Abstract
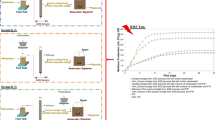
Knowledge of connections between operational conditions, process stability, and microbial community dynamics is essential to enhance anaerobic digestion (AD) process efficiency and management. In this study, the detailed temporal effects of a sudden glycerol-based organic overloading on the AD microbial community and process imbalance were investigated in two replicate anaerobic digesters by a time-intensive sampling scheme. The microbial community time response to the overloading event was shorter than the shifts of reactor performance parameters. An increase in bacterial community dynamics and in the abundances of several microbial taxa, mainly within the Firmicutes, Tenericutes, and Chloroflexi phyla and Methanoculleus genera, could be detected prior to any shift on the reactor operational parameters. Reactor acidification already started within the first 24 h of the shock and headed the AD process to total inhibition in 72 h alongside with the largest shifts on microbiome, mostly the increase of Anaerosinus sp. and hydrogenotrophic methanogenic Archaea. In sum, this work proved that AD microbial community reacts very quickly to an organic overloading and some shifts occur prior to alterations on the performance parameters. The latter is very interesting as it can be used to improve AD process management protocols.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abendroth C, Vilanova C, Günther T, Luschnig O, Porcar M (2015) Eubacteria and Archaea communities in seven mesophile anaerobic digester plants in Germany. Biotechnol Biofuels 8:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-015-0271-6
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Astals S, Nolla-Ardèvol V, Mata-Alvarez J (2012) Anaerobic co-digestion of pig manure and crude glycerol at mesophilic conditions: biogas and digestate. Bioresour Technol 110:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.01.080
Beale DJ, Karpe AV, McLeod JD, Gondalia SV, Muster TH, Othman MZ, Palombo EA, Joshi D (2016) An “omics” approach towards the characterisation of laboratory scale anaerobic digesters treating municipal sewage sludge. Water Res 88:346–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.10.029
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, Mcdonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high- throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth0510-335
Carballa M, Smits M, Etchebehere C, Boon N, Verstraete W (2011) Correlations between molecular and operational parameters in continuous lab-scale anaerobic reactors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89:303–314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2858-y
Ciriminna R, Della PC, Rossi M, Pagliaro M (2014) Understanding the glycerol market. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 116:1432–1439. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejlt.201400229
Cruaud P, Vigneron A, Lucchetti-Miganeh C, Ciron PE, Godfroy A, Cambon-Bonavita MA (2014) Influence of DNA extraction method, 16S rRNA targeted hypervariable regions, and sample origin on microbial diversity detected by 454 pyrosequencing in marine chemosynthetic ecosystems. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:4626–4639. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00592-14
De Vrieze J, Gildemyn S, Vilchez-Vargas R, Jáuregui R, Pieper DH, Verstraete W, Boon N (2014) Inoculum selection is crucial to ensure operational stability in anaerobic digestion. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:189–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6046-3
De Vrieze J, Raport L, Roume H, Vilchez-Vargas R, Jáuregui R, Pieper DH, Boon N (2016) The full-scale anaerobic digestion microbiome is represented by specific marker populations. Water Res 104:101–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.08.008
Demirel B, Scherer P (2008) The roles of acetotrophic and hydrogenotrophic methanogens during anaerobic conversion of biomass to methane: a review. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 7:173–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-008-9131-1
DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, Rojas M, Brodie EL, Keller K, Huber T, Dalevi D, Hu P, Andersen GL (2006) Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5069–5072. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03006-05
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq461
Eren AM, Vineis JH, Morrison HG, Sogin ML (2013) A filtering method to generate high quality short reads using Illumina paired-end technology. PLoS One 8:e66643. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0066643
Faust K, Lahti L, Gonze D, De VWM, Raes J (2015) Metagenomics meets time series analysis: unraveling microbial community dynamics. Curr Opin Microbiol 25:56–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2015.04.004
Ferguson RMW, Coulon F, Villa R (2016) Organic loading rate: a promising microbial management tool in anaerobic digestion. Water Res 100:348–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.05.009
Fountoulakis MS, Manios T (2009) Enhanced methane and hydrogen production from municipal solid waste and agro-industrial by-products co-digested with crude glycerol. Bioresour Technol 100:3043–3047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.01.016
García-Gen S, Sousbie P, Rangaraj G, Lema JM, Rodríguez J, Steyer JP, Torrijos M (2015) Kinetic modelling of anaerobic hydrolysis of solid wastes, including disintegration processes. Waste Manag 35:96–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2014.10.012
Goux X, Calusinska M, Lemaigre S, Marynowska M, Klocke M, Udelhoven T, Benizri E, Delfosse P (2015) Microbial community dynamics in replicate anaerobic digesters exposed sequentially to increasing organic loading rate, acidosis, and process recovery. Biotechnol Biofuels 8:122. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-015-0309-9
