Abstract
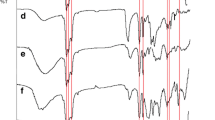
Characterizations were carried out to study on a new plasticized solid polymer electrolyte that was composed of blends of poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC), liquid 50% epoxidized natural rubber (LENR50), ethylene carbonate, and polypropylene carbonate. This freestanding solid polymer electrolyte (SPE) was successfully prepared by solution casting technique. Further analysis and characterizations were carried out by using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction, differential scanning calorimeter (DSC), Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR), and impedance spectroscopy (EIS). The SEM results show that the morphologies of SPEs are compatible with good homogeneity. No agglomeration was observed. However, upon addition of salt, formation of micropores occurred. It is worth to note that micropores improve the mobility of ions in the SPE system, thus increased the ionic conductivity whereas the crystallinity analysis for SPEs indicates that the LiClO4 salt is well complexed in the plasticized PVC-LENR50 as no sharp crystallinity peak was observed for 5–15% wt. LiClO4. This implies that LiClO4 salt interacts with polymer host as more bonds are form via coordination bonding. In DSC study, it is found that the glass temperature (T g) increased with the concentration of LiClO4. The lowest T g was obtained at 41.6 °C when incorporated with 15% wt. LiClO4. The features of complexation in the electrolyte matrix were studied using ATR-FTIR at the peaks of C=O, C–O–C, and C–Cl. In EIS analysis, the highest ionic conductivity obtained was 1.20 × 10−3 S cm−1 at 15% wt. LiClO4 at 353 K.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruce PG (1995) Solid state electrochemistry. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Gray FM (1991) Solid polymer electrolyte—fundamentals and technological applications. RSC Material Monographs, London
Noor SAM, Ahmad A, Talib IA, Rahman MYA (2010) Ionics 16:161–170
Ramesh S, Ng KY (2009) Curr App Phys 9:329–332
Baskaran R, Selvasekarapandin S, Kuwata N, Kawamura J, Hattori T (2007) J Phys Chem Sol 68:407–412
Reddy TJR, Archari VBS, Sharma AK, Rao VVRN (2007) Ionics 12:435–439
Rajendran S, Uma T (2001) Ionics 7:122–125
Ramesh S, Chai MF (2007) Mater Sci Eng B 139:240
Soo JP, Han AR, Jae SS, Kim S (2010) Macromol Res 18:336–340
Rahman CT, Zaman K (1999) Phys Res B 152:335–342
Yan JW, Dukjoon K (2007) Electrochim Acta 52:3181–3189
Rahman CT, Kamaruddin S, Sivachalam Y, Talib M, Yahya N (2006) Poly Testing 25:475–480
Famiza L, Aziz M, Katun N, Ali AMM, Yahya MZ (2006) J Power Sources 159:1401–1404
Glasses MD, Idris R, Latnam RJ, Linford RG, Schlindwein WS (2002) Solid State Ionics 147:289–294
Noor SAM, Ahmad A, Rahman MYA, Talib IA (2010) Nat Sci 3:190–196
Nair MNR, Biju PK, Thomas GV, Nair MRG (2009) J App Poly Sci 111:48–56
Rahman MYA, Ahmad A, Lee TK, Farina Y, Dahlan HM (2011) J Mater Sci App 2:817–825
Dahlan HM, Khairul ZMD, Ibrahim A (2000) J App Poly Sci 78:1776–1782
Dahlan HM, Harun AG, Mamat R (1999) J Sains Nuklear Malaysia 17(1):1–13
Dahlan HM, Khairul ZMD, Abdullah I (2000) J Sains Nuklear Malaysia 18(1):9–21
Ramesh S, Arof AK (2001) J Power Sources 99:41–47
Ahmad A, Rahman MYA, Ali MLM, Hashim H (2007) Ionics 13:67–70
Ramesh S, Chiam WL, Morris E, Durairaj R (2010) Thermochim Acta 511:140–146
Wanchart P, Jerold MS (1996) Elsevier Science 37(23):5109–5116
Fonseca CP, Cavalante JF, Amaral FA, Souza CAZ, Neves S (2007) Int J Electrochem Sci 2:52–60
Binod K, Stanley JR, Sateesh K (2002) Electrochim Acta 47:4125–4131
Shembel EM, Chervakov OV, Neduzhko LI, Maksyuta IM, Polischuk YV, Reisner DE, Novak P, Meshri D (2001) J Power Science 96:20–28
Rajendran S, Sivakumar P (2008) Physica B 403:509–516
Low SP, Ahmad A, Rahman MYA (2010) Ionics 16:821–826
Xuping Z, Lianyong S, Hua H, Hongli L, Zuhong L (1999) J Mater Sci Lett 18:1745–1747
Subramania A, Sundaram KNT, Kumar GV, Vasudevan T (2006) Ionics 12:175–178
Rajendran S, Sivakumar P, Ravi SB (2007) J Power Sources 164:815–821
Ramesh S, Yahaya AH, Arof AK (2002) Solid State Ionics 152–253:291–294
Michael MS, Jacob MME, Prabaharan SRS, Radhakrishna S (1997) Solid State Ionics 98:167–174
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank UKM and the Malaysian Nuclear Agency Malaysia (Nuclear Malaysia) for providing the needs and helps in this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, T.K., Afiqah, S., Ahmad, A. et al. Temperature dependence of the conductivity of plasticized poly(vinyl chloride)-low molecular weight liquid 50% epoxidized natural rubber solid polymer electrolyte. J Solid State Electrochem 16, 2251–2260 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-011-1633-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-011-1633-z