Abstract
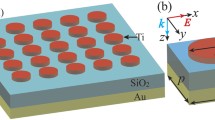
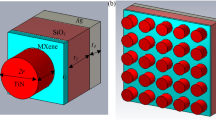
A broadband metamaterial absorber (MA) based on the titanium nitride (TiN) nano-disk array is studied using finite difference time domain simulations. The semiconducting indium tin oxide (ITO) thin film is introduced as the space layer in this sandwiched structure. Utilizing the symmetrical geometry of the MA structure, polarization insensitivity of the broadband absorption was gained. The absorber with TiN nano-disk array shows a peak absorbance of 99 % and larger than 98 % from 560 to 675 nm by numerical simulation. This compact design may have potential applications in the plasmonic sensing and photovoltaic devices.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen HT, O’Hara JF, Azad AK, Taylor AJ (2011) Manipulation of terahertz radiation using metamaterials. Laser Photon Rev 5(4):513–533
Watts CM, Liu X, Padilla WJ (2012) Metamaterial electromagnetic wave absorbers. Adv Mater 24(23):OP98–OP120
Isenstadt A, Xu J (2013) Subwavelength metal optics and antireflection. Electron Mater Lett 9(2):125–132
Akimov YA, Ostrikov K, Li EP (2009) Surface plasmon enhancement of optical absorption in thin-film silicon solar cells. Plasmonics 4(2):107–113
Pu MB, Feng Q, Hu CG, Luo XG (2012) Perfect absorption of light by coherently induced plasmon hybridization in ultrathin metamaterial film. Plasmonics 7(4):733–738
Hao J, Wang J, Liu X, Padilla WJ, Zhou L, Qiu M (2010) High performance optical absorber based on a plasmonic metamaterial. Appl Phys Lett 96(25):251104-1–251104-3
Kats MA, Sharma D, Lin J, Genevet P, Blanchard R, Yang Z, Qazilbash MM, Basov DN, Ramanathan S, Capasso F (2012) Ultra-thin perfect absorber employing a tunable phase change material. Appl Phys Lett 101(22):221101-1–221101–5
Cao T, Wei CW, Simpson RE, Zhang L, Cryan MJ (2014) Broadband polarization-independent perfect absorber using a phase-change metamaterial at visible frequencies. Sci Rep 4:3955
Wang W, Wu S, Reinhardt K, Lu Y, Chen S (2010) Broadband light absorption enhancement in thin-film silicon solar cells. Nano Lett 10(6):2012–2018
Aydin K, Ferry VE, Briggs RM, Atwater HA (2011) Broadband, polarization-independent resonant light absorption using ultrathin, plasmonic super absorbers. Nat Commun 2:517
Ko H, Ko DH, Cho Y, Han IK (2014) Broadband light absorption using a multilayered gap surface plasmon resonator. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 116(3):857–861
Naik GV, Kim J, Boltasseva A (2011) Oxides and nitrides as alternative plasmonic materials in the optical range. Opt Mater Express 1(6):1090–1099
Naik GV, Schroeder JL, Ni X, Kildishev AV, Sands TD, Boltasseva A (2012) Titanium nitride as a plasmonic material for visible and near-infrared wavelengths. Opt Mater Express 2(4):478–489
Naik GV, Shalaev VM, Boltasseva A (2013) Alternative plasmonic materials: beyond gold and silver. Adv Mater 25(24):3264–3294
Li W, Guler U, Kinsey N, Naik GV, Boltasseva A, Guan J, Shalaev VM, Kildishev A (2014) Refractory plasmonics with titanium nitride: broadband metamaterial absorber. Adv Mater 26(47):7959–7965
Abb M, Sepúlveda B, Chong MH, Muskens OL (2012) Transparent conducting oxides for active hybrid metamaterial devices. J Optics 14(11):114007-1–114007-7
Rajak S, Ray M (2014) Comparative study of plasmonic resonance in transparent conducting oxides: ITO and AZO. J Optics 43(3):231–238
Taflove A, Hagness SC (2005) Computational electrodynamics: the finite-difference time-domain method, 3rd edn. Artech House, Boston, Mass
Elsherbeni A, Demir V (2009) The finite-difference time-domain method for electromagnetics with MATLAB simulations. SciTech Publishing, Inc., Raleigh, NC
Palik ED (1985) Handbook of optical constants of solids. Academic, New York
Rottkay KV, Rubin M, Ozer N (1995) Optical indices of tin-doped indium oxide and tungsten oxide electrochromic coatings. Mater Res Soc Symp Proc 403:551–556
Wang J, Fan C, Ding P, He J, Cheng Y, Hu W, Cai G, Liang E, Xue Q (2012) Tunable broad-band perfect absorber by exciting of multiple plasmon resonances at optical frequency. Opt Express 20(14):14871–14878
Zhu J, Li JJ, Deng XC, Zhao JW (2011) Multifactor-controlled non-monotonic plasmon shift of ordered gold nanodisk arrays: shape-dependent interparticle coupling. Plasmonics 6(2):261–267
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Zhang, W., Zhu, M. et al. Broadband Perfect Absorber with Titanium Nitride Nano-disk Array. Plasmonics 10, 1473–1478 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-9962-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-9962-x