, Lima AS (2019) Pineapple crown delignification using low-cost ionic liquid based on ethanolamine and organic acids. Carbohydr Polym 206:302–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.10.112
Derman E, Abdulla R, Marbawi H, Sabullah MK (2018) Oil plam empy fruit bunches as a promising feedstock for bioethanol production in Malaysia. Renew Energy 129:285–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.06.003
Dhande DY, Nighot DV, Sinaga N, Dahe KB (2021) Extraction of bioethanol from waste pomegranate fruits as a potential feedstock and its blending effects on a performance of a single cylinder SI engine. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 149:111349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.111349
Dominik, Rutz, and Janssen Rainer . 2007. Biofuel technology handbook. WIP Renerable Energies.
Dong C, Chen J, Guan R, Li X, Xin Y (2018) Dual-frequency ultrasound combined with alkali pretreatment of corn stalk for enhanced biogas production. Renew Energy 127:444–451. https://doi.org/10.1006/j.renene.2018.03.088
Fonseca BG, Mateo S, Moya AJ, Roberto IC (2018) Biotreatment optimization of rice straw hydrolyzates for ethanolic fermentation with Scheffersomyces stipitis. Biomass Bioenerg 112:19–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2018.02.003
Fu J, Du J, Lin G, Jiang D (2021) Analysis of yield potential and regional distribution for bioethanol in China. Energies 14(15):4554. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14154554
Galbe M, Zacchi G (2007) Pretreatment of lignocellulosic materials for efficient bioethanol Production. Advances in biochemical engineering/biotechnology. Springer, Berlin, pp 41–65
Galbe M, Zacchi G (2012) Pretreatment: the key to efficient utilization of lignocellulosic materials. Biomass Bioenerg 46:70–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.03.026
Hadeel A, Hossain ABMS, Latifa K, Naqeb HAL, Abear J, Norah A (2011) Bioethanol fuel production from rambutan fruit biomass as reducing agent of global warming and greenhouse gases. Afr J Biotech 10(50):10157–10165. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB11.790
Hamelinck CN, van Hooijdonk G, Faaij APC (2005) Ethanol from lignocellulosic biomass: techno-economnic performance in short-, middle- and long-term. Biomass Bioenergy 28(4):384–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2004.09.002
Harinikumar KM, Kudahettige-Nilsson RL, Devadas A, Holmgren M, Sellstedt A (2020) Bioethanol production from four abundant Indian agricultural wastes. Biofuels 11(5):607–613. https://doi.org/10.1080/17597269.2017.1387744
Hernandez-Beltran JU, IO Hernandez-De-Lira, MM Cruz-Santos, A Saucedo-Luevanos, F Harnandez-Teran, and N Balagurusamy. 2019. "Insight in to pretretment Method of Lignocellulosic Biomass to increase Biogas Yeild: Current State, Challenges, Oppertunities." Applied Science (MDPI) 9 (18). doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/app9183721 .
