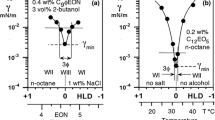
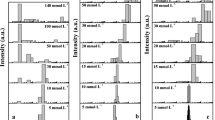
Abstract
This work introduces a simplified methodology for measuring the characteristic curvature (Cc) of commercial alkyl ethoxylate nonionic surfactants using carefully selected reference surfactants and oils that produce rapid and well defined separations in salinity scans. The Cc of the commercial reference surfactants was calculated using optimal salinities (S*) obtained from solubilization parameter curves, from interfacial tensions (for a selected system), and from emulsion stability tests. The latter provided a fast detection of S*, in a matter of minutes. The calibrated Cc of the reference surfactants was subsequently used to measure the Cc of various commercial alkyl ethoxylate surfactants. The combination of mixtures of test and reference surfactants and emulsion stability tests produced reproducible Cc values that could be obtained with simple bottle tests and in a timely manner. The values obtained using this methodology were cross-checked, and proved to be consistent, when using different combinations of reference surfactants and oils, and when conducted by different individuals. The standard deviation of Cc from these measurements was typically ±0.2 Cc units, but it could be as large as 25 % of the Cc value for highly hydrophilic surfactants. After comparing the values of Cc obtained experimentally with values calculated from nominal structures (via a group contribution model) it became clear that there are differences between these values, likely because of the polydispersity of alkyl ethoxylate surfactants.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosen MJ (2004) Surfactants and interfacial phenomena, 3rd edn. Wiley-Interscience, Hoboken
Fanun M, Papadimitriou V, Xenakis A (2011) Characterization of cephalexin loaded nonionic microemulsions. J Colloid Interface Sci 361:115–121
Chu J, Cheng Y, Rao AV, Nouraei M, Zarate-Muñoz S, Acosta EJ (2014) Lecithin-linker formulations for self-emulsifying delivery of nutraceuticals. Int J Pharm 471:92–102
Garti N, Spernath A, Aserin A, Lutz R (2005) Nano-sized self-assemblies of non-ionic surfactants as solubilization reservoirs and microreactors for food systems. Soft Matter 1:206–218
Paul BK, Moulik SP (2001) Uses and applications of microemulsions. Curr Sci 80:990–1001
Vasudevan M, Wiencek JM (1997) Role of the interface in protein extractions using nonionic microemulsions. J Colloid Interface Sci 186:185
Sottmann T, Stubenrauch C (2009) Phase behaviour, interfacial tension and microstructure of microemulsions. In: Stubenrauch C (ed) Microemulsions: background, new concepts, applications, perspectives. Wiley, Chichester, pp 1–47
Shinoda K, Kunieda H (1973) Conditions to produce so-called microemulsions: factors to increase the mutual solubility of oil and water by solubilizer. J Colloid Interface Sci 42:381–387
Antón RE, Castillo P, Salager JL (1986) Surfactant-oil-water systems near the affinity inversion Part IV: emulsion inversion temperature. J Dispersion Sci Technol 7:319–329
Kahlweit M (1995) How to prepare microemulsions at prescribed temperature, oil, and brine. J Phys Chem 99:1281–1284
Salager J, Antón RE, Sabatini DA, Harwell JH, Acosta EJ, Tolosa LI (2005) Enhancing solubilization in microemulsions—state of the art and current trends. J Surfactants Deterg 8:3–21
Salager J, Forgiarini A, Márquez L, Manchego L, Bullón J (2013) How to attain an ultralow interfacial tension and a three-phase behavior with a surfactant formulation for enhanced oil recovery: a review. Part 2. Performance improvement trends from Winsor’s Premise to currently proposed inter- and intra-molecular mixtures. J Surfactants Deterg 16:631–663
Schechter RS, Bourrel M (1988) Microemulsions and related systems: formulation, solvency, and physical properties. Marcel Dekker, New York
Salager JL (1996) Quantifying the concept of physico-chemical formulation in surfactant-oil-water systems—state of the art. Prog Colloid Polym Sci 100:137–142
