Abstract
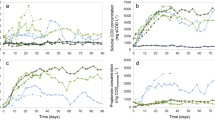
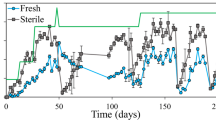
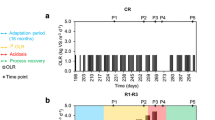
Anaerobic digestion is considered a key technology for the future bio-based economy. The microbial consortium carrying out the anaerobic digestion process is quite complex, and its exact role in terms of “elasticity”, i.e., the ability to rapidly adapt to changing conditions, is still unknown. In this study, the role of the initial microbial community in terms of operational stability and stress tolerance was evaluated during a 175-day experiment. Five different inocula from stable industrial anaerobic digesters were fed a mixture of waste activated sludge and glycerol. Increasing ammonium pulses were applied to evaluate stability and stress tolerance. A different response in terms of start-up and ammonium tolerance was observed among the different inocula. Methanosaetaceae were the dominant acetoclastic methanogens, yet, Methanosarcinaceae increased in abundance at elevated ammonium concentrations. A shift from a Firmicutes to a Proteobacteria dominated bacterial community was observed in failing digesters. Methane production was strongly positively correlated with Methanosaetaceae, but also with Bacteria related to Anaerolinaceae, Clostridiales, and Alphaproteobacteria. Volatile fatty acids were strongly positively correlated with Betaproteobacteria and Bacteroidetes, yet ammonium concentration only with Bacteroidetes. Overall, these results indicate the importance of inoculum selection to ensure stable operation and stress tolerance in anaerobic digestion.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angelidaki I, Ahring BK (1993) Thermophilic anaerobic digestion of livestock waste: the effect of ammonia. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 38(4):560–564
Angenent LT, Karim K, Al-Dahhan MH, Domiguez-Espinosa R (2004) Production of bioenergy and biochemicals from industrial and agricultural wastewater. Trends Biotechnol 22(9):477–485. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2004.07.001
Anthonisen AC, Loehr RC, Prakasam TBS, Srinath EG (1976) Inhibition of nitrification by ammonia and nitrous acid. J Water Pollut Control Fed 48(5):835–852
Bayr S, Pakarinen O, Korppoo A, Liuksia S, Vaisanen A, Kaparaju P, Rintala J (2012) Effect of additives on process stability of mesophilic anaerobic monodigestion of pig slaughterhouse waste. Bioresour Technol 120:106–113. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2012.06.009
Bengelsdorf FR, Gerischer U, Langer S, Zak M, Kazda M (2013) Stability of a biogas-producing bacterial, archaeal and fungal community degrading food residues. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 84(1):201–212. doi:10.1111/1574-6941.12055
Bohorquez LC, Delgado-Serrano L, Lopez G, Osorio-Forero C, Klepac-Ceraj V, Kolter R, Junca H, Baena S, Zambrano MM (2012) In-depth characterization via complementing culture-independent approaches of the microbial community in an acidic hot spring of the Colombian Andes. Microb Ecol 63(1):103–115. doi:10.1007/s00248-011-9943-3
Briones A, Raskin L (2003) Diversity and dynamics of microbial communities in engineered environments and their implications for process stability. Curr Opin Biotechnol 14(3):270–276. doi:10.1016/s0958-1669(03)00065-x
Calli B, Mertoglu B, Inanc B, Yenigun O (2005) Community changes during start-up in methanogenic bioreactors exposed to increasing levels of ammonia. Environ Technol 26(1):85–91
Camarinha-Silva A, Jáuregui R, Chaves-Moreno D, Oxley APA, Schaumburg F, Becker K, Wos-Oxley ML, Pieper DH (2014) Comparing the anterior nare bacterial community of two discrete human populations using illumina amplicon sequencing. Environ Microbiol. doi:10.1111/1462-2920.12362
Carballa M, Smits M, Etchebehere C, Boon N, Verstraete W (2011) Correlations between molecular and operational parameters in continuous lab-scale anaerobic reactors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89(2):303–314. doi:10.1007/s00253-010-2858-y
Chen Y, Cheng JJ, Creamer KS (2008) Inhibition of anaerobic digestion process: a review. Bioresour Technol 99(10):4044–4064. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2007.01.057
Conklin A, Stensel HD, Ferguson J (2006) Growth kinetics and competition between Methanosarcina and Methanosaeta in mesophilic anaerobic digestion. Water Environ Res 78(5):486–496. doi:10.2175/106143006x95393
De Vrieze J, Hennebel T, Boon N, Verstraete W (2012) Methanosarcina: the rediscovered methanogen for heavy duty biomethanation. Bioresour Technol 112:1–9. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2012.02.079
