Abstract
Purpose
This retrospective study aimed to evaluate the safety and local efficacy of transcatheter arterial embolization (TAE) with superabsorbent polymer microspheres (SAP-MS) in patients with pulmonary metastases from renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Methods
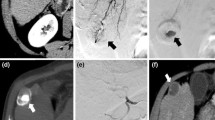
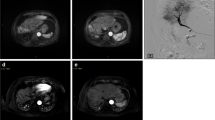
Sixteen patients with unresectable pulmonary metastases from RCC refractory to standard therapy were enrolled to undergo TAE with the purpose of mass reduction and/or palliation. The prepared SAP-MS swell to approximately two times larger than their dry-state size (100–150 μm [n = 14], 50–100 μm [n = 2]). Forty-nine pulmonary nodules (lung n = 22, mediastinal lymph node n = 17, and hilar lymph node n = 10) were selected as target lesions for evaluation. Local tumor response was evaluated 3 months after TAE according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST; version 1.1). The relationship between tumor enhancement ratio by CT during selective angiography and local tumor response was evaluated.
Results
The number of TAE sessions per patient ranged from 1 to 5 (median 2.9). Embolized arteries at initial TAE were bronchial arteries in 14 patients (87.5 %) and nonbronchial systemic arteries in 11 patients (68.8 %). Nodule-based evaluation showed that 5 (10.2 %) nodules had complete response, 17 (34.7 %) had partial response, 15 (30.6 %) had stable disease, and 12 (24.5 %) had progressive disease. The response rate was significantly greater in 22 lesions that had a high tumor enhancement ratio than in 27 lesions that had a slight or moderate ratio (90.9 vs. 7.4 %, p = 0.01). Severe TAE-related adverse events did not occur.
Conclusion
TAE with SAP-MS might be a well-tolerated and locally efficacious palliative option for patients with pulmonary metastases from RCC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nakanishi M, Umeda Y, Demura Y et al (2007) Effective use of multi-arterial infusion chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients: four clinical specified cases. Lung Cancer 55:241–247
Nakanishi M, Demura Y, Umeda Y et al (2008) Multi-arterial infusion chemotherapy for non-small cell lung carcinoma—significance of detecting feeding arteries and tumor staining. Lung Cancer 61:227–234
Vogl TJ, Lehnert T, Zangos S et al (2008) Transpulmonary chemoembolization (TPCE) as a treatment for unresectable lung metastases. Eur Radiol 18(11):2449–2455
Remy J, Voisin C, Ribet M et al (1973) Treatment, by embolization, of severe or repeated hemoptysis associated with systemic hypervascularization. Nouv Presse Med 2(31):2060
Yoon W, Kim JK, Kim YH et al (2002) Bronchial and nonbronchial systemic artery embolization for life-threatening hemoptysis: a comprehensive review. Radiographics 22(6):1395–1409
Osuga K, Hori S, Hiraishi K et al (2008) Bland embolization of hepatocellular carcinoma using superabsorbent polymer microspheres. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 31:1108–1116
Weichert W, Denkert C, Gauruder-Burmester A et al (2005) Uterine arterial embolization with trisacryl gelatin microspheres: a histopathologic evaluation. Am J Surg Pathol 29(7):955–961
Ustünsöz B, Bozlar U, Ors F et al (2006) Bronchial artery embolization: experience with 10 cases. Diagn Interv Radiol 12(1):43–46
Seki A, Hori S (2012) Switching the loaded agent from epirubicin to cisplatin: salvage transcatheter arterial chemoembolization with drug-eluting microspheres for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 35(3):555–562
de Luis E, Bilbao JI, de Ciércoles JA et al (2008) In vivo evaluation of a new embolic spherical particle (HepaSphere) in a kidney animal model. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 31(2):367–376
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J et al (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45:228–247
Pirrotta MT, Bernardeschi P, Fiorentini G (2011) Targeted-therapy in advanced renal cell carcinoma. Curr Med Chem 18(11):1651–1657
Bellmunt J, Montagut C, Albiol S et al (2007) Present strategies in the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: an update on molecular targeting agents. BJU Int 99(2):274–280
Piltz S, Meimarakis G, Wichmann MW et al (2002) Long-term results after pulmonary resection of renal cell carcinoma metastases. Ann Thorac Surg 73(4):1082–1087
Meimarakis G, Angele M, Staehler M et al (2011) Evaluation of a new prognostic score (Munich score) to predict long-term survival after resection of pulmonary renal cell carcinoma metastases. Am J Surg 202(2):158–167
Kawashima A, Nakayama M, Oka D et al (2011) Pulmonary metastasectomy in patients with renal cell carcinoma: a single-institution experience. Int J Clin Oncol 16(6):660–665
Soga N, Yamakado K, Gohara H et al (2009) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for unresectable pulmonary metastases from renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int 104(6):790–794
Den Hengst WA, Van Putte BP, Hendriks JM et al (2010) Long-term survival of a phase I clinical trial of isolated lung perfusion with melphalan for resectable lung metastases. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 38(5):621–627
Cauldwell EW, Siekert RG et al (1948) The bronchial arteries: an anatomic study of 150 human cadavers. Surg Gynecol Obstet 86(4):395–412
Derdeyn CP, Graves VB, Salamat MS et al (1997) Collagen-coated acrylic microspheres for embolotherapy: in vivo and in vitro characteristics. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18:647–653
Kalva SP (2009) Bronchial artery embolization. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol 12(2):130–138
Ma KF, Wong WH, Lui CY et al (2009) Renal and splenic micro-infarctions following bronchial artery embolization with trisacryl microspheres. Korean J Radiol 10(1):97–99
Vinaya KN, White RI Jr, Sloan JM (2004) Reassessing bronchial artery embolotherapy with newer spherical embolic materials. J Vasc Interv Radiol 15:304–305
FitzGerald DB, Suran EL, Sargent J (2005) Posterior circulation infarct after bronchial artery embolization and coiling. Neurology 65:1312
Sriram KB, Taylor DJ, Holmes M (2007) Systemic multifocal infarction following bronchial artery embolization with microsphere particles. Intern Med J 37:734–735
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seki, A., Hori, S., Sueyoshi, S. et al. Transcatheter Arterial Embolization With Spherical Embolic Agent for Pulmonary Metastases From Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 36, 1527–1535 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-013-0576-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-013-0576-4