Abstract
Background
Genetic manipulation techniques, such as transfection, have been previously reported in many protozoan parasites. In Babesia, stable transfection systems have only been established for bovine Babesia parasites. We recently reported a transient transfection system and the selection of promoter candidates for Babesia gibsoni. The establishment of a stable transfection system for B. gibsoni is considered to be urgent to improve our understanding of the basic biology of canine Babesia parasites for a better control of babesiosis.
Results
GFP-expressing parasites were observed by fluorescence microscopy as early as two weeks after drug selection, and consistently expressed GFP for more than 3 months without drug pressure. Genome integration was confirmed by PCR, sequencing and Southern blot analysis.
Conclusions
We present the first successful establishment of a stable transfection system for B. gibsoni. This finding will facilitate functional analysis of Babesia genomes using genetic manipulation and will serve as a foundation for the development of tick-Babesia and host-Babesia infection models.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Babesia gibsoni is a tick-borne intraerythrocytic apicomplexan parasite which causes canine babesiosis [1]. During the asexual phase of its life-cycle occurring in the vertebrate host, B. gibsoni causes progressive anemia, remittent fever, hemoglobinuria, marked splenomegaly, hepatomegaly and sometimes death [2]. Babesia gibsoni has a global distribution, with considerable a significant impact on canine health [3].
The difficulties in identifying B. gibsoni virulence factors and developing successful therapies have been attributed in part to the lack of genetic manipulation tools [4]. Transfection systems have been established for several apicomplexan parasites, such as Cryptosporidium parvum [5], Plasmodium falciparum [6], Toxoplasma gondii [7], Theileria annulata [8] and T. parva [9]. Among Babesia species, transient and stable transfection systems have been reported for B. bovis [10], B. ovata [11] and B. bigemina [12]. For B. gibsoni, only two reports have described transient transfection systems [13, 14]. Babesia gibsoni elongation factor-1 alpha (Bg 5′-ef-1α) promoter, Program FA113 of AMAXA 4D Nucleofector™ and Lonza buffer SF successfully supported the expression of reporter genes [13]. In addition, among the 12 promoter candidates tested, Bg 5′-actin was found to be the most active promoter [14]. Similar to B. bovis [15], the development of a stable transfection system for B. gibsoni parasites requires a drug selection system and an integration target. The WR99210/human dihydrofolate reductase gene (hdhfr) selection system and double cross-over homologous recombination locus have previously been successfully used for B. bovis [16] and B. ovata [11] stable transfection.
In this study, in order to establish B. gibsoni stable transfection, we investigated whether stable transfection of GFP-expressing B. gibsoni could be achieved using hdhfr as a selectable marker under the control of the Bg 5′-ef-1α (IG-B) and Bg 5′-actin promoters, and ef-1α locus as the integration target.
Methods
Parasite culture
In this study, B. gibsoni Oita strain [17] was cultured in vitro in 24-well culture plates (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) at 37 °C in humidified CO2 (5%) and O2 (5%) incubator (BIO-LABO, Tokyo, Japan). The parasite was cultured in 10% canine erythrocytes suspended in RPMI-1640 supplemented with 20% canine serum.
Evaluation of B. gibsoni sensitivity to WR99210
Babesia gibsoni was cultured in vitro in 96-well culture plates with 100 μl RPMI-1640 medium containing 10% canine erythrocytes supplemented with 20% dog serum and different concentrations of WR99210 (0.1, 0.5, 1, 5, 10 and 100 nM). For each drug concentration, parasites were cultured in triplicate wells and the culture medium was replaced daily. Parasitemia was calculated on day 3 by examining 3000 RBCs of a prepared thin blood smear stained with Giemsa solution.
