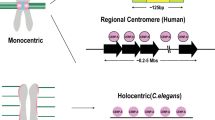
Abstract
Endogenous chromosomes contain centromeres to direct equal chromosomal segregation in mitosis and meiosis. The location and function of existing centromeres is usually maintained through cell cycles and generations. Recent studies have investigated how the centromere-specific histone H3 variant CENP-A is assembled and replenished after DNA replication to epigenetically propagate the centromere identity. However, existing centromeres occasionally become inactivated, with or without change in underlying DNA sequences, or lost after chromosomal rearrangements, resulting in acentric chromosomes. New centromeres, known as neocentromeres, may form on ectopic, non-centromeric chromosomal regions to rescue acentric chromosomes from being lost, or form dicentric chromosomes if the original centromere is still active. In addition, de novo centromeres can form after chromatinization of purified DNA that is exogenously introduced into cells. Here, we review the phenomena of naturally occurring and experimentally induced new centromeres and summarize the genetic (DNA sequence) and epigenetic features of these new centromeres. We compare the characteristics of new and native centromeres to understand whether there are different requirements for centromere establishment and propagation. Based on our understanding of the mechanisms of new centromere formation, we discuss the perspectives of developing more stably segregating human artificial chromosomes to facilitate gene delivery in therapeutics and research.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldrup-MacDonald ME, Kuo ME, Sullivan LL, Chew K, Sullivan BA (2016) Genomic variation within alpha satellite DNA influences centromere location on human chromosomes with metastable epialleles. Genome Research 26:1301–1311
Allshire RC, Ekwall K (2015a) Epigenetic regulation of chromatin states in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7:a018770
Alonso A, Fritz B, Hasson D, Abrusan G, Cheung F, Yoda K, Radlwimmer B, Ladurner AG, Warburton PE (2007) Co-localization of CENP-C and CENP-H to discontinuous domains of CENP-A chromatin at human neocentromeres. Genome Biol 8:R148
Alonso A, Hasson D, Cheung F, Warburton PE (2010) A paucity of heterochromatin at functional human neocentromeres. Epigenetics Chromatin 3:6
Alonso A, Mahmood R, Li S, Cheung F, Yoda K, Warburton PE (2003) Genomic microarray analysis reveals distinct locations for the CENP-A binding domains in three human chromosome 13q32 neocentromeres. Human Mol Genet 12:2711–2721
Ambartsumyan G, Gill RK, Perez SD, Conway D, Vincent J, Dalal Y, Clark AT (2010) Centromere protein A dynamics in human pluripotent stem cell self-renewal, differentiation and DNA damage. Hum Mol Genet 19:3970–3982
Amor DJ, Bentley K, Ryan J, Perry J, Wong L, Slater H, Choo KH (2004) Human centromere repositioning “in progress”. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:6542–6547
Amor DJ, Choo KH (2002) Neocentromeres: role in human disease, evolution, and centromere study. Am J Hum Genet 71:695–714
Athwal RK, Walkiewicz MP, Baek S, Fu S, Bui M, Camps J, Ried T, Sung MH, Dalal Y (2015) CENP-A nucleosomes localize to transcription factor hotspots and subtelomeric sites in human cancer cells. Epigenetics Chromatin 8:2
Baker RE, Rogers K (2005) Genetic and genomic analysis of the AT-rich centromere DNA element II of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 171:1463–1475
Baldini A, Ried T, Shridhar V, Ogura K, D’Aiuto L, Rocchi M, Ward DC (1993) An alphoid DNA sequence conserved in all human and great ape chromosomes: evidence for ancient centromeric sequences at human chromosomal regions 2q21 and 9q13. Hum Genet 90:577–583
Barrey EJ, Heun P (2017) Artificial chromosomes and strategies to initiate epigenetic centromere establishment. Prog Mol Subcell Biol 56:193–212
Basu J, Compitello G, Stromberg G, Willard HF, Van Bokkelen G (2005) Efficient assembly of de novo human artificial chromosomes from large genomic loci. BMC Biotechnol 5:21
Basu J, Stromberg G, Compitello G, Willard HF, Van Bokkelen G (2005) Rapid creation of BAC-based human artificial chromosome vectors by transposition with synthetic alpha-satellite arrays. Nucleic Acids Res 33:587–596
Beh TT, MacKinnon RN, Kalitsis P (2016) Active centromere and chromosome identification in fixed cell lines. Mol Cytogenet 9:28
Bergmann JH, Jakubsche JN, Martins NM, Kagansky A, Nakano M, Kimura H, Kelly DA, Turner BM, Masumoto H, Larionov V, Earnshaw WC (2012) Epigenetic engineering: histone H3K9 acetylation is compatible with kinetochore structure and function. J Cell Sci 125:411–421
Bergmann JH, Rodriguez MG, Martins NM, Kimura H, Kelly DA, Masumoto H, Larionov V, Jansen LE, Earnshaw WC (2011) Epigenetic engineering shows H3K4me2 is required for HJURP targeting and CENP-A assembly on a synthetic human kinetochore. EMBO J 30:328–340
Bernard P, Maure JF, Partridge JF, Genier S, Javerzat JP, Allshire RC (2001) Requirement of heterochromatin for cohesion at centromeres. Science 294:2539–2542
Birchler JA, Presting GG (2012) Retrotransposon insertion targeting: a mechanism for homogenization of centromere sequences on nonhomologous chromosomes. Genes Dev 26:638–640
Birchler JA (2015) Engineered minichromosomes in plants. Chromosome Res 23:77–85
Black BE, Cleveland DW (2011) Epigenetic centromere propagation and the nature of CENP-a nucleosomes. Cell 144:471–479
Black BE, Jansen LE, Foltz DR, Cleveland DW (2010) Centromere identity, function, and epigenetic propagation across cell divisions. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 75:403–418
Blom E, Heyning FH, Kroes WG (2010) A case of angioimmunoblastic T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma with a neocentric inv dup(1). Cancer Genet Cytogenet 202:38–42
Blower MD (2016) Centromeric transcription regulates Aurora-B localization and activation. Cell Rep 15:1624–1633
Bobkov GOM, Gilbert N, Heun P (2018) Centromere transcription allows CENP-A to transit from chromatin association to stable incorporation. J Cell Biol 217:1957–1972