Hiben G, Yacob Y (2013) "Long-term bioethanol shift and transport fuel substitution in Ethiopia. KTH School of Industrial Engineering and Management, Energy Technology EGI-2013-ECS, Division of Energy and Climate Studies, Stockholm
Hilares RT, Kamoei DV, Ahmed MA, da Silva SS, Han J-I, Cesar dos Santos J (2018) A new approach for bioethanol production from sugarcane bagasse using hydrodynamic cavitation assisted-pretreatment and column reactors. Ultrasonics Sonochem 43:219–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2018.01.016
Himmel ME, Adney WS, Baker JO, Elander R, McMillan JD, Nieves RA, Sheehan JJ, Thomas SR, Vinzant TB, Zhang M (1997) Advanced bioethanol production technologies: a perspective. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 666:2–45. https://doi.org/10.1021/bk-1997-0666.ch001
Huang C, Xinxing Wu, Huang Y, Lai C, Li X, Youg Q (2016) Prewashing enhances the liquid hot water pretreatment efficiency of waste wheat straw with high free ash content. Biores Technol 219:583–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.08.018
Imman S, Arnthong J, Burapatana V, Champreda V, Laosiripojana N (2015) Influence of alkaline catalyst addition on compressed liquid hot water pretreatment of rice straw. Chem Eng J 278:85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.12.032
Ingrao C, Matarazzo A, Gorjian S, Adamczyk J, Failla S, Primerano P, Huisingh D (2021) Wheat-straw derived bioethanol production: a review of life cycle assessments. Sci Total Environ 781:146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146751
Isikgor FH, Remzi Becer C (2015) Lignocellulose biomass: a sustainable platfrom for the production of biobased chemicals and polymers. R Soc Chem 6:4497–4559. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5PYU00263J
Izmirlioglu G, Demirci A (2016) Improved simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of bioethanol from industrial potato waste with co-culture of Aspergillus niger and Saccharomyces cerevisiae by medium optimization. Fuel 185:684–691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.08.035
Jacobus AP, Gross J, Evans JH, Ceccato-Antonini SR, Gombert AK (2021) Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains used industrially for bioethanol production. Essays Biochem 65(2):147–161. https://doi.org/10.1042/EBC20200160
Jaing D, Ge X, Zhang Q, Li Y (2016) omparison of liquid hot water and alkaline pretreatments of giant reed for improved enzymatic digestibility and biogas energy production. Biores Technol 216:60–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.05.025
Jeppsson H, Yu S, Hahn-Hagerdal B (1996) Xylulose and glucose fermentation by saccharomyces cerevisiae in chemostat culture. Appl Environ Microbiol 62(5):1705. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.62.5.1705-1709.1996
Jin M, Slininger JP, Dien BS, Waghmode S, Moser BR, Orjuela A, de Costa-Sousa L, Balan V (2015) Microbial lipid-based lignocellulosic biorefinery: feasibility and challenges. Cellpress 33:43–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2014.11.005
Jinkun Xu, Bingchuan L, Huijie H, Jingping Hu (2017) Pretreatment of eucalyptus with recycled ionic liquids for low-cost biorefinery. Bioresour Technol 234:406–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotech.2017.03.081
Jonathan G (2008) Transgenics are imperative for biofuel crops. Plant Sci 174(3):246–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2007.11.009
Juunchen Lu, Irfan M, Lin F (2012) Bioconversion of agricultural waste to ethanol : apotential source of energy. Arch Sci 65:626–642
Kandasamy M, Hamawand I, Bowtell L, Seneweera S, Chakrabarty S, Yusaf T, Shakoor Z, Algayyim S, Eberhard F (2017) Investigation of ethanol production potential from lignocellulosic material without enzymatic hydrolysis using the ultrasound technique. Energies 10(1):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10010062
Kang KE, Chung DP, Kim Y, Chung BW, Choi GW (2015) High-titer ethanol production from simultaneous saccharification and fermentation using a continuous feeding system. Fuel 145:18–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.12.052
Karimi S, Karri RR, Yaraki MT, Koduru JR (2021) Processes and separation technologies for the production of fuel-grade bioethanol: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19:2873–2890. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-021-01208-9
Katsimpouras C, Zacharopoulou M, Matsakas L, Rova U, Christakopoulos P, Topakas E (2017) Sequential high gravity ethanol fermentation and anaerobic digestion of steam explosion and organosolv pretreated corn stover. Biores Technol 244:1129–1136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.112
Kaya AI, Karaosmanoglu F (2022) Life cycle assessment of safflower and sugar beet molasses-based biofuels. Renew Energy 201:1127–1138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.11.041
Khatri S, Wu S, Kizito S, Zhang W, Li J, Dong R (2015) Synergistic effect of alkaline pretreatment and Fe dosing on batch anaerobic digestion of maize straw. Appl Energy 158:55–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.08.045
Khramtsov N, McDade L, Amerik A, Esther Yu, Divatia K, Tikhonov A, Minto M et al (2011) Industrial yeast strain engineered to ferment ethanol from lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol 102(17):8310–8313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.05.075