Hao L, Bize A, Conteau D, Chapleur O, Courtois S, Kroff P, Desmond-Le Quéméner E, Bouchez T, Mazéas L, Qu ED (2016) New insights into the key microbial phylotypes of anaerobic sludge digesters under different operational conditions. Water Res 102:158–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.06.014
de Jonge N, Moset V, Møller HB, Nielsen JL (2017) Microbial population dynamics in continuous anaerobic digester systems during start up, stable conditions and recovery after starvation. Bioresour Technol 232:313–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.02.036
Ju F, Lau F, Zhang T (2017) Linking microbial community, environmental variables, and methanogenesis in anaerobic biogas digesters of chemically enhanced primary treatment sludge. Environ Sci Technol 51:3982–3992. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b06344
Kampmann K, Ratering S, Geißler-Plaum R, Schmidt M, Zerr W, Schnell S (2014) Changes of the microbial population structure in an overloaded fed-batch biogas reactor digesting maize silage. Bioresour Technol 174:108–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.09.150
Kim S, Bae J, Choi O, Ju D, Lee J, Sung H, Park S, Sang BI, Um Y (2014) A pilot scale two-stage anaerobic digester treating food waste leachate (FWL): performance and microbial structure analysis using pyrosequencing. Process Biochem 49:301–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2013.10.022
Kirkegaard RH, McIlroy SJ, Kristensen JM, Nierychlo M, Karst SM, Dueholm MS, Albertsen M, Nielsen PH (2017) The impact of immigration on microbial community composition in full-scale anaerobic digesters. Sci Rep 7:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-09303-0
Kleyböcker A, Liebrich M, Verstraete W, Kraume M, Würdemann H (2012) Early warning indicators for process failure due to organic overloading by rapeseed oil in one-stage continuously stirred tank reactor, sewage sludge and waste digesters. Bioresour Technol 123:534–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.07.089
Klindworth A, Pruesse E, Schweer T, Peplies J, Quast C, Horn M, Glöckner FO (2013) Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res 41:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks808
Lagkouvardos I, Fischer S, Kumar N, Clavel T (2017) Rhea: a transparent and modular R pipeline for microbial profiling based on 16S rRNA gene amplicons. PeerJ 5:e2836. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.2836
Legendre P, Gallagher ED (2001) Ecologically meaningful transformations for ordination of species data. Oecologia 129:271–280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420100716
Lerm S, Kleyböcker A, Miethling-Graff R, Alawi M, Kasina M, Liebrich M, Würdemann H (2012) Archaeal community composition affects the function of anaerobic co-digesters in response to organic overload. Waste Manag 32:389–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2011.11.013
Li J, Ban Q, Zhang L, Jha AK (2012) Syntrophic propionate degradation in anaerobic digestion: a review. Int J Agric Biol 14:843–850
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S (2014) Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 15:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
Mao C, Feng Y, Wang X, Ren G (2015) Review on research achievements of biogas from anaerobic digestion. Renew Sust Energ Rev 45:540–555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.02.032
Marzorati M, Wittebolle L, Boon N, Daffonchio D, Verstraete W (2008) How to get more out of molecular fingerprints: practical tools for microbial ecology. Environ Microbiol 10:1571–1581. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01572.x
Mata-Alvarez J, Macé S, Llabrés P (2000) Anaerobic digestion of organic solid wastes. An overview of research achievements and perspectives. Bioresour Technol 74:3–16
McMurdie PJ, Holmes S (2013) Phyloseq: an R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS One 8:e61217. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0061217
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Friendly M, Kindt R, Legendre P, McGlinn D, Minchin PR, O’Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens MHH, Szoecs E, Wagner H (2018) Vegan: community ecology package. R package version 2.4–6
Orwin KH, Wardle DA (2004) New indices for quantifying the resistance and resilience of soil biota to exogenous disturbances. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1907–1912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.04.036
R Core Team (2016) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria, Austria
Razaviarani V, Buchanan ID (2014) Reactor performance and microbial community dynamics during anaerobic co-digestion of municipal wastewater sludge with restaurant grease waste at steady state and overloading stages. Bioresour Technol 172:232–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.09.046
Read S, Marzorati M, Guimarães BCM, Boon N (2011) Microbial Resource Management revisited: successful parameters and new concepts. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:861–871. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3223-5
Regueiro L, Veiga P, Figueroa M, Alonso-Gutierrez J, Stams AJM, Lema JM, Carballa M (2012) Relationship between microbial activity and microbial community structure in six full-scale anaerobic digesters. Microbiol Res 167:581–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2012.06.002
Regueiro L, Lema JM, Carballa M (2015) Key microbial communities steering the functioning of anaerobic digesters during hydraulic and organic overloading shocks. Bioresour Technol 197:208–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.08.076
Rétfalvi T, Tukacs-Hájos A, Albert L, Marosvölgyi B (2011) Laboratory scale examination of the effects of overloading on the anaerobic digestion by glycerol. Bioresour Technol 102:5270–5275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.02.020
Rognes T, Flouri T, Nichols B, Quince C, Mahé F (2016) VSEARCH: a versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 4:e2584. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.2584
Rosenberg E, DeLong EF, Lory S, Stackebrandt E, Thompson F (2014) The Prokaryotes: Firmicutes and Tenericutes. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg.
