Abstract
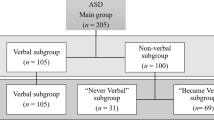
Research suggests that toddlers with no language delay (NLD) should have better outcomes than those with language delay (LD). However, the predictive utility of language milestones relative to co-varying factors such as age at diagnosis, IQ, and ASD symptomatology is unclear. This study compared school-aged children with ASD and NLD (n = 59) to a well-matched group with ASD and LD (n = 59). The LD group was diagnosed at younger ages and their historical ASD symptoms were more severe than the NLD group. The groups were similar in current ASD symptoms and adaptive functioning at school age. Language milestones were correlated with adaptive functioning, but IQ and social symptoms of ASD were stronger predictors of functioning at school age. Therefore, language milestones may not be the best indicators of prognosis for children who are diagnosed after toddlerhood.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The ADI-R provides a single set of cut-offs for Autism, with no lower cut-offs provided for ASD. Although most participants met ADI-R criteria for Autism, some met criteria provided by other authors for Borderline Autism (n = 3; Buxbaum et al. 2001, pgs. 1515–1516), Asperger’s Disorder or PDD-NOS (ns = 1 and 6, respectively; Seltzer et al. 2003, pg. 569).
Spearman correlations account for skewness and kurtosis by rank-ordering values of each variable prior to correlating them. They are also robust to outliers. The resulting value, Spearman’s rho (ρ), is equivalent to Pearson’s r in interpretation.
Although neither the current study nor the study by Frost and colleagues included children across the full range of language abilities, it is reasonable to assume that the presence vs. absence of language would be a strong predictor of functioning (e.g., Venter et al. 1992).
We thank an anonymous reviewer for this suggestion.
References
American Psychiatric Association (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-IV), (4th ed.). Washington, DC: Author.
American Psychiatric Association (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5), (5th ed.). Washington, DC: Author.
Anderson, D. K., Liang, J. W., & Lord, C. (2014). Predicting young adult outcome among more and less cognitively able individuals with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 55(5), 485–494.
Ben-Itzchak, E., & Zachor, D. A. (2007). The effects of intellectual functioning and autism severity on outcome of early behavioral intervention for children with autism. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 28(3), 287–303.
Bennett, T., Szatmari, P., Bryson, S., Volden, J., Zwaigenbaum, L., Vaccarella, L., … Boyle, M. (2008). Differentiating autism and Asperger syndrome on the basis of language delay or impairment. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38(4), 616–625.
Buxbaum, J. D., Silverman, J. M., Smith, C. J., Kilifarski, M., Reichert, J., Hollander, E., … Davis, K. L. (2001). Evidence for a susceptibility gene for autism on chromosome 2 and for genetic heterogeneity. The American Journal of Human Genetics, 68(6), 1514–1520.
Chawarska, K., Paul, R., Klin, A., Hannigen, S., Dichtel, L. E., & Volkmar, F. (2007). Parental recognition of developmental problems in toddlers with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 37(1), 62–72.
Christensen, D. L., Baio, J., Braun, K. V., Bilder, D., Charles, J., Constantino, J. N., … Lee, L. C. (2016). Prevalence and characteristics of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years: Autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2012. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report Surveillance Summaries, 65(3), 1–23.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Coonrod, E. E., & Stone, W. L. (2004). Early concerns of parents of children with autistic and nonautistic disorders. Infants & Young Children, 17(3), 258–268.
Dawson, G., Rogers, S., Munson, J., Smith, M., Winter, J., Greenson, J., … Varley, J. (2010). Randomized, controlled trial of an intervention for toddlers with autism: The early start Denver model. Pediatrics, 125(1), e17–e23.
Eaves, L. C., & Ho, H. H. (2004). The very early identification of autism: Outcome to age 4 1/2–5. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 34(4), 367–378.
Ellis Weismer, S. (2000). Intervention for children with developmental language delay. In D. V. M. Bishop & L. B. Leonard (Eds.), Speech and language impairments in children: causes, characteristics, intervention and outcome (pp. 157–176). East Sussex: Psychology Press.
Farley, M. A., McMahon, W. M., Fombonne, E., Jenson, W. R., Miller, J., Gardner, M., … Coon, H. (2009). Twenty-year outcome for individuals with autism and average or near-average cognitive abilities. Autism Research, 2(2), 109–118.
Fenson, L., Dale, P. S., Reznick, J. S., Bates, E., Thal, D. J., & Pethick, S. J. (1994). Variability in early communicative development. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 59(5), i–i173.
Frost, K. M., Hong, N., & Lord, C. (2017). Correlates of adaptive functioning in minimally verbal children with autism spectrum disorder. American Journal on Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities, 122(1), 1–10.
Gillespie-Lynch, K., Sepeta, L., Wang, Y., Marshall, S., Gomez, L., Sigman, M., & Hutman, T. (2012). Early childhood predictors of the social competence of adults with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 42(2), 161–174.
Gotham, K., Pickles, A., & Lord, C. (2009). Standardizing ADOS scores for a measure of severity in autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 39(5), 693–705.
