Abstract
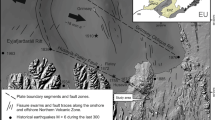
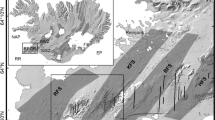
The Kane Transform offsets spreading-center segments of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge by about 150 km at 24° N latitude. In terms of its first-order morphological, geological, and geophysical characteristics it appears to be typical of long-offset (>100 km), slow-slipping (2 cm yr-1) ridge-ridge transform faults. High-resolution geological observations were made from deep-towed ANGUS photographs and the manned submersible ALVIN at the ridge-transform intersections and indicate similar relationships in these two regions. These data indicate that over a distance of about 20 km as the spreading axes approach the fracture zone, the two flanks of each ridge axis behave in very different ways. Along the flanks that intersect the active transform zone the rift valley floor deepens and the surface expression of volcanism becomes increasingly narrow and eventually absent at the intersection where only a sediment-covered ‘nodal basin’ exists. The adjacent median valley walls have structural trends that are oblique to both the ridge and the transform and have as much as 4 km of relief. These are tectonically active regions that have only a thin (<200 m), highly fractured, and discontinuous carapace of volcanic rocks overlying a variably deformed and metamorphosed assemblage of gabbroic rocks. Overprinting relationships reveal a complex history of crustal extension and rapid vertical uplift. In contrast, the opposing flanks of the ridge axes, that intersect the non-transform zones appear to be similar in many respects to those examined elsewhere along slow-spreading ridges. In general, a near-axial horst and graben terrain floored by relatively young volcanics passes laterally into median valley walls with a simple block-faulted character where only volcanic rocks have been found. Along strike toward the fracture zone, the youngest volcanics form linear constructional volcanic ridges that transect the entire width of the fracture zone valley. These volcanics are continuous with the older-looking, slightly faulted volcanic terrain that floors the non-transform fracture zone valleys. These observations document the asymmetric nature of seafloor spreading near ridge-transform intersections. An important implication is that the crust and lithosphere across different portions of the fracture zone will have different geological characteristics. Across the active transform zone two lithosphere plate edges formed at ridge-transform corners are faulted against one another. In the non-transform zones a relatively younger section of lithosphere that formed at a ridge-non-transform corner is welded to an older, deformed section that initially formed at a ridge-transform corner.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ARCYANA: 1975, ‘Transform Fault and Rift Valley from Bathyscaph and Diving Saucer’, Science 190, 108–116.
Atwater, T. et al.: 1979, ‘Expedition Cruise Report: AMAR 78 — A Coordinated Submersible, Photographic Mapping and Dredging Program in the Mid-Atlantic Rift Valleys Near 36.5° N’, Unpublished Report, 191 pp.
Atwater, T., Stakes, D., and Ballard, R. D.: 1981, ‘Structural Similarities and Differences Among the Rift Valleys Near the FAMOUS Area, Mid-Atlantic Ridge 37° N, Amer. Geophys. Union, Chapman Conf., (abstract).
BallardR. D. and vanAndelTj. H.: 1977, ‘Morphology and Tectonics of the Inner Rift Valley at Lat. 36° 50' N on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge’, Bull. Geol. Soc. Amer. 88, 507–530.
BallardR. D., vanAndelTj. H., and HolcombR. T.: 1982, ‘The Galapagos Rift at 86° W, 5, Variations in Volcanism, Structure and Hydrothermal Activity Along a 30 km Segment of the Rift Valley’, J. Geophys. Res. 87, 1149–1162.
BonattiE. and HonnorezJ.: 1976, ‘Sections of the Earth's Crust in the Equatorial Atlantic’, J. Geophys. Res. 81, 4104–4116.
BonattiE.: 1976, ‘Serpentinite Protrusions in the Oceanic Crust’, Earth Planet. Sci. Letters 37, 369–379.
BryanW. B., ThompsonG., and LuddenJ. N.: 1981, ‘Compositional Variation in Normal MORB from 22°–25° N: Mid-Atlantic Ridge and Kane Fracture Zone’, J. Geophys. Res. 86, 11815–11836.
