Abstract
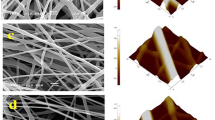
Polylactide (PLA)/cellulose nanofiber (CNF) biocomposites were prepared via solution casting and direct melt mixing. To improve the compatibility, a masterbatch of CNFs and poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) (1:2) was also prepared. The effects of PEG on the morphology and properties of the biocomposites were investigated. The dispersion/distribution of nanofibers in PLA was improved when the masterbatch was used and the composites were prepared in solution. Substantial effects on the rheological properties of solution-prepared PLA/CNF/PEG composites were observed compared to composites containing no PEG, whereas for melt-prepared composites no significant changes were detected. Increased crystalline content and crystallization temperature were observed for the composites prepared via the masterbatch and solvent casting. The storage modulus of PLA was increased by 42 and 553% at 25 and at 80 °C, respectively, for the solution-based PEG-compatibilized composite containing 2 wt% nanofibers. Also, a better light transmittance was measured for the PLA/CNF/PEG composites prepared in solution.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi S, Carreau PJ, Derdouri A, Moan M (2009) Rheological properties and percolation in suspensions of multiwalled carbon nanotubes in polycarbonate. Rheol Acta 48:943–959. doi:10.1007/s00397-009-0375-7
Abdulkhani A, Hosseinzadeh J, Ashori A, Dadashi S, Takzare Z (2014) Preparation and characterization of modified cellulose nanofibers reinforced polylactic acid nanocomposite. Polym Test 35:73–79. doi:10.1016/j.polymertesting.2014.03.002
Adamska K, Voelkel A, Berlińska A (2016) The solubility parameter for biomedical polymers-application of inverse gas chromatography. J Pharm Biomed Anal 127:202–206. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2016.04.014
Adeosun SO, Lawal GI, Balogun SA, Akpan EI (2012) Review of green polymer nanocomposites. J Miner Mater Charact Eng 11:385–416. doi:10.4236/jmmce.2012.114028
Ambrosio-Martín J, Fabra MJ, Lopez-Rubio A, Lagaron JM (2015) Melt polycondensation to improve the dispersion of bacterial cellulose into polylactide via melt compounding: enhanced barrier and mechanical properties. Cellulose 22:1201–1226. doi:10.1007/s10570-014-0523-9
Arias A, Heuzey MC, Huneault MA, Ausias G, Bendahou A (2015) Enhanced dispersion of cellulose nanocrystals in melt-processed polylactide-based nanocomposites. Cellulose 22:483–498. doi:10.1007/s10570-014-0476-z
Azizi Samir MAS, Alloin F, Paillet M, Dufresne A (2004) Tangling effect in fibrillated cellulose reinforced nanocomposites. Macromolecules 37:4313–4316. doi:10.1021/ma035939u
Azizi Samir MAS, Alloin F, Dufresne A (2005) Review of recent research into cellulosic whiskers, their properties and their application in nanocomposite field. Biomacromol 6:612–626. doi:10.1021/bm0493685
Bagheriasl D, Carreau PJ, Dubois C, Riedl B (2015) Properties of polypropylene and polypropylene/poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) blend/CNC nanocomposites. Compos Sci Technol 117:357–363. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2015.07.012
Bagheriasl D, Carreau PJ, Riedl B, Dubois C (2016a) Enhanced properties of polylactide by incorporating cellulose nanocrystals. Polym Compos. doi:10.1002/pc.24259
Bagheriasl D, Carreau PJ, Riedl B, Dubois C, Hamad WY (2016b) Shear rheology of polylactide (PLA)–cellulose nanocrystal (CNC) nanocomposites. Cellulose 23:1885–1897. doi:10.1007/s10570-016-0914-1
Baiardo M, Frisoni G, Scandola M, Rimelen M, Lips D, Ruffieux K, Wintermantel E (2003) Thermal and mechanical properties of plasticized poly(l-lactic acid). J Appl Polym Sci 90:1731–1738. doi:10.1002/app.12549
Brown EE, Laborie MPG (2007) Bioengineering bacterial cellulose/poly(ethylene oxide) nanocomposites. Biomacromol 8:3074–3081. doi:10.1021/bm700448x
