Abstract
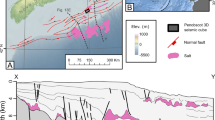
The sea floor of Fram Strait, the over 2500 m deep passage between the Arctic Ocean and the Norwegian-Greenland Sea, is part of a complex transform zone between the Knipovich mid-oceanic ridge of the Norwegian-Greenland Sea and the Nansen-Gakkel Ridge of the Arctic Ocean. Because linear magnetic anomalies formed by sea-floor spreading have not been found, the precise location of the boundary between the Eurasian and the North American plate is unknown in this region. Systematic surveying of Fram Strait with SEABEAM and high resolution seismic profiling began in 1984 and continued in 1985 and 1987, providing detailed morphology of the Fram Strait sea floor and permitting better definition of its morphotectonics. The 1984 survey presented in this paper provided a complete set of bathymetric data from the southernmost section of the Svalbard Transform, including the Molloy Fracture Zone, connecting the Knipovich Ridge to the Molloy Ridge; and the Molloy Deep, a nodal basin formed at the intersection of the Molloy Transform Fault and the Molloy Ridge. This nodal basin has a revised maximum depth of 5607 m water depth at 79°8.5′N and 2°47′E.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Augstein, E., Hempel, G., Schwarz, J., Thiede, J., and Weigel, W., 1984, Die Expedition ARKTIS II des FS “POLARSTERN”, Ber. Polarforsch. 20, Alfred-Wegener-Institut für Polarforschung, pp. 1–192.
Balakshin, L. L., 1959, AAAS, Preprints of the International Oceanographic Congress, 31 August–12 September, 1959, pp. 43D-31.
BerggrenW. A. and SchnitkerD., 1983, ‘Cenozoic marine environments in the North Atlantic and Norwegian-Greenland Sea’, in BottM. H. P., SaxovS., TalwaniM., and ThiedeJ. (eds.),Structure and Development of the Greenland-Scotland Ridge, New methods and concepts, (Plenum Press) New York and London, pp. 495–548.
BonattiE. and HamlynP. R., 1978, Mantle uplifted block in the western Indian Ocean,Science 201, 249–251.
BonattiE. and MichaelP. J., 1989, Mantle peridotites from continental rifts to ocean basins to subduction zones,Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 91, 297–311.
BoströmK. and ThiedeJ., 1984, YMER-80 Swedish Arctic Expedition,Medd. Stockh. Univ. Geol. Inst. 260, 1–123.
BrownJ. R. and KarsonJ. A., 1988, Variations in axial processes on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge: the median valley of the MARK area,Mar. Geophys. Res. 10, 109–138.
CAYTROUGH, 1979, Geological and geophysical investigation of the Mid-Cayman Rise spreading center: initial results and observations, in TalwaniM., HarrisonC., and HayesD. E. (eds.),Deep Drilling Results in the Atlantic Ocean: Ocean Crust, Maurice Ewing Series 2: Washington, D.C., American Geophys. Union, pp. 66–93.
ChenY., 1989, A mechanical model for the inside corner uplift at a ridge-transform intersection,J. Geophys. Res. 94(B7), 9275–9282.
CLIMAP Project Members, 1976, The surface of the ice-age earth,Science 191, 1131–1137.
CoachmanL. K. and AagaardK., 1974, Physical oceanography of the Arctic and Subarctic Seas, in HermanY. (ed.),Marine Geology and Oceanography of the Arctic Seas (Springer-Verlag) New York, p. 1–72.
CraneK., EldholmO., MyhreA. M., and SundvorE., 1982, Thermal implications for the evolution of the Spitsbergen Transform fault,Tectonophysics 89, 1–32.
CraneK., SundvorR., FoucherJ. P., HobartM., MyhreA. M., and LeDouaranS., 1988, Thermal evolution of the western Svalbard margin,Mar. Geophys. Res. 9, 165–194.
Crowell, J. C., 1974, Sedimentation along the San Andreas Fault, California, in Dott. R. H. and Shavers, R. H. (eds.),Modern and Ancient Geosynclinal Sedimentation, Soc. Econom. Paleont. Min., Spec. Pub.19, 292–303.
DetrickR. S., SclaterJ. G., and ThiedeJ., 1977, The subsidence of aseismic ridges,Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 34, 185–196.