Allouche J, Tyrode E, Sadtler V, Choplin L, Salager JL (2004) Simultaneous conductivity and viscosity measurements as a technique to track emulsion inversion by the phase-inversion-temperature method. Langmuir 20:2134–2140
Kahlweit M, Lessner E, Strey R (1983) Influence of the properties of the oil and the surfactant on the phase behavior of systems of the type water-oil-nonionic surfactant. J Phys Chem 87:5032–5040
Wade WH, Morgan JC, Schechter RS, Jacobson JK, Salager JL (1978) Interfacial tension and phase behavior of surfactant systems. Soc Pet Eng J. 18:242–252
Mittal KL, Kumar P (eds) (1999) Handbook of microemulsion science and technology. Marcel Dekker, New York
Salager J, Marquez N, Graciaa A, Lachaise J (2000) Partitioning of ethoxylated octylphenol surfactants in microemulsion-oil-water systems: influence of temperature and relation between partitioning coefficient and physicochemical formulation. Langmuir 16:5534–5539
Acosta EJ (2008) The HLD-NAC equation of state for microemulsions formulated with nonionic alcohol ethoxylate and alkylphenol ethoxylate surfactants. Colloids Surf A 320:193–204
Acosta EJ, Yuan JS, Bhakta AS (2008) The characteristic curvature of ionic surfactants. J Surfactants Deterg 11:145–158
Bourrel M, Salager JL, Schechter RS, Wade WH (1980) A correlation for phase behavior of nonionic surfactants. J Colloid Interface Sci 75:451–461
Acosta E, Szekeres E, Sabatini DA, Harwell JH (2003) Net-average curvature model for solubilization and supersolubilization in surfactant microemulsions. Langmuir 19:186–195
Israelachvili JN (2011) Intermolecular and surface forces, 3rd edn. Academic Press, Waltham
Hammond CE, Acosta EJ (2012) On the characteristic curvature of alkyl-polypropylene oxide sulfate extended surfactants. J Surfactants Deterg 15:157–165
Castellino V, Cheng Y-, Acosta E (2011) The hydrophobicity of silicone-based oils and surfactants and their use in reactive microemulsions. J Colloid Interface Sci 353:196–205
Salager J, Antón R, Anderez JM, Aubry J (2001) Formulation des micro-émulsions par la méthode HLD. Techniques de l’Ingénieur 1–20
Pizzino A, Rodriguez MP, Xuereb C, Catté M, Van Hecke E, Aubry J, Salager J (2007) Light backscattering as an indirect method for detecting emulsion inversion. Langmuir 23:5286–5288
Pizzino A, Catté M, Van Hecke E, Salager J, Aubry J (2009) On-line light backscattering tracking of the transitional phase inversion of emulsions. Colloids Surf A 338:148–154
Kiran SK, Nace VM, Silvestri MA, Monk KA, Moloney J, Schmidt L, Acosta EJ (2014) The HLD study of surfactant partitioning for oilfield corrosion inhibitors. J Surfactants Deterg 17:1193–1201
Acosta EJ, Bhakta AS (2009) The HLD-NAC model for mixtures of ionic and nonionic surfactants. J Surfactants Deterg 12:7–19
Kabalnov A, Wennerström H (1996) Macroemulsion stability: the oriented wedge theory revisited. Langmuir 12:276–292
Shinoda K, Saito H, Arai H (1971) The effect of the size and the distribution of the oxyethylene chain lengths of nonionic emulsifiers on the stability of emulsions. J Colloid Interface Sci 35:624–630
Acosta EJ, Le MA, Harwell JH, Sabatini DA (2003) Coalescence and solubilization kinetics in linker-modified microemulsions and related systems. Langmuir 19:566–574
Kabalnov A, Weers J (1996) Macroemulsion stability within the Winsor III region: theory versus experiment. Langmuir 12:1931–1935
Salager JL, Quintero L, Ramos E, Anderez J (1980) Properties of surfactant/oil/water emulsified systems in the neighborhood of the three-phase transition. J Colloid Interface Sci 77:288–289
Bourrel M, Graciaa A, Schechter RS, Wade WH (1979) The relation of emulsion stability to phase behavior and interfacial tension of surfactant systems. J Colloid Interface Sci 72:161–163
Kiran SK (2014) Application of the HLD and NAC Models to the Formation and Stability of Emulsions. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada
Baran JR Jr, Pope GA, Wade WH, Weerasooriya V, Yapa A (1994) Microemulsion formation with mixed chlorinated hydrocarbon liquids. J Colloid Interface Sci 168:67–72