Saito Y, Aoki M, Hatamoto M, Yamaguchi T (2015) Presence of a novel methanogenic archaeal lineage in anaerobic digesters inferred from mcrA and 16S rRNA gene phylogenetic analyses. J Water Environ Technol 13:279–289
Shade A, Gilbert JA (2015) Temporal patterns of rarity provide a more complete view of microbial diversity. Trends Microbiol 23:335–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2015.01.007
Shade A, Peter H, Allison SD, Baho DL, Berga M, Bürgmann H, Huber DH, Langenheder S, Lennon JT, Martiny JBH, Matulich KL, Schmidt TM, Handelsman J (2012) Fundamentals of microbial community resistance and resilience. Front Microbiol 3:417. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2012.00417
Shade A, Gregory Caporaso J, Handelsman J, Knight R, Fierer N, Caporaso JG, Handelsman J, Knight R, Fierer N (2013) A meta-analysis of changes in bacterial and archaeal communities with time. ISME J 7:1493–1506. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2013.54
Shin SG, Han G, Lim J, Lee C, Hwang S (2010) A comprehensive microbial insight into two-stage anaerobic digestion of food waste-recycling wastewater. Water Res 44:4838–4849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.07.019
Steinberg LM, Regan JM (2011) Response of lab-scale methanogenic reactors inoculated from different sources to organic loading rate shocks. Bioresour Technol 102:8790–8798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.07.017
Strömp C, Tindall BJ, Jarvis GN, Lünsdorf H, Moore ERB, Hippe H (1999) A re-evaluation of the taxonomy of the genus Anaerovibrio, with the reclassification of Anaerovibrio glycerini as Anaerosinus glycerini gen. nov., comb. nov., and Anaerovibrio burkinabensis as Anaeroarcus burkinensis [corrig.] gen. nov., comb. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49: 1861–1872. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-49-4-1861
Tian JH, Pourcher AM, Bureau C, Peu P (2017) Cellulose accessibility and microbial community in solid state anaerobic digestion of rape straw. Bioresour Technol 223:192–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.10.009
Viana MB, Freitas AV, Leitão RC, Pinto GAS, Santaella ST (2012) Anaerobic digestion of crude glycerol: a review. Environ Technol Rev 1:81–92. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2012.692723
Wang Z, Yang ST (2013) Propionic acid production in glycerol/glucose co-fermentation by Propionibacterium freudenreichii subsp. shermanii. Bioresour Technol 137:116–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.03.012
Wirth R, Kovács E, Maróti G, Bagi Z, Rákhely G, Kovács KL (2012) Characterization of a biogas-producing microbial community by short-read next generation DNA sequencing. Biotechnol Biofuels 5:41. https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-6834-5-41
Zhou J, Liu W, Deng Y, Jiang Y-H, Xue K, He Z, Van Nostrand JD, Wu L, Yang Y, Wang A (2013) Stochastic assembly leads to alternative communities with distinct functions in a bioreactor microbial community. MBio 4:e00584–12-e00584–12. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00584-12
Ziganshina EE, Belostotskiy DE, Ilinskaya ON, Boulygina EA, Grigoryeva TV, Ziganshin AM (2015) Effect of the organic loading rate increase and the presence of zeolite on microbial community composition and process stability during anaerobic digestion of chicken wastes. Microb Ecol 70:948–960. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-015-0635-2
Acknowledgments
Computational resources were kindly provided and supported by Fundacion Pública Galega Centro Tecnolóxico de Supercomputación de Galicia (CESGA).
Funding
This research was supported by the Spanish Government (AEI) through CDTI (SmartGreenGas project, 2014-CE224). The authors belong to the Galician Competitive Research Group GRC (ED431C 2017/29) and to the CRETUS Strategic Partnership (AGUP2015/02). All these programs are co-funded by FEDER (UE). GHRB PhD fellowship is supported by CAPES (BEX-2160/2015-03) Foundation, Ministry of Education of Brazil, Brasília – DF 70040-020, Brazil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1868 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Braz, G.H.R., Fernandez-Gonzalez, N., Lema, J.M. et al. The time response of anaerobic digestion microbiome during an organic loading rate shock. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 10285–10297 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9383-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9383-9