Abstract
Background
Poa L. is a large genus of grass in Gramineae, among which P. pratensis is widely cultivated as turf and forage. Satellite DNA is the main components of the plant genome. Information of satellites will helpful for dissection the genome composition and definition of the phylogeny relationship of these species. However, the knowledge about the satellites in genus Poa is still limited.
Results
Four satellite DNAs were identified using the Repeat Explorer pipeline in HiSeq Illumina reads from diploid plants in P. malaca (2n = 26). Two satellites showed high similarity with the previously identified PpTr-1 and PpTr-3, whereas two others are newly identified with the monomer of 326 bp (Poa-326) and 353 bp (Poa-353) respectively. The clone DNAs of PpTr-1 and PpTr-3, and oligonucleotides designed representing satellites Poa-326 and Poa-353 were probed to test on chromosomes across 13 Poa speceis with different polyploidy level by fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH). PpTr-1, PpTr-3, and Poa-362 were stably positioned in the subtelomeric regions in nearly all species with the variation of hybridization sites number. However, Poa-353 showed different FISH patterns of multiple regions with the variation of hybridization intensity and distribution sites across species. In addition, 5S rDNA and 45S rDNA were used to characterize the genome of the Poa species. Four rDNA FISH patterns were revealed in the tested species.
Conclusion
Four identified satellite were high conservable across Poa species. Genome distribution of these satellites can be characterized by FISH. The variation of satellite DNAs and rDNA chromosomal distributions between species provide useful information for phylogenetic analysis in genus Poa.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The genome of high plants contains much of repetitive sequences [1,2,3] most of which are genome dispersed transposable elements (DNA transposons and retrotransposons), and tandem arranged satellite DNA [4]. Satellite DNAs are mostly species and genus specific, and usually most variable in abundance and chromosomal distribution between species [5,6,7]. Satellite DNA is majorly distributed in chromosomal heterochromatic regions, and regarded in functions in chromosomal structure maintenance, centromere formation, homologue chromosome recognition, and even gene function adjustment [8,9,10]. Abundance and distribution of satellite DNA in chromosomes can be detected by a technique of Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Satellite DNA-based chromosomal markers are particularly useful for chromosome identification and for karyotype evolution analysis.
Poa L. is a large genus of grass, including up to 500 species mainly in temperate and arctic zones thought the world [11, 12]. The center of diversity of Poa is considered to be Eurasia [11]. About 100 species of Poa are described in China [13]. P. pratensis (Kentucky bluegrass) is a most useful Poa species, which is used worldwide as a temperate turf grass and forage crop. P. pratensis var. anceps and P. crymophila are utilized as ecology restoration plants and forage crops in Qinghai-Tibet plateau, China [14]. Poa species presents high variability with a wide range of chromosome numbers, due to high variable polyploidy, interspecific hybridization and facultative apomixis [11, 12, 15,16,17]. Characterization of the genome composition and definition of the phylogeny relationship of these species is still challenging.
Four satellite DNAs were isolated from P. pratensis by construction and screening cot-1 libraries, and the conservation and variability of these satellites was tested in only one more related Poa species [18]. It is still unknown the phylogenetic distribution of these satellite DNAs in other more Poa species. Furthermore, P. pratensis, as a facultative apomixes species, presents high polyploidy with large genomes. It is possible that the other more satellite DNAs are missed with a conventional method by screening limited libraries clones. The developed RepeatExplorer, a graph-based sequence clustering program, is powerful to identify various types of repetitive DNA elements in de novo by using a set of genomic sequences produced by the next generation sequencing technique (NGS) [19, 20]. It is possible to get the most repetitive sequences even using low-coverage sequencing data. A combination of RepeatExplorer and FISH has become a popular methodology to identify and characterize major satellite repeats in many plant species [21,22,23].
In this study, satellite DNAs was identified using low-coverage genomic DNA sequence data from the next-generation sequencing platform in a diploid Poa species. In addition, chromosomal distribution of these satellites was characterized in more than 10 different Poa species including P. pratensis by FISH. Finally, the phylogenetic significance of the satellite DNA across Poa species was discussed.
