Abstract
Rationale
The neuroactive steroid, 3α-hydroxy-5α-pregane-20-one (allopregnanolone) is a potent modulator of GABAA receptor function. Moreover, pharmacologically relevant concentrations of allopregnanolone are found in brain during physiological conditions (stress, pregnancy and menstrual cycle) and pharmacological challenge (ethanol, fluoxetine, olanzapine). Enhanced levels of neurosteroids are thought to contribute to the therapeutic effects of fluoxetine and various effects of ethanol via GABAA receptors. Moreover, neurosteroids influence rewarding effects of ethanol in some models and modulate activation of the hypothalamic pituitary adrenal (HPA) axis. Thus, it is possible that enhanced allopregnanolone levels are involved in the effects of abused drugs.
Objectives
To determine if other abused drugs elicit alterations in brain neurosteroid levels, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC), cocaine and morphine were administered to male rats.
Methods
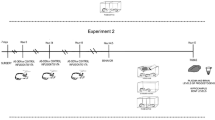
Cortical brain tissue and plasma were collected and analyzed for steroid concentrations using radioimmunoassays.
Results
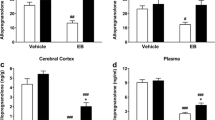
Δ9-THC (5 mg/kg, IP) elevated cortical allopregnanolone levels to pharmacologically active levels, while morphine (15 mg/kg, SC) produced a small but significant increase. Cocaine (30 mg/kg, IP) did not alter allopregnanolone levels, nor did lower doses of Δ9-THC or morphine. Plasma progesterone levels were elevated in both Δ9-THC and cocaine-treated animals.
Conclusions
Some, but not all, drugs of abuse produce increases in cortical allopregnanolone levels. In addition, increases in plasma steroid precursor levels do not always translate into increases in brain allopregnanolone levels.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbaccia ML, Roscetti G, Trabucchi M, Purdy RH, Mostallino MC, Concas A, Biggio G (1997) The effects of inhibitors of GABAergic transmission and stress on brain and plasma allopregnanolone concentrations. Br J Pharmacol 120:1582–1588
Barbaccia ML, Affricano D, Trabucchi M, Purdy RH, Colombo G, Agabio R, Gessa GL (1999) Ethanol markedly increases “GABAergic” neurosteroids in alcohol-preferring rats. Eur J Pharmacol 384:R1–R2
Barbaccia ML, Affricano D, Purdy RH, Maciocco E, Spiga F, Biggio G (2001) Clozapine, but not haloperidol, increases brain concentrations of neuroactive steroids in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 25:489–497
Beauchamp MH, Ormerod BK, Jhamandas K, Boegman RJ, Beninger RJ (2000) Neurosteroids and reward: allopregnanolone produces a conditioned place aversion in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 67:29–35
Bitran D (2001) The role of the peripheral mitochondrial benzodiazepine receptor in alcohol-induced anxiolytic effect and neurosteroidogenesis. The role of neurosteroids in alcohol-related behaviors. In: 2001 Annual meeting of the research society on alcoholism, Montreal, Canada, 5-23-2001
Bitran D, Hilvers RJ, Kellogg CK (1991) Anxiolytic effects of 3 alpha-hydroxy-5 alpha[beta]-pregnan-20-one: endogenous metabolites of progesterone that are active at the GABAA receptor. Brain Res 561:157–161
Bitran D, Purdy RH, Kellogg CK (1993) Anxiolytic effect of progesterone is associated with increases in cortical allopregnanolone and GABAA receptor function. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 45:423–428
Bitran D, Shiekh M, McLeod M (1995) Anxiolytic effect of progesterone is mediated by the neurosteroid allopregnanolone at brain GABAA receptors. J Neuroendocrinol 7:171–177
Bitran D, Klibansky DA, Martin GA (2000) The neurosteroid pregnanolone prevents the anxiogenic-like effect of inescapable shock in the rat. Psychopharmacology 151:31–37
Borowsky B, Kuhn CM (1991a) Chronic cocaine administration sensitizes behavioral but not neuroendocrine responses. Brain Res 543:301–306
Borowsky B, Kuhn CM (1991b) Monoamine mediation of cocaine-induced hypothalamo-pituitary–adrenal activation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 256:204–210
Brot MD, Akwa Y, Purdy RH, Koob GF, Britton KT (1997) The anxiolytic-like effects of the neurosteroid allopregnanolone: interactions with GABAA receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 325:1–7
Buckingham JC, Cooper TA (1984) Differences in hypothalamo–pituitary–adrenocortical activity in the rat after acute and prolonged treatment with morphine. Neuroendocrinology 38:411–417
Cabrera RJ, Bregonzio C, Laconi M, Mampel A (2002) Allopregnanolone increase in striatal N-methyl-d-aspartic acid evoked [3H]dopamine release is estrogen and progesterone dependent. Cell Mol Neurobiol 22:445–454