Eggvin, J., 1963, Bathymetric chart of the Norwegian Sea and adjacent areas, Bergen Fiskeridir. Havforsk. Inst.
EinarssonP., 1986, Seismicity along the eastern margin of the North Atlantic Plate, in VogtP. R. and TucholkeB. E. (eds.),The Western North Atlantic Region, Geol. Soc. Am., DNAG, Geology of North America, v. M, pp. 99–116. Boulder, Colorado.
EldholmO., KarasikA. M., and ReksnesP. A., 1990, The North American plate boundary, in GrantzA., JohnsonL., and SweeneyJ. F. (eds.),The Arctic Ocean region, Geol. Soc. Am., DNAG, The Geology of North America, v. L, Boulder, Colorado (in press).
EldholmO., SundvorE. and CraneK., 1984, Sonobuoy measurements during the YMER expedition,Norsk Polarinst. Skr. 180, 17–23.
Eldholm, O., Thiede, J., Taylor E.et al., 1987, Norwegian Sea, Proc. Ocean Drill. Progr. 104 A, 783 pp.
Ewing, M. and Heezen, B. C., 1956, Mid-Atlantic Ridge seismic belt, Trans. Amer. Geophys. Un. 37, pp. 343.
FoxP. J. and GalloD. G., 1984, A tectonic model for ridgetransform ridge plate boundaries: Implications for the structure of oceanic lithosphere,Tectonophysics 104, 205–242.
FoxP. J. and GalloD. G., 1986, The active transform domain, in VogtP. R. and TucholkeB. E. (eds.),The Western North Atlatic Region, Geol. Soc. Am., DNAG, Geology of North America, v. M. pp. 157–172. Boulder, Colorado.
Frolov, V. V. and Paseçki, V. M., 1958, Arctic Ocean Research center,Piroda. No. 8, 56–62.
GordienkoP. A. and LaktionovA. F., 1960, Principal results of the latest oceanographic research in the Arctic Basin,Izvestiya Akad. Nauk SSSR, Geographic Series 5, 22–33. Translated by E. R. Hope.
GrønlieG. and TalwaniM., 1978, Geophysical Atlasas: Norwegian-Greenland Sea, Vema Research Series, 4, Lamont-Doherty Geological Observatory, Palisades, New York.
GrønlieG. and TalwaniM., 1982, The free air gravity field of the Norwegian-Greenland Sea and adjacent areas,Earth Evolution Sci. 2, 79–103.
Hakkel', Ya. Ya., 1958, Signs of recent submarine volcanic activity in the Lomonosov Range,Piroda No. 4, 87–90 T 206 R*
HopeE. R., 1959, Geotectonics of the Arctic Ocean and the great magnetic anomaly, J. Geophys. Res.64(4), 407–427.
HurdleB. G. (ed.), 1986, The Nordic Seas, (Springer-Verlag) New York 777 pp.
JohannessenO. M., JohannessenJ. A., SandvenS., and DavidsenK. L., 1986, Preliminary results of the marginal ice zone experiment (MIZEX) summer operations, in HurdleB. G. (ed.),The Nordic Seas., (Springer-Verlag), New York, pp. 665–679.
Johansen, S. E., 1985, Hovgaardbruddsonen, Cand. scient. thesis, Univ. Bergen. 145 pp.
JohnsonG. L. and EckhoffO. B., 1966, Bathymetry of the north Greenland Sea,Deep-Sea Res. 13, 1161–1173.
KarsonJ. A. and DickH. J. B., 1983, Tectonics of ridge-transform intersections at the Kane Fracture Zone,Mar. Geophys. Res. 6, 51–98.
Koltermann, K. P., 1987, Die Tiefenzirkulation der Grönland-See als Folge des thermohalinen Systems des Europäischen Nordmeers, Diss, Univ. Hamburg. 287 pp.
KongL. S., DetrickR. S., FoxP. L., MayerL. A., and RyanW. B. F., 1988, The morphology and tectonics of the MARK area from Sea Beam and Sea MARC I observations (Mid-Atlantic Ridge 23° N),Mar. Geophys. Res. 10, 59–90.