Materials and methods
Plant materials
Total 13 Poa L. species were used in this study. They are P. malaca Keng ex P. C. Kuo, P. elanata Keng ex Tzvel., P. megalothysa Keng ex Tzvel., P. poophagorum Bor., P. sphondylodes Trin., Poa paucifolia Keng ex L. Liou, Poa orinosa Keng ex P. C. Kuo, P. sinoglauca Ohwi, P. crymophila Keng ex C. Ling, P. subfastigiana Trin., P. pratensis Var. anceps, P. pratensis L. Four cultivars, named P. pratensis ‘Qinghai’, ‘Park’, ‘Geronimo’, and ‘Sapphire’ were contained in species P. pratensis. All above plant materials, except P. pratensis cultivars Park, Geronimo, and Sapphire, are sourced in Qinghai-Tibet plateau, China. Seeds of cultivars ‘Park’, ‘Geronimo’, and ‘Sapphire’ were all sourced from USA.
High-throughput sequencing of genomic DNA
Total genomic DNA of the plants was isolated from your leaves. Paired-end sequencing (2 × 125 bp) of total genomic DNA was performed using Illumina HiSeq 2000 (Illumina, Inc.) at Benagen company.
Clustering of satellite DNAs
The obtained NGS reads were upload to Repeat Explorer (https://repeatexplorer.org/) for a graph-based sequence clustering using a pipeline procedure [19, 20]. The putative satellite repeats were predicted based on their unique graphic characteristics.
Chromosome preparation
Metaphase chromosomes of root tip cells were used for FISH analysis. A detailed chromosome preparation was according to Zhao et al. [18].
FISH procedure
Two kinds of labelling methods, random primer labelling and end labelling, were adopted for probe preparation. The 5S rDNA was amplified by PCR using genomic DNA of P. pratensis according to Fukui et al. [24]. The satellite DNA of PpTr-1 and PpTr-3 were amplified from the previous made clones [18]. The 5S rDNA, PpTr-1 and PpTr-3 were by a random primer labelling method, described by Dou et al. [25]. The 45S rDNA was represented by end labelled oligonucleotide pTa71-1 and pTa71-2 described by Tang et al. [26]. Two other oligonucleotide designed to represent the newly identified satellite DNAs were end-labelled with FAM (green) or TAMRA (red). The FISH hybridization procedure and micrometry followed Zhao et al. with minor modification [18]. Before hybridization reaction, the hybridization mixture with oligonucleotide probes was placed directly onto the denatured slide preparation, rather than the hybridization mixture with the ddsDNA probe was denatured in boiling water for 5 min.
Results
Identification and characterization of satellite DNAs in a diploid of P. malaca
Primary screening of the chromosome number showed that the varied polyploids were existed in the tested Poa species. Specially, the diploidy form was identified in the population of P. malaca. Taking think that the diploid form contains less genome content than the tetraploid or other high polyploidy, we selected the diploid form of P. malaca for the candidate for high-throughput sequencing. The Illumina HiSeq data (genome coverage c. 30.3%) from diploid form of P. malaca was applied to the RepeatExplorer pipeline clustering tool. Four putative satellite DNAs were identified with the monomer 365 bp, 189 bp, 326 bp, and 353 bp from the output graphs. The satellite 365 bp has the most abundance about 0.85% of the genome, while the 189 bp, 326 bp, and 353 bp satellite has about 0.52%, 0.40%, and 0.24% respectively. Additionally, to test the similarity between the identified satellites with other repetitive sequences, nucleotide BLAS was conducted in the gene bank of NCBI. (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). The results showed that the 365 bp satellite has a high similarity with the tandem repeat PpTr-1 identified in P. pratensis (KY618838.1) with an identity of 98.8% and 100% coverage, and the 189 bp satellite has a high similarity with the tandem repeat PpTr-2 and PpTr-3 in P. pratensis (KY618841.1 and KY618840.1) with the identity of 98.9% and 100% coverage both. However, no significant similarity was found for both 326 bp and 353 bp satellite. Thus, we thought that the 326 bp and 353 bp satellites are two novel satellite DNAs identified in Poa, and we named them as Poa-362 and Poa-353.