Chaperon F, Thiebot MH (1999) Behavioral effects of cannabinoid agents in animals. Crit Rev Neurobiol 13:243–281
Compagnone NA, Mellon SH (2000) Neurosteroids: biosynthesis and function of these novel neuromodulators. Front Neuroendocrinol 21:1–56
Concas A, Mostallino MC, Porcu P, Follesa P, Barbaccia ML, Trabucchi M, Purdy RH, Grisenti P, Biggio G (1998) Role of brain allopregnanolone in the plasticity of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor in rat brain during pregnancy and after delivery. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:13284–13289
Concas A, Porcu P, Sogliano C, Serra M, Purdy RH, Biggio G (2000) Caffeine-induced increases in the brain and plasma concentrations of neuroactive steroids in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 66:39–45
Coventry TL, Jessop DS, Finn DP, Crabb MD, Kinoshita H, Harbuz MS (2001) Endomorphins and activation of the hypothalamo–pituitary–adrenal axis. J Endocrinol 169:185–193
Crawley JN, Glowa JR, Majewska MD, Paul SM (1986) Anxiolytic activity of an endogenous adrenal steroid. Brain Res 398:382
Czlonkowska AI, Zienowicz M, Bidzinski A, Maciejak P, Lehner M, Taracha E, Wislowska A, Plaznik A (2003) The role of neurosteroids in the anxiolytic, antidepressive and anticonvulsive effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Med Sci Monit 9:RA270–RA275
Dazzi L, Spiga F, Pira L, Ladu S, Vacca G, Rivano A, Jentsch JD, Biggio G (2001) Inhibition of stress- or anxiogenic-drug-induced increases in dopamine release in the rat prefrontal cortex by long-term treatment with antidepressant drugs. J Neurochem 76:1212–1220
Dazzi L, Serra M, Seu E, Cherchi G, Pisu MG, Purdy RH, Biggio G (2002a) Progesterone enhances ethanol-induced modulation of mesocortical dopamine neurons: antagonism by finasteride. J Neurochem 83:1103–1109
Dazzi L, Serra M, Vacca G, Ladu S, Latrofa A, Trapani G, Biggio G (2002b) Depletion of cortical allopregnanolone potentiates stress-induced increase in cortical dopamine output. Brain Res 932:135–139
Deutch AY, Clark WA, Roth RH (1990) Prefrontal cortical dopamine depletion enhances the responsiveness of mesolimbic dopamine neurons to stress. Brain Res 521:311–315
Engel SR, Grant KA (2001) Neurosteroids and behavior. Int Rev Neurobiol 46:321–348
Finn DA, Phillips TJ, Okorn DM, Chester JA, Cunningham CL (1997) Rewarding effect of the neuroactive steroid 3alpha-hydroxy-5alpha-pregnan-20-one in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 56:261–264
Finn DA, Roberts AJ, Long S, Tanchuck M, Phillips TJ (2003) Neurosteroid consumption has anxiolytic effects in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 76:451–462
Follesa P, Concas A, Porcu P, Sanna E, Serra M, Mostallino MC, Purdy RH, Biggio G (2001) Role of allopregnanolone in regulation of GABA(A) receptor plasticity during long-term exposure to and withdrawal from progesterone. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 37:81–90
Freedland CS, Smith HR, Hart SL, Daunais JB, Davies HM, Porrino LJ (2000) A comparison of the behavioral effects of the repeated administration of PTT, 2beta-propanoyl-3beta-(4-tolyl)tropane and cocaine. Brain Res 869:98–104
Girdler SS, Straneva PA, Light KC, Pedersen CA, Morrow AL (2001) Allopregnanolone levels and reactivity to mental stress in premenstrual dysphoric disorder. Biol Psychiatry 49:788–797
Goeders NE (2002) Stress and cocaine addiction. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 301:785–789
Grant KA, Azarov A, Bowen CA, Mirkis S, Purdy RH (1996) Ethanol-like discriminative stimulus effects of the neurosteroid 3alpha-hydroxy-5alpha-pregnan-20-one in female Macaca fascicularis monkeys. Psychopharmacology 124:340–346
Grant KA, Azarov A, Shively CA, Purdy RH (1997) Discriminative stimulus effects of ethanol and 3alpha-hydroxy-5alpha-pregnan-20-one in relation to menstrual cycle phase in cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis). Psychopharmacology 130:59–68
Grobin AC, Roth RH, Deutch AY (1992) Regulation of the prefrontal cortical dopamine system by the neuroactive steroid 3alpha,21-dihydroxy-5alpha-pregnane-20-one. Brain Res 578:351–356
Harrison NL, Simmonds MA (1984) Modulation of the GABA receptor complex by a steroid anaesthetic. Brain Res 323:287–292
Hirani K, Khisti RT, Chopde CT (2002) Behavioral action of ethanol in Porsolt’s forced swim test: modulation by 3 alpha-hydroxy-5 alpha-pregnan-20-one. Neuropharmacology 43:1339–1350
Ignar DM, Kuhn CM (1990) Effects of specific mu and kappa opiate tolerance and abstinence on hypothalamo–pituitary–adrenal axis secretion in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 255:1287–1295
