Abstract
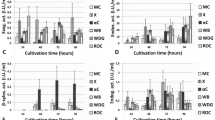
Bark beetles (Curculionidae: Scolytinae) feed on the xylem and phloem of their host, which are composed of structural carbohydrates and organic compounds that are not easily degraded by the insects. Some of these compounds might be hydrolyzed by digestive enzymes produced by microbes present in the gut of these insects. In this study, we evaluated the enzymatic capacity of bacteria (Acinetobacter lwoffii, Arthrobacter sp., Pseudomonas putida, Pseudomonas azotoformans, and Rahnella sp.) and yeasts (Candida piceae, Candida oregonensis, Cyberlindnera americana, Zygoascus sp., and Rhodotorula mucilaginosa) isolated from the Dendroctonus rhizophagus gut to hydrolyze cellulose, xylan, pectin, starch, lipids, and esters. All isolates, with the exception of C. piceae, showed lipolytic activity. Furthermore, P. putida, P. azotoformans, C. americana, C. piceae, and R. mucilaginosa presented amylolytic activity. Esterase activity was shown by A. lwoffii, P. azotoformans, and Rahnella sp. Cellulolytic and xylanolytic activities were present only in Arthrobacter sp. and P. azotoformans. The pectinolytic activity was not recorded in any isolate. This is the first study to provide evidence on the capacity of microbes associated with the D. rhizophagus gut to hydrolyze specific substrates, which might cover part of the nutritional requirements for the development, fitness, and survival of these insects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams AS, Adams SM, Currie CR, Gillette NE, Raffa KF (2010) Geographic variation in bacterial communities associated with the red turpentine beetle (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Environ Entomol 39:406–414
Anand AA, Vennison SJ, Sankar SG, Prabhu DI, Vasan PT, Raghuraman T, Geoffrey CJ, Vendan SE (2010) Isolation and characterization of bacteria from the gut of Bombyx mori that degrade cellulose, xylan, pectin and starch and their impact on digestion. J Insect Sci 10:107
Arrese EL, Soulages JL (2010) Insect fat body: energy, metabolism, and regulation. Annu Rev Entomol 55:207–225
Ayres MP, Wilkens RT, Ruel JJ, Lombardero MJ, Vallery E (2000) Nitrogen budgets of phloem-feeding bark beetles with and without symbiotic fungi. Ecology 81:2198–2210
Balogun RA (1969) Digestive enzymes of the alimentary canal of the larch bark beetle Ips cembrae heer. Comp Biochem Physiol 29:1267–1270
Bentz BJ, Six DL (2006) Ergosterol content of fungi associated with Dendroctonus ponderosae and Dendroctonus rufipennis (Coleoptera: Curculionidae, Scolytinae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 99:189–194
Bornscheuer UT (2002) Microbial carboxyl esterases: classification, properties and application in biocatalysis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 26:73–81
Castañeda-Agulló M (1956) Studies on the biosynthesis of extracellular proteases by bacteria. J Gen Physiol 89:369–373
Cenis JL (1992) Rapid extraction of fungal DNA for PCR amplification. Nucleic Acids Res 20:2380
Cibrián-Tovar D, Méndez Montiel JT, Campos Bolaños R, Yates HO III, Flores Lara J (1995) Insectos Forestales de México/Forests Insects of México (COFAN/NAFC). Universidad Autónoma Chapingo, México
Delalibera I, Handelsman J, Raffa KF (2005) Contrasts in cellulolytic activities of gut microorganisms between the wood borer, Saperda vestita (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae), and the bark beetles, Ips pini and Dendroctonus frontalis (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Environ Entomol 34:541–547
Dowd PF (1992) Insect fungal symbionts: a promising source of detoxifying enzymes. J Ind Microbiol 9:149–161
Engel P, Moran NA (2013) The gut microbiota of insects—diversity in structure and function. FEMS Microbiol Rev 37:699–735
Farrell BD, Sequeira AS, O'Meara BC, Normark BB, Chung JH, Jordal BH (2001) The evolution of agriculture in beetles (Curculionidae: Scolytinae and Platypodinae). Evolution 55:2011–2027
