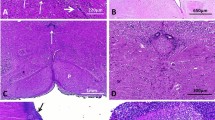
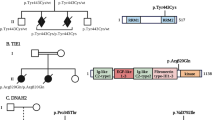
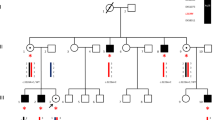
Abstract
L1 syndrome results from mutations in the L1CAM gene located at Xq28. It encompasses a wide spectrum of diseases, X-linked hydrocephalus being the most severe phenotype detected in utero, and whose pathophysiology is incompletely understood. The aim of this study was to report detailed neuropathological data from patients with mutations, to delineate the neuropathological criteria required for L1CAM gene screening in foetuses by characterizing the sensitivity, specificity and positive predictive value of the cardinal signs, and to discuss the main differential diagnoses in non-mutated foetuses in order to delineate closely related conditions without L1CAM mutations. Neuropathological data from 138 cases referred to our genetic laboratory for screening of the L1CAM gene were retrospectively reviewed. Fifty-seven cases had deleterious L1CAM mutations. Of these, 100 % had hydrocephalus, 88 % adducted thumbs, 98 % pyramidal tract agenesis/hypoplasia, 90 % stenosis of the aqueduct of Sylvius and 68 % agenesis/hypoplasia of the corpus callosum. Two foetuses had L1CAM mutations of unknown significance. Seventy-nine cases had no L1CAM mutations; these were subdivided into four groups: (1) hydrocephalus sometimes associated with corpus callosum agenesis (44 %); (2) atresia/forking of the aqueduct of Sylvius/rhombencephalosynapsis spectrum (27 %); (3) syndromic hydrocephalus (9 %), and (4) phenocopies with no mutations in the L1CAM gene (20 %) and in whom family history strongly suggested an autosomal recessive mode of transmission. These data underline the existence of closely related clinical entities whose molecular bases are currently unknown. The identification of the causative genes would greatly improve our knowledge of the defective pathways involved in these cerebral malformations.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson RB, Turner KN, Nikonenko AG, Hemperly J, Schachner M, Young HM (2006) The cell adhesion molecule l1 is required for chain migration of neural crest cells in the developing mouse gut. Gastroenterology 130(4):1221–1232
Barbin G, Aigrot MS, Charles P, Foucher A, Grumet M, Schachner M, Zalc B, Lubetzki C (2004) Axonal cell-adhesion molecule L1 in CNS myelination. Neuron Glia Biol 1(1):65–72
Basel-Vanagaite L, Straussberg R, Friez MJ, Inbar D, Korenreich L, Shohat M, Schwartz CE (2006) Expanding the phenotypic spectrum of L1CAM-associated disease. Clin Genet 69(5):414–419
Bearer CF, Swick AR, O’Riordan MA, Cheng G (1999) Ethanol inhibits L1-mediated neurite outgrowth in postnatal rat cerebellar granule cells. J Biol Chem 274(19):13264–13270
Beasley L, Stallcup WB (1987) The nerve growth factor-inducible large external (NILE) glycoprotein and neural cell adhesion molecule (N-CAM) have distinct patterns of expression in the developing rat central nervous system. J Neurosci 7(3):708–715
Bianchine JW, Lewis RC Jr (1974) The MASA syndrome: a new heritable mental retardation syndrome. Clin Genet 5(4):298–306
Bickers DS, Adams RD (1949) Hereditary stenosis of the aqueduct of Sylvius as a cause of congenital hydrocephalus. Brain 72(Pt. 2):246–262
Cohen NR, Taylor JS, Scott LB, Guillery RW, Soriano P, Furley AJ (1998) Errors in corticospinal axon guidance in mice lacking the neural cell adhesion molecule L1. Curr Biol 8(1):26–33
Dahme M, Bartsch U, Martini R, Anliker B, Schachner M, Mantei N (1997) Disruption of the mouse L1 gene leads to malformations of the nervous system. Nat Genet 17(3):346–349
Debiec H, Kutsche M, Schachner M, Ronco P (2002) Abnormal renal phenotype in L1 knockout mice: a novel cause of CAKUT. Nephrol Dial Transplant 17(Suppl 9):42–44
Demyanenko GP, Tsai AY, Maness PF (1999) Abnormalities in neuronal process extension, hippocampal development, and the ventricular system of L1 knockout mice. J Neurosci 19(12):4907–4920
