Abstract
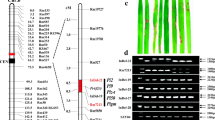
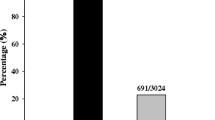
Rice (Oryza sativa L.) blast caused by fungus Magnaporthe oryzae is one of the most devastating diseases throughout the world. In the current study, a rice blast resistance gene, designated as Pike, was identified from an indica breeding line Xiangzao143 conferring a durable resistance to rice blast. A map-based cloning strategy was then employed to locate Pike to a 306-kb genomic interval in proximity of the telomeric region of the long arm of chromosome 11. Candidate gene analysis and transgenic complementation test demonstrated that two Xiangzao143-derived adjacent CC–NBS–LRR genes (Pike-1 and Pike-2) at the previously identified Pik locus were required for the Pike-mediated resistance. As compared to the previously identified Pik alleles, the putative Pike-1 peptide was found to be unique in three highly polymorphic sites, two amino acid residue sites (D153 and D229) in the CC domain and one site (L442-W443-P465) in the NBS domain. In addition, against a set of 215 M. oryzae isolates collected from diverse rice cropping areas of China, the Pike carrier Xiangzao143 showed a unique resistance spectrum and a high resistance frequency of 86.1 %. These results thus declared Pike as a novel allele of the Pik locus. Two SNPs G1328C and A3017T in Pike DNA sequence were identified and based on the SNPs, two Pike-specific dCAPS markers d-G1328C and d-A3017T were developed and have been used to effectively distinguish Pike from all of the previously identified Pik alleles.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashikawa I (2012) Regions outside the leucine-rich repeat domain determine the distinct resistance specificities of the rice blast resistance genes Pik and Pik-m. Mol Breed 30(3):1531–1535
Ashikawa I, Hayashi N, Yamane H, Kanamori H, Wu J, Matsumoto T, Ono K, Yano M (2008) Two adjacent nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat class genes are required to confer Pikm-specific rice blast resistance. Genetics 180(4):2267–2276
Bai J, Pennill LA, Ning J, Lee SW, Ramalingam J, Webb CA, Zhao B, Sun Q, Nelson JC, Leach JE, Hulbert SH (2002) Diversity in nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeat genes in cereals. Genome Res 12(12):1871–1884
Bonman JM, Dios TIVd, Khin MM (1986) Physiologic specialization of Pyricularia oryzae in the Philippines. Plant Dis 70:767–769
Bookout AL, Mangelsdorf DJ (2003) Quantitative real-time PCR protocol for analysis of nuclear receptor signaling pathways. Nucl Recept Signal 1:e012
Bryan GT, Wu KS, Farrall L, Jia Y, Hershey HP, McAdams SA, Faulk KN, Donaldson GK, Tarchini R, Valent B (2000) A single amino acid difference distinguishes resistant and susceptible alleles of the rice blast resistance gene Pi-ta. Plant Cell 12:2033–2046
Campbell MA, Chen D, Ronald PC (2004) Development of co-dominant amplified polymorphic sequence markers in rice that flank the Magnaporthe grisea resistance gene Pi7(t) in recombinant inbred line 29. Phytopathology 94(3):302–307
Cesari S, Thilliez G, Ribot C, Chalvon V, Michel C, Jauneau A, Rivas S, Alaux L, Kanzaki H, Okuyama Y, Jean-BenoitMorel Fournier E, Tharreau D, Terauchi R, Kroja T (2013) The rice resistance protein pair RGA4/RGA5 recognizes the Magnaporthe oryzae effectors AVR-Pia and AVR1-CO39 by direct binding. Plant Cell 25:1463–1481
Chen DH, dela Vina M, Inukai T, Mackill DJ, Ronald PC, Nelson RJ (1999) Molecular mapping of the blast resistance gene, Pi44(t), in a line derived from a durably resistant rice cultivar. Crop species. Theor Appl Genet 98(6–7):1046–1053
Chen X, Shang J, Chen D, Lei C, Zou Y, Zhai W, Liu G, Xu J, Ling Z, Cao G, Ma B, Wang Y, Zhao X, Li S, Zhu L (2006) A B-lectin receptor kinase gene conferring rice blast resistance. Plant J 46(5):794–804
Dai L, Wu J, Li X, Wang X, Liu X, Jantasuriyarat C, Kudrna D, Yu Y, Wing RA, Han B, Zhou B, Wang GL (2010) Genomic structure and evolution of the Pi2/9 locus in wild rice species. Theor Appl Genet 121(2):295–309