Guthrie, W., Swineford, L. B., Nottke, C., & Wetherby, A. M. (2013). Early diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder: Stability and change in clinical diagnosis and symptom presentation. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 54(5), 582–590.
Herlihy, L., Knoch, K., Vibert, B., & Fein, D. (2015). Parents’ first concerns about toddlers with autism spectrum disorder: Effect of sibling status. Autism: The International Journal of Research and Practice, 19(1), 20–28.
Hertz-Picciotto, I., & Delwiche, L. (2009). The rise in autism and the role of age at diagnosis. Epidemiology (Cambridge, Mass.), 20(1), 84–90.
Howlin, P., & Asgharian, A. (1999). The diagnosis of autism and Asperger syndrome: Findings from a survey of 770 families. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology, 41(12), 834–839.
Howlin, P., & Moore, A. (1997). Diagnosis in autism: A survey of over 1200 patients in the UK. Autism: The International Journal of Research and Practice, 1(2), 135–162.
Hus, V., Gotham, K., & Lord, C. (2014). Standardizing ADOS domain scores: Separating severity of social affect and restricted and repetitive behaviors. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 44(10), 2400–2412.
Hus, V., Taylor, A., & Lord, C. (2011). Telescoping of caregiver report on the Autism diagnostic interview: Revised. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 52(7), 753–760.
Kanne, S. M., Gerber, A. J., Quirmbach, L. M., Sparrow, S. S., Cicchetti, D. V., & Saulnier, C. A. (2011). The role of adaptive behavior in autism spectrum disorders: Implications for functional outcome. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 41(8), 1007–1018.
Kaufman, A. S., & Kaufman, N. L. (2004). Kaufman brief intelligence test (KBIT-2), (2nd ed.). Bloomington, MN: Pearson, Inc.
Kelley, E., Naigles, L., & Fein, D. (2010). An in-depth examination of optimal outcome children with a history of autism spectrum disorders. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 4(3), 526–538.
Kenworthy, L., Wallace, G. L., Powell, K., Anselmo, C., Martin, A., & Black, D. O. (2012). Early language milestones predict later language, but not autism symptoms in higher functioning children with autism spectrum disorders. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 6(3), 1194–1202.
Kjelgaard, M. M., & Tager-Flusberg, H. (2001). An investigation of language impairment in autism: Implications for genetic subgroups. Language and Cognitive Processes, 16(2–3), 287–308.
Klin, A., Saulnier, C. A., Sparrow, S. S., Cicchetti, D. V., Volkmar, F. R., & Lord, C. (2007). Social and communication abilities and disabilities in higher functioning individuals with autism spectrum disorders: The Vineland and the ADOS. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 37(4), 748–759.
Kover, S. T., Edmunds, S. R., & Ellis Weismer, S. (2016). Brief report: Ages of language milestones as predictors of developmental trajectories in young children with autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 46(7), 2501–2507.
Landa, R. (2007). Early communication development and intervention for children with autism. Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews, 13(1), 16–25.
Liss, M., Harel, B., Fein, D., Allen, D., Dunn, M., Feinstein, C., … Rapin, I. (2001). Predictors and correlates of adaptive functioning in children with developmental disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 31(2), 219–230.
Lord, C., Rutter, M., DiLavore, P. C., & Risi, S. (1999). Autism diagnostic observation schedule manual. Los Angeles, CA: Western Psychological Services.
Lord, C., Rutter, M., DiLavore, P. C., Risi, S., Gotham, K., & Bishop, S. L. (2012). Autism diagnostic observation schedule, second edition manual (part 1): Modules 1–4. Torrance, CA: Western Psychological Services.
Mandell, D. S., Listerud, J., Levy, S. E., & Pinto-Martin, J. A. (2002). Race differences in the age at diagnosis among Medicaid-eligible children with autism. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 41(12), 1447–1453.
Mandell, D. S., Novak, M. M., & Zubritsky, C. D. (2005). Factors associated with age of diagnosis among children with autism spectrum disorders. Pediatrics, 116(6), 1480–1486.
Matthews, N. L., Pollard, E., Ober-Reynolds, S., Kirwan, J., Malligo, A., & Smith, C. J. (2015). Revisiting cognitive and adaptive functioning in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 45(1), 138–156.
Mayes, S. D., & Calhoun, S. L. (2001). Non-significance of early speech delay in children with autism and normal intelligence and implications for DSM-IV Asperger’s disorder. Autism: The International Journal of Research and Practice, 5(1), 81–94.
Mayo, J., Chlebowski, C., Fein, D. A., & Eigsti, I. M. (2013). Age of first words predicts cognitive ability and adaptive skills in children with ASD. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 43(2), 253–264.
Mazurek, M. O., Kanne, S. M., & Miles, J. H. (2012). Predicting improvement in social–communication symptoms of autism spectrum disorders using retrospective treatment data. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 6(1), 535–545.