Janak PH, Redfern JEM, Samson HH (1998) The reinforcing effects of ethanol are altered by the endogenous neurosteroid, allopregnanolone. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22:1106–1112
Johnson KM, Dewey WL, Ritter KS, Beckner JS (1978) Cannabinoid effects on plasma corticosterone and uptake of 3H-corticosterone by mouse brain. Eur J Pharmacol 47:303–310
Kabbadj K, El-Etr M, Baulieu E-E, Robel P (1993) Pregnenolone metabolism in rodent embryonic neurons and astrocytes. Glia 7:170–175
Khisti RT, Penland SN, VanDoren MJ, Grobin AC, Morrow AL (2002) GABAergic neurosteroid modulation of ethanol actions. World J Biol Psychiatry 3:87–95
Khisti RT, VanDoren MJ, O’Buckley T, Morrow AL (2003) Neuroactive steroid 3 alpha-hydroxy-5 alpha-pregnan-20-one modulates ethanol-induced loss of righting reflex in rats. Brain Res 980:255–265
Kubena RK, Perhach JL Jr, Barry H III (1971) Corticosterone elevation mediated centrally by delta 1-tetrahydrocannabinol in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 14:89–92
Lau CE, Imam A, Ma F, Falk JL (1991) Acute effects of cocaine on spontaneous and discriminative motor functions: relation to route of administration and pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 257:444–456
Majewska MD, Harrison NL, Schwartz RD, Barker JL, Paul SM (1986) Steroid hormone metabolites are barbiturate-like modulators of the GABA receptor. Science 232:1004–1007
Manzanares J, Corchero J, Fuentes JA (1999) Opioid and cannabinoid receptor-mediated regulation of the increase in adrenocorticotropin hormone and corticosterone plasma concentrations induced by central administration of delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol in rats. Brain Res 839:173–179
Marx CE, Duncan GE, Gilmore JH, Lieberman JA, Morrow AL (2000) Olanzapine increases allopregnanolone in the rat cerebral cortex. Biol Psychiatry 47:1000–1004
Mizoguchi K, Yuzurihara M, Nagata M, Ishige A, Sasaki H, Tabira T (2002) Dopamine-receptor stimulation in the prefrontal cortex ameliorates stress-induced rotarod impairment. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 72:723–728
Moghaddam B (2002) Stress activation of glutamate neurotransmission in the prefrontal cortex: implications for dopamine-associated psychiatric disorders. Biol Psychiatry 51:775–787
Morley JE (1981) The endocrinology of the opiates and opioid peptides. Metabolism 30:195–209
Morrow AL, Suzdak PD, Paul SM (1987) Steroid hormone metabolites potentiate GABA receptor-mediated chloride ion flux with nanomolar potency. Eur J Pharmacol 142:483–485
Morrow AL, Janis GC, VanDoren MJ, Matthews DB, Samson HH, Janak PH, Grant KA (1999) Neurosteroids mediate pharmacological effects of ethanol: a new mechanism of ethanol action? Alcohol Clin Exp Res 23:1933–1940
Morrow AL, VanDoren MJ, Penland SN, Matthews DB (2001) The role of GABAergic neuroactive steroids in ethanol action, tolerance and dependence. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 37:98–109
Morrow AL, Khisti RT, Tokunaga S, McDaniel JR, Matthews DB (2004) GABAergic neuroactive steroids modulate selective ethanol actions: mechanisms and significance. In: Smith SH (ed) Neurosteroid effects in the central nervous system: the role of the GABAA receptor. CRC Press, Miami, pp 219–245
Murphy LL, Munoz RM, Adrian BA, Villanua MA (1998) Function of cannabinoid receptors in the neuroendocrine regulation of hormone secretion. Neurobiol Dis 5:432–446
Nie H, Janak PH (2003) Comparison of reinstatement of ethanol- and sucrose-seeking by conditioned stimuli and priming injections of allopregnanolone after extinction in rats. Psychopharmacology 168:222–228
O’Dell LE, Alomary AA, Vallee M, Koob GF, Fitzgerald RL, Purdy RH (2004) Ethanol-induced increases in neuroactive steroids in the rat brain and plasma are absent in adrenalectomized and gonadectomized rats. Eur J Pharmacol 484:241–247
Owens MJ, Ritchie JC, Nemeroff CB (1992) 5alpha-Pregnane-3alpha,21-diol-20-one (THDOC) attenuates mild stress-induced increases in plasma corticosterone via a non-glucocorticoid mechanism: comparison with alprazolam. Brain Res 573:353–355
Patchev VK, Shoaib M, Holsboer F, Almeida OFX (1994) The neurosteroid tetrahydroprogesterone counteracts corticotropin-releasing hormone-induced anxiety and alters the release and gene expression of corticotropin-releasing hormone in the rat hypothalamus. Neuroscience 62:265–271
Pearlstein T (2002) Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for premenstrual dysphoric disorder: the emerging gold standard? Drugs 62:1869–1885
