Abstract
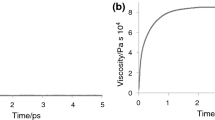
The viscosity coefficient of several model nanofluids is simulated by the molecular dynamics method. As nanofluids, argon mixtures with aluminum and lithium particles are used. The size of nanoparticles is varied from 1 to 4 nm; their volume concentration, from 1% to 12%. It is shown that the viscosity of the nanofluids is considerably higher than that of the carrier fluid. The finer the particles, the higher the viscosity of the nanofluids with the volume concentration of the particles being the same. The reason for such an effect is explained qualitatively. It is also found that the viscosity of the nanofluids depends on the material of nanoparticles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. M. Mahbubul, R. Saidur, and M. A. Amalina, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 55, 874 (2012).
S. Sh. Hosseini, A. Shahrjerdi, and Y. Vazifeshenas, Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 5, 417 (2011).
V. Ya. Rudyak, Adv. Nanopart. 2, 266 (2013).
V. Ya. Rudyak, A. A. Belkin, and V. V. Egorov, in Proceedings of the All-Russia Seminar on Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, Novosibirsk, 2007, pp. 105–110.
V. Ya. Rudyak, A. A. Belkin, E. A. Tomilina, and V. V. Egorov, Defect Diffusion Forum 273–276, 566 (2008).
V. Ya. Rudyak, A. A. Belkin, and V. V. Egorov, Tech. Phys. 54, 1102 (2009).
V. Ya. Rudyak, S. V. Dimov, V. V. Kuznetsov, and S. P. Bardakhanov, Dokl. Ross. Akad. Nauk 450, 1 (2013).
V. Ya. Rudyak, S. V. Dimov, and V. V. Kuznetsov, Tech. Phys. Lett. 39, 779 (2013).
E. V. Timofeeva, D. S. Smith, W. Yu, D. M. France, D. Singh, and J. L. Routbo, Nanotechnology 21, 215703 (2010).
Y. He, Y. Jin, H. Chen, Y. Ding, D. Cang, and H. Lu, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 50, 2272 (2007).
C. T. Nguyen, F. Desgranges, G. Roy, N. Galanis, T. Marer, S. Boucher, and H. Mintsa, Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 28, 1492 (2007).
V. Rudyak, S. Dimov, S. Krasnolutskii, and D. Ivanov, in Proceedings of the NSTI Nanotechnology Conference and Exposition NSTI-Nanotechnology, Washington, 2013, Vol. 2, pp. 370–373.
V. Ya. Rudyak and S. L. Krasnolutskii, Dokl. Phys. 48, 583 (2003).
V. Ya. Rudyak and S. L. Krasnolutskii, Opt. Atmos. Okeana 17, 468 (2004).
D. C. Rapaport, The Art of Molecular Dynamics Simulation (Cambridge Univ., Cambridge, 1995).
G. E. Norman and V. V. Stegailov, Nanostrukt. Mat. Fiz. Model. 4, 31 (2011).
G. E. Norman and V. V. Stegailov, Mat. Model. 24(6), 3 (2012).
V. Ya. Rudyak and S. L. Krasnolutskii, in Proceedings of the 21st International Symposium on Rarefied Gas Dynamics, Toulouse, 1999, Vol. 1, pp. 263–270.
V. Ya. Rudyak and S. L. Krasnolutskii, Dokl. Phys. 46, 897 (2001).
V. Ya. Rudyak and S. L. Krasnolutskii, Tech. Phys. 47, 807 (2002).
V. Ya. Rudyak, Statistical Aerohydromechanics of Inhomogeneous and Heterogeneous Media, Vol. 1: Kinetic Theory (NGASU, Novosibirsk, 2004).
V. Ya. Rudyak, S. L. Krasnolutskii, and D. A. Ivanov, Dokl. Phys. 57, 33 (2012).
P. Schofield, Comput. Phys. Comm. 5, 17 (1973).
J. O. Hirschfelder, C. F. Curtiss, and R. B. Bird, Molecular Theory of Gases and Liquids (Wiley, New York, 1954).
K. M. Aref’ev, Transfer Phenomena in Gas and Plasma (Energoatomizdat, Leningrad, 1983).
H. Heinz, R. A. Vaia, B. L. Farmer, and R. R. Naik, J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 17281 (2008).
D. N. Zubarev, Nonequilibrium Statistical Thermodynamics (Plenum, New York, 1974).
V. Ya. Rudyak, A. A. Belkin, D. A. Ivanov, and V. V. Egorov, Teplofiz. Vys. Temp. 46, 35 (2008).
V. Ya. Rudyak, Statistical Aerohydromechanics of Homogeneous and Geterogeneous Media, Vol. 2: Hydromechanics (NGASU, Novosibirsk, 2005).
G. K. Batchelor, J. Fluid Mech. 83, 97 (1977).
V. Ya. Rudyak, S. L. Krasnolutskii, and D. A. Ivanov, Microfluid. Nanofluid. 11, 501 (2011).
M. A. Bubenchikov, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Fiz. 54, 92 (2011).
A. I. Potekaev, A. M. Bubenchikov, and M. A. Bubenchikov, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Fiz. 55(12), 54 (2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.Ya. Rudyak, S.L. Krasnolutskii, 2015, published in Zhurnal Tekhnicheskoi Fiziki, 2015, Vol. 85, No. 6, pp. 9–16.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rudyak, V.Y., Krasnolutskii, S.L. Simulation of the nanofluid viscosity coefficient by the molecular dynamics method. Tech. Phys. 60, 798–804 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063784215060237
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063784215060237