Plasmid constructs
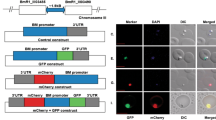
The schematic diagram of the plasmid used in this study (pBS-EGRADE) is shown in Fig. 1a. The reporter gene and drug selection gene cassettes were separated in order to drive gfp and hdhfr with Bg 5′-ef-1α (IG-B) and Bg 5′-actin promoters, respectively. Bg 5′-ef-1α (IG-B) and Bg 3′-ef-1α were used as recombination sites cloned into the upstream and downstream of the gfp and hdhfr genes, respectively. All the PCR primer pairs used for plasmid construction are listed in Table 1 and restriction sites are underlined. The constructed plasmid was purified using Qiagen® Plasmid Maxi Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer's instructions, and was confirmed by sequencing before transfection. The sequence of pBS-EGRADE plasmid was deposited in the GenBank database under the accession number MG913246.
Schematic diagram of GFP-expressing plasmid (pBS-EGRADE) construct and fluorescence microscopy images of stably expressing GFP B. gibsoni. a Plasmid construct of pBS-EGRADE showing the recombination sites for integration into ef-1α locus by double cross-over homologous recombination. The restriction site for linearization (Kpn I) is shown. b Fluorescence microscopy images of stable GFP-expressing B. gibsoni. Merged panel shows overlap of GFP and Hoechst (parasite nuclei) fluorescence. The parasite nucleus was stained with Hoechst 33342
Transfection of parasites
Babesia gibsoni-infected red blood cells (iRBCs) were pre-treated as previously described [13]. Transfection was conducted using 20 μg of linearized pBS-EGRADE plasmid. The plasmid-iRBCs mixtures were transfected using Lonza buffer SF and program FA113 of Amaxa 4D Nucleofector™ device (Lonza, Cologne, Germany) and immediately transferred into a preheated culture containing 10% fresh RBCs. To avoid the rapid in vitro aging of canine erythrocytes, transfected parasites were subcultured every week and supplemented with fresh RBCs. To select GFP-expressing transgenic parasites, 10 nM WR99210 was added to the culture medium two days after transfection. After 4 weeks of drug selection, the parasite population was cloned in a 96-well culture plate using limiting dilution as previously described [16].
PCR characterization of GFP-expressing B. gibsoni
Three sets of primers (Table 1) were used to confirm the integration of pBS-EGRADE into B. gibsoni ef-1α locus. Primer pair Integ-F and GFP-R was used to amplify a 1.6 kb DNA fragment to confirm the 5′ recombination. Primer pair hDHFR-F and Integ-R was used to amplify a 2.0 kb DNA fragment to examine the 3′ recombination whereas primer pair GFP-F and hDHFR-R was used to amplify a 4.1 kb DNA fragment to detect the insertion region. The DNA fragments amplified were confirmed by sequencing.
Southern blot analysis
Two micrograms of genomic DNA from wild type (WT) and genome integrated (GI) B. gibsoni were digested overnight with 20 units of Sca I and Sph I. The digestion products were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis, transferred onto Hybond N+ membrane (GE Healthcare, Buckinghamshire, UK) then hybridized with labeled probes using an AlkPhos Direct Kit (GE Healthcare, Buckinghamshire, UK) according to the manufacturer′s instructions. Two probes corresponding to the complete open reading frame (ORF) of gfp and the 0.4 kb length of Bg 3′-ef-1α fragment, respectively, were used. The primer pairs used to amplify the probes are listed in Table 1. Probe signal was detected using a CDP-star detection reagent (GE Healthcare).
Growth curves
WT and GI parasites were continuously cultured from approximately 0.5% parasitemia by sub-culturing every 3 days for two generations. Parasitemia were monitored daily by examining 3000 RBCs with Giemsa staining.
Results
Babesia gibsoni sensitivity to WR99210
WR99210 successfully inhibited the growth of B. gibsoni in vitro at a nanomolar concentration (Additional file 1: Figure S1). The calculated IC50 was 1.1 nM, and 10 nM WR99210 completely inhibited the growth of B. gibsoni. Thus, 10 nM WR99210 was used for the selection of transfected parasites.
