Abstract
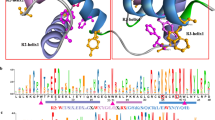
Myeloblastosis (MYB) is one of the largest transcribed factor families in plants. To gain an overall picture of the evolution of MYB genes in relict plants, we cloned nine novel MYB genes in Taxodiaceae plants (Taxodium distichum, Taxodium ascendens, Cryptomeria japonica var. Sinensis, Cryptomeria japonica cv. Araucarioides, Cryptomer Japonica, Metasequoia glyptostroboides, Cunninghamia lanceolata, Taiwania cryptomerioides and Glyptostrobus pensilis). The deduced amino acid sequences for MYBs showed that the nine MYB proteins contained two DNA binding domains. The first domain is from amino acid position 29 to 78, wherein three tryptophanes at 33, 53 and 73 were separated by 19 amino acids, respectively. The second domain is from amino acid position 82 to 127, wherein three tryptophanes at 86, 105 and 124 were separated by 18 amino acids, respectively, whereas the first tryptophane at amino acid position 86 is replaced by a phenylalanine. The characterization of these conserved domains at nine MYBs indicated that they all belong to the R2R3-MYB group. The secondary structure analysis showed that α-helix and β-turn are the major motifs of the predicted secondary structure of MYBs. The three dimensional model of each MYB protein showed that the structure is like clip, making it more flexible and mobile. The similarities between the nine MYB proteins in Taxodiaceae were calculated. The highest identical value of 99% is between CjsMYB, CjMYB and CjaMYB, whereas the lowest value of 82% is between TaMYB and ClMYB. According to the phylogenetic tree, the distances between different genera were relatively large whereas those within genera were relatively small. As expected, accessions of the same genus formed a subgroup before being grouped with other genera.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe H, Yamaguchi-Ssinozake K, Urao T, lwasaki T, Hosokawa D, Shinozaki K. 1997. Role of Arabidopsis MYC and MYB homologs in drought and abscisic acid-regulated gene expression. Plant Cell, 9: 1859–1868.
Bedon F, Grima-Pettenati J, John M. 2007. Conifer R2R3-MYB transcription factors: sequence analyses and gene expression in wood-forming tissues of white spruce (Picea glauca). BMC Plant Biology, 7:17–33
Bilaud T, Koering CE, Binet-Brasselet E, Ancelin K, Pollice A, Gasser SM, Gilson E. 1996. The telobox, a myb-related telomeric DNA binding motif found in proteins from yeast, plants and human. Nucleic Acids Res, 24: 1294–1303.
Braun EL, Grotewold E. 1999. Newly discovered plant c-myb2like genes rewrite the evolution of the plant myb gene family. Plant Physiol, 121: 21–24.
Cedroni ML, Cronn RC, Adams KL, Wilkins TA, Wende JF. 2003. Evolution and expression of MYB genes in diploid and polyploid cotton. Plant Molecular Biology, 51: 313–325.
Chen J, Wang ZY. 2002. Progress in the study of plant MYB transcription factors. Journal of Physiology and Molecular Biology, 28(2): 810–88. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen YH, Yang XY, He K, Liu MH, Li JG, Gao ZF, Lin ZQ, Zhang YF, Wang XX, Qiu XM, Shen YP, Zhang L, Deng XH, Luo JC, Deng XW, Chen ZL, Gu HY, Qu LJ. 2006. The MYB transcription factor superfamily of Arabidopsis: expression analysis and phylogenetic comparison with the rice MYB family. Plant Molecular Biology, 60: 107–124.
Don RH, Cox PT, Wainwright BJ, Baker K, Mattick JS. 1991. ‘Touchdown’ PCR to circumvent spurious priming during gene amplification. Nucleic Acids Res, 19: 4008–4008.
Du H, Yang SS, Liang Z, Feng BR, Liu L, Huang YB, Tang YX. 2012. Genome-wide analysis of the MYB transcription factor superfamily in soybean. BMC Plant Biology, 12: 106–127.
Goicoechea M, Lacombe E, Legay S. 2005. EgMYB2-a new transcriptional activator from Eucalyptus xylem, regulates secondary cell wall formation and lignin biosynthesis. Plant Journal, 43(4): 553–567.
Jin H, Martin C. 1999. Multifunctionality and diversity within the plant MYB-gene family. Plant Mol Biol, 41: 577–585.
Kirst M, Johnson AF, Baucom C, Ulrich E, Hubbard K, Staggs R, Paule C, Retzel E, Whetten R, Sederoff R. 2003. Apparent homology of expressed genes from wood-forming tissues of loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) with Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 100(12): 7383–7388.
Lipsick JS. 1996. One billion years of Myb. Oncogene, 13: 223–235.
Lopes M, Barros A, Neto C. 2001. Variability of cork from Portuguese Quercus suber studied by solidstate C-13-NMR and FTIR spectroscopies. Biopolymers, 62(5): 268–277.
Lu YQ, Jia Q, Tong ZK. 2013. Amplified consensus genetic markers in Taxodiaceae based on Cryptomeria japonica ESTs data. Journal of Forestry Research, 24(3): 503–508.
Moyano E, Martin EZ, Garcia JF, Martin C. 1996. Apparent redundancy in myb-gene function provides gearing for the control of flavonoid bio-synthesis in Antirrhinum flowers. Plant Cell, 8: 1519–1532.
Murray MG, Thompson WF. 1980. Rapid isolation of high molecular-weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res, 8: 4321–4325
Patalaff A, Mcinnis S, Courtenay A. 2003. Characterisation of a pine MYB that regulates lignification. Plant Journal, 36(6): 743–754.
Pavy N, Laroche J, Bousquet J, Mackay J. 2005. Large-scale statistical analysis of secondary xylem ESTs in pine. Plant Mol Biol, 57(2): 203–224.
Rosinski JA, Atchley WR. 1998. Molecular evolution of the Myb family of transcription factors: evidence for polyphyletic origin. J Mol Evol, 46: 74–83.
Sehlabraum SE, Tsuehiay T. 1984. Cytotaxonomy and phylogeny in certain species of Taxodiaceae. Syst Evol, 147: 29–54.
Stracke R, Werber M, Weisshaar B. 2001. The R2R3-MYB gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 4: 447–456.
Wang XQ, Chen BJ, Yin LP. 2003. The plant MYB transcription factors. Biotechnology Information, 2: 22–25.
Wu ZY. 1998. Flora of China, Volume 7: Taxodiaceae. Beijing: China Science Press.
Yu EY, Kim SE, Kim JH, Ko JH, Cho MH, Chung IK. 2000. Sequence-specific DNA recognition by the Myb-like domain of plant telomeric protein RTBP1. J Biol Chem, 275: 24208–24214.
Zhang F, Liu X, Zuo KJ, Sun XF, Tang KX. 2011. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of a novel SANT/MYB gene from Gossypium barbadense. Mol Biol Rep, 38: 2329–2336.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project funding: This work was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of China (30800879) and project 2009R50035 supported by Forest Seedling Industry Innovative Team of Zhejiang province in China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Yq., Jia, Q. & Tong, Zk. Cloning and sequence analysis of nine novel MYB genes in Taxodiaceae plants. Journal of Forestry Research 25, 795–804 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-014-0527-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-014-0527-1