Kim SR, Lee K-S, Choi J-H, Ha S-J, Kweon D-H, Seo J-H, Jin Y-S (2010) Repeated-batch fermentations of xylose and glucose–xylose mixtures using a respiration-deficient Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineered for xylose metabolism. J Biotechnol 150(3):404–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2010.09.962
Kim JS, Lee YY, Kim TH (2016a) A review on alkaline pretreatment technology for bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass. Biores Technol 199:42–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.08.085
Kim SM, Dien BS, Tumbleson ME, Rausch KD, Singh V (2016b) Improvement of sugar yields from corn stover using sequential hot water pretreatment and disk milling. Biores Technol 216:706–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.06.003
Krishna SH, Reddy TJ, Chowdary GV (2001) Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of lignocellulosic wastes to ethanol using a thermotolerant yeast. Bioresour Technol 77(2):193–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(00)00151-6
Kumar AK, Sharma S (2017) Recent updates on different methods of pretreatment of lignocellulosic feedstocks: a review. Bioresour Bioprocess 4(1):7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-017-0137-9
Kumari D, Singh R (2018) Pretreatment of lignicellulosic wastes for biofuels production: a critical review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 90:877–891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.03.111
Lachenmeier DW, Godelmann R, Steiner M, Anasy B, Weigel J, Krieg G (2010) Rapid and mobile determination of alcoholic strength in wine, beer and spirits using a flow-through infrared sensor. Chem Cent J 4:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-153X-4-5
Li H, Li S (2020) Optimization of continuous solid-state distillation process for cost-effective bioethanol production. Energies 13(4):854. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13040854x
Li H, Kim NJ, Jiang M, Kang JW, Chang HN (2009) Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of lignocellulosic residues pretreated with phosphoric acid–acetone for bioethanol production. Bioresour Techno 100(13):3245–3251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.01.021
Li M, Luo N, Yi Lu (2017) Biomass energy technological paradigm (BETP) trenda in this sector. Sustainability (MDPI) 9:1–28. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9040567
Lin Y, Tanaka S (2006) Ethanol fermentation from biomass resources: current state and prospects. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69:627–642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-0229-x
Lin TH, Guo GL, Hwang WS, Huang SL (2016) The addition of hydrolyzed rice straw in xylose fermentation by Pichia stipitis to increase bioethanol production at the pilot-scale. Biomass Bioenerg 91:204–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2016.05.012
Liu R, Shen F (2008) Impacts of main factors on bioethanol fermentation from stalk juice of sweet sorghum by immobilized Saccharomyces cerevisiae (CICC 1308). Biores Technol 99(4):847–854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.01.009
Liu Y, Tang Y, Gao H, Zhang W, Jiang Y, Xin F, Jiang M (2021) Challenges and future perspectives of promising biotechnologies for lignocellulosic biorefinery. Molecules 26(17):5411. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175411
Loow Y-L, Ta Yeong Wu, Jahim JM, Mohammad AW, Teoh WH (2016) Typical conversion of lignocellulosic biomass into reducing sugars using dilute acid hydrolysis and alkaline pretreatment. Cellulose 23(3):1491–1520. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0936-8
Luo M, Dong T, Shen F, Hu J, Hu Y (2019) A comparative investigation of H2O2-involved pretreatments on lignocellulosic biomass for enzymatic hydrolysis. Biomass Convers Biorefin 9:321–331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-018-0364-0
Machineni L (2020) Lignocellulose biofuel production: review of alternatives. Biomass Conver Biorefin 10:779–791. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-019-00445-x
Manikandan S, Vickram S, Sirohi R, Subbaiya R, Krishnan RY, Karmegam N, Sumathijones C et al (2023) Critical review of biochemical pathways to transformation of waste and biomass into bioenergy. Bioresour Technol 372:128679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2023.128679
Mardawati E, Febrianti EA, Fitriana HN, Yuliana T, Putriana NA, Suhartini S, Kasbawati (2022) An intregrated process for the xylitol and ethanol production from oil plam empty fruit bunch using debaryomyces hansenii and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microorganisms (MDPI) 10:2–11. https://doi.org/10.3390/microoganisms10102036
Martines-Patino JC, Lu-Chau TA, Gullon B, Ruiz E, Inmaculada R, Castro E, Lema JM (2018) Application of a combined fungal and diluted acid pretreatment on olive tree biomass. Ind Crops Prod 121:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.04.078
Maurya DP, A Singla, and S Negi. 2015. "An overview of key pretreatment processes for biological conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to bioethanol." biotech 5(5): 597–609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-015-0279-4.