Bouzinba-Segard H, Guais A, Francastel C (2006) Accumulation of small murine minor satellite transcripts leads to impaired centromeric architecture and function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:8709–8714
Brown KE, Barnett MA, Burgtorf C, Shaw P, Buckle VJ, Brown WR (1994) Dissecting the centromere of the human Y chromosome with cloned telomeric DNA. Human Molecular Genetics 3:1227–1237
Brown DM, Chan YA, Desai PJ, Grzesik P, Oldfield LM, Vashee S, Way JC, Silver PA, Glass JI (2017) Efficient size-independent chromosome delivery from yeast to cultured cell lines. Nucleic Acids Res 45(7):e50
Buckler ES, Phelps-Durr TL, Buckler CS, Dawe RK, Doebley JF, Holtsford TP (1999) Meiotic drive of chromosomal knobs reshaped the maize genome. Genetics 153:415–426
Bulazel KV, Ferreri GC, Eldridge MD, O’Neill RJ (2007) Species-specific shifts in centromere sequence composition are coincident with breakpoint reuse in karyotypically divergent lineages. Genome Biol 8:R170
Camahort R, Li B, Florens L, Swanson SK, Washburn MP, Gerton JL (2007) Scm3 is essential to recruit the histone h3 variant cse4 to centromeres and to maintain a functional kinetochore. Molecular Cell 26:853–865
Canzonetta C, Vernarecci S, Iuliani M, Marracino C, Belloni C, Ballario P, Filetici P (2015) SAGA DUB-Ubp8 deubiquitylates centromeric histone variant Cse4. G3 (Bethesda) 6:287–298
Capozzi O, Purgato S, Verdun di Cantogno L, Grosso E, Ciccone R, Zuffardi O, Della Valle G, Rocchi M (2008) Evolutionary and clinical neocentromeres: two faces of the same coin? Chromosoma 117:339–344
Carbone L, Nergadze SG, Magnani E, Misceo D, Francesca Cardone M, Roberto R, Bertoni L, Attolini C, Francesca Piras M, de Jong P, Raudsepp T, Chowdhary BP, Guerin G, Archidiacono N, Rocchi M, Giulotto E (2006) Evolutionary movement of centromeres in horse, donkey, and zebra. Genomics 87:777–782
Cardinale S, Bergmann JH, Kelly D, Nakano M, Valdivia MM, Kimura H, Masumoto H, Larionov V, Earnshaw WC (2009) Hierarchical inactivation of a synthetic human kinetochore by a chromatin modifier. Mol Biol Cell 20:4194–4204
Catania S, Pidoux AL, Allshire RC (2015) Sequence features and transcriptional stalling within centromere DNA promote establishment of CENP-A chromatin. PLoS Genet 11:e1004986
Chan DYL, Moralli D, Khoja S, Monaco ZL (2017) Noncoding centromeric RNA expression impairs chromosome stability in human and murine stem cells. Dis Markers 2017:7506976
Chen CC, Dechassa ML, Bettini E, Ledoux MB, Belisario C, Heun P, Luger K, Mellone BG (2014) CAL1 is the Drosophila CENP-A assembly factor. J Cell Biol 204:313–329
Chikashige Y, Kinoshita N, Nakaseko Y, Matsumoto T, Murakami S, Niwa O, Yanagida M (1989) Composite motifs and repeat symmetry in S. pombe centromeres: direct analysis by integration of NotI restriction sites. Cell 57:739–751
Chmatal L, Gabriel SI, Mitsainas GP, Martinez-Vargas J, Ventura J, Searle JB, Schultz RM, Lampson MA (2014) Centromere strength provides the cell biological basis for meiotic drive and karyotype evolution in mice. Curr Biol 24:2295–2300
Choi ES, Stralfors A, Catania S, Castillo AG, Svensson JP, Pidoux AL, Ekwall K, Allshire RC (2012) Factors that promote H3 chromatin integrity during transcription prevent promiscuous deposition of CENP-A(Cnp1) in fission yeast. PLoS Genetics 8:e1002985
Collins KA, Furuyama S, Biggins S (2004) Proteolysis contributes to the exclusive centromere localization of the yeast Cse4/CENP-A histone H3 variant. Current Biology: CB 14:1968–1972
Contreras-Galindo R, Kaplan MH, He S, Contreras-Galindo AC, Gonzalez-Hernandez MJ, Kappes F, Dube D, Chan SM, Robinson D, Meng F, Dai M, Gitlin SD, Chinnaiyan AM, Omenn GS, Markovitz DM (2013) HIV infection reveals widespread expansion of novel centromeric human endogenous retroviruses. Genome Research 23:1505–1513
Copenhaver GP, Ketel C, Wang HSW, McClellan M, Bouchonville K, Selmecki A, Lahav T, Gerami-Nejad M, Berman J (2009) Neocentromeres form efficiently at multiple possible loci in Candida albicans. PLoS Genetics 5:e1000400
Cottarel G, Shero JH, Hieter P, Hegemann JH (1989) A 125-base-pair CEN6 DNA fragment is sufficient for complete meiotic and mitotic centromere functions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 9:3342–3349
Dawe RK, Lowry EG, Gent JI, Stitzer MC, Swentowsky KW, Higgins DM, Ross-Ibarra J, Wallace JG, Kanizay LB, Alabady M, Qiu W, Tseng KF, Wang N, Gao Z, Birchler JA, Harkess AE, Hodges AL, Hiatt EN (2018) A kinesin-14 motor activates neocentromeres to promote meiotic drive in maize. Cell 173:839–850 e818
De Lorenzi L, Iannuzzi A, Rossi E, Bonacina S, Parma P (2017) Centromere repositioning in cattle (Bos taurus) chromosome 17. Cytogenetic and Genome Res 151(4):191–197
de Wolf B, Kops G (2017) Kinetochore malfunction in human pathologies. Adv Exp Med Biol 1002:69–91
Deyter GM, Biggins S (2014) The FACT complex interacts with the E3 ubiquitin ligase Psh1 to prevent ectopic localization of CENP-A. Genes & Development 28:1815–1826
Drinnenberg IA, de Young D, Henikoff S, Malik HS (2014) Recurrent loss of CenH3 is associated with independent transitions to holocentricity in insects. Elife 3
Du Y, Topp CN, Dawe RK (2010) DNA binding of centromere protein C (CENPC) is stabilized by single-stranded RNA. PLoS Genet 6:e1000835
Dunleavy EM, Roche D, Tagami H, Lacoste N, Ray-Gallet D, Nakamura Y, Daigo Y, Nakatani Y, Almouzni-Pettinotti G (2009) HJURP is a cell-cycle-dependent maintenance and deposition factor of CENP-A at centromeres. Cell 137:485–497
Fachinetti D, Han JS, McMahon MA, Ly P, Abdullah A, Wong AJ, Cleveland DW (2015) DNA sequence-specific binding of CENP-B enhances the fidelity of human centromere function. Dev Cell 33:314–327
Farr C, Fantes J, Goodfellow P, Cooke H (1991) Functional reintroduction of human telomeres into mammalian cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 88:7006–7010
Farr CJ, Stevanovic M, Thomson EJ, Goodfellow PN, Cooke HJ (1992) Telomere-associated chromosome fragmentation: applications in genome manipulation and analysis. Nature Genetics 2:275–282
