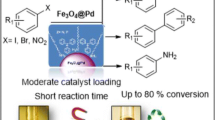
Abstract
Background
The side reactions of dehalogenation or C–N coupling tend to occur when halogenated aromatic amines are prepared by catalytic hydrogenation reduction of halogenated aromatic nitro compounds. In this paper, we prepared the sub-microspherical Fe3O4@PDA-Pd NPs catalyst apply it efficiently in the hydrogenation reduction of halogenated aromatic nitro compounds to prepare the halogenated aromatic amines under atmospheric pressure. The catalyst shows a high selectivity of greater than 96% and can effectively inhibit the occurrence of the side reactions of dehalogenation and C–N coupling.
Results
The optimum condition of the hydroreduction reaction is when tetrahydrofuran is used as solvent and the reaction happens at 50 °C for 5 h. The selectivity of the chlorinated aromatic amine and the fluorinated aromatic amine products exceed 99% and the yield exceeds 90%. Only a small amount of dehalogenated products and C–N coupling by-products were produced in the brominated aromatic compound and the iodinated aromatic compound.
Conclusion
We developed a promising method for preparing the superparamagnetic and strongly magnetic Fe3O4@PDA core–shell sub-microsphere-supported nano-palladium catalyst for catalyzing the hydrogenation reduction of halogenated aromatic nitro compounds. The halogenated aromatic amines were efficiently and highly selectively prepared under atmospheric pressure, with the side reactions of dehalogenation and C–N coupling effectively inhabited simultaneously.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Aniline compounds are important intermediates in organic synthesis and are widely used in medicines [1], additives [2], flame retardants [3], dyes and surfactants [4]. Reducing aromatic nitro compounds is the most important and simplest method for preparing the aniline compounds. And in industry, there are several major ways to prepare the aniline compounds such as catalytic hydrogenation, hydrazine hydrate, active metal and sulfide reduction. In comparison, the latter three were gradually eliminated due to their toxicity, harmfulness and sewage pollution, and only the catalytic hydrogenation gradually prevail due to its clean reaction process [5,6,7,8]. Halogenated aromatic amines are important classifications of aniline compounds especially in pesticides, such as, p-chloroaniline used to prepare Monolinuron [9], m-chloroaniline used to prepare Barban [10], and 3-chloro-4-methylaniline used to prepare Chlorotoluron [11]. However, when the halogenated aromatic amines are prepared by catalytic hydrogenation reduction of halogenated aromatic nitro compounds, the side reactions of dehalogenation [12] or C–N coupling [13] are easy to occur. Therefore, using improved highly efficient and selective catalytic hydrogenation to prepare the halogenated aromatic amines becomes a key technique to prevent the dehalogenation and C–N coupling side reactions. Recently, some useful results had been achieved by using gold complexes, palladium complexes and platinum complexes as catalysts in this reduction reaction [14,15,16,17].
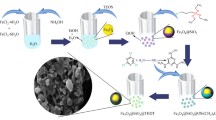
Palladium is used to catalyze the hydrogenation of many unsaturated compounds such as olefins [18], alkynes [19], nitro compounds [20], carbonyl compounds [21] and nitriles [22], as well as to catalyze the dehalogenation, debenzylation, Suzuki–Miyaura coupling, Heck and Sonogashira reactions [23,24,25]. It is known that nano-palladium particles (Pd NPs) supported on the Fe3O4 particles can improve both the catalytic performance of palladium and the selectivity of the catalytic reactions; also, the separation and recycling of the catalyst is very simple [26,27,28,29,30,31]. In this paper, we prepared the sub-micro-spherical Fe3O4@PDA-Pd NPs complex as a high performance catalyst. The preparation procedures include: first, the surface of the Fe3O4 particles are covered by polydopamine (PDA) layer through the dopamine autoagglutination to form the Fe3O4@PDA core–shell structures. Then the amino group of the sub-microspheres are combined with proton through protonation with positive electricity. The PdCl42− ions are then dispersed on the Fe3O4@PDA core–shell surface by charge attraction. And the nano-palladium supported on the sub-microspheres is further prepared by reduction to form the Fe3O4@PDA-Pd NPs complex. This complex catalyst is used to catalyze the hydrogenation reduction of a halogenated aromatic nitro compound to produce the halogenated aromatic amine (Fig. 1). The conversion and selectivity of the reaction are both very high, and the occurrence of the dehalogenation and C–N coupling side reactions are effectively suppressed at the same time.