Kristoffersen, Y. and Huseby, E. S., 1985, Multi-channel seismic reflection measurements in the Eurasian Basin, Arctic Ocean, from the US Ice Station Fram-IV, in Husebye, E. S., Johnson, G. L., and Kristoffersen, Y. (eds.),Geophysics of the Polar Regions, Tectonophysics 114 (1–4), pp. 103–115.
LaBrecqueJ. L., KentD. V., and CandeS. C., 1977, Revised magnetic polarity time scale for Late Cretaceous and Cenozoic time,Geology 5, 330–335.
Laktionov, A. F., 1959, Bottom topography of the Greenland Sea in the region of Nansen's Sill, Piroda, 10, 95–97 (DRB translation T 333 R).
LangsethM. G. and ZielinskiG. W., 1974, Marine heat flow measurements in the Norwegian-Greenland Sea and in the vicinity of Iceland, in KristjanssonL. (ed.),Geodynamics of Iceland and the North Atlantic Area, Kluwer Acad. Publ., Dordrecth, Holland, pp. 277–295.
LowellJ. D., 1972, Spitsbergen Tertiary orogenic belt and the Spitsbergen Fracture Zone,Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 83, 3091–3102.
MacdonaldK. C., CastilloD. A., and MillerS. P., 1986, Deep-tow studies of the Vema Fracture Zone, 1. Tectonics of a major slow slipping transform fault and its intersection with the Mid-Atlantic Ridge,J. Geophys. Res. 91(B3), 3334–3354.
MillerK. G. and TucholkeB. E., 1983, Development of Cenozoic abyssal circulation south of the Greenland-Scotland Ridge, in BottM. H. P., SaxovS., TalwaniM., and ThiedeJ. (eds.),Structure and Development of the Greenland-Scotland Ridge, New Methods and Concepts, Plenum Press, New York and London, pp. 549–590.
Myhre, A. M., Eldholm O., and Sundvor, E., 1982, The margin between Senja and Spitsbergen fracture zones: implications from plate tectonics, in Johnson, G. L. and Sweeney, J. F. (eds.),Structure of the Arctic. Tectonophysics 89, 33–50.
MyhreA. M. and EldholmO., 1988, The western Svalbard margin (74–80° N),Marine and Petroleum Geology 5, 134–156.
NansenF., 1904, The bathymetrical features of the North Polar Seas, with a discussion of continental shelves and previous oscillations of the shoreline, Norwegian North Polar Expedition. 1893–1896,Sci. Research v 4, 1–232.
NeumannE.-R. and SchillingJ.-G., 1984, Petrology of basalts from the Mohns-Knipovich Ridge; The Norwegian-Greenland Sea,Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 85, 209–223.
OhtaY., 1982, Morpho-tectonic studies around Svalbard and the northernmost Atlantic,Can. Soc. Petrol. Geol. Mem. 8, 415–429.
PaquetteR. G., BourkeR. H., NewtonJ. F., and PerdueW. F., 1985, The East Greenland Polar Front in autumn,J. Geophys. Res. 90(C3), 4866–4882.
PerryR. K., 1986, Bathymetry, in HurdleB. G. (ed.),The Nordic Seas, (Springer-Verlag) New York, pp. 211–234.
PerryR. K., FlemingH. S., CherkisN. Z., FedenR. H., and VogtP. R., 1980, Bathymetry of the Norwegian-Greenland and western Barents Seas, (Map) naval Research Laboratory, Washington, D.C.
Perry, R. K., Fleming, H. S., Weber, J. R., Kristoffersen, Y., Hall, J. K., Grantz, A., Johnson, G. L., Cherkis, N. Z., and Larsen, B., 1986, Bathymetry of the Arctic Ocean, (Map) Naval Research Laboratory — Acoustics Division, printed by the Geological Society of America.
Phillips, J. D. and Fleming, H. S., 1978, Multi-beam sonar study of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge rift valley, 36°–37° N, Geol. Soc. Amer. Map MC-19.
PockalnyR. A., DetrickR. S., and FoxP. J., 1988, The Morphology and Tectonics of the Kane Transform from Sea Beam Bathymetry Data,J. Geophys. Res. 93(B4), 3179–3193.
QuadfaselD., GascardJ.-C., and KoltermannK. P., 1987, Large scale oceanography in Fram Strait during MIZEX 84',J. Geophys. Res. 92(C7), 6719–6728.