De Vrieze J, Verstraete W, Boon N (2013) Repeated pulse feeding induces functional stability in anaerobic digestion. Microb Biotechnol 6(4):414–424. doi:10.1111/1751-7915.12025
Dearman B, Marschner P, Bentham RH (2006) Methane production and microbial community structure in single-stage batch and sequential batch systems anaerobically co-digesting food waste and biosolids. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69(5):589–596. doi:10.1007/s00253-005-0076-9
Dechrugsa S, Kantachote D, Chaiprapat S (2013) Effects of inoculum to substrate ratio, substrate mix ratio and inoculum source on batch co-digestion of grass and pig manure. Bioresour Technol 146:101–108. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2013.07.051
Delbes C, Moletta R, Godon JJ (2001) Bacterial and archaeal 16S rDNA and 16S rRNA dynamics during an acetate crisis in an anaerobic digestor ecosystem. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 35(1):19–26. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2001.tb00784.x
Demirel B, Scherer P (2008) The roles of acetotrophic and hydrogenotrophic methanogens during anaerobic conversion of biomass to methane: a review. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 7(2):173–190. doi:10.1007/s11157-008-9131-1
Fernandez AS, Hashsham SA, Dollhopf SL, Raskin L, Glagoleva O, Dazzo FB, Hickey RF, Criddle CS, Tiedje JM (2000) Flexible community structure correlates with stable community function in methanogenic bioreactor communities perturbed by glucose. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(9):4058–4067
Gallert C, Winter J (1997) Mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic digestion of source-sorted organic wastes: effect of ammonia on glucose degradation and methane production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 48(3):405–410
Gallert C, Bauer S, Winter J (1998) Effect of ammonia on the anaerobic degradation of protein by a mesophilic and thermophilic biowaste population. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 50(4):495–501
Greenberg AE, Clesceri LS, Eaton AD (1992) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater 18th edn. American Public Health Association Publications, Washington
Gujer W, Zehnder AJB (1983) Conversion processes in anaerobic digestion. Water Sci Technol 15(8–9):127–167
Hansen KH, Angelidaki I, Ahring BK (1998) Anaerobic digestion of swine manure: inhibition by ammonia. Water Res 32(1):5–12. doi:10.1016/s0043-1354(97)00201-7
Hao LP, Lu F, He PJ, Li L, Shao LM (2011) Predominant contribution of syntrophic acetate oxidation to thermophilic methane formation at high acetate concentrations. Environ Sci Technol 45(2):508–513. doi:10.1021/es102228v
Hashimoto AG (1986) Ammonia inhibition of methanogenesis from cattle wastes. Agric Wastes 17(4):241–261. doi:10.1016/0141-4607(86)90133-2
Hattori S (2008) Syntrophic acetate-oxidizing microbes in methanogenic environments. Microbes Environ 23(2):118–127. doi:10.1264/jsme2.23.118
Holm-Nielsen JB, Al Seadi T, Oleskowicz-Popiel P (2009) The future of anaerobic digestion and biogas utilization. Bioresour Technol 100(22):5478–5484. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2008.12.046
Hurlbert SH (1971) The nonconcept of species diversity: a critique and alternative parameters. Ecology 52(4):577–586. doi:10.2307/1934145
Jukes TH, Cantor CR (1969) Evolution of protein molecules. In: Munro HN (ed) Mammalian protein metabolism. Academy Press, New York
Karakashev D, Batstone DJ, Trably E, Angelidaki I (2006) Acetate oxidation is the dominant methanogenic pathway from acetate in the absence of Methanosaetaceae. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(7):5138–5141. doi:10.1128/aem.00489-06
Kato S, Watanabe K (2010) Ecological and evolutionary interactions in syntrophic methanogenic consortia. Microbes Environ 25(3):145–151. doi:10.1264/jsme2.ME10122
Krakat N, Schmidt S, Scherer P (2011) Potential impact of process parameters upon the bacterial diversity in the mesophilic anaerobic digestion of beet silage. Bioresour Technol 102(10):5692–5701. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2011.02.108
Krober M, Bekel T, Diaz NN, Goesmann A, Jaenicke S, Krause L, Miller D, Runte KJ, Viehover P, Puhler A, Schluter A (2009) Phylogenetic characterization of a biogas plant microbial community integrating clone library 16S-rDNA sequences and metagenome sequence data obtained by 454-pyrosequencing. J Biotechnol 142(1):38–49. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2009.02.010
Lee S-H, Kang H-J, Lee YH, Lee TJ, Han K, Choi Y, Park H-D (2012) Monitoring bacterial community structure and variability in time scale in full-scale anaerobic digesters. J Environ Monit 14(7):1893–1905. doi:10.1039/c2em10958a