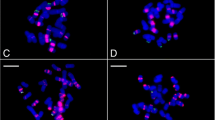
Examination of chromosomal distribution of the four above satellites carried out in the diploid form of P. malaca with the chromosome number of 14. Since the satellite 365 bp and 189 bp showed the high similarity with the previous identified tandem repeatsPpTr-1, PpTr-2 and PpTr-3 in P. pratensis, the clone sequence probes PpTr-1 and PpTr-3 [18] were used for representing the satellite 365 bp and 189 respectively in this study. Oligonucleotide FISH probes were designed for Poa-362 and Poa-353 from the sequences of the monomers using DNAman software package (Lynnon Biosoft, Quebec, Canada) (Table 1). The FISH patterns showed that PpTr-1, PpTr-3, and Poa-362 produced high intensity signals of 12, 3, and 2 respectively, which are all located in the terminal positions of the chromosomes. Relatively, Poa-353 produced less and weak hybridization signals of 2–3 in the subtelomeric and intercalary regions (Fig. 1a1–d1). The opulence of the four satellites detected by FISH is appropriate to the abundance of those derived from the high-throughput data analysis in some extent.
Characterization of satellite DNA across different Poa species
In total, 12 different Poa species are involved in this study. Additionally, P. pratensis contains one subspecies P. pratensis Var. anceps, and four P. pratensis cultivars ‘Qinghai’, ‘Park’, ‘Geronimo’, and ‘Sapphire’. The investigated species appeared different ploidy levels with one diploidy form, 10 tetraploid species with 28 chromosomes, and 2 high polyploidy species (P. subfastigiana and P. pratensis) with a variable chromosome number (Table 2). All the probes PpTr-1, PpTr-3, and Poa-362 produced hybridization signals in the subtelomeric regions across all the investigated positive species (Fig. 1a–c). However, hybridizations of Poa-353 were detected in subtelomeric, intercalary, and pericentric regions in the investigated samples (Fig. 1c). It suggests that the genomic distribution pattern of Poa-353 is totally different from those of the other three satellites in genus Poa.
The mitotic metaphase FISH patterns in representative species: a–d were probed by PpTr-1 (red), PpTr-2 (red), Poa-362 (red) plus Poa-353 (green), and 5S rDNA (red) plus 45S rDNA (green) respectively. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 were P. malaca (2n = 14), P. malaca (2n = 28), P. sphondylodes (2n = 28), P. elanata (2n = 28), P. subfastigiana (2n = 52–56), and P. pratensis ‘Sapphire’ (2n = 44–53). (bar = 10 μm)
The number of hybridization sites between different satellites is varied. About 14, 4, 8, and 12 hybridizations were detected by PpTr-1, PpTr-3, Poa-362, and Poa-353 respectively in an average in the total investigated samples, although varied hybridization numbers were observed in the different species. The PpTr-1 presents the intense hybridization in each species, and high sites number varied from 6 to 26 (Fig. 1a, Table 2). In the tetraploid Poa species, the PpTr-1 produced about 15 hybridization sites averagely, with more than 20 hybridization sites in P. malaca, P. sinoglauca and P. orinosa. In the high polyploidy species, the PpTr-1 probed about 12 hybridization sites averagely (Table 2). The PpTr-3 produced intense hybridizations in all species except in P. orinosa and P. paucifolia. The PpTr-3 probed about 1.5 hybridization sites in tetraploid species, whereas about 7 in high polyploidy species averagely. The hybridization sites of Poa-362 were detected in all tested species except in P. pratensis cultivar ‘Geronimo’ and ‘Sapphire’ (Table 2). The average of 12 hybridization sites of Poa-362 was probed in tetraploid species with an exceptional number of 24 in P. paucifolia, while about 1 site was detected in the high polyploidy species averagely. The hybridization sites of Poa-353 were detected in all tested species except in P. elanata (Table 2). The average of 12 hybridization sites of Poa-353 of 8 was probed in tetraploid species with an exceptional number of 20 in P. paucifolia, while about 22 sites were detected in the high polyploidy species with an exceptional small number of 5 in P. subfastigiana averagely. Roughly. The hybridization sites number of PpTr-1 and Poa-362 is decreasing by the increasing of the polyploidy, but that of PpTr-3 and Poa-353 is increasing by the increasing of the polyploidy. Specially, P. pratensis nearly contains the least number or none of Poa-362, and most number of Poa-353.