Ferreri GC, Liscinsky DM, Mack JA, Eldridge MD, O’Neill RJ (2005) Retention of latent centromeres in the mammalian genome. J Hered 96:217–224
Ferreri GC, Marzelli M, Rens W, O’Neill RJ (2004) A centromere-specific retroviral element associated with breaks of synteny in macropodine marsupials. Cytogenetic and Genome Research 107:115–118
Ferri F, Bouzinba-Segard H, Velasco G, Hube F, Francastel C (2009) Non-coding murine centromeric transcripts associate with and potentiate Aurora B kinase. Nucleic Acids Res 37:5071–5080
Folco HD, Pidoux AL, Urano T, Allshire RC (2008) Heterochromatin and RNAi are required to establish CENP-A chromatin at centromeres. Science 319:94–97
Foltz DR, Jansen LE, Bailey AO, Yates JR 3rd, Bassett EA, Wood S, Black BE, Cleveland DW (2009) Centromere-specific assembly of CENP-a nucleosomes is mediated by HJURP. Cell 137:472–484
Fukagawa T, Nogami M, Yoshikawa M, Ikeno M, Okazaki T, Takami Y, Nakayama T, Oshimura M (2004) Dicer is essential for formation of the heterochromatin structure in vertebrate cells. Nat Cell Biol 6:784–791
Gaeta RT, Masonbrink RE, Krishnaswamy L, Zhao C, Birchler JA (2012) Synthetic chromosome platforms in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 63:307–330
Gambogi CW, Black BE (2019) The nucleosomes that mark centromere location on chromosomes old and new. Essays Biochem 63:15–27
Garsed DW, Marshall OJ, Corbin VD, Hsu A, Di Stefano L, Schroder J, Li J, Feng ZP, Kim BW, Kowarsky M, Lansdell B, Brookwell R, Myklebost O, Meza-Zepeda L, Holloway AJ, Pedeutour F, Choo KH, Damore MA, Deans AJ, Papenfuss AT, Thomas DM (2014) The architecture and evolution of cancer neochromosomes. Cancer Cell 26:653–667
Gascoigne KE, Takeuchi K, Suzuki A, Hori T, Fukagawa T, Cheeseman IM (2011) Induced ectopic kinetochore assembly bypasses the requirement for CENP-A nucleosomes. Cell 145:410–422
Gassmann R, Rechtsteiner A, Yuen KW, Muroyama A, Egelhofer T, Gaydos L, Barron F, Maddox P, Essex A, Monen J, Ercan S, Lieb JD, Oegema K, Strome S, Desai A (2012) An inverse relationship to germline transcription defines centromeric chromatin in C. elegans. Nature 484:534–537
Giordano-Santini R, Milstein S, Svrzikapa N, Tu D, Johnsen R, Baillie D, Vidal M, Dupuy D (2010) An antibiotic selection marker for nematode transgenesis. Nature Methods 7:721–723
Gonzalez M, He H, Dong Q, Sun S, Li F (2014) Ectopic centromere nucleation by CENP—a in fission yeast. Genetics 198:1433–1446
Goodspeed A, Heiser LM, Gray JW, Costello JC (2016) Tumor-derived cell lines as molecular models of cancer pharmacogenomics. Mol Cancer Res 14:3–13
Grimes BR, Rhoades AA, Willard HF (2002) Alpha-satellite DNA and vector composition influence rates of human artificial chromosome formation. Mol Ther 5:798–805
Guo X, Su H, Shi Q, Fu S, Wang J, Zhang X, Hu Z, Han F (2016) De novo centromere formation and centromeric sequence expansion in wheat and its wide hybrids. PLoS Genetics 12:e1005997
Hahnenberger KM, Baum MP, Polizzi CM, Carbon J, Clarke L (1989) Construction of functional artificial minichromosomes in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 86:577–581
Han Y, Zhang Z, Liu C, Liu J, Huang S, Jiang J, Jin W (2009) Centromere repositioning in cucurbit species: implication of the genomic impact from centromere activation and inactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:14937–14941
Harrington JJ, Van Bokkelen G, Mays RW, Gustashaw K, Willard HF (1997) Formation of de novo centromeres and construction of first-generation human artificial microchromosomes. Nat Genet 15:345–355
Hasson D, Alonso A, Cheung F, Tepperberg JH, Papenhausen PR, Engelen JJ, Warburton PE (2011) Formation of novel CENP-A domains on tandem repetitive DNA and across chromosome breakpoints on human chromosome 8q21 neocentromeres. Chromosoma 120(6):621–632
Hayden KE, Strome ED, Merrett SL, Lee HR, Rudd MK, Willard HF (2013) Sequences associated with centromere competency in the human genome. Molecular and Cellular Biology 33:763–772
Hedouin S, Grillo G, Ivkovic I, Velasco G, Francastel C (2017) CENP-A chromatin disassembly in stressed and senescent murine cells. Sci Rep 7:42520
Helfricht A, Wiegant W, Thijssen P, Vertegaal A, Luijsterburg M, Van Attikum H (2013) Remodeling and spacing factor 1 (RSF1) deposits centromere proteins at DNA double-strand breaks to promote non-homologous end-joining. Cell Cycle 12:3070–3082
Henikoff S, Ahmad K, Malik HS (2001) The centromere paradox: stable inheritance with rapidly evolving DNA. Science 293:1098–1102
Heun P, Erhardt S, Blower MD, Weiss S, Skora AD, Karpen GH (2006) Mislocalization of the Drosophila centromere-specific histone CID promotes formation of functional ectopic kinetochores. Dev Cell 10:303–315
Hewawasam G, Shivaraju M, Mattingly M, Venkatesh S, Martin-Brown S, Florens L, Workman JL, Gerton JL (2010) Psh1 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that targets the centromeric histone variant Cse4. Molecular Cell 40:444–454
Hiatt EN, Kentner EK, Dawe RK (2002) Independently regulated neocentromere activity of two classes of tandem repeat arrays. Plant Cell 14:407–420
Hill A, Bloom K (1987) Genetic manipulation of centromere function. Mol Cell Biol 7:2397–2405
Hiratsuka M, Ueda K, Uno N, Uno K, Fukuhara S, Kurosaki H, Takehara S, Osaki M, Kazuki Y, Kurosawa Y, Nakamura T, Katoh M, Oshimura M (2015) Retargeting of microcell fusion towards recipient cell-oriented transfer of human artificial chromosome. BMC Biotechnol 15:58
Ho KH, Tsuchiya D, Oliger AC, Lacefield S (2014) Localization and function of budding yeast CENP-A depends upon kinetochore protein interactions and is independent of canonical centromere sequence. Cell Rep 9:2027–2033
Hori T, Shang WH, Takeuchi K, Fukagawa T (2013) The CCAN recruits CENP-A to the centromere and forms the structural core for kinetochore assembly. The Journal of Cell Biology 200:45–60
Houben A, Dawe RK, Jiang J, Schubert I (2008) Engineered plant minichromosomes: a bottom-up success? The Plant Cell 20:8–10