Letunic I, Bork P (2011) Interactive tree of life v2: online annotation and display of phylogenetic trees made easy. Nucleic Acids Res 39:W475–W478. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr201
Li Q, Wang C, Tang C, Li N, Li J (2012) Molecular-Phylogenetic Characterization of the Microbiota in Ulcerated and Non-Ulcerated Regions in the Patients with Crohn's Disease. PLoS One 7(4) doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0034939
Liu FH, Wang SB, Zhang JS, Zhang J, Yan X, Zhou HK, Zhao GP, Zhou ZH (2009) The structure of the bacterial and archaeal community in a biogas digester as revealed by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and 16S rDNA sequencing analysis. J Appl Microbiol 106(3):952–966. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2008.04064.x
Lu F, Hao LP, Guan DX, Qi YJ, Shao LM, He PJ (2013) Synergetic stress of acids and ammonium on the shift in the methanogenic pathways during thermophilic anaerobic digestion of organics. Water Res 47(7):2297–2306. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2013.01.049
Marzorati M, Wittebolle L, Boon N, Daffonchio D, Verstraete W (2008) How to get more out of molecular fingerprints: practical tools for microbial ecology. Environ Microbiol 10(6):1571–1581. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01572.x
Mata-Alvarez J, Mace S, Llabres P (2000) Anaerobic digestion of organic solid wastes. An Overview of Res Achievements and Perspect Bioresour Technol 74(1):3–16. doi:10.1016/s0960-8524(00)00023-7
McMahon KD, Zheng DD, Stams AJM, Mackie RI, Raskin L (2004) Microbial population dynamics during start-up and overload conditions of anaerobic digesters treating municipal solid waste and sewage sludge. Biotechnol Bioeng 87(7):823–834. doi:10.1002/bit.20192
Michail S, Durbin M, Turner D, Griffiths AM, Mack DR, Hyams J, Leleiko N, Kenche H, Stolfi A, Wine E (2012) Alterations in the gut microbiome of children with severe ulcerative colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 18(10):1799–1808. doi:10.1002/ibd.22860
Mondot S, Kang S, Furet JP, de Carcer DA, McSweeney C, Morrison M, Marteau P, Dore J, Leclerc M (2011) Highlighting new phylogenetic specificities of Crohn’s disease microbiota. Inflamm Bowel Dis 17(1):185–192. doi:10.1002/ibd.21436
Nettmann E, Bergmann I, Pramschufer S, Mundt K, Plogsties V, Herrmann C, Klocke M (2010) Polyphasic analyses of methanogenic Archaeal communities in agricultural biogas plants. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(8):2540–2548. doi:10.1128/aem.01423-09
Oksanen, J, Blanchet, G, Kindt, R, Legendre, P, Minchin, PR, O’Hara, RB, Simpson, GL, Solymos, P, Henry, M., Stevens, H, Wagner, H (2012) Vegan: Community ecology package. R package version 2.0-1. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan
Peterson G, Allen CR, Holling CS (1998) Ecological resilience, biodiversity, and scale. Ecosystems 1(1):6–18. doi:10.1007/s100219900002
Pitk P, Kaparaju P, Palatsi J, Affes R, Vilu R (2013) Co-digestion of sewage sludge and sterilized solid slaughterhouse waste: methane production efficiency and process limitations. Bioresour Technol 134:227–232. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2013.02.029
Pruesse E, Quast C, Knittel K, Fuchs BM, Ludwig W, Peplies J, Gloeckner FO (2007) SILVA: a comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res 35(21):7188–7196. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm864
Qu X, Vavilin VA, Mazeas L, Lemunier M, Duquennoi C, He PJ, Bouchez T (2009) Anaerobic biodegradation of cellulosic material: batch experiments and modelling based on isotopic data and focusing on aceticlastic and non-aceticlastic methanogenesis. Waste Manage 29(6):1828–1837. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2008.12.008
R Development Core Team (2013) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 3.0 ed. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing
Rajagopal R, Masse DI, Singh G (2013) A critical review on inhibition of anaerobic digestion process by excess ammonia. Bioresour Technol 143:632–641. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2013.06.030
Riviere D, Desvignes V, Pelletier E, Chaussonnerie S, Guermazi S, Weissenbach J, Li T, Camacho P, Sghir A (2009) Towards the definition of a core of microorganisms involved in anaerobic digestion of sludge. ISME J 3(6):700–714. doi:10.1038/ismej.2009.2
Sanders HL (1968) Marine benthic diversity: a comparative study. Am Nat 102(925):243–282. doi:10.1086/282541
Sawayama S, Tada C, Tsukahara K, Yagishita T (2004) Effect of ammonium addition on methanogenic community in a fluidized bed anaerobic digestion. J Biosci Bioeng 97(1):65–70
