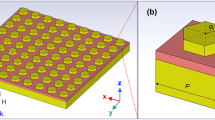
Abstract
Solar radiation is mainly concentrated in visible light region (50%), to achieve the perfect absorption of this spectral band is significant for many energy-related fields include solar cells, hot-electron devices, and perfect cloaking. In this paper, we theoretically designed and numerically demonstrated a broadband perfect absorber that works in visible light (400–800 nm). The perfect absorber consists of silica-titanium nitride-silica-titanium nitride four-layer structure, which has an ultra-thin thickness of 325 nm. This broadband absorber can continuously achieve light absorption from 400 to 800 nm, with an average absorption rate as 99.52% under normal incidence. This absorber obtained 99.98% maximum absorption rate at wavelength 620 nm and 97.18% minimum absorption rate at 400 nm. The multiple integration of propagating surface plasmon resonance, localized surface plasmon resonance, and Fabry-Perot resonance generates the perfect absorption function for this device. The high refractory, polarization independence, large incident angle insensitivity, and simple manufacturing method make this absorber more suitable for solar energy collection and thermal photovoltaics application.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Landy NI, Sajuyigbe S, Mock JJ, Smith D, Padilla W (2008) Perfect metamaterial absorber. Phys Rev Lett 100:207402
Tao H, Bingham CM, Strikwerda AC (2008) Highly flexible wide angle of incidence terahertz metamaterial absorber: design, fabrication, and characterization. Phys Rev B 78:241103
Wu PC, Liao CY, Chen JW (2017) Isotropic absorption and sensor of vertical split-ring resonator. Adv Opt Mater 5:1600581
Zhou JY, Yan S, Li CW (2018) Perfect ultraviolet absorption in graphene using the magnetic resonance of an all-dielectric nanostructure. Opt Express 26:18155–18163
Liu N, Mesch M, Weiss T (2010) Infrared perfect absorber and its application as plasmonic sensor. Nano Lett 10:2342–2348
Zhang BX, Zhao YH, Hao QZ (2011) Polarization-independent dual-band infrared perfect absorber based on a metal-dielectric-metal elliptical nanodisk array. Opt Express 19:15221–15228
Shen XP, Cui TJ, Zhao JM (2011) Polarization-independent wide-angle triple-band metamaterial absorber. Opt Express 19:9401–9407
Zhao L, Liu H, He ZH (2018) Design of multi-narrowband metamaterial perfect absorbers in near-infrared band based on resonators asymmetric method and modified resonators stacked method. Opt Commun 420:95–103
Liu ZQ, Liu GQ, Huang ZP (2018) Ultra-broadband perfect solar absorber by an ultra-thin refractory titanium nitride meta-surface. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 179:346–352
Lei L, Li S, Huang HX (2018) Ultra-broadband absorber from visible to near-infrared using plasmonic metamaterial. Opt Express 26:5686–5693
Huang YJ, Liu L, Pu MB (2018) A refractory metamaterial absorber for ultra-broadband, omnidirectional and polarization-independent absorption in the UV-NIR spectrum. Nanoscale 10:8298–8303
Liu ZQ, Liu GQ, Liu XS (2018) Titanium resonators based ultra-broadband perfect light absorber. Opt Mater 83:118–123
Haegglund C, Apell SP (2012) Plasmonic near-field absorbers for ultrathin solar cells. J Phys Chem Lett 3:1275–1285
Muhammad N, Fu T, Liu Q (2018) Plasmonic metasurface absorber based on electro-optic substrate for energy harvesting. Materials 11:2315
Iqbal T, Ijaz M, Javaid M (2019) An Optimal Au Grating Structure for Light Absorption in Amorphous Silicon Thin Film Solar Cell. Plasmonics 14:147–154
Meng LJ, Zhao D, Ruan ZC (2014) Optimized grating as an ultra-narrow band absorber or plasmonic sensor. Opt Lett 39:1137–1140
Luo SW, Zhao J, Zuo DL (2016) Perfect narrow band absorber for sensing applications. Opt Express 24:9288–9294
