Abstract
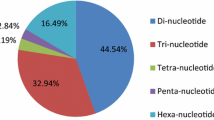
Eucalyptus globulus is the most commonly planted hardwood species for pulpwood in temperate regions. We aimed to develop and characterize functional molecular markers for population genetic analyses and molecular breeding in this model tree species. Public expressed sequence tag (EST) databases were screened for nonredundant sequences to predict putative gene functions and to discover simple sequence repeats (EST-SSRs), which were then validated in E. globulus and six other Eucalyptus species. A total of 4,924 nonredundant sequences were identified from 12,690 updated E. globulus ESTs. Approximately 19.3% (952) were unigenes and contained 1,140 EST-SSR markers, which were mainly trimeric (58.6%). A set of 979 primers for putative SSR markers was designed after bioinformatic analysis. The predicted functions of these ESTs containing SSR were classified according to their gene ontology (GO) categories (biological process, molecular function, and cellular component). GO categories were assigned to 226 ESTs (30.2%). Most ESTs containing SSR (78.7%) had significant matches (E ≤ 10−5) with the nonredundant protein database using BLASTX. From a set of 56 random primer pairs, 37 could be validated in eight E. globulus genotypes and were also tested for cross-transferability to other six Eucalyptus species (Eucalyptus grandis, Eucalyptus saligna, Eucalyptus dunnii, Eucalyptus viminalis, Eucalyptus camaldulensis, Eucalyptus tereticornis). Seventeen polymorphic EST-SSR markers for E. globulus were evaluated in 60 unrelated trees, being representative of the species’ natural distribution. As a result, six highly informative markers were proposed for genetic diversity analyses, fingerprinting, and comparative population studies, between different species of E. globulus.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H et al (2000) Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet 25:25–29. doi:10.1038/75556
Bossinger G, Leitch M (2000) Isolation of cambium-specific genes from Eucalyptus globulus Labill. In: Savidge R, Barnett J, Napier R (eds) Cell and molecular biology of wood formation. BIOS Scientific, Oxford, UK, pp 203–207
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RW (1980) Construction of genetic linkage map in man using restriction length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 32:314–331
Brondani RP, Williams ER, Brondani C, Grattapaglia D (2006) A microsatellite-based consensus linkage map for species of Eucalyptus and a novel set of 230 microsatellite markers for the genus. BMC Plant Biol 6:20. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-6-20
Bundock PC, Potts BM, Vaillancourt RE (2008) Detection and stability of quantitative trait loci (QTL) in Eucalyptus globulus. Tree Genet Genome 4:85–95. doi:10.1007/s11295-007-0090-4
Byrne M, Marquezgarcia M, Uren T, Smith D, Moran G (1996) Conservation and genetic diversity of microsatellite loci in the genus Eucalyptus. Aust J Bot 44:331–341. doi:10.1071/BT9960331
Ceresini PC, Silva CLSP, Missio RF, Souza EC, Fischer CN et al (2005) Satellyptus: analysis and database of microsatellites from ESTs of Eucalyptus. Genet Mol Biol 28:589–600. doi:10.1590/S1415-47572005000400014
Cho YG, Ishii T, Temnykh S, Chen X, Lipovich L et al (2000) Diversity of microsatellites derived from genomic libraries and GenBank sequences in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 100:713–722. doi:10.1007/s001220051343
Chybicki IJ, Burczyk J (2009) Simultaneous estimation of null alleles and inbreeding coefficients. J Hered 100:106–113. doi:10.1093/jhered/esn088
Conesa A, Götz S, García-Gómez JM, Terol J, Talón M, Robles M (2005) Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 21:3674–3676. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bti610
Cordeiro GM, Casu R, McIntyre CL, Manners JM, Henry RJ (2001) Microsatellite markers from sugarcane (Saccharum spp.) ESTs cross transferable to erianthus and sorghum. Plant Sci 160:1115–1123. doi:10.1016/S0168-9452(01)00365
Dauchot N, Mingeot D, Purnelle B, Muys C, Watillon B, Boutry M, Van Cutsem P (2009) Construction of 12 EST libraries and characterization of a 12,226 EST dataset for chicory (Cichorium intybus) root, leaves and nodules in the context of carbohydrate metabolism investigation. BMC Plant Biol 9:14