Results and discussion
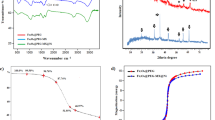
The prepared Fe3O4@PDA-Pd NPs catalyst was characterized by the transmission electron microscopy (TEM) observation and magnetic testing. The TEM image (Fig. 2) shows that the Fe3O4@PDA-Pd NPs catalyst presents core–shell micro structures which are centered on the Fe3O4 sub-microspheres. The dopamine layer is uniformly coated on the surface of the Fe3O4 sub-microspheres for form the shell-like dopamine with thickness distributed in the range of 80–90 nm. The nano palladium particles, with diameters ranging from 7 to 12 nm and average diameter of 9.2 nm, are dispersed on the dopamine shell.
Figure 3 shows the magnetization curves of the Fe3O4, Fe3O4@PDA and the Fe3O4@PDA-Pd NPs sub-microspheres under room temperature (300 K). It can be seen that the maximum saturation magnetic field strengths of the three kinds of sub-microspheres are 75, 48 and 45 emu/g, respectively, and their coercivity is 0. The presence of the PDA layer reduced the maximum saturation value of the magnetic field strength of the Fe3O4@PDA-Pd NPs sub-microspheres, but the Fe3O4@PDA-Pd NPs sub-microspheres still have superparamagnetic and strongly magnetic properties. Therefore, the Fe3O4@PDA-Pd NPs sub-microspheres can be easily dispersed into and then separated from the reaction system.
We then used the prepared Fe3O4@PDA-Pd NPs sub-microspheres as catalyst for the halogenated aromatic amines preparation through hydrogenation of the halogenated aromatic nitro compounds. In order to investigate the exact role which the Fe3O4@PDA-Pd NPs played in the catalytic hydrogenation reduction of the halogenated aromatic nitro compounds and its effect on inhibiting the side reaction of dehalogenation, the reaction temperature, solvent and reaction time were optimized under atmospheric pressure using p-nitrochlorobenzene as the substrate (Table 1). The results show that when ethanol is used as the solvent, the hydrogenation reaction rate is the fastest (Table 1, entry 1); but due to the alkylation reaction of ethanol and p-chloroaniline to form about 4% of N-ethyl-p-chloroaniline, the selectivity of p-chloroaniline (I) is lowered. The N-ethyl-p-chloroaniline was determined by GC–MS. Then when tetrahydrofuran is used as the reaction solvent (Table 1, entry 2), the reaction rate becomes slow; but the selectivity to p-chloroaniline (I) becomes higher, and the by-product of dechlorination (II) becomes rare. The reaction rate increases with increase in the reaction temperature, and the conversion rate of p-nitrochlorobenzene and the selectivity to p-chloroaniline (I) are both greater than 99% at 50 °C (Table 1, entry 3). The selectivity of p-chloroaniline (I) with Fe3O4@PDA-Pd NPs as catalyst is much higher than that with Pd/C as catalyst (Table 1, entry 4). Under the same conditions, about 13% of the products dechlorinated with the latter as catalyst. Therefore, the optimum condition of the hydroreduction reaction is to use tetrahydrofuran as solvent and keep the reaction at 50 °C for a reaction time of 5 h (Table 1, entry 3).