Mazhad MM, Ramos LP, Paszner L, Saddler JN (1995) Structural constraints affecting the initial enzymatic hydrolysis of recycled paper. Enzym Microb Technol 17(1):68–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/0141-0229(94)00057-X
Melendez JR, Matyas B, Hena S, Lowy DA, El Salous A (2022) Perspectives in the production of bioethanol: a review of sustainable methods, technologies, and bioprocesses. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 160:112260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2022.112260
Merino O, Almazan V, Martiner-Palou R, Aburto J (2017) Screening of ionic liquids for pretreatment of taiwan grass in Q-Tube minireactors for improving bioethanol production. Waste Biomass Valoriz 8:733–742. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12649-016-9612-3
Mikulski D, Klosowski G, Menka A, Koim Puchowska B (2019) Microwave-assisted pretreatment of maize distillery stillage with the use of dilute sulfuric acid in the production of cellulosic ethanol. Biores Technol 278:318–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.01.068
Mohammad JN, Keikhosro K, Morteza S (2018) Improvment of ethanol and biogas production from sugarcane bagasse using sodium alkaline pretreatments. J Environ Manag 226:329–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.08.058
Molaverdi M, Karimi K, Mirmohamadsadeghi S (2019) Improvement of dry simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of rice straw to high concentration ethanol by sodium carbonate pretreatment. Energy 167(15):654–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.11.017
Monschein M, Nidetzky B (2016) Effect of pretreatment severity in continuous steam explosion on enzymatic conversion of wheat straw: evidence from kinetic analysis of hydrolysis time courses. Biores Technol 200:287–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.10.020
Morshabul H, Abedin MZ, Amin MB, Nekmahmud M, Olah J (2023) Sustainable biofuel economy: amapping through bibliometric research. J Environ Manag 336:11764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envman.2023.117644
Mukherjee A, Mandal T, Ganguly A, Chatterjee PK (2016) Lignin degradation in the production of bioethanol–a review. Chembioeng Rev 3(2):89–96. https://doi.org/10.1002/cben.201500016
Mustafa MA, Poulsen GT, Kuichuan S (2016) Fungal pretreatment of rice straw with Pleurotus ostreatus and Trichoderma reesei to enhance methane production under solid-state anaerobic digestion. Appl Energy 108:661–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.07.135
Niklitschek T, Salazar O, Carmona R, Garcia A, Lienqueo ME (2010) Comparison of SHF and SSF processes from forest residues pretrated with ionic liquid to obtain bioethanol. J Biotechnol 150:181–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2010.08.472
Noelia PR, Bernet GD, Dominguez MJ (2017) Extrusion and enzymatic hydrolysis as preteatment on corn cob for biogas production. Renew Energy 107:597–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.02.030f
Nosratpour MJ, Karimi K, Sadeghi M (2018) Improvement of ethanol and biogas production from sugarcane bagasse using sodium alkaline pretreatments. J Environ Manag 226:329–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.08.058
Ohgren K, Bengtsson O, Gorwa-Grauslunda MF, Galbe M, Hagerdal BH, Zacch G (2006) Simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation of glucose and xylose in steam-pretreated corn stover at high fiber content with Saccharomyces cerevisiae TMB3400. J Biotechnol 126(4):488–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2006.05.001
Oliver JD, Gaborieau M, Castignolles P (2014) Ethanol determination using pressure mobilization and free solution capillary electrophoresis by photo-oxidation assisted ultraviolet detection. J Chromatogr A 1348(27):150–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.04.076
Olofsson K, Wiman M, Liden G (2010) Controlled feeding of cellulases improves conversion of xylose in simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation for bioethanol production. J Biotechnol 145(2):168–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2009.11.001
Olugbenga AG (2023) Cost determination of using bioethanol to improve properties of Nigerian gasoline. Case Stud Chem Environ Eng 7:100358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscee.2023.100358
Ornaghi HL Jr, Ornaghi FG, Neves RM, Monticeli F, Bianchi O (2020) Mechanisms involved in thermal degradation of lignocellulosic fibers: a survey based on chemical composition. Cellulose 27:4949–4961. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03132-7