rDNA distribution patterns
rDNA (45S rDNA and 5S rDNA) are expressed, and highly tandem-repeated in plant genomes. Commonly, the distribution pattern and abundance of rDNA are highly stable in a species. The variable rDNA distribution patterns across different species can provide valuable information to infer the phylogenetic relationship between species. The phylogeny of the Poa species used in this study is not clear. It was thought that description of the rDNA patterns across species might be helpful to explain the phylogenetic relationship of the investigated species as well as the satellite DNAs.
Three different FISH patterns of rDNA were uncovered in tetraploid species, while one representative pattern was in high polyploidy species. In tetraploid, most of the species showed four chromosomes containing both 5S rDNA and 45S rDNA each in discrete sites as well as other four chromosomes including only one 45S rDNA site respectively (Fig. 1d2, d3; Table 2). Two tetroploid species P. paucifolia and P. crymophila showed four chromosomes containing both 5S rDNA and 45S rDNA each in discrete sites as well as other two chromosomes including only one 45S rDNA site respectively (Table 2). One tetroploid species P. elanata showed four chromosomes containing both 5S rDNA and 45S rDNA each in discrete sites, two chromosomes containing other more solely 5S rDNA site, and other two chromosomes including only one 45S rDNA site respectively (Fig. 1d4). Identical FISH pattern of rDNA was difficult to obtain due to the variable chromosome number in each high polyploidy species. However, a common feature of FISH pattern of rDNA is distinguished from the most of the tetrploid species, which showed that 2–3 chromosomes shared with 5S rDNA and 45S rDNA sites, 1–4 chromosomes had only 5S rDNA site, and 2–6 chromosome had solely 4SrDNA site (Fig. 1d5, d6; Table 2).
Discussion
Evolution of satellite DNAs in Poa
Satellite DNAs PpTr-1, PpTr-3, Poa-362, and Poa-535 were detected nearly in all the tested Poa species. It suggests that the satellite DNAs identified in Poa shared a common satDNA library from a common ancestor. Differential amplification of satellites from this library and acquisition of mutations may lead to interspecific differences in that fraction [27, 28]. Relatively, a rapid sequences divergence rate of satellites has shown to be species-specific [29]. In this study, the highly variable hybridization sites number was observed across different species. The rate of satellite repeat replacement was proposed to occur with the deletion of large chromatin blocks and re-amplification [30]. It implies that detected hybridization sites variation is due to the increasing or decreasing of the repetitive copies number rather than the sequences divergence across the Poa species. In addition, the chromosomal distribution of PpTr-1, PpTr-3, and Poa-362 are stably detected in the subtelomeric regions, but the hybridization number variations between these satellites are not accordingly related. It suggests independent evolving way of the repeats.
The abundance variation of repetitive sequence is following the polyploidy process in plant [31]. In this study, distinct increasing hybridization sites of PpTr-3 and Poa-353, and decreasing hybridization sites of Poa-362 were observed in the high polyploidy species P. pratensis. It proposed the different reaction way of the different satellites to the genome size change.
Phylogenetic relationship among Poa species
Poa is large polyploid complex [15] with high degree of poluploids, which are originated by alloypolyploiy or autopolyploidy [15, 32, 33]. Poa is with a basic chromosome number of x = 7 [34]. In this study, most of the investigated species are tetraploid species with a chromosome number of 28, with occasionally diploid plants identified in P. malaca; two species P. subfastigiana and P. pratensis, are high polyploidy species with a chromosome number more than 42. From the polyploidy level, these species could be divided into two major groups.
