Abstract
Purpose
The association between serum zinc level and overweight/obesity remains controversial. Hence, we performed a meta-analysis to summarize the relationships.
Methods
A systematic literature search was performed in PubMed, Web of Science and Embase for relevant English articles up to April 20, 2018. The pooled standardized mean difference (SMD) with 95% confidence interval (CI) was calculated with the random-effect model.
Results
For children and adults, the results showed that serum zinc level was significantly lower in the cases compared to controls ([SMD (95% CI): − 1.13 (− 2.03, − 0.23), Z = 2.45, P for Z = 0.014; I2 = 97.1%, P for I2 < 0.001] and [SMD (95% CI): − 0.41 (− 0.68, − 0.15), Z = 3.03, P for Z = 0.002; I2 = 62.9%, P for I2 = 0.009], respectively). The difference of serum zinc level between overweight adults and controls was not statistically significant [SMD (95% CI): − 0.09 (− 0.27, 0.09), Z = 0.97, P for Z = 0.334; I2 = 0.0%, P for I2 = 0.411]. In subgroup analyses, a lower serum zinc level in obese children compared with non-obese controls was observed [SMD (95% CI): − 2.14 (− 3.20, − 1.09)], and the SMD differ significantly between obese adults and controls in the case–control studies [SMD (95% CI): − 0.49 (− 0.90, − 0.08)].
Conclusion
Our meta-analysis suggested that the serum zinc level was significantly lower in obese children and adults. More large observational studies are required to confirm these results in future research.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tang L, Ye H, Hong Q, Chen F, Wang Q, Xu L, Bu S, Liu Q, Ye M, Wang DW, Mai Y, Duan S (2014) Meta-analyses between 18 candidate genetic markers and overweight/obesity. Diagn Pathol 9:56. https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-1596-9-56
Fan Y, Zhang CL, Bu J (2017) Relationship between selected serum metallic elements and obesity in children and adolescent in the US. Nutrients 9 (2):104. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9020104
Qin Q, Xu X, Wang X, Zheng XY (2013) Obesity and risk of bladder cancer: a meta-analysis of cohort studies. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 14(5):3117–3121
Li JS, Han TJ, Jing N, Li L, Zhang XH, Ma FZ, Liu JY (2014) Obesity and the risk of cholangiocarcinoma: a meta-analysis. Tumour Biol 35(7):6831–6838. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1939-4
Zhang Y, Liu H, Yang S, Zhang J, Qian L, Chen X (2014) Overweight, obesity and endometrial cancer risk: results from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Biol Markers 29(1):e21–e29. https://doi.org/10.5301/jbm.5000047
WHO (2018) Obesity and overweight. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/zh/. Accessed 9 Sep 2018
Kim TJ, von dem Knesebeck O (2018) Income and obesity: what is the direction of the relationship? A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 8(1):e019862. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2017-019862
Pereira-Santos M, Costa PR, Assis AM, Santos CA, Santos DB (2015) Obesity and vitamin D deficiency: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev 16(4):341–349. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12239
Grundy SM (1998) Multifactorial causation of obesity: implications for prevention. Am J Clin Nutr 67 (3 Suppl):563 s-572 s. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/67.3.563S
Mytton OT, Nnoaham K, Eyles H, Scarborough P, Ni Mhurchu C (2014) Systematic review and meta-analysis of the effect of increased vegetable and fruit consumption on body weight and energy intake. BMC Public Health 14:886. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-14-886
Rouhani MH, Salehi-Abargouei A, Surkan PJ, Azadbakht L (2014) Is there a relationship between red or processed meat intake and obesity? A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Obes Rev 15(9):740–748. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12172
Habib SA, Saad EA, Elsharkawy AA, Attia ZR (2015) Pro-inflammatory adipocytokines, oxidative stress, insulin, Zn and Cu: interrelations with obesity in Egyptian non-diabetic obese children and adolescents. Adv Med Sci 60(2):179–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advms.2015.02.002