Orozco RS, Hernandez PB, Morales GR, Nunez FU, Villafuerte JO, Lugo VL, Ramirez NF, Diaz CEB, Vazquez PC (2014) Characterization of lignocellulosic fruit waste as an alternative feedstock for bioethanol production. Bioresources 9(2):1873–1885
Panagiotis T, Panagiotis KG, Angelidaki I (2018) Mechanical pretreatment for increased biogas production from lignecellulose biomass; predicting the methane yield from structural plant components. Waste Manag 78:903–910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.07.017
Pattanakittivorakul S, Tsuzuno T, Kosaka T, Murata M, Kanesaki Y, Yoshikawa H, Limtong S, Yamada M (2022) Evolutionary adaptation by repetitive long-term cultivation with gradual increase in temperature for acquiring multi-stress tolerance and high ethanol productivity in Kluyveromyces marxianus DMKU 3–1042. Microorganisms 10(4):798. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10040798
Paulova L, Patakova P, Branska B, Rychtera M, Melzoch K (2015) Lignocellulosic ethanol: technology design and its impact on process efficiency. Biotechnol Adv 33(6):1091–1107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2014.12.002
Pejo ET, Oliva JM, Ballesteros M, Olsson L (2008) Comparison of SHF and SSF processes from steam-exploded wheat straw for ethanol production by xylose-fermenting and robust glucose-fermentation Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains. Biotechnol Bioeng 100(6):1122–1131. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.2849
Pinal L, Cedeno M, Gutierrez H, Jacobs JA (1997) Fermentation parameters influencing higher alcohol production in the tequila process. Biotechnol Lett 19(1):45–47. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018362919846
Prasad S, Malav MK, Kumar S, Singh A, Pant D, Radhakrishnan S (2018) Enhancement of bio-ethanol production potential of wheat straw by reducing furfural and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF). Bioresour Technol Rep 4:50–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2018.09.007
Rabbani M, Momen S, Akbarian-Saravi N, Farrokhi Asl H, Ghlinchi Z (2020) Optimal design for sustainable bioethanol supply chain considering the bioethanol production strategies: a case study. Comput Chem Eng 134:106720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2019.106720
Rana V, Eckard AD, Ahring BK (2014) Comparison of SHF and SSF of wet exploded corn stover and loblolly pine using in-house enzymes produced from T. reesei RUT C30 and A. saccharolyticus. J Korean Phys Soc 3(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-3-516
Rangel AOSS, Toth IV (2000) Enzymatic determination of ethanol and glycerol by flow injection parallel multi-site detection. Anal Chim Acta 416(2):205–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(00)00905-3
Robak K, Balcerek M (2018) Review of second generation bioethanol production from residual biomass. Food Technol Biotechnol 56(2):174–187. https://doi.org/10.17113/ftb.56.02.18.5428
Roca C, Olsson L (2003) Increasing ethanol productivity during xylose fermentation by cell recycling of recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60(5):560–563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-002-1147-9
Rotariu L, Bala C, Magearu V (2003) New potentiometric microbial biosensor for ethanol determination in alcoholic beverages. Anal Chim Acta 513(1):119–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2003.12.048
Saini S, Sharma KK (2021) Fungal lignocellulolytic enzymes and lignocellulose: a critical review on their contribution to multiproduct biorefinery and global biofuel research. Int J Biol Macromol 193:2304–2319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.11.063
Saini BL, Gaur NR, Sahoo NR, Naha BC, Baranwal A (2019) Assessment of meat quality defect genes in indigenous pigs of Bareilly region. Trop Anim Health Prod 51:1329–1335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-018-01795-w
Saleh SM, Al-Azzawi AGS (2023) Optimizing bioethanol production for high octane bioethanol-gasoline. J Turk Chem Soc 10(2):475–486. https://doi.org/10.18596/jotcsa.1250955
Salehian P, Keikhosro K, Hamid Z, Azam J (2013) Improvement of biogas production from pine wood by alkali pretreatment. Fuel 106:484–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2012.12.092
Sanchez S, Bravo V, Castro E, Moya AJ, Camacho F (2002) The fermentation of mixtures of D-glucose and D-xylose by Candida shehatae, Pichia stipitis or Pachysolen tannophilus to produce ethanol. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 77(6):641–648. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.622