Ideue T, Cho Y, Nishimura K, Tani T (2014) Involvement of satellite I noncoding RNA in regulation of chromosome segregation. Genes Cells 19:528–538
Ishii K, Ogiyama Y, Chikashige Y, Soejima S, Masuda F, Kakuma T, Hiraoka Y, Takahashi K (2008) Heterochromatin integrity affects chromosome reorganization after centromere dysfunction. Science 321:1088–1091
Iwata-Otsubo A, Dawicki-McKenna JM, Akera T, Falk SJ, Chmatal L, Yang K, Sullivan BA, Schultz RM, Lampson MA, Black BE (2017) Expanded satellite repeats amplify a discrete CENP-A nucleosome assembly site on chromosomes that drive in female meiosis. Curr Biol 27:2365–2373 e2368
Jaco I, Canela A, Vera E, Blasco MA (2008) Centromere mitotic recombination in mammalian cells. Journal of Cell Biology 181:885–892
Jain M, Olsen HE, Turner DJ, Stoddart D, Bulazel KV, Paten B, Haussler D, Willard HF, Akeson M, Miga KH (2018) Linear assembly of a human centromere on the Y chromosome. Nat Biotechnol 36:321–323
Jansen LE, Black BE, Foltz DR, Cleveland DW (2007) Propagation of centromeric chromatin requires exit from mitosis. J Cell Biol 176:795–805
Jiang J, Birchler JA, Parrott WA, Dawe RK (2003) A molecular view of plant centromeres. Trends Plant Sci 8:570–575
Johnson WL, Yewdell WT, Bell JC, McNulty SM, Duda Z, O’Neill RJ, Sullivan BA, Straight AF (2017) RNA-dependent stabilization of SUV39H1 at constitutive heterochromatin. eLife 6
Jolly C, Metz A, Govin J, Vigneron M, Turner BM, Khochbin S, Vourc’h C (2004) Stress-induced transcription of satellite III repeats. J Cell Biol 164:25–33
Kagansky A, Folco HD, Almeida R, Pidoux AL, Boukaba A, Simmer F, Urano T, Hamilton GL, Allshire RC (2009) Synthetic heterochromatin bypasses RNAi and centromeric repeats to establish functional centromeres. Science 324:1716–1719
Kalitsis P, Choo KH (2012) The evolutionary life cycle of the resilient centromere. Chromosoma 121:327–340
Kanellopoulou C, Muljo SA, Kung AL, Ganesan S, Drapkin R, Jenuwein T, Livingston DM, Rajewsky K (2005) Dicer-deficient mouse embryonic stem cells are defective in differentiation and centromeric silencing. Genes Dev 19:489–501
Kanizay LB, Albert PS, Birchler JA, Dawe RK (2013) Intragenomic conflict between the two major knob repeats of maize. Genetics 194:81–89
Kapoor M, Montes de Oca Luna R, Liu G, Lozano G, Cummings C, Mancini M, Ouspenski I, Brinkley BR, May GS (1998) The cenpB gene is not essential in mice. Chromosoma 107:570–576
Kapusi E, Ma L, Teo CH, Hensel G, Himmelbach A, Schubert I, Mette MF, Kumlehn J, Houben A (2012) Telomere-mediated truncation of barley chromosomes. Chromosoma 121:181–190
Kasinathan S, Henikoff S (2018) Non-B-form DNA is enriched at centromeres. Molecular Biology and Evolution 35:949–962
Katoh M, Ayabe F, Norikane S, Okada T, Masumoto H, Horike S, Shirayoshi Y, Oshimura M (2004) Construction of a novel human artificial chromosome vector for gene delivery. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 321:280–290
Kattermann G (1939) Ein neuer Karyotyp bei Roggen. Zeitschrift für Zellforschung und Mikroskopische Anatomie Abt B Chromosoma 1:284–299
Kazuki Y, Oshimura M (2011) Human artificial chromosomes for gene delivery and the development of animal models. Mol Ther 19:1591–1601
Ketel C, Wang HS, McClellan M, Bouchonville K, Selmecki A, Lahav T, Gerami-Nejad M, Berman J (2009) Neocentromeres form efficiently at multiple possible loci in Candida albicans. PLoS Genet 5:e1000400
Kim JH, Kononenko A, Erliandri I, Kim TA, Nakano M, Iida Y, Barrett JC, Oshimura M, Masumoto H, Earnshaw WC, Larionov V, Kouprina N (2011) Human artificial chromosome (HAC) vector with a conditional centromere for correction of genetic deficiencies in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:20048–20053
Klein E, Rocchi M, Ovens-Raeder A, Kosyakova N, Weise A, Ziegler M, Meins M, Morlot S, Fischer W, Volleth M, Polityko A, Ogilvie CM, Kraus C, Liehr T (2012) Five novel locations of neocentromeres in human: 18q22.1, Xq27.1 approximately 27.2, Acro p13, Acro p12, and heterochromatin of unknown origin. Cytogenet Genome Res 136:163–166
Kobayashi T, Yamada F, Hashimoto T, Abe S, Matsuda Y, Kuroiwa A (2008) Centromere repositioning in the X chromosome of XO/XO mammals, Ryukyu spiny rat. Chromosome Res 16:587–593
Koo DH, Han F, Birchler JA, Jiang J (2011) Distinct DNA methylation patterns associated with active and inactive centromeres of the maize B chromosome. Genome Res 21:908–914
Lacoste N, Woolfe A, Tachiwana H, Garea AV, Barth T, Cantaloube S, Kurumizaka H, Imhof A, Almouzni G (2014) Mislocalization of the centromeric histone variant CenH3/CENP-A in human cells depends on the chaperone DAXX. Mol Cell 53:631–644
Lam AL, Boivin CD, Bonney CF, Rudd MK, Sullivan BA (2006) Human centromeric chromatin is a dynamic chromosomal domain that can spread over noncentromeric DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:4186–4191
Lampson MA, Black BE (2017) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of centromere drive. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 82:249–257
Lawrence KS, Chau T, Engebrecht J (2015) DNA damage response and spindle assembly checkpoint function throughout the cell cycle to ensure genomic integrity. PLoS Genet 11:e1005150
Lee BC, Lin Z, Yuen KW (2016) RbAp46/48(LIN-53) Is required for holocentromere assembly in Caenorhabditis elegans. Cell Rep 14:1819–1828
Lefrancois P, Auerbach RK, Yellman CM, Roeder GS, Snyder M (2013) Centromere-like regions in the budding yeast genome. PLoS Genet 9:e1003209
Ling YH, Yuen KWY (2019a) Centromeric non-coding RNA as a hidden epigenetic factor of the point centromere. Curr Genet 65(5):1165–1171
Ling YH, Yuen KWY (2019b) Point centromere activity requires an optimal level of centromeric noncoding RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116:6270–6279
Liskovykh M, Lee NC, Larionov V, Kouprina N (2016) Moving toward a higher efficiency of microcell-mediated chromosome transfer. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev 3:16043