Establishment of stable GFP expression in B. gibsoni
GFP-expressing parasites emerged as early as two weeks after drug selection with 10 nM WR99210. The parasite population was cloned by limiting dilution and consistently expressed GFP for more than 3 months without drug pressure (Fig. 1b). After obtaining parasite clonal lines, the correct integration of pBS-EGRADE into the ef-1α locus was confirmed by the results of both PCR and Southern blot analysis. The PCR-1, -2 and -3 primer pairs successfully amplified 1.6, 2.0 and 4.1 kb DNA fragments, respectively, using DNA template from one clonal line named GI parasite (Fig. 2a) and the amplified DNA fragments were validated by sequencing. The sequences of the above DNA fragments were deposited in the GenBank database under the accession numbers MH087225-MH087227. No amplicons were obtained with DNA template from the WT parasite. In Southern blot analysis, both gfp and 3′-ef-1α probes detected a single 5.5 kb band for GI parasite, while the 3′-ef-1α probe detected a single 2.1 kb band, and the gfp probe did not detect any band for the WT parasite (Fig. 2b). In addition, the growth curves of WT and GI parasites showed high similarity (Additional file 2: Figure S2).
Confirmation of integration of pBS-EGRADE into the ef-1α locus. a Schematic diagram and results of PCR to confirm the integration of pBS-EGRADE into the ef-1α locus. PCR-1, -2 and -3 were done with primer sets Integ-F/GFP-R, hDHFR-F/Integ-R and GFP-F/hDHFR-R, respectively. b Schematic diagram and Southern blot analysis to confirm the integration of pBS-EGRADE into ef-1α locus. Two μg of samples genomic DNA were digested with Sca I and Sph I, and hybridized with 3′-ef-1α and gfp probes. Abbreviations: GI, genome-integrated; WT, wild type; C-, pBS-EGRADE plasmid control
Discussion
Transfection systems improve our understanding of the molecular biology of parasites and pave the way for genetic manipulation [18]. The application of transfection systems can also lead to a better understanding of the mechanisms underlying drug resistance, host-parasite interactions, and provide novel information for vaccine development and drug target discovery [19]. Currently, there is a lack of techniques for the genetic manipulation of B. gibsoni. In order to fill this gap, we describe herein the development of a stable transfection system for B. gibsoni.
In this study, we employed a WR99210/hdhfr selection system for B. gibsoni stable transfection. The IC50 of WR99210 against B. gibsoni was 1.1 nM (Additional file 1: Figure S1), which is similar to B. bovis (1 nM) [16] and almost twice that of the one reported for B. ovata (0.56 nM) [11]. The transfected parasite selected with WR99210/hdhfr emerged as early as two weeks after adding the drug, indicating the suitability of this selection system for stable transfection of B. gibsoni. Babesia bovis 3′-rap was successfully used as terminator in this study (Fig. 1a). This result is consistent with our previous work [14], confirming that Bb 3′-rap heterologous terminator is fully functional in B. gibsoni. These findings provide considerable flexibility in the construction of plasmid vectors to be used for transfection systems in Babesia species. The cloned GI parasite stably expressed GFP (Fig. 1b) and PCR amplicons (Fig. 2a) and Southern blot analyses (Fig. 2b) indicated that pBS-EGRADE was integrated into B. gibsoni genome by homologous recombination as expected. In addition, the growth of GI parasite was comparable with that of the WT parasite (Additional file 2: Figure S2). These results indicate that the genetic manipulations in this study did not affect the growth of parasite in vitro.
The proliferation of Babesia organisms in the vectors is an essential part of their survival. However, the detailed life-cycle of the parasite in ticks, including information about the timing of migration, remains unknown [20]. Haemaphysalis longicornis, a vector for B. gibsoni [21], is widely used as a model tick to study pathophysiology in tick infestation [22]. Therefore, transfected B. gibsoni and H. longicornis could be used for developing tick-Babesia experimental models for clarifying the kinetics of the tick stage of canine Babesia parasites. A tick-Babesia interactions model may contribute to a better understanding of tick transmission as well as the way Babesia species interact with the ticks.