Sanchez C, Santos S, Sanchez R, Lienemann CP, Todoli JL (2020) Profiling of organic compounds in bioethanol samples of different nature and the related fractions. Am Chem Soc 5(33):20912–20921. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c02360
Satari B, Karimi K, Kumar R (2019) Cellulose solvent-based pretreatment for enhanced second-generation biofuel production: a review. Sustain Energy Fuels 3(1):11–62. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SE00287H
Schwab C, Tveit AT, Schleper C, Urich T (2016) Gene expression of lactobacilli in murine forestomach biofilms. Microbl biotechnol 9(4):436–440. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12126
Setyo WC, Setiady NI, Masuku M, Hamzah A, Fedori I, Maymuchar, Nugroho YS, Bambang S (2020) The performance of a spark ignition engine using 92 RON gasoline with varying blends of bioethanol (E40, E50, E60) measured using a dynamometer test. Int J Technol 11(7):1380–1387
Shah AT, Ullah R (2019) Pretreatment of wheat straw with ligninoytic fungi for increased biogas productivity. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:7497–7508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762.019-02277-8
Shah KR, Vyas R, Patel G (2019) Bioethanol production from pulp of fruits. Biotechnol Commun 12:464–471. https://doi.org/10.21786/bbrc/12.2/32
Sharma S, Basu S, Shetti NP, Aminabhavi TM (2020) Waste-to-energy nexus for circular economy and environment protection: Recent trends in hydrogen energy. Sci Total Environ 713:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136633
Shih CJ, Smith EA (2009) Determination of glucose and ethanol after enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation of biomass using Raman spectroscopy. Anal Chim Acta 653(2):200–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2009.09.012
Sindhu R, Kuttiraja M, Binod P, Sukumaran RK, Ashok P (2014) Bioethanol production from dilute acid pretreated Indian bamboo variety (Dendrocalamus sp.) by separate hydrolysis and fermentation. Ind Crops Prod 52:169–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.10.021
Singh R, Shukla A, Tiwari S, Srivastava M (2014) A review on delignification of lignocellulosic biomass for enhancement of ethanol production potential. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 32:713–728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.01.051
Singh J, Suhag M, Dhaka A (2015) Augmented digestion of lignocellulose by steam explosion, acid and alkaline pretreatment methods: a review. Carbohyd Polym 117:624–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.10.012
Smuga K, Kazimiera Z, Daria PS (2016) Influence of the crystalline structure of cellulose on the production of ethanol from lignocellulose biomass. Int Agrophys 30:83–88. https://doi.org/10.1515/intag-2015-0072
Solarte-Toro JC, Romero-Garcia JM, Martinez-Patino JC, Ruiz-Ramos E, Castro-Galiano E, Cardona-Alzate CA (2019) Acid pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for energy vectors production: a review focused on operational conditions and techno-economic assessment for bioethanol production. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 107:587–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.02.024
Song Z, Gaihe Y, Xiaofeng L, Zhiying Y, Yuexiang Y, Liao Y (2014) Comparison of seven chemical pretretment of corn straw for improving methane yeild by anaerobic digestion. PLOS ONE 9(6):456. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0101617
Sreemahadevan S, Roychoudhury PK, Thankamani V, Ahammad SZ (2018) Biological pretreatment of rice straw using an alkalophilic fungus MVI.2011 for enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis yield. Sustain Energy Technol Assess 30:304–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2018.10.015
Su T, Zhao D, Khodadadi M, Len C (2020) Lignocellulosic biomass for bioethanol: recent advances, technology trends, and barriers to industrial development. Current Opin Green Sustain Chem 24:56–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsc.2020.04.005
Tanaka K, Hilary ZD, Ishizaki A (1999) Investigation of the utility of pineapple juice and pineapple waste material as low-cost substrate for ethanol fermentation by Zymomonas mobilis. J Biosci Bioeng 87(5):642–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1389-1723(99)80128-5
Tavva SSMD, Deshpande A, Durbha SR, Palakollu VAR, Goparaju AU, Yechuri VR, Muktinutalapati VR, Muktinutalapati VSR (2016) Bioethanol production through separate hydrolysis and fermentation of Parthenium hysterophorus biomass. Renew Energy 86:1317–1323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2015.09.074