Feng W, Wang XQ, Zhou W, Liu GY, Wan YJ (2011) Isolation and characterization of lipase-producing bacteria in the intestine of the silkworm, Bombyx mori, reared on different forage. J Insect Sci 11:135
Gessner RV (1980) Degradative enzyme production by salt marsh fungi. Bot Mar 23:133–139
Hankin L, Zucker M, Sands DC (1971) Improved solid medium for the detection and enumeration of pectolytic bacteria. Appl Microbiol 22:205–209
Hodges JD, Lorio PL Jr (1969) Carbohydrate and nitrogen fractions of the inner bark of loblolly pines under moisture stress. Can J Bot 47:1651–1657
Hoffman CS, Winston F (1987) A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene 57:267–272
Hols P, Ferain T, Garmyn D, Bernard N, Delcour J (1994) Use of homologous expression-secretion signals and vector-free stable chromosomal integration in engineering of Lactobacillus plantarum for alpha-amylase and levanase expression. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:1401–1413
Horne I, Haritos VS, Oakeshott JG (2009) Comparative and functional genomics of lipases in holometabolous insects. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 39:547–567
Hu X, Wang C, Chen H, Ma J (2013) Differences in the structure of the gut bacteria communities in development stages of the Chinese white pine beetle (Dendroctonus armandi). Int J Mol Sci 14:21006–21020
Hu X, Yu J, Wang C, Chen H (2014) Cellulolytic bacteria associated with the gut of Dendroctonus armandi larvae (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae). Forests 5:455–465
Kaur R, Kaur N, Gupta AK (2014) Structural features, substrate specificity, kinetic properties of insect α-amylase and specificity of plant α-amylase inhibitors. Pestic Biochem Physiol 116:83–93
Kim YM, Wang MH, Rhee HI (2004) A novel alpha-glucosidase inhibitor from pine bark. Carbohydr Res 339:715–717
Kurtzman CP, Fell JW, Boekhout T (2011) The yeasts, a taxonomic study, 5th edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acids techniques in bacterial systematic. Wiley, Chichester, pp. 115–175
Lou QZ, Lu M, Sun JH (2014) Yeast diversity associated with invasive Dendroctonus valens killing Pinus tabuliformis in China using culturing and molecular methods. Microb Ecol 68:397–415
Madigan MT, Martinko JM, Bender KS, Buckley DH, Stahl DA, Brock T (2015) Brock biology of microorganisms, 14th edn. US, Pearson
Montella IR, Schama R, Valle D (2012) The classification of esterases: an important gene family involved in insecticide resistance—a review. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 107:437–449
Morales-Jiménez J, Zúñiga G, Villa-Tanaca L, Hernández-Rodríguez C (2009) Bacterial community and nitrogen fixation in the red turpentine beetle, Dendroctonus valens LeConte (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae). Microb Ecol 58:879–891
Morales-Jimenez J, Zuniga G, Ramirez-Saad HC, Hernandez-Rodriguez C (2012) Gut-associated bacteria throughout the life cycle of the bark beetle Dendroctonus rhizphagous Thomas and Bright (Curculionidae: Scolytinae) and their cellulytic activities. Microb Ecol 64:268–278
Morales-Jiménez J, Vera-Ponce de León A, García-Domínguez A, Martínez-Romero E, Zúñiga G, Hernández-Rodríguez C (2013) Nitrogen-fixing and uricolytic bacteria associated with the gut of Dendroctonus rhizophagus and Dendroctonus valens (Curculionidae: Scolytinae). Microb Ecol 66:200–210
Naidu MA, Saranraj P (2013) Bacterial amylase: a review. Int j pharm biol sci arch 4:274–287
O’Donnell K (1993) Fusarium and its near relatives. In: Reynolds DR, Taylor JW (eds) The fungal holomorph: mitotic, meiotic and pleomorphic speciation in fungal systematics. CAB International, Wallingford, UK, pp. 225–233
Pallardy SG (2008) Physiology of woody plants, 3rd edn. Elsevier, US
Park DS, Oh HW, Jeong WJ, Kim H, Park HY, Bae KS (2007) A culture-based study of the bacterial communities within the guts of nine longicorn beetle species and their exo-enzyme producing properties for degrading xylan and pectin. J Microbiol 45:394–401