In the tetraploid group, the species can be tentatively separated into three sections by the rDNA FISH patterns., Most of the species in “Background” section, shared a common of rDNA FISH pattern showing a duplicated rDNA pattern revealed in diploid form in P. malaca. However, the cytogenetic discrepancy between these species is still apparent, while they were detected by probes PpTr-1, PpTr-3, Poa-362, and Poa-353. Specially, P. orinosa was distinct with no hybridization of PpTr-3. In “Materials and methods” section, one species P. paucifolia is far distant from the others with unique rDNA FISH pattern and no hybridizations of Poa-535. Two species in “Results” section shared an rDNA FISH pattern different from the others, but P. paucifolia is distinguished from P. crymophila by carrying no hybridizations of PpTr-3. More than 7 maternal genome lineage clades were uncovered in low polyploidy Poa species by using chloroplast sequences [35, 36]. It suggests that the diverse genomes may be involved in the tetraploid species in this study. Autopolyplody or alloypolyploidy origins of the species still need further investigation.
In the high polyploidy group, P. subfastigiana id distinguished from P. pratensis with highly lower hybridization sites of Poa-535. P. pratensis is a most studied species in genus Poa, due to its wide cultivation as forage and turf grass. Genome relationships in P. pratensis and other Poa species by nuclear sequences revealed four distinct classes of sequences corresponding to 4 putative within polyploidy, and 15 other Poa species were found to group with at least 1 P. pratensis homoeolog[3330]. Further cytogenetic investigation of the P. pratensis related species may provide valuable information to analysis of the genome donors of P. pratensis. P. pratensis cultivar ‘Qinghai’ and P. pratensis Var. anceps include much less PpTr-3 and more Poa-362 hybridization sites than cultivar ‘Park’, ‘Geronimo’ and ‘Sapphire’. Cultivar ‘Qinghai’ and P. pratensis Var. anceps are nearly wild population collections used in Qinghai, China, while ‘Park’, ‘Geronimo’ and ‘Sapphire’ highly breeding improved by the seed company of USA. Since P. pratensis is a facultative apomixes species, the apomictic individuals which can fix the heterosis quickly are usually selected in a breeding scheme [37]. Whether the variation of PpTr-3 and Poa-362 is related to breeding selection or even to apomictic, it is valuable to elucidate further.
Efficient exploring satellite DNAs and chromosomal marker in de novo
In the previous study [18], four satellite DNAs were identified by construction and screening of Cot-1DNA libraries by using genomic DNA of P. prantensis ‘Qinghai’. Though apparent hybridizations of Poa-362 and Poa-535 were identified in P. prantensis ‘Qinghai’ in this study, tandem repeats of those were missing in previous study. It suggests that identification of satellite DNA by RepeatExplorer in de novo is more efficient than traditional approach. Additionally, oligonucleotide desigened probes were used for newly identified Poa-362 and Poa-535. Prominent hybridizations were produced by these probes. By the decreasing of the NGS cost, it is highly efficient and convenient to identify and characterize satellite repeats by combination of RepeatExplorer and Oligo-FISH.
Conclusions
Four satellite DNAs were identified by using the RepeatExplorer pipeline to analyse HiSeq Illumina reads in Poa. Two showed the high similarity with the previously identified repeats PpTr-1 and PpTr-3, while two were newly identified (Poa-362 and Poa-353). By using labelled clone DNA and oligonucleotide designed probes, PpTr-1, PpTr-3, and Poa-362 were exclusively physically mapped on the subtelomeric regions of the chromosomes in Poa species. Poa-353 produced hybridization on multiple regions. The variation of hybridization sites number of each satellite was observed in 13 Poa species. The tested species could be divided into tetraploidy and high polyploidy species by the chromosome number. In tetraploidy group, P. elanata is distant from others with unique rDNA FISH pattern and absence of Poa-353 hybridization, as well as P. paucifolia is distinct from most species with the different rDNA FISH pattern and absence of Poa-Tr3 hybridization. Comparing with tetraploids, high polyploidy species P. subfatigiana and P. prantensis contained least hybridization sites number of Poa-363, and P. prantensis involved most number of Poa-353. The usefulness of the satellites for the genome dissection and the phylogeny definition between Poa species can be enforced by involving the application of phylogenomic and bioinformatic approaches further.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due individual privacy but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- FISH:
-
Fluorescent in situ hybridization
- NGS:
-
Next generation sequencing technique
References
Hemleben V, Kovarik A, Torres-Ruiz RA, et al. Plant highly repeated satellite DNA: molecular evolution, distribution and use for identification of hybrids. Syst Biodivers. 2007;5(3):277–89.
