Abstract
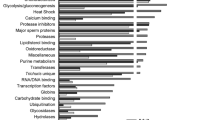
Clonorchis sinensis is a food-borne zoonotic parasite that resides in bile ducts and causes clonorchiasis, which may result in cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, hepatic fibrosis, and liver tumors. Although total excretory secretory products (ESP) of C. sinensis adults induce hepatic fibrosis in vivo in rats, the causative mechanism is not well understood. To study components of the ESP, C. sinensis culture medium was collected and analyzed using shotgun LC–MS/MS. We identified a total of 110 proteins, including glycometabolic enzymes (such as fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase) and enolase), detoxification enzymes (such as glutamate dehydrogenase, dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase and cathepsin B endopeptidase), and a number of RAB family proteins. To identify a potential causative agent for hepatic fibrosis, we expressed and purified a recombinant FBPase, a 1,041-bp gene product that encodes a 41.7-kDa protein with prototypical FBPase domains and that can form a tetramer with a molecular mass of 166.8 kDa. In addition, we found that FBPase is an antigen present in the ESP and in circulation. Immunofluorescence showed that FBPase localizes to the intestinal cecum and vitellarium in C. sinensis adults. Our results describe the components of the excretory secretory products from C. sinensis adult worms and suggest that FBPase may be an important antigen present in the ESP of C. sinensis and may lay the foundation for additional studies on the development of clonorchiasis-associated hepatic fibrosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen X, Hu X, Wu Z, Yu X, Ma C, Zhou Z (2007) Immunological cross-reactivity analysis on recombinant histamine-releasing factors from Schistosoma japonicum, Clonorchis sinensis, and Wistar rat. Parasitol Res 100:749–754
Ch’In KY, Lei AT, Wang TY (1955) Primary mucinous carcinoma of liver associated with Clonorchis sinensis infection. Chin Med J 73:26–35
Chung YY, Ko RC (1999) A novel cDNA clone encoding a specific excretory/secretory antigen of larval Trichinella pseudospiralis. Parasitol Res 85:685–691
Donahue JL, Bownas JL, Niehaus WG, Larson TJ (2000) Purification and characterization of glpX-encoded fructose 1, 6-bisphosphatase, a new enzyme of the glycerol 3-phosphate regulon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 182:5624–5627
Enes P, Panserat S, Kaushik S, Oliva-Teles A (2009) Nutritional regulation of hepatic glucose metabolism in fish. Fish Physiol Biochem 35:519–539
Fried B, Abruzzi A (2010) Food-borne trematode infections of humans in the United States of America. Parasitol Res 106:1263–1280
Gould TD, Quiroz JA, Singh J, Zarate CA, Manji HK (2004) Emerging experimental therapeutics for bipolar disorder: insights from the molecular and cellular actions of current mood stabilizers. Mol Psychiatry 9:734–755
Gressner AM, Weiskirchen R (2006) Modern pathogenetic concepts of liver fibrosis suggest stellate cells and TGF-beta as major players and therapeutic targets. J Cell Mol Med 10:76–99
Haas W, Faherty BK, Gerber SA, Elias JE, Beausoleil SA, Bakalarski CE, Li X, Villen J, Gygi SP (2006) Optimization and use of peptide mass measurement accuracy in shotgun proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics 5:1326–1337
Hu F, Chen W, Li L, Lu Y, Song W, Kuang Y, Zhang F (2009a) Cloning, characterization, and expression of a novel secretory lipase-like gene from Clonorchis sinensis. Parasitol Res 105:1661–1666
Hu F, Hu X, Ma C, Zhao J, Xu J, Yu X (2009b) Molecular characterization of a novel Clonorchis sinensis secretory phospholipase A(2) and investigation of its potential contribution to hepatic fibrosis. Mol Biochem Parasitol 167:127–134
Hu FY, Hu XC, Ma CL, Xu J, Yu XB (2009c) Excretory/secretory antigens from Clonorchis sinensis induces hepatic fibrosis in rats. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 29:393–396
Kepka A, Dariusz Szajda S, Stypulkowska A, Waszkiewicz N, Jankowska A, Chojnowska S, Zwierz K (2008) Urinary fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase activity as a marker of the damage to the renal proximal tubules in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Clin Chem Lab Med 46:831–835
Kim YJ, Choi MH, Hong ST, Bae YM (2008) Proliferative effects of excretory/secretory products from Clonorchis sinensis on the human epithelial cell line HEK293 via regulation of the transcription factor E2F1. Parasitol Res 102:411–417
Kim DM, Ko BS, Ju JW, Cho SH, Yang SJ, Yeom YI, Kim TS, Won Y, Kim IC (2009a) Gene expression profiling in mouse liver infected with Clonorchis sinensis metacercariae. Parasitol Res 106:269–278
Kim YJ, Choi MH, Hong ST, Bae YM (2009b) Resistance of cholangiocarcinoma cells to parthenolide-induced apoptosis by the excretory-secretory products of Clonorchis sinensis. Parasitol Res 104:1011–1016
Kuznetsova E, Xu L, Singer A, Brown G, Dong A, Flick R, Cui H, Cuff M, Joachimiak A, Savchenko A, Yakunin AF (2010) Structure and activity of the metal-independent fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase YK23 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 285:21049–21059