The extent of the reaction under the optimal reaction conditions (Table 1, entry 3) were examined and the results are shown in Table 2. It can be seen that the Fe3O4@PDA-Pd NPs catalyst has high selectivity and high yield for the hydroreduction of halogenated aromatic nitro compounds in preparing the halogenated aromatic amines. The halogenated aromatic amine has a selectivity of more than 96% and a yield of over 84%. In particular, the selectivity of the chlorinated aromatic amine and the fluorinated aromatic amine exceeds 99%, and the yield exceeds 90%. There is no C–N coupling reaction in the fluorinated aromatic compounds happened (Table 2, entry 8, 9, 12), and the dechlorination of chlorinated aromatic compounds (Table 2, entry 1–5, 13) is rare. Only a small amount of dehalogenated products and C–N coupling by-products was produced in the brominated aromatic compound (Table 2, entry 7) and the iodinated aromatic compound (Table 2, entry 6).

Experimental
General
All reagents used in the experiment are commercially available without further purification. The transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image was obtained on a JEOL JEM-2100F field transmission electron microscope. The magnetic property information of the Fe3O4@PDA-Pd NPs was obtained on a Quantum Design DynaCool-9 vibrating sample magnetometer. And the 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker Avance 400 MHz spectrometer using tetramethylsilane (TMS) as internal standards.
The Fe3O4 particles were prepared according to the method specified in Ref. [32].
General procedure for the preparation of the Fe3O4 @PDA
About 0.15 g of strong aqueous ammonia was dissolved in 50 mL of deionized water. Then, 0.1 g of Fe3O4 and 0.16 g of dopamine hydrochloride were added into the solution, and the mixture was placed under uniform ultrasonic dispersion and mechanically stirred at 40 °C for 24 h. After the reaction is completed, the solid and the liquid are separated by a magnet. The solid product was then placed under ultrasonic washing using 25 mL * 3 deionized water and 25 mL * 3 ethanol, and the washed solid was used directly in the next step.
General method for the preparation of the Fe3O4 @PDA-Pd NPs
The Fe3O4@PDA was taken and placed under ultrasonic washing using 25 mL of deionized water, 0.1 N of 25 mL hydrochloric acid, 25 mL of deionized water, and 25 mL of ethanol. Approximately 40 mL of ethanol and 4 mL of deionized water were added into the mixture, which was then mechanically stirred at 10 °C. Subsequently, about 0.3 mL NaPdCl4 aqueous solution (palladium content 2.5 mg) was slowly added into the mixture dropwise, and then the mixture was continuously stirred for another 3 h. A solution containing 60 mg of ascorbic acid and 6 mL of deionized water was slowly added into the mixture in 20 min. Then, the reaction was continued for another 2 h. The solid and liquid were separated by a magnet. The reaction product was placed under ultrasonic washing using 25 mL of ethanol, 25 mL * 3 of deionized water and 25 mL * 3 of ethanol. The solid was stored in 25 mL of ethanol and sealed with nitrogen (about 0.1 g after drying).
General procedure for the hydrogenation of halogenated aromatic nitro compounds to prepare halogenated aromatic amines 2a–m
Approximately 0.1 g of Fe3O4@PDA-Pd NPs catalyst was used. The aforementioned solid and liquor were separated using a magnet and placed under ultrasonic washing using 10 mL * 3 THF. Then, 10 mL THF and 4.3 mmol halogenated aromatic nitro compounds were added. Nitrogen and hydrogen were introduced alternatively. The magnetic stirring was carried out at 50 °C. Hydrogen (hydrogen balloon) was introduced into the reaction at atmospheric pressure for 4–6 h. At the end of the reaction, the catalyst was separated and recovered by a magnet, and the product was separated by column chromatography (n-hexane/dichloromethane) after the reaction liquid was concentrated.
2-Chloroaniline (2a)
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.23 (dd, J = 8.0, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 7.05 (td, J = 8.0, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 6.74 (dt, J = 8.8, 4.4 Hz, 1H), 6.68 (td, J = 7.8, 1.4 Hz, 1H), 4.02 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.92 (s), 129.44 (s), 127.66 (s), 119.31 (s), 119.05 (s), 115.90 (s).