Finckh U, Schroder J, Ressler B, Veske A, Gal A (2000) Spectrum and detection rate of L1CAM mutations in isolated and familial cases with clinically suspected L1-disease. Am J Med Genet 92(1):40–46
Fransen E, D’Hooge R, Van Camp G, Verhoye M, Sijbers J, Reyniers E, Soriano P, Kamiguchi H, Willemsen R, Koekkoek SK, De Zeeuw CI, De Deyn PP, Van der Linden A, Lemmon V, Kooy RF, Willems PJ (1998) L1 knockout mice show dilated ventricles, vermis hypoplasia and impaired exploration patterns. Hum Mol Genet 7(6):999–1009
Fransen E, Lemmon V, Van Camp G, Vits L, Coucke P, Willems PJ (1995) CRASH syndrome: clinical spectrum of corpus callosum hypoplasia, retardation, adducted thumbs, spastic paraparesis and hydrocephalus due to mutations in one single gene, L1. Eur J Hum Genet 3(5):273–284
Fransen E, Van Camp G, Vits L, Willems PJ (1997) L1-associated diseases: clinical geneticists divide, molecular geneticists unite. Hum Mol Genet 6(10):1625–1632
Fryns JP, Spaepen A, Cassiman JJ, van den Berghe H (1991) X linked complicated spastic paraplegia, MASA syndrome, and X linked hydrocephalus owing to congenital stenosis of the aqueduct of Sylvius: variable expression of the same mutation at Xq28. J Med Genet 28(6):429–431
Graf WD, Born DE, Sarnat HB (1998) The pachygyria-polymicrogyria spectrum of cortical dysplasia in X-linked hydrocephalus. Eur J Pediatr Surg 8(Suppl 1):10–14
Guihard-Costa AM, Larroche JC (1990) Differential growth between the fetal brain and its infratentorial part. Early Hum Dev 23(1):27–40
Guihard-Costa AM, Menez F, Delezoide AL (2002) Organ weights in human foetuses after formalin fixation: standards by gestational age and body weight. Pediatr Dev Pathol 5(6):559–578
Itoh K, Cheng L, Kamei Y, Fushiki S, Kamiguchi H, Gutwein P, Stoeck A, Arnold B, Altevogt P, Lemmon V (2004) Brain development in mice lacking L1–L1 homophilic adhesion. J Cell Biol 165(1):145–154
Kanemura Y, Okamoto N, Sakamoto H, Shofuda T, Kamiguchi H, Yamasaki M (2006) Molecular mechanisms and neuroimaging criteria for severe L1 syndrome with X-linked hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg 105(5 Suppl):403–412
Kenwrick S, Jouet M, Donnai D (1996) X linked hydrocephalus and MASA syndrome. J Med Genet 33(1):59–65
Kowitz A, Kadmon G, Eckert M, Schirrmacher V, Schachner M, Altevogt P (1992) Expression and function of the neural cell adhesion molecule L1 in mouse leukocytes. Eur J Immunol 22(5):1199–1205
Kujat R, Miragall F, Krause D, Dermietzel R, Wrobel KH (1995) Immunolocalization of the neural cell adhesion molecule L1 in non-proliferating epithelial cells of the male urogenital tract. Histochem Cell Biol 103(4):311–321
Lagenaur C, Lemmon V (1987) An L1-like molecule, the 8D9 antigen, is a potent substrate for neurite extension. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84(21):7753–7757
Landrieu P, Ninane J, Ferriere G, Lyon G (1979) Aqueductal stenosis in X-linked hydrocephalus: a secondary phenomenon? Dev Med Child Neurol 21(5):637–642
Liebau MC, Gal A, Superti-Furga A, Omran H, Pohl M (2007) L1CAM mutation in a boy with hydrocephalus and duplex kidneys. Pediatr Nephrol 22(7):1058–1061
Lindner J, Rathjen FG, Schachner M (1983) L1 mono- and polyclonal antibodies modify cell migration in early postnatal mouse cerebellum. Nature 305(5933):427–430
Luthl A, Laurent JP, Figurov A, Muller D, Schachner M (1994) Hippocampal long-term potentiation and neural cell adhesion molecules L1 and NCAM. Nature 372(6508):777–779
Michelson P, Hartwig C, Schachner M, Gal A, Veske A, Finckh U (2002) Missense mutations in the extracellular domain of the human neural cell adhesion molecule L1 reduce neurite outgrowth of murine cerebellar neurons. Hum Mutat 20(6):481–482