Dutkowski GW, Potts BM (1999) Geographic patterns of genetic variation in Eucalyptus globulus ssp. globulus and a revised racial classification. Aust J Bot 47:237–263. doi:10.1071/BT97114
Faria DA, Mamani EMC, Pappas MR, Pappas GJ Jr, Grattapaglia D (2010) A selected set of EST-derived microsatellites, polymorphic and transferable across 6 species of Eucalyptus. J Hered 101:512–520. doi:10.1093/jhered/esq024
Faria DA, Mamani EMC, Pappas GJ, Grattapaglia D (2011) Genotyping systems for Eucalyptus based on tetra-, penta-, and hexanucleotide repeat EST microsatellites and their use for individual fingerprinting and assignment tests. Tree Genet Genome 7:63–77. doi:10.1007/s11295-010-0315-9
Fernandez-Silva I, Eduardo I, Blanca J, Esteras C, Picó B et al (2008) Bin mapping of genomic and EST-derived SSRs in melon (Cucumis melo L.). Theor Appl Genet 118:139–150. doi:10.1007/s00122-008-0883-3
Freeman JS, Whittock SP, Potts BM, Vaillancourt RE (2009) QTL influencing growth and wood properties in Eucalyptus globulus. Tree Genet Genome 5:713–722. doi:10.1007/s11295-009-0222-0
Glaubitz JC, Emebiri LC, Moran GF (2001) Dinucleotide microsatellites from Eucalyptus sieberi: inheritance, diversity, and improved scoring of single-base differences. Genome 44:1041–1045
Grattapaglia D (2008) Genomics of Eucalyptus, a global tree for energy, paper, and wood. Genomics Trop Crop Plant 1:259–298. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-71219-2_11
Grattapaglia D, Kirst M (2008) Eucalyptus applied genomics: from gene sequences to breeding tools. New Phytol 179:911–929. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02503.x
Grattapaglia D, Resende MVD (2011) Genomic selection in forest tree breeding. Tree Genet Genome. doi:10.1007/s11295-010-0328-4
Gupta PK, Varshney RK (2000) The development and use of microsatellite markers for genetic analysis and plant breeding with emphasis on bread wheat. Euphytica 113:163–185. doi:10.1023/A:1003910819967
Harper GL, Maclean N, Goulson D (2003) Microsatellite markers to assess the influence of population size, isolation and demographic change on the genetic structure of the UK butterfly Polyommatus bellargus. Mol Ecol 12:3349–3357. doi:10.1046/j.1365-294X.2003.02012.x
Hoisington D, Khairallah M, Gonzalez-de-Leon D (1994) Laboratory protocols: CIMMYT applied molecular genetics laboratory. CIMMYT, Mexico, DF
Junghans DT, Alfenas AC, Brommonschenkel SH, Oda S, Mello EJ, Grattapaglia D (2003) Resistance to rust (Puccinia psidii Winter) in Eucalyptus: mode of inheritance and mapping of a major gene with RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 108:175–180. doi:10.1007/s00122-003-1415-9
Kim K, Ratcliffe S, Wade French B, Liu L, Sappington T (2008) Utility of EST-derived SSRs as population genetics markers in a beetle. J Hered 99(2):112–124. doi:10.1093/jhered/esm104
Külheim C, Yeoh SH, Maintz J, Foley WJ, Moran GF (2009) Comparative SNP diversity among four Eucalyptus species for genes from secondary metabolite biosynthetic pathways. BMC Genomics 10:452. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-10-452
Kumpatla SP, Mukhopadhyay S (2005) Mining and survey of simple sequence repeats in expressed sequence tags of dicotyledonous species. Genome 48:985–998. doi:10.1139/G05-060
La Rota M, Kantety R, Yu JK, Sorrells M (2005) Nonrandom distribution and frequencies of genomic and EST-derived microsatellite markers in rice, wheat, and barley. BMC Genomics 6(1):23. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-6-23
Lima LS, Peres Gramacho K, Pires JL, Clement D, Vanderlei Lopes U, Carels N, da Silva Gesteira A, Gaiotto F, de Mattos Cascardo JC, Micheli F (2010) Development, characterization, validation, and mapping of SSRs derived from Theobroma cacao L.–Moniliophthora perniciosa interaction ESTs. Tree Genet Genome 6:663–676. doi:10.1007/s11295-010-0282-1
Lopez GA, Potts BM, Dutkowski GW, Rodriguez Traverso JM (2001) Quantitative genetics of Eucalyptus globulus: affinities of land race and native stand localities. Silvae Genet 50:244–252
Marcucci Poltri SN, Zelener N, Rodriguez Traverso J, Gelid P, Hopp HE (2003) Selection of a seed orchard of Eucalyptus dunnii based on genetic diversity criteria calculated using molecular markers. Tree Physiol 23:625–632. doi:10.1093/treephys/23.9.625
Marques CM, Carocha VJ, Pereira de Sá AR, Oliveira MR, Pires AM, Sederoff R, Borralho NMG (2005) Verification of QTL linked markers for propagation traits in Eucalyptus. Tree Genet Genome 1:103–108. doi:10.1007/s11295-005-0013-1