3-Chloroaniline (2b)
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.05 (dd, J = 10.4, 5.6 Hz, 1H), 6.71 (ddd, J = 7.9, 1.8, 0.7 Hz, 1H), 6.65 (t, J = 2.1 Hz, 1H), 6.53 (ddd, J = 8.1, 2.2, 0.6 Hz, 1H), 4.17–3.03 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 147.66 (s), 134.85 (s), 130.36 (s), 118.48 (s), 114.95 (s), 113.23 (s).
4-Chloroaniline (2c)
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.09 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 6.59 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 3.56 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 144.99 (s), 129.14 (s), 123.13 (s), 116.27 (s).
5-Chloro-2-methylaniline (2d)
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.94 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 6.65 (d, J = 5.5 Hz, 2H), 3.65 (s, 2H), 2.10 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 145.72 (s), 132.06 (s), 131.34 (s), 120.59 (s), 118.23 (s), 114.48 (s), 16.87 (s).
6-Chloro-2-methylaniline (2e)
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.12 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 6.94 (dd, J = 7.5, 0.5 Hz, 1H), 6.61 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 3.97 (s, 2H), 2.18 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 141.18 (s), 128.72 (s), 127.07 (s), 123.56 (s), 119.15 (s), 118.32 (s), 17.98 (s).
4-Iodoaniline (2f)
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.40 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 6.46 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 3.97–3.33 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 146.08 (s), 137.92 (s), 117.32 (s), 79.41 (s).
4-Bromoaniline (2 g)
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.22 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 6.56 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 3.70 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 145.50 (s), 131.99 (s), 116.71 (s), 110.10 (s).
4-Fluoroaniline (2 h)
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.95–6.78 (m, 2H), 6.72–6.50 (m, 2H), 3.48 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 157.60 (s), 155.26 (s), 142.43 (d), 115.80 (m).
4-Fluoro-3-chloroaniline (2i)
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.91 (t, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 6.69 (dd, J = 6.1, 2.8 Hz, 1H), 6.60–6.40 (m, 1H), 3.59 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 152.79 (s), 150.42 (s), 143.16 (d), 120.94 (d), 116.75 (m), 114.28 (d).
4-Bromo-2-chloroaniline (2j)
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.37 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H), 7.15 (dd, J = 8.5, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 6.69–6.57 (m, 2H), 4.04 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.11 (s), 131.63 (s), 130.54 (s), 119.93 (s), 116.87 (s), 109.36 (s).
2-Chloro-4-iodoaniline (2k)
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.53 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.31 (dd, J = 8.4, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 6.52 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 4.05 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 142.73 (s), 137.18 (s), 136.33 (s), 120.23 (s), 117.43 (s), 77.97 (s).
2,4-Difluoroaniline (2l)
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.82–6.73 (m, 1H), 6.73–6.64 (m, 2H), 3.46 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 156.49 (d), 154.12 (d), 152.22 (d), 149.82 (d), 130.68 (dd), 116.88 (dd), 110.88 (dd), 103.79 (dd).
3,4-Dichloroaniline (2m)
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.17 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 6.75 (d, J = 2.7 Hz, 1H), 6.50 (dd, J = 8.6, 2.7 Hz, 1H), 3.72 (s, 2H). 13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 146.02 (s), 132.67 (s), 130.73 (s), 121.08 (s), 116.41 (s), 114.62 (s).
Conclusions
We developed a method for preparing superparamagnetic and strongly magnetic Fe3O4@PDA core–shell sub-microsphere-supported nano-palladium catalyst, i.e. Fe3O4@PDA-Pd NPs. The catalyst was characterized and successfully catalyzed the hydrogenation reduction of halogenated aromatic nitro compounds. The halogenated aromatic amines were efficiently and selectively prepared under atmospheric pressure, which could effectively inhibit the occurrence of the side reactions of dehalogenation and C–N coupling.
Availability of data and materials
All data and material analyzed or generated during this investigation are included in this manuscript. The raw data can be requested from email of AX: xiaaibao@zjut.edu.cn.