Heslop-Harrison JS, Schwarzacher T. Organisation of the plant genome in chromosomes. Plant J Cell Mol Biol. 2011;66(1):18–33.
Jiang JM, Gill BS. Current status and the future offluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) in plant genome research. Genome. 2006;49:1057–68.
Biscotti MA, Olmo E, Heslop-Harrison JS. Repetitive DNA in eukaryotic genomes. Chromosome Res. 2015;23(3):415–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-015-9499-z.
Schmidt-Lorenz W, Hauert W, Kiss G, et al. Environmental microbiology. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1983;39(12):1418–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01990136
Cuadrado A, Cardoso M, Jouve N. Physical organisation of simple sequence repeats (SSRs) in Triticeae: structural, functional and evolutionary implications. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2008;120(3–4):210–9. https://doi.org/10.1159/000121069.
Dou Q, Liu R, Yu F. Chromosomal organization of repetitive DNAs in Hordeum bogdanii and H. brevisubulatum (Poaceae). Comp Cytogenet. 2016;10(4):465–81.
Mehrotra S, Goyal V. Repetitive sequences in plant nuclear DNA: types, distribution, evolution and function. Genom Proteom Bioinform. 2014;12:164–71.
Garrido-Ramos MA. SatDNA in plants: more than just rubbish. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2015;146:153–70.
Meštrović N, Mravinac B, Pavlek M, Vojvoda-Zeljko T, Šatović E, Plohl M. Structural and functional liaisons between transposable elements and satellite DNAs. Chromosome Res. 2015;23:583–96.
Soreng RJ. Chloroplast DNA phylogenetics and biogeography in a reticulating group: study in Poa (Poaceae). Am J Bot. 1990;77:1383–400. https://doi.org/10.2307/2444749.
Gillespie LJ, Soreng RJ. A phylogenetic analysis of the bluegrass genus Poa L. (Poaceae) based on cpDNA restriction site data. Syst Bot. 2005;30:84–105. https://doi.org/10.1600/0363644053661940.
Lu SL, Sun YH, Liu SW, Yang YC, Wu ZL, Guo BZ. Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae, vol 9(3). Beijing: Science Press; 1987.
Lu SL, Liu SW, Wu ZL, He TN, Zhou LH, et al. Flora Qinghaiica, vol. 4. Xining: Qinghai People’s Publishing Press; 1999.
Stebbins GL. Variation and evolution in plants. New York: Columbia University Press; 1950.
Tzvelev NN (1976) Zlaki SSSR. Nauka Publishers, Leningrad, Russia. Grasses of the Soviet Union, vols 1 and 2. Amerind Publishing Co., New Delhi. 1196 (English translation: 1983)
Hunziker JH, Stebbins GL. Chromosomal evolution in the Gramineae. In: Soderstrom TR, Hilu KW, Campbell CS, Barkworth ME, editors. Grass systematics and evolution. Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution Press; 1987. p. 179–87.
Zhao Y, Yu F, Liu R, Dou Q. Isolation and characterization of chromosomal markers in Poa pratensis. Mol Cytogenet. 2017;10:5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13039-017-0307-7.
Novak P, Neumann P, Macas J. Graph-based clustering and characterization of repetitive sequences in next-generation sequencing data. BMC Bioinform. 2010;11:378.
Novak P, Neumann P, Pech J, Steinhaisl J, Macas J. RepeatExplorer: a galaxy-based web server for genomewide characterization of eukaryotic repetitive elements from next-generation sequence reads. Bioinformatics. 2013;29:792–3.
Belyayev A, Josefiova J, Jandova M, Kalendar R, Krak K, Mandak B. Natural history of a satellite DNA family: from the ancestral genome component to species-specific sequences, concerted and non-concerted evolution. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(5):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051201.
Jiang J. Fluorescence in situ hybridization in plants: recent developments and future applications. Chromosome Res. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-019-09607-z.