Lo AW, Craig JM, Saffery R, Kalitsis P, Irvine DV, Earle E, Magliano DJ, Choo KH (2001) A 330 kb CENP-A binding domain and altered replication timing at a human neocentromere. EMBO J 20:2087–2096
Lo AW, Magliano DJ, Sibson MC, Kalitsis P, Craig JM, Choo KH (2001) A novel chromatin immunoprecipitation and array (CIA) analysis identifies a 460-kb CENP-A-binding neocentromere DNA. Genome Res 11:448–457
Logsdon GA, Barrey EJ, Bassett EA, DeNizio JE, Guo LY, Panchenko T, Dawicki-McKenna JM, Heun P, Black BE (2015) Both tails and the centromere targeting domain of CENP-A are required for centromere establishment. The Journal of Cell Biology 208:521–531
Logsdon GA, Gambogi CW, Liskovykh MA, Barrey EJ, Larionov V, Miga KH, Heun P, Black BE (2019) Human artificial chromosomes that bypass centromeric DNA. Cell 178:624–639 e619
Lorincz MC, Dickerson DR, Schmitt M, Groudine M (2004) Intragenic DNA methylation alters chromatin structure and elongation efficiency in mammalian cells. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11:1068–1075
Lu J, Gilbert DM (2007) Proliferation-dependent and cell cycle regulated transcription of mouse pericentric heterochromatin. J Cell Biol 179:411–421
Lyttle TW (1991) Segregation distorters. Annu Rev Genet 25:511–557
Macchia G, Nord KH, Zoli M, Purgato S, D’Addabbo P, Whelan CW, Carbone L, Perini G, Mertens F, Rocchi M, Storlazzi CT (2015) Ring chromosomes, breakpoint clusters, and neocentromeres in sarcomas. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 54:156–167
Macnab S, Whitehouse A (2009) Progress and prospects: human artificial chromosomes. Gene Ther 16:1180–1188
Maggert KA, Karpen GH (2001) The activation of a neocentromere in Drosophila requires proximity to an endogenous centromere. Genetics 158:1615–1628
Mahajan S, Wei KH, Nalley MJ, Gibilisco L, Bachtrog D (2018) De novo assembly of a young Drosophila Y chromosome using single-molecule sequencing and chromatin conformation capture. PLoS Biology 16:e2006348
Maison C, Bailly D, Peters AH, Quivy JP, Roche D, Taddei A, Lachner M, Jenuwein T, Almouzni G (2002) Higher-order structure in pericentric heterochromatin involves a distinct pattern of histone modification and an RNA component. Nature Genetics 30:329–334
Maison C, Bailly D, Roche D, Montes de Oca R, Probst AV, Vassias I, Dingli F, Lombard B, Loew D, Quivy JP, Almouzni G (2011) SUMOylation promotes de novo targeting of HP1alpha to pericentric heterochromatin. Nat Genet 43:220–227
Malik HS, Henikoff S (2009) Major evolutionary transitions in centromere complexity. Cell 138:1067–1082
Maloney KA, Sullivan LL, Matheny JE, Strome ED, Merrett SL, Ferris A, Sullivan BA (2012) Functional epialleles at an endogenous human centromere. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 109:13704–13709
Manzanero S, Puertas MJ (2003) Rye terminal neocentromeres: characterisation of the underlying DNA and chromatin structure. Chromosoma 111:408–415
Marshall OJ, Chueh AC, Wong LH, Choo KH (2008) Neocentromeres: new insights into centromere structure, disease development, and karyotype evolution. Am J Hum Genet 82:261–282
McClintock B (1939) The behavior in successive nuclear divisions of a chromosome broken at meiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 25:405–416
McClintock B (1941) The stability of broken ends of chromosomes in Zea mays. Genetics 26:234–282
McKinley KL, Cheeseman IM (2016) The molecular basis for centromere identity and function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 17:16–29
McNulty SM, Sullivan LL, Sullivan BA (2017) Human centromeres produce chromosome-specific and array-specific alpha satellite transcripts that are complexed with CENP-A and CENP-C. Developmental Cell 42:226–+
Mello CC, Kramer JM, Stinchcomb D, Ambros V (1991) Efficient gene transfer in C. elegans: extrachromosomal maintenance and integration of transforming sequences. EMBO J 10:3959–3970
Mellone BG, Grive KJ, Shteyn V, Bowers SR, Oderberg I, Karpen GH (2011) Assembly of Drosophila centromeric chromatin proteins during mitosis. PLoS Genetics 7:e1002068
Melters DP, Bradnam KR, Young HA, Telis N, May MR, Ruby JG, Sebra R, Peluso P, Eid J, Rank D, Garcia JF, Derisi JL, Smith T, Tobias C, Ross-Ibarra J, Korf I, Chan SW (2013) Comparative analysis of tandem repeats from hundreds of species reveals unique insights into centromere evolution. Genome Biol 14:R10
Meluh PB, Koshland D (1997) Budding yeast centromere composition and assembly as revealed by in vivo cross-linking. Genes Dev 11:3401–3412
Mendiburo MJ, Padeken J, Fulop S, Schepers A, Heun P (2011) Drosophila CENH3 is sufficient for centromere formation. Science 334:686–690
Meraldi P, McAinsh AD, Rheinbay E, Sorger PK (2006) Phylogenetic and structural analysis of centromeric DNA and kinetochore proteins. Genome Biol 7:R23
Mette MF, Houben A (2015) Engineering of plant chromosomes. Chromosome Res 23:69–76
Molina O, Vargiu G, Abad MA, Zhiteneva A, Jeyaprakash AA, Masumoto H, Kouprina N, Larionov V, Earnshaw WC (2016) Epigenetic engineering reveals a balance between histone modifications and transcription in kinetochore maintenance. Nat Commun 7:13334
Montefalcone G, Tempesta S, Rocchi M, Archidiacono N (1999) Centromere repositioning. Genome Res 9:1184–1188
Moreno-Moreno O, Torras-Llort M, Azorin F (2006) Proteolysis restricts localization of CID, the centromere-specific histone H3 variant of Drosophila, to centromeres. Nucleic Acids Research 34:6247–6255
Murchison EP, Partridge JF, Tam OH, Cheloufi S, Hannon GJ (2005) Characterization of Dicer-deficient murine embryonic stem cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 102:12135–12140
Murray AW, Schultes NP, Szostak JW (1986) Chromosome length controls mitotic chromosome segregation in yeast. Cell 45:529–536
Murray AW, Szostak JW (1983) Construction of artificial chromosomes in yeast. Nature 305:189–193
Nagaki K, Cheng Z, Ouyang S, Talbert PB, Kim M, Jones KM, Henikoff S, Buell CR, Jiang J (2004) Sequencing of a rice centromere uncovers active genes. Nature Genetics 36:138–145
Nagaki K, Neumann P, Zhang D, Ouyang S, Buell CR, Cheng Z, Jiang J (2005) Structure, divergence, and distribution of the CRR centromeric retrotransposon family in rice. Mol Biol Evol 22: 845–855