Tenkolu GA, Kuffi KD, Gindaba GT (2022) Optimization of fermentation condition in bioethanol production from waste potato and product characterization. Biomass Convers Biorefin 45:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-02974-4
Thomas HL, Arnoult S, Hulmel MB, Carrere H (2019) Methane production variability according to miscanthus genotype and alkaline pretreatments at high solid content. Bioenergy Res 12:335–337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-018-9957-5
Torreiro MG, Lopez Abelairas M, Lu Chau TA, Lema JM (2016) Fungal pretreatment of agricultural residues for bioethanol production. Ind Crops Prod 89:486–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.05.036
Tovar FG, Celis LB, Flores ER, Mondragon FA (2012) Chemical and enzymatic sequential pretreatment of oat straw for methane production. Biores Technol 116:372–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.03.109
Trejo M, Bhuyar P, Unpaprom Y, Dussadee N, Ramaraj R (2022) Advancement of fermentable sugars from fresh elephant ear plant weed for efficient bioethanol production. Environ Dev Sustain 24(5):7377–7387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01753-x
Triwahyuni E, Muryanto YS, Abimanyu H (2015) The effect of substrate loading on simultaneous saccharification and fermentation process for bioethanol production from oil palm empty fruit bunches. Energy Procedia 68:138–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2015.03.242
Tsegaye B, Balomajumder C, Roy P (2019) Optimization of microwave and NaOH pretreatments of wheat straw for enhancing biofuel yield. Energy Convers Manag 186:82–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2019.02.049
Ullah K, Sharma VK, Ahmad M, Lv P, Krahi J, Wang Z, Sofia S (2017) The insight views of advanced technologies and its application in bio-origin fuel synthesis from lignocellulose biomasse waste, a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 82:1364–0321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.074
Usmani Z, Sharma M, Gupta P, Karpichev Y, Gathergood N, Bhat R, Gupta VK (2020) Ionic liquid based pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for enhanced bioconversion. Biores Technol 304:123003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123003
Vallet C, Said R, Rabiller C, Martin ML (1996) Natural Abundance isotopic fractionation in the fermentation reaction: influence of the nature of the yeast. Bioorg Chem 24(4):319–330. https://doi.org/10.1006/bioo.1996.0028
Vergara P, Ladero M, Garcia-Ochoa F, Villlar JC (2018) Pre-treatment of corn stover, Cynara cardunculus L. stems and wheat straw by ethanol-water and diluted sulfuric acid: comparison under different energy input conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 270:449–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioetech.2018.09.058
Walker GM (2010) Bioethanol: science and technology of fuel alcohol. Ventus Publishing ApS, Telluride
Wang ML, Choong YM, Su NW, Lee MS (2003) A rapid method for determination of ethanol in alcoholic beverages using capillary gas chromatography. J Food Drug Anal 11(2):133–140. https://doi.org/10.38212/2224-6614.2710
Wayman M, Parekh SR (1990) Biotchnology of biomass consevation. Open University Press, Maidenhead
Wu X, Zhang J, Erni Xu, Liu Y, Cheng Y, Addy M, Zhou W, Griffith R, Chen P, Ruan R (2016) Microbial hydrolysis and fermentation of rice straw for ethanol production. Fuel 180:679–686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.04.087
Xue SJ, Chi Z, Zhang Y, Li Y-F, Liu G-L, Jiang H, Hu Z, Chi Z-M, Chi ZM (2018) Fatty acids from oleaginous yeasts and yeast-like fungi and their potential applications. Crit Rev Biotechnol 38:1049. https://doi.org/10.1080/0738855102018.1428167
Yang H, Shi Z, Gaofeng Xu, Qin Y, Deng J, Yang J (2019) Bioethanol production from bamboo with alkali-catalyzed liquid hot water pretreatment. Biores Technol 274:261–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.11.088
Yang P, Jiang S, Shuhua Lu, Jiang S, Jiang S, Deng Y, Jiuling Lu, Wang Hu, Zhou Y (2022) Ethanol yield improvement in Saccharomyces cerevisiae GPD2 Delta FPS1 Delta ADH2 Delta DLD3 Delta mutant and molecular mechanism exploration based on the metabolic flux and transcriptomics approaches. Microb Cell Fact 21(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-022-01885-3
Ye C, Mark SA, Yongming Z, Jason H, Hui Xu (2013) Understanding of alkaline pretreatment parameters for corn stover enzymatic saccharification. Biotechnol Biofuels 6(8):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-6834-6-8