Schink B (1997) Energetics of syntrophic cooperation in methanogenic degradation. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 61(2):262
Schnurer A, Nordberg A (2008) Ammonia, a selective agent for methane production by syntrophic acetate oxidation at mesophilic temperature. Water Sci Technol 57(5):735–740. doi:10.2166/wst.2008.097
Steinberg LM, Regan JM (2011) Response of lab-scale methanogenic reactors inoculated from different sources to organic loading rate shocks. Bioresour Technol 102(19):8790–8798. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2011.07.017
Sundberg C, Al-Soud WA, Larsson M, Alm E, Yekta SS, Svensson BH, Sørensen SJ, Karlsson A (2013) 454 pyrosequencing analyses of bacterial and archaeal richness in 21 full-scale biogas digesters. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 85(3):612–626. doi:10.1111/1574-6941.12148
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739. doi:10.1093/molbev/msr121
Tyagi VK, Lo SL (2013) Sludge: a waste or renewable source for energy and resources recovery? Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev 25:708–728. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2013.05.029
Vanwonterghem I, Jensen PD, Ho DP, Batstone DJ, Tyson GW (2014) Linking microbial community structure, interactions and function in anaerobic digesters using new molecular techniques. Curr Opin Biotechnol 27:55–64. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2013.11.004
Venables WN, Ripley BD (2002) Modern applied statistics with S, 4th edn. Springer, New York
Verstraete W, Morgan-Sagastume F, Aiyuk S, Waweru M, Rabaey K, Lissens G (2005) Anaerobic digestion as a core technology in sustainable management of organic matter. Water Sci Technol 52(1–2):59–66
Westerholm M, Roos S, Schnurer A (2010) Syntrophaceticus schinkii gen. nov., sp nov., an anaerobic, syntrophic acetate-oxidizing bacterium isolated from a mesophilic anaerobic filter. FEMS Microbiol Lett 309(1):100–104. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2010.02023.x
Williams J, Williams H, Dinsdale R, Guwy A, Esteves S (2013) Monitoring methanogenic population dynamics in a full-scale anaerobic digester to facilitate operational management. Bioresour Technol 140:234–242. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2013.04.089
Wittebolle L, Verstraete W, Boon N (2009) The inoculum effect on the ammonia-oxidizing bacterial communities in parallel sequential batch reactors. Water Res 43(17):4149–4158. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2009.06.034
Yu Y, Lee C, Kim J, Hwang S (2005) Group-specific primer and probe sets to detect methanogenic communities using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Biotechnol Bioeng 89(6):670–679. doi:10.1002/bit.20347
Yu Y, Kim J, Hwang S (2006) Use of real-time PCR for group-specific quantification of aceticlastic methanogens in anaerobic processes: population dynamics and community structures. Biotechnol Bioeng 93(3):424–433. doi:10.1002/bit.20724
Zinder SH, Koch M (1984) Non-acetoclastic methanogenesis from acetate: acetate oxidation by a thermophilic syntrophic coculture. Arch Microbiol 138(3):263–272. doi:10.1007/bf00402133
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ghent University Multidisciplinary Research Partnership (MRP) “Biotechnology for a Sustainable Economy” (01 MRA 510 W). S.G. is funded by the Special Research Fund (BOF) of the University of Ghent (Belgium). R.V.V. is supported by the Inter-University Attraction Pole (IUAP) “μ-manager” funded by the Belgian Science Policy (BELSPO, P7/25). The authors would like to thank Tim Lacoere for his assistance during the molecular work and Jan Arends, Hugo Roume, Eline Vanlancker, and Jana Wijnsouw for the useful suggestions and critically reading the manuscript. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
Specific details concerning the waste activated sludge characterization, experimental set-up, qPCR quality control, and biogas and VFA analyses can be found in SI, together with total VFA, TAN, and pH profiles in the reactors. A heatmap at family level, the rarefaction curves, and a detailed overview of correlations between the microbial community and the main operational conditions are also presented. (PDF 1511 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Vrieze, J., Gildemyn, S., Vilchez-Vargas, R. et al. Inoculum selection is crucial to ensure operational stability in anaerobic digestion. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 189–199 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6046-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6046-3