Nakano M, Cardinale S, Noskov VN, Gassmann R, Vagnarelli P, Kandels-Lewis S, Larionov V, Earnshaw WC, Masumoto H (2008) Inactivation of a human kinetochore by specific targeting of chromatin modifiers. Dev Cell 14:507–522
Nakano M, Okamoto Y, Ohzeki J, Masumoto H (2003) Epigenetic assembly of centromeric chromatin at ectopic alpha-satellite sites on human chromosomes. J Cell Sci 116:4021–4034
Nakaseko Y, Adachi Y, Funahashi S, Niwa O, Yanagida M (1986) Chromosome walking shows a highly homologous repetitive sequence present in all the centromere regions of fission yeast. EMBO J 5:1011–1021
Nakashima H, Nakano M, Ohnishi R, Hiraoka Y, Kaneda Y, Sugino A, Masumoto H (2005) Assembly of additional heterochromatin distinct from centromere-kinetochore chromatin is required for de novo formation of human artificial chromosome. Journal of Cell Science 118:5885–5898
Nechemia-Arbely Y, Miga KH, Shoshani O, Aslanian A, McMahon MA, Lee AY, Fachinetti D, Yates JR 3rd, Ren B, Cleveland DW (2019) DNA replication acts as an error correction mechanism to maintain centromere identity by restricting CENP-A to centromeres. Nature Cell Biology 21:743–754
Nelson AD, Lamb JC, Kobrossly PS, Shippen DE (2011) Parameters affecting telomere-mediated chromosomal truncation in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell 23:2263–2272
Nergadze SG, Piras FM, Gamba R, Corbo M, Cerutti F, McCarter JGW, Cappelletti E, Gozzo F, Harman RM, Antczak DF, Miller D, Scharfe M, Pavesi G, Raimondi E, Sullivan KF, Giulotto E (2018) Birth, evolution, and transmission of satellite-free mammalian centromeric domains. Genome Res 28:789–799
Nonaka N, Kitajima T, Yokobayashi S, Xiao G, Yamamoto M, Grewal SI, Watanabe Y (2002) Recruitment of cohesin to heterochromatic regions by Swi6/HP1 in fission yeast. Nat Cell Biol 4:89–93
Nye J, Sturgill D, Athwal R, Dalal Y (2018) HJURP antagonizes CENP-A mislocalization driven by the H3.3 chaperones HIRA and DAXX. PLoS One 13:e0205948
Ohkuni K, Kitagawa K (2012) Role of transcription at centromeres in budding yeast. Transcription 3:193–197
Ohkuni K, Takahashi Y, Fulp A, Lawrimore J, Au WC, Pasupala N, Levy-Myers R, Warren J, Strunnikov A, Baker RE, Kerscher O, Bloom K, Basrai MA (2016) SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligase (STUbL) Slx5 regulates proteolysis of centromeric histone H3 variant Cse4 and prevents its mislocalization to euchromatin. Mol Biol Cell
Ohzeki J, Bergmann JH, Kouprina N, Noskov VN, Nakano M, Kimura H, Earnshaw WC, Larionov V, Masumoto H (2012) Breaking the HAC barrier: histone H3K9 acetyl/methyl balance regulates CENP-A assembly. EMBO J 31:2391–2402
Ohzeki J, Larionov V, Earnshaw WC, Masumoto H (2015) Genetic and epigenetic regulation of centromeres: a look at HAC formation. Chromosome Research: an International Journal on the Molecular, Supramolecular and Evolutionary Aspects of Chromosome Biology 23:87–103
Ohzeki J, Nakano M, Okada T, Masumoto H (2002) CENP-B box is required for de novo centromere chromatin assembly on human alphoid DNA. J Cell Biol 159:765–775
Okada T, Ohzeki J, Nakano M, Yoda K, Brinkley WR, Larionov V, Masumoto H (2007) CENP-B controls centromere formation depending on the chromatin context. Cell 131:1287–1300
Okamoto Y, Nakano M, Ohzeki J, Larionov V, Masumoto H (2007) A minimal CENP-A core is required for nucleation and maintenance of a functional human centromere. EMBO J 26:1279–1291
Olszak AM, van Essen D, Pereira AJ, Diehl S, Manke T, Maiato H, Saccani S, Heun P (2011) Heterochromatin boundaries are hotspots for de novo kinetochore formation. Nat Cell Biol 13:799–808
Papenfuss AT, Thomas DM (2015) The life history of neochromosomes revealed. Mol Cell Oncol 2:e1000698
Partridge JF, Borgstrom B, Allshire RC (2000) Distinct protein interaction domains and protein spreading in a complex centromere. Genes Dev 14:783–791
Peacock WJ, Dennis ES, Rhoades MM, Pryor AJ (1981) Highly repeated DNA sequence limited to knob heterochromatin in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 78:4490–4494
Piras FM, Nergadze SG, Poletto V, Cerutti F, Ryder OA, Leeb T, Raimondi E, Giulotto E (2009) Phylogeny of horse chromosome 5q in the genus Equus and centromere repositioning. Cytogenet Genome Res 126:165–172
Ranjitkar P, Press MO, Yi X, Baker R, MacCoss MJ, Biggins S (2010) An E3 ubiquitin ligase prevents ectopic localization of the centromeric histone H3 variant via the centromere targeting domain. Mol Cell 40:455–464
Ren X, Katoh M, Hoshiya H, Kurimasa A, Inoue T, Ayabe F, Shibata K, Toguchida J, Oshimura M (2005) A novel human artificial chromosome vector provides effective cell lineage-specific transgene expression in human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells 23:1608–1616
Rhoades MM (1942) Preferential segregation in maize. Genetics 27:395–407
Rocchi M, Archidiacono N (2006) Genome plasticity in evolution. In: Lupski JR, Stankiewicz P (eds) Genomic disorders: the genomic basis of disease. Humana, Totowa, pp 153–165
Rocchi M, Archidiacono N, Schempp W, Capozzi O, Stanyon R (2012) Centromere repositioning in mammals. Heredity (Edinb) 108:59–67
Roure V, Medina-Pritchard B, Anselm E, Jeyaprakash AA, Heun P (2019) Epigenetic inheritance of centromere identity in a heterologous system. biorxiv
Rudert F, Bronner S, Garnier JM, Dolle P (1995) Transcripts from opposite strands of gamma satellite DNA are differentially expressed during mouse development. Mamm Genome 6:76–83
Saffery R, Sumer H, Hassan S, Wong LH, Craig JM, Todokoro K, Anderson M, Stafford A, Choo KH (2003) Transcription within a functional human centromere. Mol Cell 12:509–516
Saksouk N, Simboeck E, Dejardin J (2015) Constitutive heterochromatin formation and transcription in mammals. Epigenetics Chromatin 8:3
Sandler L, Novitski E (1957) Meiotic drive as an evolutionary force. The American Naturalist 91:105–110
Schaefer H, Heibl C, Renner SS (2009) Gourds afloat: a dated phylogeny reveals an Asian origin of the gourd family (Cucurbitaceae) and numerous oversea dispersal events. Proc Biol Sci 276:843–851