Lee YI, Yap JW, Izan S, Leitch IJ, Fay MF, Lee YC, et al. Satellite DNA in Paphiopedilum subgenus Parvisepalum as revealed by high-throughput sequencing and fluorescent in situ hybridization. Bmc Genomics. 2018;19(1):578. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-4956-7.
Fukui K, Kamisugi Y, Sakai F. Physical mapping of 5S rDNA loci by direct-cloned biotinylated probes in barley chromosomes. Genome. 1994;37(1):105–11. https://doi.org/10.1139/g94-013 (PMID:8181730).
Dou QW, Chen ZG, Liu YA, Tsujimoto H. High frequency of karyotype variation revealed by sequential FISH and GISH in plateau perennial grass forage Elymus nutans. Breed Sci. 2009;59:651–6.
Tang ZX, Yang ZJ, Fu SL. Oligonucleotides replacing the roles of repetitive sequences pAs1, pSc119.2, pTa-535, pTa71, CCS1, and pAWRC.1 for FISH analysis. J Appl Genet. 2014;55:313–8.
Salser W, Bowen S, Browne D, et al. Investigation of the organization of mammalian chromosomes at the DNA sequence level. Fed Proc. 1976;35(1):23–35.
Plohl M, Meštrović MN, et al. Satellite DNA evolution. Genome Dyn. 2012;7:126.
Macas J, Novák P, Pellicer J, et al. In depth characterization of repetitive DNA in 23 plant genomes reveals sources of genome size variation in the legume tribe Fabeae. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0143424.
Koukalova B, Moraes AP, Renny-Byfield S, Matyasek R, Leitch A, Kovarik A. Fall and rise of satellite repeats in allopolyploids of Nicotiana over c. 5 million years. New Phytol. 2009;186:148–60.
Leitch IJ, Hanson L, Lim KY, Kovarik A, Chase MW, Clarkson JJ. The ups and downs of genome size evolution in polyploid species of Nicotiana (solanaceae). Ann Bot. 2008;101(6):6.
Darmency H, Gasquez J. Spontaneous hybridization of the putative ancestors of the allotetraploid Poa annua. New Phytol. 1997;136:497–501. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.1997.00772.x.
Patterson JT, Larson SR, Johnson PG. Genome relationships in polyploid Poa pratensis and other Poa species inferred from phylogenetic analysis of nuclear and chloroplast DNA sequences. Genome. 2005;48(1):76–87. https://doi.org/10.1139/g04102 (PMID:15729399).
Gould FW. Grass systematics. New York: McGraw-Hill Inc; 1968.
Soreng RJ, Bull RD, Gillespie LJ. Phylogeny and reticulation in Poa L. based on plastid trnTLF and nrITS sequences with attention to diploids. In: Seberg O, Petersen G, Barfod AS, Davis JI, editors. Diversity, phylogeny,and evolution in the monocotyledons. Aarhus: Aarhus University Press; 2010. p. 619–43.
Joshi A, Bushman BS, Pickett B, Robbins MD, Staub JE, Johnson PG. Phylogenetic relationships among low-ploidy species of Poa using chloroplast sequences. Genome. 2017;60(5):384–92. https://doi.org/10.1139/gen-2016-0110.
Bashaw EC, Hanna WW. Apomixis: its identification and use in plant breeding. Crop Sci. 1987;27:1136–9.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Yongcui Wang (Northwest Institute of Plateau Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences) for help in process of the high-throughput DNA sequences data. We would like to thank Dr. Wenhui Liu for their invaluable assistance with the laboratory work and provide the seeds.
Funding
This work was supported by the Technology development and model demonstration of modern pasture in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau (2018-NK-A2) and the Open Project of Qinghai Provincial Key Laboratory of Crop Molecular Breeding, Grant No. 2017-ZJ-Y14. Dr. Quanmin Dong was supported by ‘1000 Talent’ programs of Qinghai Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QD and BL: Designed the study: CZ, YY and XY: Participated in the experiments; LW: Wrote the manuscript, performed the experiments; QD: Corrected the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, L., Liu, B., Zhang, C. et al. Identification and characterization of satellite DNAs in Poa L.. Mol Cytogenet 13, 47 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13039-020-00518-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13039-020-00518-x