Abstract
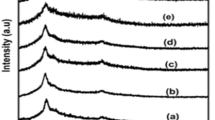
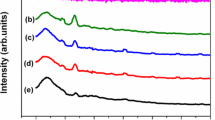
A polymer blend electrolyte based on polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and polyacrylonitrile (PAN) was prepared by a simple solvent casting technique in different compositions. The ionic conductivity of polymer blend electrolytes was investigated by varying the PAN content in the PVA matrix. The ionic conductivity of polymer blend electrolyte increased with the increase of PAN content. The effect of lithium salt concentrations was also studied for the polymer blend electrolyte of high ionic conductivity system. A maximum ionic conductivity of 3.76×10−3 S/cm was obtained in 3 M LiClO4 electrolyte solution. The effect of ionic conductivity of polymer blend electrolyte was measured by varying the temperature ranging from 298 to 353 K. Linear sweep voltammetry and DC polarization studies were carried out to find out the stability and lithium transference number of the polymer blend electrolyte. Finally, a prototype cell was assembled with graphite as anode, LiMn2O4 as cathode, and polymer blend electrolyte as the electrolyte as well as separator, which showed good compatibility and electrochemical stability up to 4.7 V.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi NS, Lee YG, Park JK, Ko JM (2001) Electrochim Acta 46:1581
Min HS, Ko JM, Kim DW (2003) J Power Sources 119–121:469
Feria LO, Moreira RL (2000) J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 38:34
Manuel Stephan A, Thirunakaran R, Muniyandi N, Gangadharan R, Ramamoorthy P (1999) J Power Sources 81–82:752
Coleman MM, Painter PC (1995) Prog Polym Sci 20:1
Abraham KM, Jiang Z, Carroll B (1997) Chem Mater 9:1978
Armand MB, Chabagno JM, Duclot MJ (1979) In: Mundy JN, Shenoy G (eds) Fast-ion transport in solid. North-Holland, Amsterdam, p 131
Rater M, Shriver DF (1988) Chem Rev 88:109
Rajendran S, Sivakumer M, Subadevi R (2003) J Power Sources 124:225
Subramania A, Kalyana Sundaram NT, Sukumar N (2005) J Power Sources 141:188
Okamota Y, Ych TF, Lee S, Skutheimk TA (1993) J Polym Sci A Polym Chem 31:2573
Acknowledgement
This work has been carried out with the financial support of DST, New Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Subramania, A., Kalyana Sundaram, N.T., Vijaya Kumar, G. et al. New polymer electrolyte based on (PVA–PAN) blend for Li-ion battery applications. Ionics 12, 175–178 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-006-0018-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-006-0018-2