CAYTROUGH: 1979, ‘Geological and Geophysical Investigation of the Mid-Cayman Rise Spreading Center: Initial Results and Observations’, in M.Talwani, C. G.Harrison, D. E.Hayes (eds.), Deep Drilling Results in the Atlantic Ocean: Oceanic Crust, Maurice Ewing Series, 2, Amer. Geophys. Union, Wash., D.C., 66–95.
ChoukrouneP., FrancheteauJ., and LePichonX.: 1978, ‘In situ Structural Observations along Transform Fault A in the FAMOUS Area, Mid-Atlantic Ridge’, Bull. Geol. Soc. Amer. 89, 1013–1029.
CNEXO: 1979, ‘Bilan des Releves SEA-BEAM et Etablissement de Cartes, Realisées au Sein du Departement’, CNEXO Rapport Scientifique 1979, 96.
CormierM. H., DetrickR. S., and PurdyG. M.: 1982, ‘Seismic Constraints on Crustal Thickness Variations along the Kane Fracture Zone’, Trans. Amer. Geophys. Union, EOS 63, 1100.
CortillotV. P., TapponierP., and VaretJ.: 1974, ‘Surface Features Associated With Transform Faults: A Comparison between Observed Examples and an Experimental Model’, Tectonophysics 24, 317–329.
CraneK.: 1976, ‘The Intersection of the Siquieros Transform Fault and the East Pacific Rise’, Marine Geology 21, 25–46.
CraneK. and BallardR. D.: 1981, ‘Volcanics and Structure of the FAMOUS Narrowgate Rift: Evidence for Cyclic Evolution’, J. Geophys. Res. 86, 5112–5124.
CYAMEX Scientific Team: 1981, ‘First Manned Submersible Dives on the East Pacific Rise at 21° N (Project RITA): General Results’, Marine Geophys. Res. 4, 345–379.
CYAMEX Scientific Team and Pastouret, L.: 1981, ‘Submersible Structural Study of Tamayo Transform Fault: East Pacific Rise, 23° N (Project RITA)’, Marine Geophys. Res. 4, 381–401.
DelaneyJ. R., MogkD. W., and MottlM. J.: 1980, ‘High-Temperature Sulphide-Bearing Hydrothermal System in the Mid-Atlantic Ridge at 23.6° N’, Geol. Soc. Amer., Abstracts with Programs 12, 411.
DeLongS. E., DeweyJ. F., and FoxP. J.: 1977, ‘Displacement History of Oceanic Fracture Zones’, Geology 5, 199–202.
DeLongS. E., DeweyJ. F., and FoxP. J.: 1979, ‘Topographic and Geologic Evolution of Fracture Zones’, J. Geol. Soc. of London 136, 303–310.
DetrickR. S. and PurdyG. M.: 1980, ‘Crustal Structure of the Kane Fracture Zone from Seismic Refraction Studies’, J. Geophys. Res. 85, 3759–3777.
DetrickR. S., MudieJ. D., LuyendykB. P., and MacdonaldK. C.: 1973, ‘Near Bottom Observations of an Active Transform Fault: Atlantic Ridge at 37° N’, Nature 246, 56–61.
DickH. J. B., ThompsonG., and LowensteinT.: 1980, ‘Layered Gabbros from the Kane Fracture Zone Near 23° 45' N on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge’, Geol. Soc. Amer. Abstracts with Programs 12, 412–413.
DickH. J. B., ThompsonG. A., and BryanW. B.: 1981, ‘Low-Angle Faulting and Steady-State Emplacement of Plutonic Rocks at Ridge-Transform Intersections’, Amer. Geophys. Union, EOS 62, 406.
EittreimS. and EwingJ.: 1975, ‘Vema Fracture Zone Transform Fault’, Geology 3, 555–558.
FoxP. J., PitmanW. C.III, and ShepardF.: 1969, ‘Crustal Plates in the Central Atlantic: Evidence for at Least Two Poles of Rotation’, Science 165, 487–489.
Fox, P. J., Detrick, R. S., and Purdy, G. M.: 1980, ‘Evidence for Crustal Thinning Near Fracture Zones: Implications for Ophiolites’, in A. Panayiotou, (ed.), Proceedings of the International Ophiolite Symposium, Cyprus Geological Survey Dept. 161–168.