Lawton DE, Wigger H, Simcock DC, Simpson HV (2002) Effect of Ostertagia circumcincta excretory/secretory products on gastrin release in vitro. Vet Parasitol 104:243–255
Lee JH, Rim HJ, Bak UB (1993) Effect of Clonorchis sinensis infection and dimethylnitrosamine administration on the induction of cholangiocarcinoma in Syrian golden hamsters. Korean J Parasitol 31:21–30
Li S, Chung YB, Chung BS, Choi MH, Yu JR, Hong ST (2004) The involvement of the cysteine proteases of Clonorchis sinensis metacercariae in excystment. Parasitol Res 93:36–40
Lun ZR, Gasser RB, Lai DH, Li AX, Zhu XQ, Yu XB, Fang YY (2005) Clonorchiasis: a key foodborne zoonosis in China. Lancet Infect Dis 5:31–41
Ma C, Hu X, Hu F, Li Y, Chen X, Zhou Z, Lu F, Xu J, Wu Z, Yu X (2007) Molecular characterization and serodiagnosis analysis of a novel lysophospholipase from Clonorchis sinensis. Parasitol Res 101:419–425
Ma CL, Hu XC, Hu FY, Zhou HJ, Xue L, Yu XB (2008) The effects of Lysophospholipase from Clonorchis sinensis on the hepatic stellate cells and oval cells of rat. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi 24:692–695
Nagano I, Wu Z, Takahashi Y (2009) Functional genes and proteins of Trichinella spp. Parasitol Res 104:197–207
Pak JH, Kim DW, Moon JH, Nam JH, Kim JH, Ju JW, Kim TS, Seo SB (2009) Differential gene expression profiling in human cholangiocarcinoma cells treated with Clonorchis sinensis excretory-secretory products. Parasitol Res 104:1035–1046
Rana SS, Bhasin DK, Nanda M, Singh K (2007) Parasitic infestations of the biliary tract. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 9:156–164
Santra A, Chowdhury A, Ghosh A, Mazumder DN (2000) Development of an animal model of hepatic fibrosis by excretory-secretory antigen of Ascaris suum. Indian J Gastroenterol 19:119–121
Snabel V, Hanzelova V, Scholz T, Gerdeaux D, Cabaret J (2004) Allozyme analysis of genetic variation and polymorphism in Eubothrium salvelini and E. crassum (Cestoda: Pseudophyllidea) from alpine lakes. Parasitol Res 93:290–295
Stec B, Yang H, Johnson KA, Chen L, Roberts MF (2000) MJ0109 is an enzyme that is both an inositol monophosphatase and the ‘missing’ archaeal fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Nat Struct Biol 7:1046–1050
Strand A, Zrenner R, Trevanion S, Stitt M, Gustafsson P, Gardestrom P (2000) Decreased expression of two key enzymes in the sucrose biosynthesis pathway, cytosolic fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase and sucrose phosphate synthase, has remarkably different consequences for photosynthetic carbon metabolism in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 23:759–770
Tielens AG, Van der Meer P, van den Heuvel JM, van den Bergh SG (1991) The enigmatic presence of all gluconeogenic enzymes in Schistosoma mansoni adults. Parasitology 102(Pt 2):267–276
Verhees CH, Akerboom J, Schiltz E, de Vos WM, van der Oost J (2002) Molecular and biochemical characterization of a distinct type of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase from Pyrococcus furiosus. J Bacteriol 184:3401–3405
Wang Y, Tomlinson B (2007) Managlinat dialanetil, a fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 8:849–858
Williamson HJ, Allardyce RA, Clemett RS, Hidajat RR (1990) Serum and neutrophils alter the rate of excretory/secretory antigen release by Toxocara canis infective larvae in vitro. Parasite Immunol 12:175–187
Yamasaki H, Araki K, Lim PK, Zasmy N, Mak JW, Taib R, Aoki T (2000) Development of a highly specific recombinant Toxocara canis second-stage larva excretory-secretory antigen for immunodiagnosis of human toxocariasis. J Clin Microbiol 38:1409–1413
Yoon BI, Jung SY, Hur K, Lee JH, Joo KH, Lee YS, Kim DY (2000) Differentiation of hamster liver oval cell following Clonorchis sinensis infection. J Vet Med Sci 62:1303–1310
Zhang X, Jin Z, Da R, Dong Y, Song W, Chen X, Huang Q, Ling H, Che Y, Li Y, Zhang F (2008) Fas/FasL-dependent apoptosis of hepatocytes induced in rat and patients with Clonorchis sinensis infection. Parasitol Res 103:393–399
Zheng N, Xu J, Wu Z, Chen J, Hu X, Song L, Yang G, Ji C, Chen S, Gu S, Ying K, Yu X (2005) Clonorchis sinensis: molecular cloning and functional expression of novel cytosolic malate dehydrogenase. Exp Parasitol 109:220–227
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Science and Technology Major Project of China (No. 2008ZX10004-011), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30671831), and National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (973 program, No. 2010CB530000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, M., Hu, K., Liu, W. et al. Proteomic analysis of excretory secretory products from Clonorchis sinensis adult worms: molecular characterization and serological reactivity of a excretory–secretory antigen-fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Parasitol Res 109, 737–744 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2316-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2316-5