Reil, W., 1987, Bericht über die Auswertung der bathymetrischen Aufzeichungen der Meßfahrt ARKTIS II/4, 1984 des Forschungsschiffes POLARSTERN, PRAKLA-SEISMOS AG. Hannover 30.03.1987, 7 pp.
Savostin, L. A. and Karasik, A. M., 1981, Recent plate movements of the Arctic Basin and of northeastern Asia, in Solomon, S. C., Van der Voo, R., and Chinnery, M. A. (eds.),Quantitative Methods of Assessing Plate Motions. Tectonophysics 74, 111–145.
SchlüterH.-U. and HinzK., 1978, The continental margin of west Spitsbergen,Polarforschung 48, 151–169.
SeveringhausJ. P. and MacdonaldK. C., 1988, High inside corners at ridge-transform intersections,Mar. Geophys. Res. 9, 353–367.
SleepN. H. and BiehlerS., 1970, Topography and tectonics at the intersections of fracture zones and central rifts,J. Geophys. Res. 75, 2748–2752.
SmithD. C., MorisonJ., JohannessenJ. A., and UntersteinerN., 1984, Topographic generation of an eddy at the edge of the East Greenland Current,J. Geophys. Res. 89, 8205–8208.
SteelR. L. GjelbergJ., NøttvedtA., Helland-HansenW., KleinspehnK., and Rye-LarsenM., 1985, The Tertiary strikeslip basins and orogenic belt of Spitsbergen,Soc. Econ. Paleont. Mineral. Spec. Publ. 37, 339–359.
StocksT., 1950, Depth conditions of the European portion of the Arctic Ocean,Hydr, Zeit. 3(1/2), 93–100.
StroupJ. B. and FoxP. J., 1981, Geologic investigations in the Cayman Trough: evidence for thin oceanic crust along the Mid-Cayman Rise,J. Geol. 89, 395–420.
SundvorE. and EldholmO., 1979, The western and northern margin off Svalbard,Tectonophysics 59, 239–250.
Sundvor, E., Myhre, A. M., Eldholm, O., and Austegaard, A., 1982, The Arctic west and north of Svalbard, ONS conference, Stavanger, Norway, 26 pp.
SwiftJ. H., 1986, The Arctic waters, in HurdleB. G. (ed.),The Nordic Seas, Springer-Verlag, New York, pp. 129–153.
Tamayo TectonicTeam, 1984, Tectonics at the intersection of the East Pacific Rise with the Tamayo Transform Fault,Mar. Geophys. Res. 6, 159–185.
TucholkeB. E. and MountainG. S., 1986, Tertiary paleoceanography of the western North Atlantic Ocean, in VogtP. R. and TucholkeB. E. (eds.),The Western North Atlantic Region Geol. Soc. Am., DNAG, Geology of North America, v. M, Boulder, Colorado, pp. 631–650.
Vinje, T. and Finnekåsa, Ø., 1986, The ice trasport through Fram Strait,Norsk Polarinst. Skr. 186, 39 pp.
VogtP. R., 1986, Sea floor topography, sediments and paleoenvironments and geophysical and geochemical structures of plate tectonics, in HurdleB. G. (ed.),The Nordic Seas. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp. 237–662.
Vogt, P. R., Bernero, C., Kovacs, L., and Taylor, P., 1981, Structure and plate tectonic evolution of the marine Arctic as revealed by aeromagnetics,Oceanol. Acta, Proc. 26th Inter. Geol. Cong., paris, 1980 pp. 25–40.
Volkov, P., 1961, New explorations of the bottom topography in the Greenland Sea, Translated from Morskoi Flot, 1961, 3, 35–37 by E. R. Hope DRB T 356 R.
WadhamsP. and SquireV. A., 1983, An ice-water vortex at the edge of the East Greenland Current,J. Geophys. Res. 88, 2770–2780.
Wüst, G., 1942, The morphological and oceanographic relations in the North Pole Basin, Dt. Wiss. Inst. Kopenhagen Veroeff., Ist. Ser., Arktis, No. 6, pp. 1–21.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thiede, J., Pfirman, S., Schenke, HW. et al. Bathymetry of Molloy Deep: Fram Strait between Svalbard and Greenland. Mar Geophys Res 12, 197–214 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02266713
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02266713