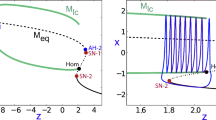
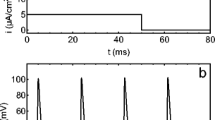
Abstract
We present a two-variable delay-differential-equation model of a pyramidal cell from the electrosensory lateral line lobe of a weakly electric fish that is capable of burst discharge. It is a simplification of a six-dimensional ordinary differential equation model for such a cell whose bifurcation structure has been analyzed (Doiron et al., J. Comput. Neurosci., 12, 2002). We have modeled the effects of back-propagating action potentials by a delay, and use an integrate-and-fire mechanism for action potential generation. The simplicity of the model presented here allows one to explicitly derive a two-dimensional map for successive interspike intervals, and to analytically investigate the effects of time-dependent forcing on such a model neuron. Some of the effects discussed include ‘burst excitability’, the creation of resonance tongues under periodic forcing, and stochastic resonance. We also investigate the effects of changing the parameters of the model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Av-Ron, E., H. Parnas and L. A. Segel (1993). A basic biophysical model for bursting neurons. Biol. Cybern. 69, 87–95.
Booth, V. and A. Bose (2001). Neural mechanisms for generating rate and temporal codes in model CA3 pyramidal cells. J. Neurophysiol. 85, 2432–2445.
Chacron, M. J., A. Longtin and L. Maler (2001). Negative interspike interval correlations increase the neuronal capacity for encoding time-dependent stimuli. J. Neurosci. 21, 5328–5343.
Coombes, S. and P. C. Bressloff (1999). Mode locking and Arnold tongues in integrate-and-fire neural oscillators. Phys. Rev. E 60, 2086–2096.
Coombes, S., M. R. Owen and G. D. Smith (2001). Mode locking in a periodically forced integrate-and-fire-or-burst neuron model. Phys. Rev. E 64, 041914.
de Vries, G. (1998). Multiple bifurcations in a polynomial model of bursting oscillations. J. Nonlinear Sci. 8, 281–316.
Doiron, B., A. Longtin, R. W. Turner and L. Maler (2001a). Model of gamma frequency burst discharge generated by conditional backpropagation. J. Neurophysiol. 86, 1523–1545.
Doiron, B., L. Noonan, R. W. Turner, A. Longtin and L. Maler (2001b). Shifting burst threshold with dendritic conductances, XXXI Proc. Soc. Neurosci., San Diego.
Doiron, B., C. R. Laing, A. Longtin and L. Maler (2002). “Ghostbursting”: a novel bursting mechanism in pyramidal cells. J. Comput. Neurosci. 12, 5–25.
Drazin, P. G. (1992). Nonlinear Systems, Cambridge University Press.
Ermentrout, G. B. and N. Kopell (1998). Fine structure of neural spiking and synchronization in the presence of conduction delays. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 1259–1264.
Gammaitoni, L., P. Hänggi, P. Jung and F. Marchesoni (1998). Stochastic resonance. Rev. Mod. Phys. 70, 223–287.
Glass, L. and M. C. Mackey (1988). From Clocks to Chaos: The Rhythms of Life, Princeton University Press.
Glass, L. (1991). Cardiac arrhythmias and circle maps—a classical problem. Chaos 1, 13–19.
Goldbeter, A. (1996). Biochemical Oscillations and Cellular Rhythms: The Molecular Bases of Periodic and Chaotic Behaviour, Cambridge University Press.
Guevara, M. L., L. Glass and A. Shrier (1981). Phase locking, period-doubling bifurcations, and irregular dynamics in periodically stimulated cardiac cells. Science 214, 1350–1353.
Gutkin, B. S. and G. B. Ermentrout (1998). Dynamics of membrane excitability determine interspike interval variability: a link between spike generation mechanism and cortical spike train statistics. Neural Comput. 10, 1047–1065.
Häusser, M., N. Spruston and G. J. Stuart (2000). Diversity and dynamics of dendritic signaling. Science 290, 739–744.
Izhikevich, E. M. (2000). Neural excitability, spiking, and bursting. Int. J. Bifn. Chaos 10, 1171–1266.
Johnston, D., J. C. Magee, C. M. Colbert and B. R. Christie (1996). Active properties of neuronal dendrites. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 19, 165–186.
Keener, J. P., F. C. Hoppensteadt and J. Rinzel (1981). Integrate-and-fire models of nerve membrane response to oscillatory input. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 41, 503–517.
Keener, J. and J. Sneyd (1998). Mathematical Physiology, Interdisciplinary Applied Mathematics, Vol. 8, New York: Springer.
Kepecs, A. and X.-J. Wang (2000). Analysis of complex bursting in cortical pyramidal neuron models. Neurocomputing 32–33, 181–187.