Pasquier L, Marcorelles P, Loget P, Pelluard F, Carles D, Perez MJ, Bendavid C, de La Rochebrochard C, Ferry M, David V, Odent S, Laquerriere A (2009) Rhombencephalosynapsis and related anomalies: a neuropathological study of 40 fetal cases. Acta Neuropathol 117(2):185–200
Ramanathan R, Wilkemeyer MF, Mittal B, Perides G, Charness ME (1996) Alcohol inhibits cell–cell adhesion mediated by human L1. J Cell Biol 133(2):381–390
Rolf B, Kutsche M, Bartsch U (2001) Severe hydrocephalus in L1-deficient mice. Brain Res 891(1–2):247–252
Saugier-Veber P, Martin C, Le Meur N, Lyonnet S, Munnich A, David A, Henocq A, Heron D, Jonveaux P, Odent S, Manouvrier S, Moncla A, Morichon N, Philip N, Satge D, Tosi M, Frebourg T (1998) Identification of novel L1CAM mutations using fluorescence-assisted mismatch analysis. Hum Mutat 12(4):259–266
Schmid RS, Maness PF (2008) L1 and NCAM adhesion molecules as signaling coreceptors in neuronal migration and process outgrowth. Curr Opin Neurobiol 18(3):245–250
Schrander-Stumpel C, Fryns JP (1998) Congenital hydrocephalus: nosology and guidelines for clinical approach and genetic counselling. Eur J Pediatr 157(5):355–362
Schrander-Stumpel C, Legius E, Fryns JP, Cassiman JJ (1990) MASA syndrome: new clinical features and linkage analysis using DNA probes. J Med Genet 27(11):688–692
Skaper SD (2012) Neuronal growth-promoting and inhibitory cues in neuroprotection and neuroregeneration. Methods Mol Biol 846:13–22
Takenouchi T, Nakazawa M, Kanemura Y, Shimozato S, Yamasaki M, Takahashi T, Kosaki K (2012) Hydrocephalus with Hirschsprung disease: severe end of X-linked hydrocephalus spectrum. Am J Med Genet A 158A(4):812–815
Thor G, Probstmeier R, Schachner M (1987) Characterization of the cell adhesion molecules L1, N-CAM and J1 in the mouse intestine. EMBO J 6(9):2581–2586
Vits L, Chitayat D, Van Camp G, Holden JJ, Fransen E, Willems PJ (1998) Evidence for somatic and germline mosaicism in CRASH syndrome. Hum Mutat Suppl 1:S284–S287
Vos YJ, de Walle HE, Bos KK, Stegeman JA, Ten Berge AM, Bruining M, van Maarle MC, Elting MW, den Hollander NS, Hamel B, Fortuna AM, Sunde LE, Stolte-Dijkstra I, Schrander-Stumpel CT, Hofstra RM (2010) Genotype-phenotype correlations in L1 syndrome: a guide for genetic counselling and mutation analysis. J Med Genet 47(3):169–175
Vos YJ, Hofstra RM (2010) An updated and upgraded L1CAM mutation database. Hum Mutat 31(1):E1102–E1109
Welzl H, Stork O (2003) Cell adhesion molecules: key players in memory consolidation? News Physiol Sci 18:147–150
Willems PJ, Brouwer OF, Dijkstra I, Wilmink J (1987) X-linked hydrocephalus. Am J Med Genet 27(4):921–928
Williams EJ, Furness J, Walsh FS, Doherty P (1994) Activation of the FGF receptor underlies neurite outgrowth stimulated by L1, N-CAM, and N-cadherin. Neuron 13(3):583–594
Wong EV, Kenwrick S, Willems P, Lemmon V (1995) Mutations in the cell adhesion molecule L1 cause mental retardation. Trends Neurosci 18(4):168–172
Acknowledgments
This study was performed in the frame of the European Commission’s 7th Framework Programme under GA No 278486, “ DEVELAGE” and a “Contrat Interface Inserm” to Homa Adle-Biassette. The authors wish to thank the following fetopathologists for their contribution to this work: Patricia Blanchet (Montpellier), Maryse Bonnière (Paris), Bernard Gasser (Mulhouse), Antoinette Gelot (Paris), Didier Menzies (Nancy), Hanitra Randianaivo (La Réunion). They wish also to thank all the geneticists who set up this series.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
H. Adle-Biassette and P. Saugier-Veber contributed equally to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adle-Biassette, H., Saugier-Veber, P., Fallet-Bianco, C. et al. Neuropathological review of 138 cases genetically tested for X-linked hydrocephalus: evidence for closely related clinical entities of unknown molecular bases. Acta Neuropathol 126, 427–442 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-013-1146-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-013-1146-1