Abstract
Purpose
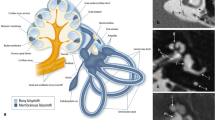
Forking of the cerebral aqueduct is a developmental malformation that is infrequently encountered by neurosurgeons as a rare cause of hydrocephalus, sometimes with a delayed onset. The etiology of an apparently forked aqueduct might be different. However, neuroendoscopy can often be the optimal treatment. The purpose of this study was to review the literature by analyzing the anatomical, functional, diagnostic, and therapeutic features of this unusual condition and adding our personal cases.
Methods
We present a case of forking of the cerebral aqueduct that was detected in vivo and treated with a flexible scope. A thorough review of the pertinent literature is also discussed. In the past years, diagnosis of forked aqueduct was possible only postmortem.
Results
A forked aqueduct is occasionally encountered in patients when a delayed hydrocephalic decompensation occurs.
Conclusions
Flexible neuroendoscopy enables for a direct, in vivo diagnosis and immediate treatment through a third ventriculostomy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adle-Biassette H, Saugier-Veber P, Fallet-Bianco C, Delezoide AL, Razavi F, Drouot N, et al (2013) Neuropathological review of 138 cases genetically tested for X-linked hydrocephalus: evidence for closely related clinical entities of unknown molecular bases. Acta Neuropathol 126:427–442
Cinalli G, Spennato P, Nastro A, Aliberti F, Trischitta V, Ruggiero C, et al (2011) Hydrocephalus in aqueductal stenosis. Childs Nerv Syst 27:1621–1642
Conover PT, Roessmann U (1990) Malformational complex in an infant with intrauterine influenza viral infection. Arch Pathol Lab Med 114:535–538
Drachman DA, Richardson EP (1961) Aqueductal narrowing congenital and acquired. Arch Neurol (Chic) 5:552–559
Foltz EL, Shurtleff DB (1966) Conversion of communicating hydrocephalus to stenosis or occlusion of the aqueduct during ventricular shunt. J Neurosurg 24:520–529
Friede RL (1975) Developmental neuropathology. Springer, Vienna
Hori A, Eubel R, Ulbrich R (1984) Congenital ventricular diverticulum in the brainstem. Acta Neuropathol 63:330–333
Jacobson EE, Fletcher DF, Morgan MK, Johnston IH (1999) Computer modelling of the cerebrospinal fluid flow dynamics of aqueduct stenosis. Med Biol Eng Comput 37:59–63
Jellinger G (1986) Anatomopathology of non-tumoral aqueductal stenosis. J Neurosurg Sci 30:1–16
Kepes JJ, Clough C, Villanueva A (1969) Congenital fusion of the thalami (atresia of the third ventricle) and associated anomalies in a 6-months-old infant. Acta Neuropathol 13:97–104
Kim TS, Cho S, Dickson DW (1990) Aprosencephaly: review of the literature and report of a case with cerebellar hypoplasia, pigmented epithelial cyst and Rathke’s cleft cyst. Acta Neuropathol 79:424–431
Lendon RG, Emery JL (1970) Forking of the central canal in the equinal cord of children. J Anat 106:499–505
Longatti P, Basaldella L, Feletti A, Fiorindi A, Billeci D (2005) Endoscopic navigation of the fourth ventricle. Technical note and preliminary experience. Neurosurg Focus 19:E12
Longatti P, Fiorindi A, Feletti A, Baratto V (2006) Endoscopic opening of the foramen on Magendie using transaqueductal navigation for membrane obstruction of the fourth ventricle outlets. Technical note. J Neurosurg 105:924–927
Longatti P, Fiorindi A, Feletti A, d’Avella D, Martinuzzi A (2008) Endoscopic anatomy of the fourth ventricle. J Neurosurg 109:530–535
Longatti P, Fiorindi A, Perin A, Martinuzzi A (2007) Endoscopic anatomy of the cerebral aqueduct. Neurosurgery 61(3 Suppl):1–5
MacFarlane A, Maloney AF (1957) The appearance of the aqueduct and its relationship to hydrocephalus in the Arnold-Chiari malformation. Brain 80:479–491
McMillan JJ, Williams B (1977) Aqueduct stenosis. Case review and discussion. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 40:521–532
Oberson R, Gessaga E (1972) Forking of the aqueduct in an adult. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 13:441–448
Parker HL, Kernohan JW (1933) Stenosis of the aqueduct of Sylvius. Arch Neurol (Chic) 29:538–558
Pasquier L, Marcorelles P, Loget P, Pelluard F, Carles D, Perez MJ, et al (2009) Rhombencephalosynapsis and related anomalies: a neuropathological study of 40 fetal cases. Acta Neuropathol 117:185–200
Russell DS (1949) Observations on the pathology of hydrocephalus. Medical Research Council Special Report Series No. 265. His Majesty’s Stationery Office, London
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. No funding nor financial support was received for this work. The authors declare no industry affiliation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feletti, A., Fiorindi, A. & Longatti, P. Split cerebral aqueduct: a neuroendoscopic illustration. Childs Nerv Syst 32, 199–203 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2827-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-015-2827-y