McDonald, C. A., Thomeer, M. L., Lopata, C., Fox, J. D., Donnelly, J. P., Tang, V., & Rodgers, J. D. (2015). VABS-II ratings and predictors of adaptive behavior in children with HFASD. Journal of Developmental and Physical Disabilities, 27(2), 235–247.
McDuffie, A., Thurman, A. J., Hagerman, R. J., & Abbeduto, L. (2015). Symptoms of autism in males with fragile X syndrome: A comparison to nonsyndromic ASD using current ADI-R scores. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 45(7), 1925–1937.
McGrath, R. E., & Meyer, G. J. (2006). When effect sizes disagree: The case of r and d. Psychological Methods, 11(4), 386–401.
Mitchell, S., Cardy, J. O., & Zwaigenbaum, L. (2011). Differentiating autism spectrum disorder from other developmental delays in the first two years of life. Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews, 17(2), 130–140.
Perry, A., Flanagan, H. E., Geier, J. D., & Freeman, N. L. (2009). Brief report: The Vineland adaptive behavior scales in young children with autism spectrum disorders at different cognitive levels. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 39(7), 1066–1078.
Rodrigue, J. R., Morgan, S. B., & Geffken, G. R. (1991). A comparative evaluation of adaptive behavior in children and adolescents with autism, Down syndrome, and normal development. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 21(2), 187–196.
Rogers, S. J., Estes, A., Lord, C., Vismara, L., Winter, J., Fitzpatrick, A., … Dawson, G. (2012). Effects of a brief early start Denver model (ESDM)-based parent intervention on toddlers at risk for autism spectrum disorders: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 51(10), 1052–1065.
Roid, G. H. (2003). Stanford-binet intelligence scales (SB-5), (5th ed.). Itasca, IL: Riverside Publishing.
Rutter, M., Le Couteur, A., & Lord, C. (2003). Autism diagnostic interview-revised (ADI-R) manual. Los Angeles, CA: Western Psychological Services.
Sallows, G. O., & Graupner, T. D. (2005). Intensive behavioral treatment for children with autism: Four-year outcome and predictors. American Journal on Mental Retardation, 110(6), 417–438.
Seltzer, M. M., Krauss, M. W., Shattuck, P. T., Orsmond, G., Swe, A., & Lord, C. (2003). The symptoms of autism spectrum disorders in adolescence and adulthood. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 33(6), 565–581.
Sigman, M., & McGovern, C. W. (2005). Improvement in cognitive and language skills from preschool to adolescence in autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 35(1), 15–23.
Sparrow, S. S., Balla, D. A., & Cicchetti, D. V. (1984). Vineland adaptive behavior scales, survey form manual. Circle Pines, MN: American Guidance Service.
Sparrow, S. S., Cicchetti, D. V., & Balla, D. A. (2005). Vineland adaptive behavior scales, survey forms manual (2nd ed.). Bloomington, MN: Pearson, Inc.
Szatmari, P., Bryson, S., Duku, E., Vaccarella, L., Zwaigenbaum, L., Bennett, T., & Boyle, M. H. (2009). Similar developmental trajectories in autism and Asperger syndrome: From early childhood to adolescence. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 50(12), 1459–1467.
Szatmari, P., Bryson, S. E., Streiner, D. L., Wilson, F., Archer, L., & Ryerse, C. (2000). Two-year outcome of preschool children with autism or Asperger’s syndrome. American Journal of Psychiatry, 157(12), 1980–1987.
Thurm, A., Manwaring, S. S., Swineford, L., & Farmer, C. (2015). Longitudinal study of symptom severity and language in minimally verbal children with autism. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 56(1), 97–104.
Venter, A., Lord, C., & Schopler, E. (1992). A follow-up study of high-functioning autistic children. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 33(3), 489–597.
Wodka, E. L., Mathy, P., & Kalb, L. (2013). Predictors of phrase and fluent speech in children with autism and severe language delay. Pediatrics, 131(4), e1128–e1134.
Zablotsky, B., Colpe, L. J., Pringle, B. A., Kogan, M. D., Rice, C., & Blumberg, S. J. (2017). Age of parental concern, diagnosis, and service initiation among children with autism spectrum disorder. American Journal on Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities, 122(1), 49–61.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the contributions of SARRC research staff to data collection. We also thank all children and families whose participation made this research possible.
Funding
This study was supported by internal funds at SARRC.
Author Contributions
AG conceived of the study, performed the statistical analysis, interpreted the results, drafted and revised the manuscript. NLM edited the manuscript and contributed to its design. CJS supervised data collection, edited the manuscript and contributed to its design. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. This study involved retrospective review of previously-collected de-identified data; as such, it was exempt from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Human Subjects Research policy 45 CFR 46.
Informed Consent
This research met criteria for the American Psychological Association’s ethical standard 8.05: Dispensing with Informed Consent for Research. For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Appendix
Appendix
See Table 6.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goodwin, A., Matthews, N.L. & Smith, C.J. The Effects of Early Language on Age at Diagnosis and Functioning at School Age in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. J Autism Dev Disord 47, 2176–2188 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-017-3133-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-017-3133-1