Schneider KL, Xie Z, Wolfgruber TK, Presting GG (2016) Inbreeding drives maize centromere evolution. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 113:E987–E996
Schubert I (2018) What is behind “centromere repositioning”? Chromosoma 127:229–234
Semple JI, Garcia-Verdugo R, Lehner B (2010) Rapid selection of transgenic C. elegans using antibiotic resistance. Nature Methods 7:725–727
Shang WH, H, Ori T, Martins NM, Toyoda A, Misu S, Monma N, Hiratani I, Maeshima K, Ikeo K, Fujiyama A, Kimura H, Earnshaw WC, Fukagawa T (2013) Chromosome engineering allows the efficient isolation of vertebrate neocentromeres. Dev Cell 24:635–648
Shang WH, Hori T, Martins NM, Toyoda A, Misu S, Monma N, Hiratani I, Maeshima K, Ikeo K, Fujiyama A, Kimura H, Earnshaw WC, Fukagawa T (2013) Chromosome engineering allows the efficient isolation of vertebrate neocentromeres. Dev Cell 24:635–648
Sharma S (2011) Non-B DNA secondary structures and their resolution by RecQ helicases. Journal of Nucleic Acids 2011:Article ID 724215 15 pages
Sharma AB, Dimitrov S, Hamiche A, Van Dyck E (2019) Centromeric and ectopic assembly of CENP-A chromatin in health and cancer: old marks and new tracks. Nucleic Acids Research 47:1051–1069
Sharma A, Wolfgruber TK, Presting GG (2013) Tandem repeats derived from centromeric retrotransposons. BMC Genomics 14:142
Shelby RD, Monier K, Sullivan KF (2000) Chromatin assembly at kinetochores is uncoupled from DNA replication. The Journal of Cell Biology 151:1113–1118
Shrestha RL, Ahn GS, Staples MI, Sathyan KM, Karpova TS, Foltz DR, Basrai MA (2017) Mislocalization of centromeric histone H3 variant CENP-A contributes to chromosomal instability (CIN) in human cells. Oncotarget 8:46781–46800
Shukla M, Tong P, White SA, Singh PP, Reid AM, Catania S, Pidoux AL, Allshire RC (2018) Centromere DNA destabilizes H3 nucleosomes to promote CENP-A deposition during the cell cycle. Current Biology: CB 28:3924–3936 e3924
Sirvent N, Forus A, Lescaut W, Burel F, Benzaken S, Chazal M, Bourgeon A, Vermeesch JR, Myklebost O, Turc-Carel C, Ayraud N, Coindre JM, Pedeutour F (2000) Characterization of centromere alterations in liposarcomas. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 29:117–129
Steiner FA, Henikoff S (2014) Holocentromeres are dispersed point centromeres localized at transcription factor hotspots. Elife 3:e02025
Stimpson KM, Sullivan BA (2011) Histone H3K4 methylation keeps centromeres open for business. EMBO J 30:233–234
Stinchcomb DT, Shaw JE, Carr SH, Hirsh D (1985) Extrachromosomal DNA transformation of Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Cell Biol 5:3484–3496
Stirzaker C, Song JZ, Davidson B, Clark SJ (2004) Transcriptional gene silencing promotes DNA hypermethylation through a sequential change in chromatin modifications in cancer cells. Cancer Res 64:3871–3877
Sullivan LL, Maloney KA, Towers AJ, Gregory SG, Sullivan BA (2016) Human centromere repositioning within euchromatin after partial chromosome deletion. Chromosome Research: an International Journal on the Molecular, Supramolecular and Evolutionary Aspects of Chromosome Biology 24:451–466
Suzuki T, Kazuki Y, Oshimura M, Hara T (2016) Highly efficient transfer of chromosomes to a broad range of target cells using Chinese hamster ovary cells expressing murine leukemia virus-derived envelope proteins. PLoS One 11:e0157187
Teo CH, Ma L, Kapusi E, Hensel G, Kumlehn J, Schubert I, Houben A, Mette MF (2011) Induction of telomere-mediated chromosomal truncation and stability of truncated chromosomes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 68:28–39
Thakur J, Sanyal K (2013) Efficient neocentromere formation is suppressed by gene conversion to maintain centromere function at native physical chromosomal loci in Candida albicans. Genome Res 23:638–652
Tomonaga T, Matsushita K, Yamaguchi S, Oohashi T, Shimada H, Ochiai T, Yoda K, Nomura F (2003) Overexpression and mistargeting of centromere protein-A in human primary colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 63:3511–3516
Tong P, Pidoux AL, Toda NRT, Ard R, Berger H, Shukla M, Torres-Garcia J, Muller CA, Nieduszynski CA, Allshire RC (2019) Interspecies conservation of organisation and function between nonhomologous regional centromeres. Nat Commun 10:2343
Tsukahara S, Kawabe A, Kobayashi A, Ito T, Aizu T, Shin-i T, Toyoda A, Fujiyama A, Tarutani Y, Kakutani T (2012) Centromere-targeted de novo integrations of an LTR retrotransposon of Arabidopsis lyrata. Genes Dev 26:705–713
Valgardsdottir R, Chiodi I, Giordano M, Rossi A, Bazzini S, Ghigna C, Riva S, Biamonti G (2008) Transcription of Satellite III non-coding RNAs is a general stress response in human cells. Nucleic Acids Res 36:423–434
Van Hooser AA, Ouspenski II, Gregson HC, Starr DA, Yen TJ, Goldberg ML, Yokomori K, Earnshaw WC, Sullivan KF, Brinkley BR (2001) Specification of kinetochore-forming chromatin by the histone H3 variant CENP-A. J Cell Sci 114:3529–3542
Ventura M, Antonacci F, Cardone MF, Stanyon R, D’Addabbo P, Cellamare A, Sprague LJ, Eichler EE, Archidiacono N, Rocchi M (2007) Evolutionary formation of new centromeres in macaque. Science 316:243–246
Verdel A, Jia S, Gerber S, Sugiyama T, Gygi S, Grewal SI, Moazed D (2004) RNAi-mediated targeting of heterochromatin by the RITS complex. Science 303:672–676
Villasante A, Abad JP, Mendez-Lago M (2007) Centromeres were derived from telomeres during the evolution of the eukaryotic chromosome. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 104:10542–10547
Villasante A, Mendez-Lago M, Abad JP, Montejo de Garcini E (2007) The birth of the centromere. Cell Cycle 6:2872–2876
Voullaire LE, Slater HR, Petrovic V, Choo KH (1993) A functional marker centromere with no detectable alpha-satellite, satellite III, or CENP-B protein: activation of a latent centromere? Am J Hum Genet 52:1153–1163