Fox, P. J. and Gallo, D. G.: 1983, ‘A Tectonic Model for Ridge-Transform-Ridge Plate Boundaries: Implications for the Structure of Oceanic Lithosphere’, Tectonophysics (in press).
Fox, P. J., Schroeder, F., Moody, R., and Pitman, W. C.: 1983, ‘The Morphotectonic Character of the Oceanographer Fracture Zone’, (in prep.).
FoxP. J., SchreiberE., RowlettH., and McCamyK.: 1976, ‘Geology of the Oceanographer Fracture Zone: A Model for Fracture Zones’, J. Geophys. Res. 81, 4117–4128.
FrancheteauJ., ChoukrouneP., HekinianR., LePichonX., and NeedhamH. D.: 1976, ‘Oceanic Fracture Zones Do not Provide Deep Sections of the Crust’, Can. J. Earth Sci. 13, 1223–1235.
GalloD. G. and FoxP. J.: 1979, ‘The Influence of Transform Faults on the Generation of Oceanic Lithosphere’, Trans. Amer. Geophys. Union, EOS 60, 376.
HeyR., DuennebierR. K., and MorganW. J.: 1980, ‘Propagating Rifts on Mid-Ocean Ridges’, J. Geophys. Res. 85, 3647–3658.
JohnsonG. L. and VogtP. R.: 1973, ‘Mid-Atlantic Ridge from 47° to 51° N’, Geol. Soc Amer. Bull. 84, 3443–3462.
Karson, J. A.: 1981, ‘Shallow Crustal Deformation on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge at 24° N Lat’, Amer. Geophys. Union, Chapman Conf. (abstract).
KarsonJ. A. and DeweyJ. F.: 1978, ‘Coastal Complex, Western Newfoundland: an Early Ordovician Oceanic Fracture Zone’, Bull. Geol. Soc. Amer. 89, 1037–1049.
KarsonJ. A., DickH. J. B., BryanW. B., and ThompsonG.: 1980, ‘Tectonics of Ridge-Transform Intersections at the Kane Fracture Zone’, Geol. Soc. Amer. Abstracts with Programs 12, 458.
Karson, J. A.: 1983, ‘Variations in Structure and Petrology in the Coastal Complex, Newfoundland: The Anatomy of an Oceanic Fracture Zone’, J. Geol. Soc. London (in press).
KarsonJ. A., ElthonD. E., and DeLongS. E.: 1983, ‘Intrusive Lherzolites of the Lewis Hills Massif, Bay of Islands Ophiolite Complex: Implications for Igneous Processes along Oceanic Fracture Zones’, Bull. Geol. Soc. Amer. 94, 15–29.
LonsdaleP. and ShorA.: 1979, ‘The Oblique Intersection of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge with the Charlie-Gibbs Transform Fault’, Tectonophysics 54, 195–209.
LoudenK. E. and ForsythD. W.: 1982, ‘Crustal Structure and Isostatic Compensation Near the Kane Fracture Zone from Topography and Gravity Measurements — I. Spectral Analysis Approach’, Geophys. J. Royal Astr. Soc. 68, 725–750.
LuyendykB. P. and MacdonaldK. C.: 1977, ‘Physiography and Structure of the Inner Floor of the FAMOUS Rift Valley: Observations with a Deep-Towed Instrument Package’, Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull. 88, 648–663.
MacdonaldK. C. and LuyendykB. P.: 1977, ‘Deep-Tow Studies of the Structure of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge Crest Near Lat. 37° N’, Bull. Geol. Soc. Amer. 89, 621–636.
MacdonaldK. C., KastensK., SpiessF. N., and MillerS. P.: 1979, ‘Deep-Tow Studies of the Tamayo Transform Fault’, Marine Geophys. Res. 4, 37–70.
Machado, N., Ludden, J., and Brooks, C.: 1981, ‘The Isotropic Character of the Atlantic Ocean Mantle at 23° N’, Amer. Geophys. Union, Chapman Conf. (abstract).
MalcolmF. L.: 1981, ‘Microstructures of the Cayman Trough Gabbros’, J. Geol. 89, 675–688.