Deng Y, Zhu X, Shen Y, He Z (2006) Genetic characterization and fine mapping of the blast resistance locus Pigm(t) tightly linked to Pi2 and Pi9 in a broad-spectrum resistant Chinese variety. Theor Appl Genet 113(4):705–713
Fjellstrom R, Conaway-Bormans CA, McClung AM, Marchetti MA, Shank AR, Park WD (2004) Development of DNA markers suitable for marker assisted selection of three Pi genes conferring resistance to multiple Pyricularia grisea pathotypes. Crop Sci 44(5):1790–1798
Flor HH (1971) Current status of gene-for-gene concept. Annu Rev Phytopathol 9:275–296
Fukuoka S, Saka N, Koga H, Ono K, Shimizu T, Ebana K, Hayashi N, Takahashi A, Hirochika H, Okuno K, Yano M (2009) Loss of function of a proline-containing protein confers durable disease resistance in rice. Science 325(5943):998–1001
Fukuoka S, Yamamoto S-I, Mizobuchi R, Yamanouchi U, Ono K, Kitazawa N, Yasuda N, Fujita Y, Thi Thanh Nguyen T, Koizumi S, Sugimoto K, Matsumoto T, Yano M (2014) Multiple functional polymorphisms in a single disease resistance gene in rice enhance durable resistance to blast. Sci Rep. doi:10.1038/srep04550
Hittalmani S, Parco A, Mew TV, Zeigler RS, Huang N (2000) Fine mapping and DNA marker-assisted pyramiding of the three major genes for blast resistance in rice. Theor Appl Genet 100(7):1121–1128
Hua L, Wu J, Chen C, Wu W, He X, Lin F, Wang L, Ashikawa I, Matsumoto T, Pan Q (2012) The isolation of Pi1, an allele at the Pik locus which confers broad spectrum resistance to rice blast. Theor Appl Genet 125(5):1047–1055
Jia Y, McAdams SA, Bryan GT, Hershey HP, Valent B (2000) Direct interaction of resistance gene and avirulence gene products confers rice blast resistance. EMBO J 19(15):4004–4014
Kanzaki H, Yoshida K, Saitoh H, Fujisaki K, Hirabuchi A, Alaux L, Fournier E, Tharreau D, Terauchi R (2012) Arms race co-evolution of Magnaporthe oryzae AVR-Pik and rice Pik genes driven by their physical interactions. Plant J 72:894–907
Lee SK, Song MY, Seo YS, Kim HK, Ko S, Cao PJ, Suh JP, Yi G, Roh JH, Lee S, An G, Hahn TR, Wang GL, Ronald P, Jeon JS (2009) Rice Pi5-mediated resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae requires the presence of two coiled-coil–nucleotide–binding-leucine-rich repeat genes. Genetics 181(4):1627–1638
Leister D (2004) Tandem and segmental gene duplication and recombination in the evolution of plant disease resistance gene. Trends Genet 20(3):116–122
Liu W, Wang F, Liu Z, Zhu X, Li X, Huang H, Liao Y, Zhu M, Fu C, Chen J (2012) Improvement of rice blast resistance in CMS line Rongfeng A by pyramiding Pi-1 and Pi-2 with molecular marker techniques. Mol Plant Breed 10(5):575–582 (in Chinese)
Liu W, Liu J, Ning Y, Ding B, Wang X, Wang Z, Wang GL (2013) Recent progress in understanding PAMP- and effector-triggered immunity against the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Mol Plant 6(3):605–620
McDonnell AV, Jiang T, Keating AE, Berger B (2006) Paircoil2: improved prediction of coiled coils from sequence. Bioinformatics 22(3):356–358
Neff MM, Neff JD, Chory J, Pepper AE (1998) dCAPS, a simple technique for the genetic analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms: experimental applications in Arabidopsis thaliana genetics. Plant J 14(3):387–392
Okuyama Y, Kanzaki H, Abe A, Yoshida K, Tamiru M, Saitoh H, Fujibe T, Matsumura H, Shenton M, Galam DC, Undan J, Ito A, Sone T, Terauchi R (2011) A multifaceted genomics approach allows the isolation of the rice Pia-blast resistance gene consisting of two adjacent NBS–LRR protein genes. Plant J 66(3):467–479
Pink DAC (2002) Strategies using genes for non-durable disease resistance. Euphytica 124(2):227–236
Qu S, Liu G, Zhou B, Bellizzi M, Zeng L, Dai L, Han B, Wang GL (2006) The broad-spectrum blast resistance gene Pi9 encodes a nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat protein and is a member of a multigene family in rice. Genetics 172(3):1901–1914
Richly E, Kurth J, Leister D (2002) Mode of amplification and reorganization of resistance genes during recent Arabidopsis thaliana evolution. Mol Biol Evol 19(1):76–84