Wade CM, Giulotto E, Sigurdsson S, Zoli M, Gnerre S, Imsland F, Lear TL, Adelson DL, Bailey E, Bellone RR, Blocker H, Distl O, Edgar RC, Garber M, Leeb T, Mauceli E, MacLeod JN, Penedo MC, Raison JM, Sharpe T, Vogel J, Andersson L, Antczak DF, Biagi T, Binns MM, Chowdhary BP, Coleman SJ, Della Valle G, Fryc S, Guerin G, Hasegawa T, Hill EW, Jurka J, Kiialainen A, Lindgren G, Liu J, Magnani E, Mickelson JR, Murray J, Nergadze SG, Onofrio R, Pedroni S, Piras MF, Raudsepp T, Rocchi M, Roed KH, Ryder OA, Searle S, Skow L, Swinburne JE, Syvanen AC, Tozaki T, Valberg SJ, Vaudin M, White JR, Zody MC, Broad Institute Genome Sequencing P, Broad Institute Whole Genome Assembly T, Lander ES, Lindblad-Toh K (2009) Genome sequence, comparative analysis, and population genetics of the domestic horse. Science 326:865–867
Wang K, Wu Y, Zhang W, Dawe RK, Jiang J (2014) Maize centromeres expand and adopt a uniform size in the genetic background of oat. Genome Research 24:107–116
Warburton PE, Dolled M, Mahmood R, Alonso A, Li S, Naritomi K, Tohma T, Nagai T, Hasegawa T, Ohashi H, Govaerts LC, Eussen BH, Van Hemel JO, Lozzio C, Schwartz S, Dowhanick-Morrissette JJ, Spinner NB, Rivera H, Crolla JA, Yu C, Warburton D (2000) Molecular cytogenetic analysis of eight inversion duplications of human chromosome 13q that each contain a neocentromere. Am J Hum Genet 66:1794–1806
Waye JS, Willard HF (1987) Nucleotide sequence heterogeneity of alpha satellite repetitive DNA: a survey of alphoid sequences from different human chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res 15:7549–7569
Willard HF, Waye JS (1987) Chromosome-specific subsets of human alpha satellite DNA: analysis of sequence divergence within and between chromosomal subsets and evidence for an ancestral pentameric repeat. J Mol Evol 25:207–214
Williams BC, Murphy TD, Goldberg ML, Karpen GH (1998) Neocentromere activity of structurally acentric mini-chromosomes in Drosophila. Nat Genet 18:30–37
Wolfgruber TK, Sharma A, Schneider KL, Albert PS, Koo DH, Shi J, Gao Z, Han F, Lee H, Xu R, Allison J, Birchler JA, Jiang J, Dawe RK, Presting GG (2009) Maize centromere structure and evolution: sequence analysis of centromeres 2 and 5 reveals dynamic Loci shaped primarily by retrotransposons. PLoS Genet 5: e1000743
Wong LH, Choo KH (2001) Centromere on the move. Genome Res 11:513–516
Wong NC, Wong LH, Quach JM, Canham P, Craig JM, Song JZ, Clark SJ, Choo KH (2006) Permissive transcriptional activity at the centromere through pockets of DNA hypomethylation. PLoS Genet 2:e17
Wu JC, Manuelidis L (1980) Sequence definition and organization of a human repeated DNA. J Mol Biol 142:363–386
Xu C, Cheng Z, Yu W (2012) Construction of rice mini-chromosomes by telomere-mediated chromosomal truncation. Plant J 70:1070–1079
Yan X, Li C, Yang J, Wang L, Jiang C, Wei W (2017) Induction of telomere-mediated chromosomal truncation and behavior of truncated chromosomes in Brassica napus. Plant J 91:700–713
Yang L, Koo DH, Li D, Zhang T, Jiang J, Luan F, Renner SS, Henaff E, Sanseverino W, Garcia-Mas J, Casacuberta J, Senalik DA, Simon PW, Chen J, Weng Y (2014) Next-generation sequencing, FISH mapping and synteny-based modeling reveal mechanisms of decreasing dysploidy in Cucumis. Plant J 77:16–30
Yang JW, Pendon C, Yang J, Haywood N, Chand A, Brown WR (2000) Human mini-chromosomes with minimal centromeres. Human Molecular Genetics 9:1891–1902
Yu W, Han F, Gao Z, Vega JM, Birchler JA (2007) Construction and behavior of engineered minichromosomes in maize. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 104:8924–8929
Yu HG, Hiatt EN, Chan A, Sweeney M, Dawe RK (1997) Neocentromere-mediated chromosome movement in maize. J Cell Biol 139:831–840
Yu W, Lamb JC, Han F, Birchler JA (2006) Telomere-mediated chromosomal truncation in maize. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 103:17331–17336
Yu Z, Zhou X, Wang W, Deng W, Fang J, Hu H, Wang Z, Li S, Cui L, Shen J, Zhai L, Peng S, Wong J, Dong S, Yuan Z, Ou G, Zhang X, Xu P, Lou J, Yang N, Chen P, Xu RM, Li G (2015) Dynamic phosphorylation of CENP-A at Ser68 orchestrates its cell-cycle-dependent deposition at centromeres. Dev Cell 32:68–81
Yuan J, Shi Q, Guo X, Liu Y, Su H, Guo X, Lv Z, Han F (2017) Site-specific transfer of chromosomal segments and genes in wheat engineered chromosomes. J Genet Genomics 44:531–539
Yuen KW, Nabeshima K, Oegema K, Desai A (2011) Rapid de novo centromere formation occurs independently of heterochromatin protein 1 in C. elegans embryos. Curr Biol 21:1800–1807
Zahn J, Kaplan MH, Fischer S, Dai M, Meng F, Saha AK, Cervantes P, Chan SM, Dube D, Omenn GS, Markovitz DM, Contreras-Galindo R (2015) Expansion of a novel endogenous retrovirus throughout the pericentromeres of modern humans. Genome Biology 16:74
Zeitlin SG, Baker NM, Chapados BR, Soutoglou E, Wang JY, Berns MW, Cleveland DW (2009) Double-strand DNA breaks recruit the centromeric histone CENP-A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:15762–15767
Zeng K, de las Heras JI, Ross A, Yang J, Cooke H, Shen MH (2004) Localisation of centromeric proteins to a fraction of mouse minor satellite DNA on a mini-chromosome in human, mouse and chicken cells. Chromosoma 113:84–91
Zhang W, Mao JH, Zhu W, Jain AK, Liu K, Brown JB, Karpen GH (2016) Centromere and kinetochore gene misexpression predicts cancer patient survival and response to radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Nat Commun 7:12619
Zhang K, Mosch K, Fischle W, Grewal SI (2008) Roles of the Clr4 methyltransferase complex in nucleation, spreading and maintenance of heterochromatin. Nat Struct Mol Biol 15:381–388
Zhu J, Cheng KCL, Yuen KWY (2018) Histone H3K9 and H4 acetylations and transcription facilitate the initial CENP-A(HCP-3) deposition and de novo centromere establishment in Caenorhabditis elegans artificial chromosomes. Epigenetics Chromatin 11:16
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ling, Y.H., Lin, Z. & Yuen, K.W.Y. Genetic and epigenetic effects on centromere establishment. Chromosoma 129, 1–24 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-019-00727-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-019-00727-3