MelsonW. G., JarosewichE., BowenV. T., and ThompsonG.: 1967, ‘St. Peter and St. Paul Rocks: A High-Temperature Mantle-Derived Intrusion’, Science 155, 1532–1535.
MinsterJ. B. and JordanT.: 1978, ‘Present Day Plate Motions’, J. Geophys. Res. 83, 5331–5354.
MiyashiroA., ShidoF., and EwingM.: 1969, ‘Composition and Origin of Serpentinites from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge Near 24° and 30° North Latitude’, Contrib Min. Petrol. 23, 117–127.
MiyashiroA., ShidoF., and EwingM.: 1970, ‘Crystallization and Differentiation in Abyssal Tholeiites and Gabbros from Mid-Ocean Ridges’, Earth Planet. Sci. Letters 7, 361–365.
MiyashiroA., ShidoF., and EwingM.: 1971, ‘Metamorphism in the Mid-Atlantic Ridge Near 24° and 30° N’, Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London (A), 268, 589–603.
OTTER Scientific Team (a): 1983, ‘The Geology of Oceanographer Transform: The Ridge-Transform Intersection’, Marine Geophys. Res. (in press).
OTTER Scientific Team (b): 1983, ‘The Geology of the Oceanographer Transform: The Transform Domain’, (in press).
PhillipsJ. D., DriscollA. H., PealK. R., MarquetW. M., and OwenD. M.: 1979, ‘A New Undersea Geological Survey Tool: ANGUS’, Deep-Sea Res. 26A, 211–226.
Phillips, J. D., and Fleming, H. S.: 1978, ‘Multi-Beam Sonar Study of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge Rift Valley, 36°–37° N’, Geol. Soc. Amer. Map MC-19.
PurdyG. M. and RabinowitzP. D.: 1978, ‘The Kane Fracture Zone at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge: IPOD sites 395 and 396’, in W. G. Melson, P. D. Rabinowitz, et al., Initial Reports of the DSDP, Leg 45, U.S. Govt. Printing Office, Washington, D.C., color map supplement.
PurdyG. M., RabinowitzP. D., and SchoutenH.: 1978, ‘The Mid-Atlantic Ridge at 23° N: Bathymetry and Magnetics’, in W. G. Melson, P. D. Rabinowitz, et al., Initial Reports of the Deep-Sea Drilling Project, Leg 45, U.S. Govt. Printing Office, Washington, D.C., 119–128.
PurdyG. M., RabinowitzP. D., and VelteropJ. J. A.: 1979, ‘The Kane Fracture Zone in the Central Atlantic Ocean’, Earth Planet. Sci. Letters 45, 429–434.
PurdyG. M., SchoutenH., CroweJ. et al.: 1978, ‘IPOD Survey Area AT-6: A Site Survey’, in W. G. Melson, P. D. Rabinowitz, et al., Initial Reports of the Deep-Sea Drilling Project, Leg 45, U.S. Govt. Printing Office, Washington, D.C., 39–48.
PurdyG. M., DetrickR. S., and CormierM. H.: 1982, ‘Seismic Constraints on the Crustal Structure at a Ridge-Fracture Zone Intersection’, Trans. Amer. Geophys. Union, 63, 1100.
RabinowitzP. D. and PurdyG. M.: 1976, ‘The Kane Fracture Zone in the Western Central Atlantic Ocean’, Earth Planet. Sci. Letters 33, 21–26.
RonaP. A. and GrayD. F.: 1980, ‘Structural Behavior of Fracture Zones Symmetric and Asymmetric About a Spreading Axis: Mid-Atlantic Ridge (latitude 23° N to 27° N)’, Bull. Geol. Soc. Amer. 91, 485–494.
RowlettH.: 1981, ‘Seismicity at Intersections of Spreading Centers and Transform Faults’, J. Geophys. Res. 86, 3815–3820.
ScholzC. H., WyssM., and SmithS. W.: 1969, ‘Seismic and Aseismic Slip on the San Andreas Fault’, J. Geophys. Res. 74, 2049–2069.
SchoutenH., KarsonJ. A., and DickH. J. B.: 1980, ‘Geometry of Transform Zones’, Nature 288, 470–473.