Kuznetsov, Y. A. (1995). Elements of Applied Bifurcation Theory, Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 112, Springer.
Laing, C. R. (2002). The response of bursting neurons to sinusoidal inputs. In preparation.
Laing, C. R., B. Doiron, A. Longtin and L. Maler (2002a). Ghostbursting: the effects of dendrites on spike patterns. To appear in Neurocomputing.
Laing, C. R., B. Doiron, A. Longtin, L. Noonan, R. W. Turner and L. Maler (2002b). Burst excitability. Submitted to J. Comput. Neurosci.
Lemon, N. and R. W. Turner (2000). Conditional spike backpropagation generates burst discharge in a sensory neuron. J. Neurophysiol. 84, 1519–1530.
Lisman, J. E. (1997). Bursts as units of neural information: making unreliable synapses reliable. Trends Neurosci. 20, 38–43.
Mainen, Z. F. and T. J. Sejnowski (1996). Influence of dendritic structure on firing pattern in model neocortical neurons. Nature 382, 363–366.
Nelson, M. E., Z. Xu and J. R. Payne (1997). Characterization and modeling of P-type electrosensory afferent responses to amplitude modulations in a wave-type electric fish. J. Comp. Physiol. A 181, 532–544.
Noonan, L., B. Doiron, C. R. Laing, A. Longtin and R. W. Turner (2002). Dendritic spike repolarization generates a dynamic refractory period to control burst discharge. In preparation.
Pinsky, P. F. and J. Rinzel (1994). Intrinsic and network rhythmogenesis in a reduced Traub model for CA3 neurons. J. Comput. Neurosci. 1, 39–60.
Pomeau, Y. and P. Manneville (1980). Intermittent transition to turbulence in dissipative dynamical systems. Comm. Math. Phys. 74, 189–197.
Press, W. H., S. A. Teukolsky, W. T. Vetterling and B. P. Flannery (1992). Numerical Recipes in C, 2nd edn, Cambridge University Press.
Rinzel, J. and G. B. Ermentrout (1998). Analysis of neural excitability and oscillations, in Methods in Neuronal Modeling: From Ions to Networks, C. Koch and I. Segev (Eds), MIT Press.
Rulkov, N. F. (2000). Regularization of synchronized chaotic bursts. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 183–186.
Segev, I. and W. Rall (1998). Excitable dendrites and spines: earlier theoretical insights elucidate recent direct observations. Trends Neurosci. 21, 453–460.
Sivan, E., L. Segel and H. Parnas (1995). Modulated excitability: a new way to obtain bursting neurons. Biol. Cybern. 72, 455–461.
Smith, G. D., C. L. Cox, S. M. Sherman and J. Rinzel (2000). Fourier analysis of sinusoidally driven thalamocortical relay neurons and a minimal integrate-and-fire-or-burst model. J. Neurophysiol. 83, 588–610.
Steriade, M., I. Timofeev, N. Dürmüller and F. Grenie (1998). Dynamic properties of corticothalamic neurons and local cortical interneurons generating fast rhythmic (30–40 Hz) spike bursts. J. Neurophysiol. 79, 483–490.
Strogatz, S. H. (1994). Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos: With Applications to Physics, Biology, Chemistry, and Engineering, Reading: Addison-Wesley.
Terman, D. (1992). The transition from bursting to continuous spiking in excitable membrane models. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2, 135–182.
Traub, R. D., M. A. Whittington, I. M. Stanford and J. G. Jefferys (1996). A mechanism for generation of long-range synchronous fast oscillations in the cortex. Nature 383, 621–624.
Turner, R. W. (2002). Personal communication.
Vetter, P., A. Roth and M. Häusser (2001). Propagation of action potentials in dendrites depends on dendritic morphology. J. Neurophysiol. 85, 926–937.
Wang, X.-J. (1993). Genesis of bursting oscillations in the Hindmarsh-Rose model and homoclinicity to a chaotic saddle. Physica D 62, 263–274.
Wang, X.-J. (1999). Fast burst firing and short-term synaptic plasticity: a model of neocortical chattering neurons. Neuroscience 89, 347–362.
Yoshino, K., T. Nomura, K. Pakdaman and S. Sato (1999). Synthetic analysis of periodically stimulated excitable and oscillatory membrane models. Phys. Rev. E 59, 956–969.
Zupanc, G. K. H. and L. Maler (1993). Evoked chirping in the weakly electric fish (Apteronotus leptorhynchus): a quantitative biophysical analysis. Can. J. Zool. 71, 2301–2310.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laing, C.R., Longtin, A. A two-variable model of somatic-dendritic interactions in a bursting neuron. Bull. Math. Biol. 64, 829–860 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1006/bulm.2002.0303
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/bulm.2002.0303