Abbreviations
- PDA:
-
polydopamine
- Pd NPs:
-
nano-palladium particles
- THF:
-
tetrahydrofuran
- TEM:
-
the transmission electron microscopy
References
Didehban K, Vessally E, Salary M et al (2018) Synthesis of a variety of key medicinal heterocyclic compounds via chemical fixation of CO2 onto o-alkynylaniline derivatives. J CO2 Util 23:42–50
Lundell CE, OSullivan OT, Gau MR et al (2017) Synthesis of two lead complexes of propellant stabilizer compounds: in pursuit of novel propellant additives. Chemistryselect 2(35):11673–11676
Lyu WY, Cui YH, Zhang XJ et al (2017) Fire and thermal properties of PA 66 resin treated with poly-N-aniline-phenyl phosphamide as a flame retardant. Fire Mater 41(4):349–361
Ameuru US, Yakubu MK, Bello KA et al (2018) Synthesis of disperse dyes derived from 4-amino-N-decyl-1,8-naphthalimide and their dyeing properties on polyester fabrics. Dyes Pigm 157:190–197
Greenfield H, Dovell FS (1967) Metal sulfide catalysts for hydrogenation of halonitrobenzenes to haloanilines. J Org Chem 32(11):92–95
Yan X, Sun J, Xu YH et al (2006) Liquid-phase hydrogenation of chloronitrobenzene to chloroaniline over Ni–Co–B amorphous alloy catalyst. Chin J Catal 27(2):119–123
Jagadeesh RV, Surkus AE, Junge H et al (2013) Nanoscale Fe2O3-based catalysts for selective hydrogenation of nitroarenes to anilines. Science 342(6162):1073–1076
Wang F, Ma XX, Liu X et al (2015) Synthesis of aromatic amines by Pd/C catalytic hydrogenation aromatic nitro-compounds. Chin J Synth Chem 23(7):594–598
Scherer O, Horlein, Hartel K (2010) Preparation of N-alkoxyureas and their use as selective herbicides. Angew Chem Int Ed 2(11):670–673
Charlotta M, Hugo MV, Bjorn R (1989) Dimethylsulfonium analogs of the muscarinic agent McN-A-343: [4-[[N-(3-or4-halophenyl)carbamoyl]oxy]-2-butynyl]dimethylsulfonium perchlorates. J Med Chem 32(7):1590–1593
Xu XS, Du XH, Hu ZY et al (2005) One-pot preparation of 1-aryl-3,3-dimethylureas herbicides utilizing bis(trichloromethyl)carbonate. Nongyao 44(5):210–211
Jiang WD, Xu B, Fan GG et al (2018) UV Light-assisted synthesis of highly efficient Pd-based catalyst over NiO for hydrogenation of o-chloronitrobenzene. Nanomaterials 8(4):1–16
Zhao J, Ma L, Xu XL et al (2014) Synthesis of carbon-supported Pd/SnO2 catalyst for highly selective hydrogenation of 2,4-difluoronitrobenzene. Chin Chem Lett 25(8):1137–1140
Iihama S, Furukawa S, Komatsu T (2015) Efficient catalytic system for chemoselective hydrogenation of halonitrobenzene to haloaniline using PtZn intermetallic compound. ACS Catalysis 6(2):742–746
Zhang J, Wang L, Shao Y et al (2017) A Pd@Zeolite catalyst for nitroarene hydrogenation with high product selectivity by sterically controlled adsorption in the zeolite micropores. Angew Chem Int Ed 56(33):9747–9751
Hu Z, Tan SQ, Mi RL et al (2018) Formic acid or formate derivatives as the in situ hydrogen source in Au-catalyzed reduction of para-chloronitrobenzene. Chemistryselect 3(10):2850–2853
Yan XL, Duan P, Zhang FW et al (2019) Stable single-atom platinum catalyst trapped in carbon onion graphitic shells for improved chemoselective hydrogenation of nitroarenes. Carbon 143:378–384
Bulushev DA, Ross JRH (2011) Vapour phase hydrogenation of olefins by formic acid over a Pd/C catalyst. Catal Today 163(1):42–46
Marín-Astorga N, Pecchi G, Fierro JLG et al (2003) Alkynes hydrogenation over Pd-supported catalysts. Catal Lett 91(1–2):115–121