Buddhiranon S, Kim N, Kyu T (2011) Morphology development in relation to the ternary phase diagram of biodegradable PDLLA/PCL/PEO blends. Macromol Chem Phys 212:1379–1391. doi:10.1002/macp.201100042
Courgneau C, Ducruet V, Avérous L, Grenet J, Domenek S (2013) Nonisothermal crystallization kinetics of poly(lactide)—effect of plasticizers and nucleating agent. Polym Eng Sci 53:1085–1098. doi:10.1002/pen.23357
Eichhorn SJ, Dufresne A, Aranguren M, Marcovich NE, Capadona JR, Rowan SJ, Weder C, Thielemans W, Roman M, Renneckar S, Gindl W, Veigel S, Keckes J, Yano H, Abe K, Nogi M, Nakagaito AN, Mangalam A, Simonsen J, Benight AS, Bismarck A, Berglund LA, Peijs T (2010) Review: current international research into cellulose nanofibres and nanocomposites. J Mater Sci 45:1–33. doi:10.1007/s10853-009-3874-0
Frone AN, Berlioz S, Chailan JF, Panaitescu DM, Donescu D (2011) Cellulose fiber-reinforced polylactic acid. Polym Compos 32:976–985. doi:10.1002/pc.21116
Frone AN, Berlioz S, Chailan JF, Panaitescu DM (2013) Morphology and thermal properties of PLA-cellulose nanofibers composites. Carbohydr Polym 91:377–384. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.08.054
Ghanbari A, Heuzey MC, Carreau PJ, Ton-That MT (2013a) Morphological and rheological properties of PET/clay nanocomposites. Rheol Acta 52:59–74. doi:10.1007/s00397-012-0667-1
Ghanbari A, Heuzey MC, Carreau PJ, Ton-That MT (2013b) A novel approach to control thermal degradation of PET/organoclay nanocomposites and improve clay exfoliation. Polymer 54:1361–1369. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2012.12.066
Hendrick E, Frey M (2014) Increasing surface hydrophilicity in poly(lactic acid) electrospun fibers by addition of PLA-b-PEG co-polymers. J Eng Fibers Fabr 9:153–164
Iwatake A, Nogi M, Yano H (2008) Cellulose nanofiber-reinforced polylactic acid. Compos Sci Technol 68:2103–2106. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2008.03.006
Janardhnan S, Sain M (2011) Bio-treatment of natural fibers in isolation of cellulose nanofibres: impact of pre-refining of fibers on bio-treatment efficiency and nanofiber yield. J Polym Environ 19:615–621. doi:10.1007/s10924-011-0312-6
Jonoobi M, Harun J, Mathew AP, Oksman K (2010) Mechanical properties of cellulose nanofiber (CNF) reinforced polylactic acid (PLA) prepared by twin screw extrusion. Compos Sci Technol 70:1742–1747. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2010.07.005
Jonoobi M, Mathew AP, Abdi MM, Makinejad MD, Oksman K (2012) A comparison of modified and unmodified cellulose nanofiber reinforced polylactic acid (PLA) prepared by twin screw extrusion. J Polym Environ 20:991–997. doi:10.1007/s10924-012-0503-9
Kalia S, Boufi S, Celli A, Kango S (2014) Nanofibrillated cellulose: surface modification and potential applications. Colloid Polym Sci 292:5–31. doi:10.1007/s00396-013-3112-9
Kamal MR, Khoshkava V (2015) Effect of cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) on rheological and mechanical properties and crystallization behavior of PLA/CNC nanocomposites. Carbohydr Polym 123:105–114. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.01.012
Khoshkava V, Kamal MR (2014) Effect of cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) particle morphology on dispersion and rheological and mechanical properties of polypropylene/CNC nanocomposites. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:8146–8157. doi:10.1021/am500577e
Kowalczyk M, Piorkowska E, Kulpinski P, Pracella M (2011) Mechanical and thermal properties of PLA composites with cellulose nanofibers and standard size fibers. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 42:1509–1514. doi:10.1016/j.compositesa.2011.07.003
La Mantia FP, Morreale M (2011) Green composites: a brief review. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 42:579–588. doi:10.1016/j.compositesa.2011.01.017