Yuan X, Ma L, Wan B, Zhou D, Kuang M, Yang W, Cui Z (2016) Enhancing anaeribic digestion of cotton satalk by pretretment with a microbial consortium (MC1). Biores Technol 207:293–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotech.2016.02.037
Yuan Z, Wen Y, Li G (2018a) Production of bioethanol and value added compounds from wheat straw through combined alkaline/alkaline-peroxide pretreatment. Bioresour Technol 259:228–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.03.044
Yuan Z, Wen Y, Kapu NS (2018b) Ethanol production from bamboo using mild alkaline pre-extraction followed by alkaline hydrogen peroxide pretreatment. Bioresour Technol 247:242–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.080
Yuan Z, Wen Y, Li G (2018c) Production of bioethanol and value added compounds from wheat straw through combined alkaline/alkaline-peroxide pretreatment. Biores Technol 259:228–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.03.044
Yuangsaar N, Yongmanitchai W, Yamada M, Limtong S, van Leeuwenhoek A (2013) Selection and characterization of a newly isolated thermotolerant Pichia kudriavzevii strain for ethanol production at high temperature from cassava starch hydrolysate. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 103:577–588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-012-9842-8
Zabed H, Sahu JN, Boyce AN, Faruq G (2016) Fuel ethanol production from lignocellulose biomass: an overview on feedstocks and technological approaches. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 66:751–774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.08.038
Zabed HM, Akter S, Yun J, Zhang G, Awad FN, Qi X, Sahu JN (2019) Recent advances in biological pretreatment of microalgae and lignocellulosic biomass for biofuel production. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 105:105–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.01.048
Zerva A, Savvides AL, Katsifas EA, Karagouni AD, Hatzinikolaou DG (2014) Evaluation of Paecilomyces variotii potential in bioethanol production from lignocellulose through consolidated bioprocessing. Biores Technol 162:249–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.03.137
Zhang H, Zhang P, Ye J, Yan Wu, Liu J, Fang W, Dong Xu, Wang B, Yan Li, Zeng G (2018) Comparison of various pretreatments for ethanol production enhancement from solid residue after rumen fluid digestion of rice straw. Biores Technol 247:147–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.065
Zhao X, Cheng K, Liu D (2009) Organosolv pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for enzymatic hydrolysis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82(5):815. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-1883-1
Zhao C, Qiao X, Shao Q, Hassan M, Ma Z (2020) Evolution of the lignin chemical structure during the bioethanol production process and its inhibition to enzymatic hydrolysis. Am Chem Soc 34(5):5938–5947. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.0c00293
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Department of Environment Science and the Department of Chemistry, Gujarat University for providing access to e-sources facilities.
Funding
One of the authors, Shreya J Chauhan, acknowledges the support of the Education Department, Government of Gujarat, under the SHODH - Scheme of Developing High-Quality Research, reference number 2022013896. Additionally, Bimalkumar Patel is grateful for the support from the DST Inspire Fellowship, with grant ID 220066.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shreya J Chauhan significantly contributed through formal analysis, investigation, methodology, and authoring the initial draft. Bimalkumar Patel provided essential conceptual input and resources. Bhargav Devliya created the graphical abstract and provided other technical support. Dr. Hitesh D Patel and Dr. Hitesh Solanki guided and supervised with technical assistance and access to library resources.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that there are no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could influence the work reported in this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: Author contribution and funding section are updated.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chauhan, S.J., Patel, B., Devliya, B. et al. Recent advancement in production of bioethanol from waste biomass: a review. Clean Techn Environ Policy (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-023-02710-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-023-02710-0