Abstract
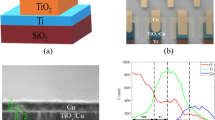
Memristors based on films of Cu and Cr, as well as their chlorides, which provide better characteristics of electronic components compared to the commonly used ones, are investigated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim, K.-H. et al., A functional hybrid memristor crossbar-array/CMOS system for data storage and neuromorphic applications, Nano Lett., 2012, vol. 12, pp. 389–395.
Lee, M.-J. et al., A fast, high-endurance and scalable non-volatile memory device made from asymmetric Ta2O5–x /TaO2–x bilayer structures, Nature Mater., 2011, vol. 10, pp. 625–630.
Strukov, D.B. and Likharev, K.K., CMOL FPGA: a reconfigurable architecture for hybrid digital circuits with two-terminal nanodevices, Nanotechnology, 2005, vol. 16, p. 888.
Ohno, T. et al., Short-term plasticity and long-term potentiation mimicked in single inorganic synapses, Nature Mater., 2011, vol. 10, pp. 591–595.
Likharev, K., Mayr, A., Muckra, I., and Türel, Ö., CrossNets: high-performance neuromorphic architectures for CMOL circuits, Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 2003, vol. 1006, pp. 146–163.
Sakamoto, T. et al., Electronic transport in Ta2O5 resistive switch, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2007, vol. 91, p. 092110.
Kever, T., Bottger, U., Schindler, C., and Waser, R., On the origin of bistable resistive switching in metal organic charge transfer complex memory cells, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2007, vol. 91, p. 083506.
Russo, U., Kamalanathan, D., Ielmini, D., Lacaita, A.L., and Kozicki, M.N., Study of multilevel programming in programmable metallization cell (PMC) memory, IEEE Trans. Electron Dev., 2009, vol. 56, pp. 1040–1047.
Banno, N., Sakamoto, T., Hasegawa, T., Terabe, K., and Aono, M., Effect of ion diffusion on switching voltage of solid-electrolyte nanometer switch, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2006, vol. 45, pp. 3666–3668.
Wang, Z. et al., Resistive switching mechanism in ZnxCd1–xS nonvolatile memory devices, IEEE Electron Dev. Lett., 2007, vol. 28, pp. 14–16.
Mitkova, M. and Kozicki, M.N., Mass transport in chalcogenide electrolyte films-materials and applications, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 2006, vol. 352, pp. 567–577.
Rabinovich, V.A. and Khavin, Z.Ya., Kratkii khimicheskii spravochnik (Short Chemical Manual), Leningrad: Khimiya, 1991, p. 24.
Yoon, In-Sung et al., Memristor behaviors of highly oriented anatase TiO2 film sandwiched between top Pt and bottom SrRuO3 electrodes, Appl. Phys. Express, 2011, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 041101–041101-3.
Jeong, D.S., Schroeder, H., and Waser, R., Coexistence of bipolar and unipolar resistive switching behaviors in a Pt/TiO2/Pt stack, Electrochem. Solid-State Lett., 2007, vol. 10, no. 8, pp. G51–G53.
Yang, J.J. et al., The mechanism of electroforming of metal oxide memristive switches, Nanotechnology, 2009, vol. 20, no. 21, pp. 215201–215209.
Berzina, T.S., Gorshkov, K.V., Erokhin, V.V., Nevolin, V.K., and Chaplygin, Yu.A., Investigation of electrical properties of organic memristors based on thin polyaniline–graphene films, Russ. Microelectron., 2013, vol. 42, no. 1, pp. 27–32.
Ageev, O.A., Alyab’eva, N.I., Konoplev, B.G., Polyakov, V.V., and Smirnov, V.A., Photoactivation of nanostructure formation processes by local anodic oxidation of titanium film, Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Elektron., 2010, no. 2 (82), pp. 23–31.
Prodromakis, Th., Toumazou, Ch., and Chua, L., Two centuries of memristors, Nature Mater., 2012, vol. 11, no. 6, pp. 478–481.
Yang, J.Y. et al., Memristive switching mechanism for metal/oxide/metal nanodevices, Nature Nanotechnol., 2008, vol. 3, no. 7, pp. 429–433.
Jeong, D.S., Schroeder, H., Breuer, U., and Waser, R., Characteristic electroforming behavior in Pt/TiO2/Pt resistive switching cells depending on atmosphere, J. Appl. Phys., 2008, vol. 104, no. 12, pp. 123716–123716-8.
Kim, K.M. et al., Electrically configurable electroforming and bipolar resistive switching in Pt/TiO2/Pt structures, Nanotechnology, 2010, vol. 21, no. 30, pp. 305203–305210.
Tanimizu, M., Takahashi, Yo., and Nomura, M., Spectroscopic study on the anion exchange behavior of Cu chloro-complexes in HCl solutions and its implication to Cu isotopic fractionation, Geochem. J., 2007, vol. 41, no. 4, pp. 291–295.
Irwin, J.C., Chrzanowski, J., Wei, T., Lockwood, D.J., and Wold, A., Raman scattering from single crystals of cupric oxide, Physica C, 1990, vol. 166, nos. 5–6, pp. 456–464.
Sopotrajanov, B., Stefov, V., Zugic, M., and Petrusevski, V.M., Fourier transform infrared and Raman spectra of the green chromium(III) chloride hexahydrate, J. Mol. Struct., 1999, vols. 482–483, pp. 109–113.
Liao et al., Evolution of resistive switching over bias duration of single Ag2S nanowires, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2010, vol. 96, no. 20, pp. 203109–2031090-3.
Hashema, N. and Das, Sh., Switching-time analysis of binary-oxide memristors via a nonlinear model, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2012, vol. 100, no. 26, pp. 262106–262106-3.
Khrapovitskaya, Yu.V., Maslova, N.E., Zanaveskin, M.L., and Marchenkov, A.N., Modeling of frequency and power characteristics of a memristor based on titanium oxide, Nauka Obrazov., 2012, no. 5, pp. 290–305.
Lu, Y.M. et al., Thermographic analysis of localized conductive channels in bipolar resistive switching devices, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2011, vol. 44, p. 185103.
Kyriakides, E. et al., Low-cost, CMOS compatible, Ta2O5-based hemi-memristor for neuromorphic circuits, Electron. Lett., 2012, vol. 48, no. 23, pp. 1451–1452.
Zhu, Yo. and Li, M., Bipolar resistive switching characteristic of epitaxial NiO thin film on Nb-doped SrTiO3 substrate, Adv. Condens. Matter Phys., 2012, vol. 2012, pp. 1–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © R.Yu. Rozanov, V.A. Kondrashov, V.K. Nevolin, Yu.A. Chaplygin, 2016, published in Mikroelektronika, 2016, Vol. 45, No. 1, pp. 29–35.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rozanov, R.Y., Kondrashov, V.A., Nevolin, V.K. et al. Characteristics of chloride memristors based on nanothick metal films. Russ Microelectron 45, 26–32 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063739716010091
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063739716010091