Zavala G, Long KZ, Garcia OP, Caamano Mdel C, Aguilar T, Salgado LM, Rosado JL (2013) Specific micronutrient concentrations are associated with inflammatory cytokines in a rural population of Mexican women with a high prevalence of obesity. Br J Nutr 109(4):686–694. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0007114512001912
Cayir Y, Cayir A, Turan MI, Kurt N, Kara M, Laloglu E, Ciftel M, Yildirim A (2014) Antioxidant status in blood of obese children: the relation between trace elements, paraoxonase, and arylesterase values. Biol Trace Elem Res 160(2):155–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-0038-0
Olza J, Aranceta-Bartrina J, Gonzalez-Gross M, Ortega RM, Serra-Majem L, Varela-Moreiras G, Gil A (2017) Reported Dietary Intake And Food Sources Of Zinc, Selenium, And Vitamins A, E and C in the Spanish population: findings from the ANIBES Study. Nutrients 9 (7):E697. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9070697
Kim HN, Song SW, Choi WS (2017) Association between serum zinc level and body composition: the Korean national health and nutrition examination survey. J Nutr Nutr 10(3–4):107. https://doi.org/10.1159/000480052
Feitosa MCP, Lima VBD, Neto JMM, Marreiro DD (2013) Plasma concentration of IL-6 and TNF-alpha and its relationship with zincemia in obese women. Rev Assoc Med Bras 59(5):429–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ramb.2013.03.003
Ghayour-Mobarhan M, Taylor A, New SA, Lamb DJ, Ferns GA (2005) Determinants of serum copper, zinc and selenium in healthy subjects. Ann Clin Biochem 42(Pt 5):364–375. https://doi.org/10.1258/0004563054889990
Mota Martins L, Soares de Oliveira AR, Climaco Cruz KJ, Borges de Araujo CG, de Oliveira FE, Marreiro D de Sousa GS, do Nogueira NN (2014) Influence of cortisol on zinc metabolism in morbidly obese women. Nutr Hosp 29(1):57–63. https://doi.org/10.3305/nh.2014.29.1.6890
Suliburska J, Cofta S, Gajewska E, Kalmus G, Sobieska M, Samborski W, Krejpcio Z, Drzymala-Czyz S, Bogdanski P (2013) The evaluation of selected serum mineral concentrations and their association with insulin resistance in obese adolescents. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 17(17):2396–2400
Marreiro DN, Fisberg M, Cozzolino SM (2004) Zinc nutritional status and its relationships with hyperinsulinemia in obese children and adolescents. Biol Trace Elem Res 100(2):137–149
Perrone L, Gialanella G, Moro R, Feng SL, Boccia E, Palombo G, Carbone MT, Di Toro R (1998) Zinc, copper and iron in obese children and adolescents. Nutr Res 18(2):183–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0271-5317(98)00011-6
Azab SF, Saleh SH, Elsaeed WF, Elshafie MA, Sherief LM, Esh AM (2014) Serum trace elements in obese Egyptian children: a case-control study. Ital J Pediatr 40:20. https://doi.org/10.1186/1824-7288-40-20
Yerlikaya FH, Toker A, Aribas A (2013) Serum trace elements in obese women with or without diabetes. Indian J Med Res 137(2):339–345
Yakinci C, Pac A, Kucukbay FZ, Tayfun M, Gul A (1997) Serum zinc, copper, and magnesium levels in obese children. Acta Paediatr Jpn 39(3):339–341
Marotta A, Todisco N, Ditoro A, Toraldo R, Ponte G, Perrone L (1995) Zinc content of lymphomonocytes in obese children. Nutr Res 15(10):1411–1415. https://doi.org/10.1016/0271-5317(95)02013-l
Herter-Aeberli I, Thankachan P, Bose B, Kurpad AV (2016) Increased risk of iron deficiency and reduced iron absorption but no difference in zinc, vitamin A or B-vitamin status in obese women in India. Eur J Nutr 55(8):2411–2421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-015-1048-1
Tascilar ME, Ozgen IT, Abaci A, Serdar M, Aykut O (2011) Serum trace elements in obese Egyptian children: a case-control study. Biol Trace Elem Res 143(1):188–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8878-8
Bouglé DL, Bureau F, Laroche D (2009) Trace element status in obese children: relationship with metabolic risk factors. e-SPEN 4(2):e98–e100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclnm.2009.01.012
Dambal SS (2011) Relationship of obesity with micronutrient status IJABPT 2(1):280–284
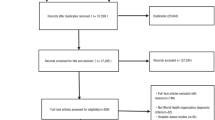
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2010) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Int J Surg 8(5):336–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2010.02.007