Acosta E, Do MP, Harwell JH, Sabatini DA (2003) Linker-modified microemulsions for a variety of oils and surfactants. J Surfactants Deterg 6:353–363
Salager J, Morgan J, Schechter R, Wade W, Vasquez E (1979) Optimum formulation of surfactant/water/oil systems for minimum interfacial tension or phase behavior. Soc Pet Eng J 19:107–115
Salager JL, Bourrel M, Schechter RS, Wade WH (1979) Mixing rules for optimum phase-behavior formulations of surfactant/oil/water systems. Soc Pet Eng J 19:271–278
Tham MK, Lorenz PB (1981) The EACN of a crude oil: variations with cosurfactant and water oil ratio. In: Fayers FJ (ed) Enhanced oil recovery: proceedings of the Third European Symposium on Enhanced Oil Recovery. Elsevier, New York, pp 123–134
Kahlweit M, Strey R, Haase D (1985) Phase behavior of multicomponent systems water-oil-amphiphile-electrolyte. 3. J Phys Chem 89:163–171
Pardoe I (2012) Applied regression modeling, 2nd edn. Wiley, Hoboken
Salager JL, Anton RE (1999) Ionic microemulsions. In: Kumar P, Mittal KL (eds) Handbook of microemulsion science and technology. Marcel Dekker, Inc, New York, pp 247–280
D’Errico G, Ciccarelli D, Ortona O, Vitagliano V (2002) Mixed micellar aggregates of nonionic surfactants with short hydrophobic tails. J Mol Liq 100:241–253
D’Errico G (2011) On the segregative tendency of ethoxylated surfactants in nonionic mixed micelles. Langmuir 27:3317–3323
Sabatini DA, Acosta E, Harwell JH (2003) Linker molecules in surfactant mixtures. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 8:316–326
Márquez N (2002) Analysis of polyethoxylated surfactants in microemulsion–oil–water systems Part II. Anal Chim Acta 452:129–141
Holmberg K (ed) (2003) Novel surfactants: preparation, applications, and biodegradability, 2nd edn. M. Dekker, New York
Matheson KL, Matson TP, Yang K (1986) Peaked distribution ethoxylates—their preparation, characterization and performance evaluation. J Am Oil Chem Soc 63:365–370
Ontiveros JF, Pierlot C, Catté M, Molinier V (2014) A simple method to assess the hydrophilic lipophilic balance of food and cosmetic surfactants using the phase inversion temperature of C10E4/n-octane/water emulsions. Colloids Surf A 458:32–39
The 30 day Formulation Challenge Project. Speeding up the transition to greener surfactants. http://www.vlci.biz/doc/30%20day%20challange%20summary.pdf. Accessed 28 Aug 2015
Queste S, Salager JL, Strey R, Aubry JM (2007) The EACN scale for oil classification revisited thanks to fish diagrams. J Colloid Interface Sci 312:98–107
Tchakalova V, Fieber W (2012) Classification of fragrances and fragrance mixtures based on interfacial solubilization. J Surfactants Deterg 15:167–177
Ontiveros JF, Pierlot C, Catté M, Molinier V, Pizzino A, Salager J, Aubry J (2013) Classification of ester oils according to their equivalent alkane carbon number (EACN) and asymmetry of fish diagrams of C10E4/ester oil/water systems. J Colloid Interface Sci 403:67–76
Graciaa A, Lachaise J, Sayous JG, Grenier P, Yiv S, Schechter RS, Wade WH (1983) The partitioning of complex surfactant mixtures between oil/water/microemulsion phases at high surfactant concentrations. J Colloid Interface Sci 93:474–486
Boza Troncoso A, Acosta E (2015) The UNIFAC model and the partition of alkyl and alkylphenol ethoxylate surfactants in the excess phases of middle phase microemulsions. Fluid Phase Equilib 397:117–125
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Sasol North America, and BASF North America for donating the reference surfactant samples. This work was supported by the National Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Zarate-Muñoz, S., Texeira de Vasconcelos, F., Myint-Myat, K. et al. A Simplified Methodology to Measure the Characteristic Curvature (Cc) of Alkyl Ethoxylate Nonionic Surfactants. J Surfact Deterg 19, 249–263 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-016-1787-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-016-1787-x