Pistis M, Ferraro L, Pira L, Flore G, Tanganelli S, Gessa GL, Devoto P (2002) Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol decreases extracellular GABA and increases extracellular glutamate and dopamine levels in the rat prefrontal cortex: an in vivo microdialysis study. Brain Res 948:155–158
Porcu P, Sogliano C, Cinus M, Purdy RH, Biggio G, Concas A (2003) Nicotine-induced changes in cerebrocortical neuroactive steroids and plasma corticosterone concentrations in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 74:683–690
Porrino LJ (1993) Functional consequences of acute cocaine treatment depend on route of administration. Psychopharmacology 112:343–351
Purdy RH, Morrow AL, Moore PH Jr, Paul SM (1991) Stress-induced elevations of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor-active steroids in the rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:4553–4557
Reeve VC, Grant JD, Robertson W, Gillespie HK, Hollister LE (1983) Plasma concentrations of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol and impaired motor function. Drug Alcohol Depend 11:167–175
Rouge-Pont F, Mayo W, Marinelli M, Gingras M, Le Moal M, Piazza PV (2002) The neurosteroid allopregnanolone increases dopamine release and dopaminergic response to morphine in the rat nucleus accumbens. Eur J Neurosci 16:169–173
Sagratella S, Scotti DC, Longo VG (1986) EEG interaction between delta 8-tetrahydrocannabinol and some sedative-anxiolytic drugs. Is the anxiogenic effect of cannabis related to an action on the GABAergic system? Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol 41:203–209
Sinnott RS, Mark GP, Finn DA (2002a) Reinforcing effects of the neurosteroid allopregnanolone in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 72:923–929
Sinnott RS, Phillips TJ, Finn DA (2002b) Alteration of voluntary ethanol and saccharin consumption by the neurosteroid allopregnanolone in mice. Psychopharmacology 162(4):438–447
Spanagel R, Weiss F (1999) The dopamine hypothesis of reward: past and current status. Trends Neurosci 22:521–527
Steger RW, DePaolo L, Asch RH, Silverman AY (1983) Interactions of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) with hypothalamic neurotransmitters controlling luteinizing hormone and prolactin release. Neuroendocrinology 37:361–370
Sundström Poromaa, I, Smith S, Gulinello M (2003) GABA receptors, progesterone and premenstrual dysphoric disorder. Arch Women Ment Health 6:23–41
Uzunov DP, Cooper TB, Costa E, Guidotti A (1996) Fluoxetine-elicited changes in brain neurosteroid content measured by negative ion mass fragmentography. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:12599–12604
Uzunova V, Sheline Y, Davis JM, Rasmusson A, Uzunov DP, Costa E, Guidotti A (1998) Increase in the cerebrospinal fluid content of neurosteroids in patients with unipolar major depression who are receiving fluoxetine or fluvoxamine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:3239–3244
VanDoren MJ, Matthews DB, Janis GC, Grobin AC, Devaud LL, Morrow AL (2000) Neuroactive steroid 3alpha-hydroxy-5alpha-pregnan-20-one modulates electrophysiological and behavioral actions of ethanol. J Neurosci 20:1982–1989
Whitlow CT, Freedland CS, Porrino LJ (2002) Metabolic mapping of the time-dependent effects of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol administration in the rat. Psychopharmacology 161:129–136
Wiechman BE, Wood TE, Spratto GR (1981) Locomotor activity in morphine-treated rats: effects of and comparisons between cocaine, procaine, and lidocaine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 15:425–433
Wise RA (2002) Brain reward circuitry: insights from unsensed incentives. Neuron 36:229–240
Zuardi AW, Teixeira NA, Karniol IC (1984) Pharmacological interaction of the effects of delta 9-trans-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol on serum corticosterone levels in rats. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 269:12–19
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Tejas Patel and Todd O’Buckley for excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by NIAAA grants AA10564 (A.L.M.) and AA09291 and DA006634 (L.J.P.) and a NRSA award (to M.J.V.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grobin, A.C., VanDoren, M.J., Porrino, L.J. et al. Cortical 3α-hydroxy-5α-pregnan-20-one levels after acute administration of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, cocaine and morphine. Psychopharmacology 179, 544–550 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-2084-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-2084-3