Lee KY, Blaker JJ, Bismarck A (2009) Surface functionalisation of bacterial cellulose as the route to produce green polylactide nanocomposites with improved properties. Compos Sci Technol 69:2724–2733. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2009.08.016
Lee KY, Tang M, Williams CK, Bismarck A (2012) Carbohydrate derived copoly(lactide) as the compatibilizer for bacterial cellulose reinforced polylactide nanocomposites. Compos Sci Technol 72:1646–1650. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2012.07.003
Li ZQ, Zhou XD, Pei CH (2010) Preparation and characterization of bacterial cellulose/polylactide nanocomposites. Polym Plast Technol 49:141–146. doi:10.1080/03602550903284198
Lu T, Liu S, Jiang M, Xu X, Wang Y, Wang Z, Gou J, Hui D, Zhou Z (2014) Effects of modifications of bamboo cellulose fibers on the improved mechanical properties of cellulose reinforced poly(lactic acid) composites. Compos Part B Eng 62:191–197. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2014.02.030
Marais A, Kochumalayil JJ, Nilsson C, Fogelström L, Gamstedt EK (2012) Toward an alternative compatibilizer for PLA/cellulose composites: grafting of xyloglucan with PLA. Carbohydr Polym 89:1038–1043. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.03.051
Mathew AP, Chakraborty A, Oksman K, Sain M (2006) The structure and mechanical properties of cellulose nanocomposites prepared by twin screw extrusion. In: Oksman K, Sain M (eds) Cellulose nanocomposites: processing, characterization, and properties, vol 938. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 114–131. doi:10.1021/bk-2006-0938.ch009
Miao C, Hamad WY (2013) Cellulose reinforced polymer composites and nanocomposites: a critical review. Cellulose 20:2221–2262. doi:10.1007/s10570-013-0007-3
Nakagaito AN, Fujimura A, Sakai T, Hama Y, Yano H (2009) Production of microfibrillated cellulose (MFC)-reinforced polylactic acid (PLA) nanocomposites from sheets obtained by a papermaking-like process. Compos Sci Technol 69:1293–1297. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2009.03.004
Petersson L, Oksman K (2006) Biopolymer based nanocomposites: comparing layered silicates and microcrystalline cellulose as nanoreinforcement. Compos Sci Technol 66:2187–2196. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2005.12.010
Plummer CG, Choo CC, Boissard CR, Bourban PE, Månson JA (2013) Morphological investigation of polylactide/microfibrillated cellulose composites. Colloid Polym Sci 291:2203–2211. doi:10.1007/s00396-013-2968-z
Qu P, Gao Y, Wu G, Zhang L (2010) Nanocomposites of poly(lactic acid) reinforced with cellulose nanofibrils. BioResources 5:1811–1823
Ramezani Kakroodi A, Cheng S, Sain M, Asiri A (2014) Mechanical, thermal, and morphological properties of nanocomposites based on polyvinyl alcohol and cellulose nanofiber from aloe vera rind. J Nanomater 2014:1–7. doi:10.1155/2014/903498
Raquez JM, Habibi Y, Murariu M, Dubois P (2013) Polylactide (PLA)-based nanocomposites. Prog Polym Sci 38:1504–1542. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2013.05.014
Safdari F, Bagheriasl D, Carreau PJ, Heuzey MC, Kamal MR (2016a) High-performance polylactide biocomposites reinforced with cellulose nanofibers. SPE Plast Res. doi:10.2417/spepro.006650
Safdari F, Bagheriasl D, Carreau PJ, Heuzey MC, Kamal MR (2016b) Rheological, mechanical, and thermal properties of polylactide/cellulose nanofiber biocomposites. Polym Compos. doi:10.1002/pc.24127
Safdari F, Carreau PJ, Heuzey MC, Kamal MR, Sain MM (2016c) Enhanced properties of poly(ethylene oxide)/cellulose nanofiber biocomposites. Cellulose. doi:10.1007/s10570-016-1137-1
Saffar A, Jalali Dil E, Carreau PJ, Ajji A, Kamal MR (2016) Phase behavior of binary blends of PP/PP-g-AA: limitations of the conventional characterization techniques. Polym Int 65:508–515. doi:10.1002/pi.5082
Sanchez-Garcia M, Lagaron J (2010) On the use of plant cellulose nanowhiskers to enhance the barrier properties of polylactic acid. Cellulose 17:987–1004. doi:10.1007/s10570-010-9430-x