Young DS (1990) Implementation of SI units for clinical laboratory data: style specifications and conversion tables. J Nutr Biochem 1(11):599–613
Tobias A (1999) Assessing the influence of a single study in the meta-analysis estimate. Stata Tech Bull 8:7526–7529
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315(7109):629–634
King JC (1990) Assessment of zinc status. J Nutr 11 (120 Suppl):1474–1479. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/120.suppl_11.1474
Alikasifoglu A, Gonc N, Ozon ZA, Sen Y, Kandemir N (2009) The relationship between serum adiponectin, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, leptin levels and insulin sensitivity in childhood and adolescent obesity: adiponectin is a marker of metabolic syndrome. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 1(5):233–239. https://doi.org/10.4274/jcrpe.v1i5.233
Egefjord L, Jensen JL, Bang-Berthelsen CH, Petersen AB, Smidt K, Schmitz O, Karlsen AE, Pociot F, Chimienti F, Rungby J, Magnusson NE (2009) Zinc transporter gene expression is regulated by pro-inflammatory cytokines: a potential role for zinc transporters in beta-cell apoptosis? BMC Endocr Disord 9:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6823-9-7
Iuliano L (2011) Pathways of cholesterol oxidation via non-enzymatic mechanisms. Chem Phys Lipids 164(6):457–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2011.06.006
Mantzoros CS, Prasad AS, Beck FW, Grabowski S, Kaplan J, Adair C, Brewer GJ (1998) Zinc may regulate serum leptin concentrations in humans. J Am Coll Nutr 17(3):270–275
Garcia OP, Ronquillo D, Caamano Mdel C, Camacho M, Long KZ, Rosado JL (2012) Zinc, vitamin A, and vitamin C status are associated with leptin concentrations and obesity in Mexican women: results from a cross-sectional study. Nutr Metab (Lond) 9(1):59. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-7075-9-59
Crujeiras AB, Carreira MC, Cabia B, Andrade S, Amil M, Casanueva FF (2015) Leptin resistance in obesity: An epigenetic landscape. Life Sci 140:57–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2015.05.003
Sainz N, Gonzalez-Navarro CJ, Martinez JA, Moreno-Aliaga MJ (2015) Leptin signaling as a therapeutic target of obesity. Expert Opin Ther Targets 19(7):893–909. https://doi.org/10.1517/14728222.2015.1018824
Jung CH, Kim MS (2013) Molecular mechanisms of central leptin resistance in obesity. Arch Pharm Res 36(2):201–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0020-y
Myers MG Jr, Leibel RL, Seeley RJ, Schwartz MW (2010) Obesity and leptin resistance: distinguishing cause from effect. Trends Endocrinol Metab 21(11):643–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2010.08.002
Shintani M, Ogawa Y, Ebihara K, Aizawa-Abe M, Miyanaga F, Takaya K, Hayashi T, Inoue G, Hosoda K, Kojima M, Kangawa K, Nakao K (2001) Ghrelin, an endogenous growth hormone secretagogue, is a novel orexigenic peptide that antagonizes leptin action through the activation of hypothalamic neuropeptide Y/Y1 receptor pathway. Diabetes 50(2):227–232
Stofkova A (2009) Leptin and adiponectin: from energy and metabolic dysbalance to inflammation and autoimmunity. Endocr Regul 43(4):157–168
Popko K, Gorska E, Stelmaszczyk-Emmel A, Plywaczewski R, Stoklosa A, Gorecka D, Pyrzak B, Demkow U (2010) Proinflammatory cytokines Il-6 and TNF-alpha and the development of inflammation in obese subjects. Eur J Med Res 15(Suppl 2):120–122
Wu Y, Sun JT, Wang MS, Yu GX, Yu LP, Wang CH (2018) The relationship of children’s intelligence quotient and blood lead and zinc levels: a meta-analysis and system review. Biol Trace Elem Res 182(2):185–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1093-0
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Provincial Natural Science Foundation of the Province of Shandong (< Grant number ZR2015HM029> [to < XJ >]).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, K., Xiang, W., Zhang, Y. et al. The association between serum zinc level and overweight/obesity: a meta-analysis. Eur J Nutr 58, 2971–2982 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-018-1876-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-018-1876-x