All previously established transfection systems for Babesia focused on bovine Babesia species, which were transfected using Gene Pulser Xcell™ Electroporation system (Bio-Rad, VA, USA) and AMAXA Nucleofector™ 2b device (Lonza) [10,11,12]. However, these transfection systems were not effective for B. gibsoni [13]. Therefore, the present method based on 4D Nucleofector™ may provide a more suitable transfection system for non-bovine Babesia parasites, such as B. gibsoni. The rapid in vitro aging of canine erythrocytes [23] may play an important role in restricting a successful transfection. Therefore, to avoid the rapid aging of canine erythrocytes, we strongly suggest subculturing every week by fresh RBCs after transfection. A host-Babesia infection model may be easier to achieve using canine Babesia rather than bovine Babesia because using dogs for animal experiments is more feasible than using cattle. The urgently needed genome edited host-Babesia infection model may help us monitor transmission in vivo, investigate mechanisms of infection and immunity, and also improve the development of novel strategies for controlling babesiosis.
Conclusions
In summary, we established a stable transfection system for B. gibsoni and successfully integrated exogenous genes into the B. gibsoni genome. The establishment of this system is critical to fulfill genome editing, which may contribute to determining gene function, discovery of novel drug targets, establishment of infection model and evaluation of the interactions between the parasite and the host.
Abbreviations
- ef-1α :
-
Elongation factor-1 alpha
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- GI:
-
Genome integrated
- hdhfr :
-
Human dihydrofolate reductase
- IG:
-
Intergenic region
- iRBCs:
-
Infected red blood cell
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- rap-1 :
-
Rhoptry associated protein-1
- RBCs:
-
Red blood cell
- RT:
-
Room temperature
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- WT:
-
Wild type
References
Irwin PJ. Canine babesiosis: from molecular taxonomy to control. Parasit Vectors. 2009;2(Suppl. 1):S4.
Schnittger L, Rodriguez AE, Florin-Christensen M, Morrison DA. Babesia: a world emerging. Infect Genet Evol. 2012;12:1788–809.
Homer MJ, Aguilar-Delfin I, Telford SR, Krause PJ, Persing DH. Babesiosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2000;13:451–69.
Goo YK, Xuan X. New molecules in Babesia gibsoni and their application for diagnosis, vaccine development, and drug discovery. Korean J Parasitol. 2014;52:345–53.
Vinayak S, Pawlowic MC, Sateriale A, Brooks CF, Studstill CJ, Bar-Peled Y, et al. Genetic modification of the diarrhoeal pathogen Cryptosporidium parvum. Nature. 2015;523(7561):477–80.
Ganesan SM, Morrisey JM, Ke H, Painter HJ, Laroiya K, Phillips MA, et al. Yeast dihydroorotate dehydrogenase as a new selectable marker for Plasmodium falciparum transfection. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2011;177:29–34.
Donald RG, Roos DS. Stable molecular transformation of Toxoplasma gondii: a selectable dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase marker based on drug-resistance mutations in malaria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:11703–7.
Adamson R, Lyons K, Sharrard M, Kinnaird J, Swan D, Graham S, et al. Transient transfection of Theileria annulata. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2001;114:53–61.
De Goeyse I, Jansen F, Madder M, Hayashida K, Berkvens D, Dobbelaere D, et al. Transfection of live, tick derived sporozoites of the protozoan apicomplexan parasite Theileria parva. Vet Parasitol. 2015;208:238–41.
Suarez CE, McElwain TF. Stable expression of a GFP-BSD fusion protein in Babesia bovis merozoites. Int J Parasitol. 2009;39:289–97.