Masoudi-Nejad A, Tonomura K, Kawashima S, Moriya Y, Suzuki M et al (2006) EGassembler: online bioinformatics service for large-scale processing, clustering and assembling ESTs and genomic DNA fragments. Nucleic Acids Res 34:W459–W462. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl066
Metzgar D, Bytof J, Wills C (2000) Selection against frameshift mutations limits microsatellite expansion in coding DNA. Genome Res 10:72–80. doi:10.1101/gr.10.1.72
Missiaggia AA, Piacezzi AL, Grattapaglia D (2005) Genetic mapping of Eef1, a major effect QTL for early flowering in Eucalyptus grandis. Tree Genet Genome 1:79–84. doi:10.1007/s11295-005-0011-3
Morgante M, Olivieri AM (1993) PCR-amplified microsatellites as markers in plant genetics. Plant J 3:175–182. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.1993.t01-9-00999.x
Morgante M, Hanafey M, Powell W (2002) Microsatellites are preferentially associated with nonrepetitive DNA in plant genomes. Nat Genet 30:194–200. doi:10.1038/ng822
Nascimento de Sousa S, Finkeldey R, Gailing O (2005) Experimental verification of microsatellite null alleles in Norway spruce (Picea abies [L.] Karst.): implications for population genetic studies. Plant Mol Biol Rep 23:113–119. doi:10.1007/bf02772701
Paniego N, Echaide M, Munoz M, Fernandez L, Torales S, Faccio P, Fuxan I, Carrera M, Zandomeni R, Suárez EY, Hopp HE (2002) Microsatellite isolation and characterization in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Genome 45:34–43. doi:10.1139/g01-120
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2006) Genalex 6: genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol Ecol Notes 6:288–295. doi:10.1111/j.1471-8286.2005.01155.x
Poke FS, Vaillancourt RE, Potts BM, Reid JB (2005) Genomic research in Eucalyptus. Genetica 125:79–101. doi:10.1007/s10709-005-5082-4
Potts BM, Vaillancourt RE, Jordan GJ, Dutkowski GW, Costa e Silva J, McKinnon GE, Steane DA, Volker PW, Lopez GA, Apiolaza L, Li J, Marques C, Borralho NMG (2004) Exploration of the Eucalyptus globulus gene pool. In: Eucalyptus in a changing world. International IUFRO Conference, Aveiro, Portugal, pp 46–61
Powell W, Morgante M, Andre C, Hanafey M, Vogel J, Tingey S, Rafalski A (1996) The comparison of RFLP, RAPD, AFLP and SSR (microsatellite) markers for germplasm analysis. Mol Breed 2:225–238. doi:10.1007/BF00564200
Rabello E, Nunes de Souza A, Saito D, Tsai SM (2005) In silico characterization of microsatellites in Eucalyptus spp.: abundance, length variation and transposon associations. Genet Mol Bio 28:582–588. doi:10.1590/S1415-47572005000400013
Rasmussen-Poblete S, Valdés J, Gamboa MC, Valenzuela PDT, Krauskopf E (2008) Generation and analysis of an Eucalyptus globulus cDNA library constructed from seedlings subjected to low temperature conditions. In: Electron J Biotechnol. Pontificia Universidad Católica de Valparaíso, Chile. Available via DIALOG http://www.ejbiotechnology.info/content/vol11/issue2/full/14/ Accessed Dec 6 2007
Rengel D, San Clemente H, Servant F, Ladouce N, Paux E, Wincker P, Couloux A, Sivadon P, Grima-Pettenati J (2009) A new genomic resource dedicated to wood formation in Eucalyptus. BMC Plant Biol 9:36. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-9-36
Rozen S, Skaletsky HJ (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. In: Krawetz S, Misener S (eds) Bioinformatics methods and protocols: methods in molecular biology. Humana, Totowa, NJ, pp 365–386
Sharma RK, Bhardwaj P, Negi R, Mohapatra T, Ahuja PS (2009) Identification, characterization and utilization of unigene derived microsatellite markers in tea (Camellia sinensis L.). BMC Plant Biol 9:53. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-9-53
Steane DA, Vaillancourt RE, Russell J, Powell W, Marshall D, Potts BM (2001) Development and characterisation of microsatellite loci in Eucalyptus globulus (Myrtaceae). Silvae Genet 50:89–91
Temnykh S, DeClerck G, Lukashova A, Lipovich L, Cartinhour S, McCouch S (2001) Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza sativa L.): frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential. Genome Res 11:1441–1452. doi:10.1101/gr.184001
Teulières C, Marque C (2007) Eucalyptus. In: Pua EC, Davey MR (eds) Transgenic crops, vol 60. Springer, Berlin, pp 387–406