SearleR. C.: 1979, ‘Side-Scan Sonar Studies of North Atlantic Fracture Zones’, J. Geol. Soc. London 136, 283–292.
SearleR. C.: 1981, ‘The Active Part of the Charlie-Gibbs Fracture Zone: A Study Using Sonar and Other Geophysical Techniques’, J. Geophys. Res. 86, 243–262.
SearleR. C. and LaughtonA. S.: 1977, ‘Sonar Studies of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and Kurchatov Fracture Zone’, J. Geophys. Res. 82, 5313–5328.
Shih, J. S.-F.: 1980, ‘The Nature and Origin of Fine-Scale Sea-Floor Relief’, Unpubl. Ph.D. Dissert., MIT/WHOI Joint Program in Oceanography, 222 p.
SleepN. H. and BiehlerS.: 1970, ‘Topography and Tectonics of the Intersections of Fracture Zones with Central Rifts’, J. Geophys. Res. 75, 2748–2752.
StroupJ. B. and FoxP. J.: 1981, ‘Geologic Investigations in the Cayman Trough: Evidence for Thin Crust along the Mid-Cayman Rise’, J. Geol. 89, 395–420.
SykesL. R.: 1967, ‘Mechanism of Earthquakes and Nature of Faulting on the Mid-Oceanic Ridge’, J. Geophys. Res. 72, 2131–2153.
Tamayo Scientific Team: 1983, ‘Tectonics at the East Pacific Rise/Tamayo Transform Fault Intersection’, Marine Geophys. Res. (in press).
TchalenkoJ. S.: 1970, ‘Similarities Between Shear Zones of Different Magnitudes’, Bull. Geol. Soc. Amer. 81, 1625–1640.
TempleD. G., ScottR. B., and RonaP. A.: 1979, ‘Geology of a Submarine Hydrothermal Field, Mid-Atlantic Ridge, 26° N Latitude’, J. Geophys. Res. 84, 7453–7466.
Thompson, G., Bryan, W. B., Dick, H. J. B., Mottl, M., Karson, J. A., and Delaney, J.: 1981, ‘Stratigraphic, Lithologic, and Geochemical Variations in Layer 2 and 3 as Observed at the Intersection of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and the Kane Fracture Zone’, Amer. Geophys. Union, Chapman Conf. (abstract).
ThompsonG. and MelsonW. G.: 1972, ‘The Petrology of Oceanic Crust Across Fracture Zones in the Atlantic Ocean: Evidence of a New Kind of Seafloor Spreading’, J. Geol. 80, 526–538.
TucholkeB. E., HoutzR. E., and LudwigW. J.: 1982, ‘Sediment Thickness and Depth to Basement in the Western North Atlantic Ocean Basin’, Amer. Assoc. Petrol. Geol. Bull. 66, 1384–1395.
vanAndelTj. H., VonHerzenR. P., and PhillipsJ. D.: 1971, ‘The Vema Fracture Zone and the Tectonics of Transform Shear Zones in Oceanic Crustal Plates’, Mar. Geophys. Res. 1, 261–283.
VogtP. R., JohnsonG. L., HolcombeT. L., GiilgJ. G., and AveryA. E.: 1971, ‘Episodes of Seafloor Spreading Recorded by the North Atlantic Basement’, Tectonophysics 12, 211–234.
WhitmarshR. B. and LaughtonA. S.: 1975, ‘The Fault Pattern of a Slow-Spreading Ridge Near a Fracture Zone’, Nature 258, 509–510.
WilcoxR., HardingT., and SealyD. R.: 1973, ‘Basic Wrench Tectonics’, Amer. Assoc. Petrol. Geol. Bull. 57, 74–96.
WilsonJ. T.: 1965, ‘A New Class of Faults and Their Bearing on Continental Drift’, Nature 207, 343–347.
YuenD. A., FleitoutL., SchubertG., and FroidevauxC.: 1978, ‘Shear Deformation Zones along Major Transform Faults and Subducting Slabs’, Geophys. J. Royal Astr. Soc. 54, 94–119.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karson, J.A., Dick, H.J.B. Tectonics of ridge-transform intersections at the Kane fracture zone. Mar Geophys Res 6, 51–98 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00300398
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00300398