Sheth M, Kumar RA, Davé V, Gross RA, McCarthy SP (1997) Biodegradable polymer blends of poly(lactic acid) and poly(ethylene glycol). J Appl Polym Sci 66:1495–1505. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4628(19971121)66:8<1495:AID-APP10>3.0.CO;2-3
Siró I, Plackett D (2010) Microfibrillated cellulose and new nanocomposite materials: a review. Cellulose 17:459–494. doi:10.1007/s10570-010-9405-y
Suryanegara L, Nakagaito AN, Yano H (2009) The effect of crystallization of PLA on the thermal and mechanical properties of microfibrillated cellulose-reinforced PLA composites. Compos Sci Technol 69:1187–1192. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2009.02.022
Tercjak A, Gutierrez J, Barud HS, Domeneguetti RR, Ribeiro SJL (2015) Nano- and macroscale structural and mechanical properties of in situ synthesized bacterial cellulose/PEO-b-PPO-b-PEO biocomposites. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:4142–4150. doi:10.1021/am508273x
Tingaut P, Zimmermann T, Lopez-Suevos F (2010) Synthesis and characterization of bionanocomposites with tunable properties from poly(lactic acid) and acetylated microfibrillated cellulose. Biomacromol 11:454–464. doi:10.1021/bm901186u
Tome LC, Pinto RJB, Trovatti E, Freire CSR, Silvestre AJD, Neto CP, Gandini A (2011) Transparent bionanocomposites with improved properties prepared from acetylated bacterial cellulose and poly(lactic acid) through a simple approach. Green Chem 13:419–427. doi:10.1039/C0GC00545B
Wang T, Drzal LT (2012) Cellulose-nanofiber-reinforced poly(lactic acid) composites prepared by a water-based approach. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:5079–5085. doi:10.1021/am301438g
Wang B, Sain M (2007) The effect of chemically coated nanofiber reinforcement on biopolymer based nanocomposites. BioResources 2:371–388
Wang Y, Li M, Hu D, Shen C (2010) Accelerating the crystallization of poly(lactic acid). SPE Plast Res. doi:10.1002/spepro.002983
Wu CS (2009) Renewable resource-based composites of recycled natural fibers and maleated polylactide bioplastic: characterization and biodegradability. Polym Degrad Stab 94:1076–1084. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2009.04.002
Xu X, Liu F, Jiang L, Zhu JY, Haagenson D, Wiesenborn DP (2013) Cellulose nanocrystals vs. cellulose nanofibrils: a comparative study on their microstructures and effects as polymer reinforcing agents. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:2999–3009. doi:10.1021/am302624t
Xu X, Wang H, Jiang L, Wang X, Payne SA, Zhu JY, Li R (2014) Comparison between cellulose nanocrystal and cellulose nanofibril reinforced poly(ethylene oxide) nanofibers and their novel shish-kebab-like crystalline structures. Macromolecules 47:3409–3416. doi:10.1021/ma402627j
Zhang K, Nagarajan V, Misra M, Mohanty AK (2014) Supertoughened renewable PLA reactive multiphase blends system: phase morphology and performance. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:12436–12448. doi:10.1021/am502337u
Zhou C, Shi Q, Guo W, Terrell L, Qureshi AT, Hayes DJ, Wu Q (2013) Electrospun bio-nanocomposite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering by cellulose nanocrystals reinforcing maleic anhydride grafted PLA. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:3847–3854. doi:10.1021/am4005072
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) through the Network for Innovative Plastic Materials and Manufacturing Processes (NIPMMP). The authors also wish to thank Professor Mohini M. Sain of the University of Toronto for providing the CNFs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Safdari, F., Carreau, P.J., Heuzey, M.C. et al. Effects of poly(ethylene glycol) on the morphology and properties of biocomposites based on polylactide and cellulose nanofibers. Cellulose 24, 2877–2893 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1327-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1327-5