Yang J, Wang WD, Dong Z (2018) PdCo nanoparticles supported on carbon fibers derived from cotton: maximum utilization of Pd atoms for efficient reduction of nitroarenes. J Colloid Interface Sci 524:84–92
Nindakova LO, Strakhov VO, Kolesnikov SS (2018) Hydrogenation of ketones on dispersed chiral-modified palladium nanoparticles. Russ J Gen Chem 88(2):199–207
Nandi S, Patel P, Jakhar A et al (2017) Cucurbit [6] uril-stabilized palladium nanoparticles as a highly active catalyst for chemoselective hydrogenation of various reducible groups in aqueous media. ChemistrySelect 2(31):9911–9919
La SG, Sperni L, Canton P et al (2018) Selective hydrogenationsand dechlorinations in water mediated by anionic surfactant-stabilized Pd nanoparticles. J Org Chem 83(14):7438–7446
Santra S, Hota PK, Bhattacharyya R et al (2013) Palladium nanoparticles on graphite oxide: a recyclable catalyst for the synthesis of biaryl cores. ACS Catal 3(12):2776–2789
Shen HG, Shen C, Chen C et al (2015) Novel glycosyl pyridyl-triazole@palladium nanoparticles: efficient and recoverable catalysts for C–C cross-coupling reactions. Catal Sci Technol 5(4):2065–2071
Zhang F, Jin J, Zhong X et al (2011) Pd immobilized on amine-functionalized magnetite nanoparticles: a novel and highly active catalyst for hydrogenation and Heck reactions. Green Chem 13(5):1238–1243
Zhang F, Niu J, Wang H et al (2012) Palladium was supported on superparamagnetic nanoparticles: a magnetically recoverable catalyst for Heck reaction. Mater Res Bull 47(2):504–507
Hosseini-Sarvari M, Khanivar A, Moeini F (2016) Palladium immobilized on Fe3O4/ZnO nanoparticles: a novel magnetically recyclable catalyst for Suzuki-Miyaura and heck reactions under ligand-free conditions. J Iran Chem Soc 13(1):45–53
Nangoi IM, Kiyohara PK, Rossi LM (2010) Catalytic hydrodechlorination of chlorobenzene over supported palladium catalyst in buffered medium. Appl Catal B 100(1):42–46
Shen C, Xu J, Yu WB et al (2014) A highly active and easily recoverable chitosan@copper catalyst for the C-S coupling and its application in the synthesis of zolimidine. Green Chem 16(6):3007–3012
Shen C, Xu J, Yin BB et al (2016) Heterogeneous catalyst CS@Copper(II)-catalyzed remote trifluoromethylation of aminoquinolines with CF3SO2Na via radical cross-coupling. Chemcatchem 8(23):3560–3564
Deng H, Li XL, Peng Q et al (2005) Monodisperse magnetic single-crystal ferrite microspheres. Angew Chem Int Ed 44(18):2782–2785
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Zhejiang University of Technology and Taizhou University.
Funding
This work was supported by the Zhejiang Province Public Welfare Technology Research Program (LGG19B040001), Zhejiang Natural Science Foundation (LY18B020017), and Taizhou Science and Technology Project (1801gy21). All funding bodies played no role in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HCG, HJJ and ZYX designed the research. HCG and RHZ performed the research. HCG and ABX analyzed the data. HJJ, RHZ, ABX and ZYX contributed the reagent/material/analysis tools. HCG wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, H., Zheng, R., Jiang, H. et al. Preparation of sub-microspherical Fe3O4@PDA-Pd NPs catalyst and application in catalytic hydroreduction reaction of halogenated aromatic nitro compounds to prepare halogenated aromatic amines. BMC Chemistry 13, 130 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-019-0649-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-019-0649-9