Rybka K, Miyamoto M, Ando I, Saito A, Kawasaki A (1997) High resolution mapping of the indica-derived rice blast resistance genes II. Pi-ta2 and Pi-ta and a consideration of their origin. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 10:517–524
Ryu HS, Han M, Lee SK, Cho JI, Ryoo N, Heu S, Lee YH, Bhoo SH, Wang GL, Hahn TR, Jeon JS (2006) A comprehensive expression analysis of the WRKY gene superfamily in rice plants during defense response. Plant Cell Rep 25(8):836–847
Skamnioti P, Gurr SJ (2009) Against the grain: safeguarding rice from rice blast disease. Trends Biotechnol 27(3):141–150
Sun X, Yang Z, Wang S, Zhang Q (2003) Identification of a 47-kb DNA fragment containing Xa4, a locus for bacterial blight resistance in rice. Theor Appl Genet 106(4):683–687
Sun XL, Cao YL, Yang ZF, Xu CG, Li XH, Wang SP, Zhang QF (2004) Xa26, a gene conferring resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in rice, encodes an LRR receptor kinase-like protein. Plant J 37(4):517–527
Wang Z, Yano M, Yamanouchi U, Iwamoto M, Monna L, Hayasaka H, Katayose Y, Sasaki T (1999) The Pib gene for rice blast resistance belongs to the nucleotide binding and leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes. Plant J 19(1):55–64
Wang CT, Tan MP, Xu X, Wen GS, Zhang DP, Lin XH (2003) Localizing the bacterial blight resistance gene, Xa22(t), to a 100-kilobase bacterial artificial chromosome. Phytopathology 93(10):1258–1262
Wang L, Yu Y, Wu Y, Wang J, Xiao F, Gong H, Zhang Q (2006) Breeding and application of an quality early indica resistant cultivar Xiangzao143. China Rice (5):24–25 (in Chinese)
Yuan B, Zhai C, Wang W, Zeng X, Xu X, Hu H, Lin F, Wang L, Pan Q (2011) The Pik-p resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae in rice is mediated by a pair of closely linked CC–NBS–LRR genes. Theor Appl Genet 122(5):1017–1028
Zhai C, Lin F, Dong Z, He X, Yuan B, Zeng X, Wang L, Pan Q (2011) The isolation and characterization of Pik, a rice blast resistance gene which emerged after rice domestication. New Phytol 189(1):321–334
Zhai C, Zhang Y, Yao N, Lin F, Liu Z, Dong Z, Wang L, Pan Q (2014) Function and interaction of the coupled genes responsible for Pik-h encoded rice blast resistance. PLoS ONE 9(6):e98067
Zhou T, Wang Y, Chen JQ, Araki H, Jing Z, Jiang K, Shen J, Tian D (2004) Genome-wide identification of NBS genes in japonica rice reveals significant expansion of divergent non-TIR NBS–LRR genes. Mol Genet Genomics 271(4):402–415
Zhou B, Qu S, Liu G, Dolan M, Sakai H, Lu G, Bellizzi M, Wang G (2006) The eight amino-acid differences within three leucine-rich repeats between Pi2 and Piz-t resistance proteins determine the resistance specificity to Magnaporthe grisea. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 19(11):1216–1228
Zhu X, Chen S, Yang J, Zhou S, Zeng L, Han J, Su J, Wang L, Pan Q (2012) The identification of Pi50(t), a new member of the rice blast resistance Pi2/Pi9 multigene family. Theor Appl Genet 124(7):1295–1304
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Cailin Lei of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences and Prof. Weiren Wu of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University for providing rice blast R gene monogenic lines and Dr. Dazhao Yu of the Hubei Academy of Agricultural Sciences of China for providing some of the M. oryzae isolates inoculated in the present study. This work was financed by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 0.30771153) and the Science and Technology Project of Hubei Province in China (No. 2010CBB02401).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Peng, P., Tian, J. et al. Pike, a rice blast resistance allele consisting of two adjacent NBS–LRR genes, was identified as a novel allele at the Pik locus. Mol Breeding 35, 117 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-015-0305-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-015-0305-6