Thamarus K, Groom K, Bradley A, Raymond CA, Schimleck LR, Williams ER, Moran GF (2004) Identification of quantitative trait loci for wood and fibre properties in two full-sib properties of Eucalyptus globulus. Theor Appl Genet 109:856–864. doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1699-4
Thiel T, Michalek W, Varshney RK, Graner A (2003) Exploiting EST databases for the development and characterization of gene-derived SSR-markers in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor Appl Genet 106:411–422. doi:10.1007/s00122-002-1031-0
Thumma BR, Southerton SG, Bell JC, Owen JV, Henery ML, Moran GF (2010) Quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis of wood quality traits in Eucalyptus nitens. Tree Genet Genome 6:305–317. doi:10.1007/s11295-009-0250-9
Van der Nest MA, Steenkamp ET, Wingfield BD, Wingfield MJ (2000) Development of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers in Eucalyptus from amplified inter-simple sequence repeats (ISSR). Plant Breed 119:433–436. doi:10.1046/j.1439-0523.2000.00515.x
Voiblet C, Duplessis S, Encelot N, Martin F (2001) Identification of symbiosis-regulated genes in Eucalyptus globulus–Pisolithus tinctorius ectomycorrhiza by differential hybridization of arrayed cDNAs. Plant J 25:181–191. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2001.00953.x
Yasodha R, Sumathi R, Chezhian P, Kavitha S, Ghosh M (2008) Eucalyptus microsatellites mined in silico: survey and evaluation. J Genet 87:21–25. doi:10.1007/s12041-008-0003-9
Zhang LY, Bernard M, Leroy P, Feuillet C, Sourdille P (2005) High transferability of bread wheat EST-derived SSRs to other cereals. Theor Appl Genet 111:677–687. doi:10.1007/s00122-005-2041-5
Acknowledgments
Cintia Acuña thanks Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET), Buenos Aires, Argentina for a fellowship to support her PhD studies. Special thanks to Pablo Pathauer for collecting and selecting the plant material. We are grateful to Dr. Norma Paniego for their scientific assistance during the first part of this work. Special thanks go to Eleonora Campos and Verónica Villalba for the critical reading of the manuscript. We gratefully acknowledge the excellent assistance of the Bioinformatics Unit at the Biotechnology Institute, INTA Castelar, especially Dr. Marcelo Soria. We thank the anonymous reviewers for their comments and suggestions on the manuscript. This research was supported by the ANPCyT/FONCYT, BID 1728 OC/AR, PICT-2008-00118, INTA-PE 041120, and BiotecSur UE 127118.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. G. Vendramin
Authors’ information
CVA is a PhD student supported by a fellowship from Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET, Argentina). Dr. PF is a career member of the Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET, Argentina). Dr. HEH is also a career member of the Comisión de Investigaciones Científicas de la Provincia de Buenos Aires (CIC) and Professor at the Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales, Universidad de Buenos Aires (UBA).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Online Resource 1
In silico EST-SSRs derived from curated public E. globulus libraries. The data describe the 1,140 EST-SSRs: unigenes names, similarity matches, E value, similarity mean, GO term, sequence length, SSR description, primers description (sequence of forward and reverse primers, annealing temperature (°C)), expected product size (bp), and unigene sequences (XLS 1295 kb)
Online Resource 2
Gene ontology annotation. This table provides the detailed information of sequence distribution in graph levels, GO term, number of sequences and parents for biological process, molecular function, and component categories (XLS 112 kb)
Online Resource 3
Pathways maps. This table provides information on the enzymes putatively encoded by the ESTs containing SSR, based on homology prediction and their associated pathways. This includes KEGG maps, enzyme names, and sequences (XLS 54 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Acuña, C.V., Fernandez, P., Villalba, P.V. et al. Discovery, validation, and in silico functional characterization of EST-SSR markers in Eucalyptus globulus . Tree Genetics & Genomes 8, 289–301 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-011-0440-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-011-0440-0