Raffa KF, Aukema BH, Bentz BJ, Carroll AL, Hicke JA, Turner MG, Romme WH (2008) Cross-scale drivers of natural disturbances prone to anthropogenic amplification: dynamics of biome-wide bark beetle eruptions. Bioscience 58:501–517
Rivera FN, González E, Gómez Z, López N, Hernández-Rodríguez C, Berkov A, Zúñiga G (2009) Gut-associated yeast in bark beetles of the genus Dendroctonus Erichson (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae). Biol J Linnean Society 98:325–342
Rosselló-Mora R, Amann R (2001) The species concept for prokaryotes. FEMS Microbiol Rev 25:39–67
Six DL (2013) The bark beetle holobiont: why microbes matter. J Chem Ecol 39:989–1002
Six DL, Klepzig KD (2004) Dendroctonus bark beetles as model systems for the study of symbiosis. Symbiosis 37:207–232
Sudachkova NE, Milutina IL, Romanova LI, Semenova GP (2004) The annual dynamics of reserve compounds and hydrolic enzymes activity in the tissues of Pinus sylvestris L. and Larix sibirica Ledeb.: the metabolism of reserve compounds in the tissues of Siberian conifers. Eur J For Res 7:1–10
Thornber JP, Northcote DH (1962) Changes in the chemical composition of a cambial cell during its differentiation into xylem and phloem tissue in trees. Biochem J 82:340–346
Valiev AZ, Ogel B, Klepzig KD (2009) Analysis of cellulase and polyphenol oxidase production by southern pine beetle associated fungi. Symbiosis 49:37–42
Vasanthakumar A, Delalibera I, Handelsman J, Klepzig K, Schloss P, Raffa K (2006) Characterization of gut-associated bacteria in larvae and adults of the southern pine beetle, Dendroctonus frontalis Zimmermann. Environ Entomol 35:1710–1717
Viktorinova I, Kucerova L, Bohmova M, Henry I, Jindra M, Dolezal P, Zurovcova M, Zurovec M (2011) Characterization of two closely related α-amylase paralogs in the bark beetle, Ips typographus (L.). Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 77:179–198
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor JW (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, Inc., New York, pp. 315–322
Wood PJ (1980) Specify in the interaction of direct dyes with polysaccharides. Carbohydr Res 85:271–287
Wood SL (1982) The bark and ambrosia beetles of North and Central America (Coleoptera: Scolytidae), a taxonomic monograph. Great Basin Nat Mem 6:1–1356
Yaman M, Ertürk O, Aslan I (2010) Isolation of some pathogenic bacteria from the great spruce bark beetle, Dendroctonus micans and its specific predator, Rhizophagus grandis. Folia Microbiol 55:35–38
Yilmaz H, Sezen K, Kati H, Demirgağ Z (2006) The first study on the bacterial flora of the European spruce bark beetle, Dendroctonus micans (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Biol Brat 61:679–686
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Compañía Papelera Mexicana (COPAMEX) for providing us the access to the installations in San Juanito, Chihuahua. We also thank Fabiola Hernández, Gabriel Obregón, Salvador Embarcadero, En Tao Wang Hu, and Ma. Eugenia Hidalgo for their comments and valuable suggestions regarding the manuscript. This project was funded by Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACyT 169494/CB2011) and Secretaría de Investigación y Posgrado del Instituto Politécnico Nacional (SIP 20120753). This work was part of Carlos I. Briones-Roblero PhD dissertation. He was a fellow of CONACyT (227280) and of the Programa Institucional de Formación de Investigadores del Instituto Politécnico Nacional (PIFI-IPN B110598).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 57287 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Briones-Roblero, C.I., Rodríguez-Díaz, R., Santiago-Cruz, J.A. et al. Degradation capacities of bacteria and yeasts isolated from the gut of Dendroctonus rhizophagus (Curculionidae: Scolytinae). Folia Microbiol 62, 1–9 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-016-0469-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-016-0469-4