Wu D, Liu YM, Li RF (2016) Infrared perfect ultra-narrow band absorber as plasmonic sensor. Nanoscale Res Lett 11:483
Chen C, Wang G, Zhang ZY (2018) Dual narrow-band absorber based on metal-insulator-metal configuration for refractive index sensing. Opt Lett 43:3630–3633
Cui YX, Fung KH, Xu J (2012) Ultrabroadband light absorption by a sawtooth anisotropic metamaterial slab. Nano Lett 12:1443–1447
Ding F, Cui YX, Ge XC (2012) Ultra-broadband microwave metamaterial absorber. Appl Phys Lett 100:103506
Cui YX, Xu J, Fung KH (2011) A thin film broadband absorber based on multi-sized nanoantennas. Appl Phys Lett 99:253101
Ye YQ, Jin Y, He SL (2010) Omnidirectional, polarization-insensitive and broadband thin absorber in the terahertz regime. J Opt Soc Am B 27:498–504
Li W, Guler U, Kinsey N (2014) Refractory plasmonics with titanium nitride: broadband metamaterial absorber. Adv Mater 26:7959
Deng HX, Li ZG, Stan LL (2015) Broadband perfect absorber based on one ultrathin layer of refractory metal. Opt Lett 40:2592–2595
Zhou Y, Luo MH, Shen S (2018) Cost-effective near-perfect absorber at visible frequency based on homogenous meta-surface nickel with two-dimension cylinder array. Opt Express 26:27482–27491
Hedayati MK, Javaherirahim M, Mozooni B (2011) Design of a perfect black absorber at visible frequencies using plasmonic metamaterials. Adv Mater 23:5410
Hedayati MK, Faupel F, Elbahri M (2012) Tunable broadband plasmonic perfect absorber at visible frequency. Appl Phys A-Mater Sci Process 109:769–773
Liang QQ, Fu YQ, Xia XP (2018) Titanium nitride nano-disk arrays-based metasurface as a perfect absorber in the visible range. Modern Phys Lett B 32:1750365
Qian QY, Yan Y, Wang CH (2018) Flexible metasurface black nickel with stepped nanopillars. Opt Lett 43:1231–1234
Kim I, So S, Rana AS (2018) Thermally robust ring-shaped chromium perfect absorber of visible light. Nanophotonics 7:1827–1833
Gao HX, Zhou DP, Cui WL, Liu Z, Liu Y, Jing ZG, Peng W (2019) Ultraviolet broadband plasmonic absorber with dual visible and near-infrared narrow bands. J Opt Soc Am A 36:264–269
Luo X, Zhai X, Wang LL (2018) Enhanced dual-band absorption of molybdenum disulfide using a plasmonic perfect absorber. Opt Express 26:11658–11666
Dao TD, Chen K, Nagao T (2019) Dual-band in situ molecular spectroscopy using single-sized Al-disk perfect absorbers. Nanoscale
Wang JG, Zhang WL, Zhu MP (2015) Broadband perfect absorber with titanium nitride nano-disk array. Plasmonics 10:1473–1478
Gao HX, Peng W, Chu SW, Cui WL, Liu Z, Yu L, Jing ZG (2018) Refractory ultra-broadband perfect absorber from visible to near-infrared. Nanomaterials 8:1038
Ghobadi A, Hajian H, Rashed AR (2018) Tuning the metal filling fraction in metal-insulator-metal ultra-broadband perfect absorbers to maximize the absorption bandwidth. Photon Res 6:168–176
Luo MH, Zhou Y, Wu SL (2017) Wide-angle broadband absorber based on one-dimensional metasurface in the visible region. Appl Phys Express 10:092601
Palik ED (1985) Handbook of optical constants of solids (Orlando)
Guler U, Ndukaife JC, Naik GV (2013) Local heating with lithographically fabricated plasmonic titanium nitride nanoparticles. Nano Lett 13:6078–6083
Wang HC, Chen Q, Wen L (2015) Titanium-nitride-based integrated plasmonic absorber/emitter for solar thermophotovoltaic application. Photon Res 3:329–334
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (61520106013, 61727816) and the Dalian University of Technology (DUT) (DUT18RC016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, H., Peng, W., Liang, Y. et al. Plasmonic Broadband Perfect Absorber for Visible Light Solar Cells Application. Plasmonics 15, 573–580 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-019-01087-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-019-01087-5