Hakimi H, Yamagishi J, Kegawa Y, Kaneko O, Kawazu S, Asada M. Establishment of transient and stable transfection systems for Babesia ovata. Parasit Vectors. 2016;9:171.
Silva MG, Knowles DP, Suarez CE. Identification of interchangeable cross-species function of elongation factor-1 alpha promoters in Babesia bigemina and Babesia bovis. Parasit Vectors. 2016;9:576.
Liu M, Asada M, Cao S, Adjou Moumouni PF, Vudriko P, Efstratiou A, et al. Transient transfection of intraerythrocytic Babesia gibsoni using elongation factor-1 alpha promoter. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2017;216:56–9.
Liu M, Adjou Moumouni PF, Cao S, Asada M, Wang G, Gao Y, et al. Identification and characterization of interchangeable cross-species functional promoters between Babesia gibsoni and Babesia bovis. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018;9:330–3.
Suarez CE, McElwain TF. Transfection systems for Babesia bovis: a review of methods for the transient and stable expression of exogenous genes. Vet Parasitol. 2010;167:205–15.
Asada M, Tanaka M, Goto Y, Yokoyama N, Inoue N, Kawazu S. Stable expression of green fluorescent protein and targeted disruption of thioredoxin peroxidase-1 gene in Babesia bovis with the WR99210/dhfr selection system. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2012;181:162–70.
Sunaga F, Namikawa K, Kanno Y. Continuous in vitro culture of erythrocytic stages of Babesia gibsoni and virulence of the cultivated parasite. J Vet Med Sci. 2002;64:571–5.
Suarez CE, Bishop RP, Alzan HF, Poole WA, Cooke BM. Advances in the application of genetic manipulation methods to apicomplexan parasites. Int J Parasitol. 2017;47:701–10.
Suarez CE, Noh S. Emerging perspectives in the research of bovine babesiosis and anaplasmosis. Vet Parasitol. 2011;180:109–25.
Maeda H, Hatta T, Alim MA, Tsubokawa D, Mikami F, Matsubayashi M, et al. Establishment of a novel tick-Babesia experimental infection model. Sci Rep. 2016;6:37039.
Iwakami S, Ichikawa Y, Inokuma H. Molecular survey of Babesia gibsoni using Haemaphysalis longicornis collected from dogs and cats in Japan. J Vet Med Sci. 2014;76:1313–6.
Islam MK, Tsuji N, Miyoshi T, Alim MA, Huang X, Hatta T, et al. The Kunitz-like modulatory protein haemangin is vital for hard tick blood-feeding success. PLoS Pathog. 2009;5:e1000497.
Lehtinen LE, Birkenheuer AJ, Droleskey RE, Holman PJ. In vitro cultivation of a newly recognized Babesia sp. in dogs in North Carolina. Vet Parasitol. 2008;151:150–7.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Miss Artemis Efstratiou for help with English in the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (26304036), and Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) Core-to-Core program, both from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ML and XX designed the study. ML and PFAM carried out the experiments. MA, HH, TM, SK and JY contributed reagents/materials/genome sequence. ML, PFAM, PV and SL wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All procedures were carried out according to ethical guidelines which were approved by Obihiro University of Agriculture and Veterinary Medicine (Permit for animal experiment: 29-135; DNA experiment: 1725; Pathogen: 201712).
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Additional files
Additional file 1:
Figure S1. Babesia gibsoni sensitivity to WR99210. All data are expressed as means ± SD of triplicate cultures. (PPTX 100 kb)
Additional file 2:
Figure S2. Growth curves of wild type (WT) and genome integrated (GI) parasites. WT and GI parasites were maintained by sub-culturing every 3 days and parasitemia were monitored daily. All data are expressed as means ± SD of triplicate cultures. (PPTX 69 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Adjou Moumouni, P.F., Asada, M. et al. Establishment of a stable transfection system for genetic manipulation of Babesia gibsoni. Parasites Vectors 11, 260 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-018-2853-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-018-2853-1