Abstract
Background
Allopregnanolone plays a role in the stress response and homeostasis. Alterations in the estrogen milieu during the perinatal period influence brain development in a manner that persists into adulthood. Accordingly, we showed that a single administration of estradiol benzoate (EB) on the day of birth decreases brain allopregnanolone concentrations in adult female rats.
Objective
We examined whether the persistent decrease in allopregnanolone concentrations, induced by neonatal EB treatment, might affect sensitivity to stress during adulthood.
Methods
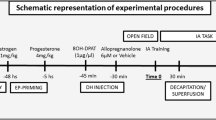
Female rats were treated with 10 μg of EB or vehicle on the day of birth. During adulthood, the response to acute foot shock stress was assessed by measuring changes in brain allopregnanolone and corticosterone levels, as well as extracellular dopamine output in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC).
Results
Neonatal EB treatment enhanced stress-stimulated allopregnanolone levels in the hypothalamus, as well as extracellular dopamine output in the mPFC; this latest effect is reverted by subchronic progesterone treatment. By contrast, neonatal EB treatment did not alter stress-induced corticosterone levels, sensitivity to hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis negative feedback, or abundance of glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors.
Conclusions
The persistent decrease in brain allopregnanolone concentrations, induced by neonatal EB treatment, enhances stress-stimulated allopregnanolone levels and extracellular dopamine output during adulthood. These effects are not associated to an impairment in HPA axis activity. Heightened sensitivity to stress is a risk factor for several neuropsychiatric disorders; these results suggest that exposure to estrogen during development may predispose individuals to such disorders.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbaccia ML, Roscetti G, Trabucchi M, Mostallino MC, Concas A, Purdy RH, Biggio G (1996) Time-dependent changes in rat brain neuroactive steroid concentrations and GABAA receptor function after acute stress. Neuroendocrinology 63:166–172
Barbaccia ML, Roscetti G, Trabucchi M, Purdy RH, Mostallino MC, Concas A, Biggio G (1997) The effects of inhibitors of GABAergic transmission and stress on brain and plasma allopregnanolone concentrations. Br J Pharmacol 120:1582–1588
Bernardi F, Pluchino N, Pieri M, Begliuomini S, Lenzi E, Puccetti S, Casarosa E, Luisi M, Genazzani AR (2006) Progesterone and medroxyprogesterone acetate effects on central and peripheral allopregnanolone and beta-endorphin levels. Neuroendocrinology 83:348–359
Berretti R, Santoru F, Locci A, Sogliano C, Calza A, Choleris E, Porcu P, Concas A (2014) Neonatal exposure to estradiol decreases hypothalamic allopregnanolone concentrations and alters agonistic and sexual but not affective behavior in adult female rats. Horm Behav 65:142–153
Biggio G, Concas A, Follesa P, Sanna E, Serra M (2007) Stress, ethanol, and neuroactive steroids. Pharmacol Ther 116:140–171
Brunton PJ, McKay AJ, Ochedalski T, Piastowska A, Rebas E, Lachowicz A, Russell JA (2009) Central opioid inhibition of neuroendocrine stress responses in pregnancy in the rat is induced by the neurosteroid allopregnanolone. J Neurosci 29:6449–6460
Calza A, Sogliano C, Santoru F, Marra C, Angioni MM, Mostallino MC, Biggio G, Concas A (2010) Neonatal exposure to estradiol in rats influences neuroactive steroid concentrations, GABAA receptor expression, and behavioral sensitivity to anxiolytic drugs. J Neurochem 113:1285–1295
Carver CM, Reddy DS (2013) Neurosteroid interactions with synaptic and extrasynaptic GABAA receptors: regulation of subunit plasticity, phasic and tonic inhibition, and neuronal network excitability. Psychopharmacology 230:151–188
Cozzoli DK, Tanchuck-Nipper MA, Kaufman MN, Horowitz CB, Finn DA (2014) Environmental stressors influence limited-access ethanol consumption by C57BL/6J mice in a sex-dependent manner. Alcohol 48:741–754
Croft AP, O’Callaghan MJ, Shaw SG, Connolly G, Jacquot C, Little HJ (2008) Effects of minor laboratory procedures, adrenalectomy, social defeat or acute alcohol on regional brain concentrations of corticosterone. Brain Res 1238:12–22
Dazzi L, Serra M, Seu E, Cherchi G, Pisu MG, Purdy RH, Biggio G (2002a) Progesterone enhances ethanol-induced modulation of mesocortical dopamine neurons: antagonism by finasteride. J Neurochem 83:1103–1109
Dazzi L, Serra M, Vacca G, Ladu S, Latrofa A, Trapani G, Biggio G (2002b) Depletion of cortical allopregnanolone potentiates stress-induced increase in cortical dopamine output. Brain Res 932:135–139
Dazzi L, Seu E, Cherchi G, Biggio G (2003) Antagonism of the stress-induced increase in cortical norepinephrine output by the selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor reboxetine. Eur J Pharmacol 476:55–61
Dazzi L, Seu E, Cherchi G, Biggio G (2004) Inhibition of stress-induced dopamine output in the rat prefrontal cortex by chronic treatment with olanzapine. Biol Psychiatry 55:477–483
Dazzi L, Seu E, Cherchi G, Barbieri PP, Matzeu A, Biggio G (2007) Estrous cycle-dependent changes in basal and ethanol-induced activity of cortical dopaminergic neurons in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:892–901
Droogleever Fortuyn HA, van Broekhoven F, Span PN, Backstrom T, Zitman FG, Verkes RJ (2004) Effects of PhD examination stress on allopregnanolone and cortisol plasma levels and peripheral benzodiazepine receptor density. Psychoneuroendocrinology 29:1341–1344
Droste SK, de Groote L, Atkinson HC, Lightman SL, Reul JM, Linthorst AC (2008) Corticosterone levels in the brain show a distinct ultradian rhythm but a delayed response to forced swim stress. Endocrinology 149:3244–3253
Finlay JM, Zigmond MJ, Abercrombie ED (1995) Increased dopamine and norepinephrine release in medial prefrontal cortex induced by acute and chronic stress: effects of diazepam. Neuroscience 64:619–628
Follesa P, Porcu P, Sogliano C, Cinus M, Biggio F, Mancuso L, Mostallino MC, Paoletti AM, Purdy RH, Biggio G, Concas A (2002) Changes in GABAA receptor γ2 subunit gene expression induced by long-term administration of oral contraceptives in rats. Neuropharmacology 42:325–336
Frye CA, Rhodes ME (2005) Estrogen-priming can enhance progesterone’s anti-seizure effects in part by increasing hippocampal levels of allopregnanolone. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 81:907–916
Genazzani AR, Petraglia F, Bernardi F, Casarosa E, Salvestroni C, Tonetti A, Nappi RE, Luisi S, Palumbo M, Purdy RH, Luisi M (1998) Circulating levels of allopregnanolone in humans: gender, age, and endocrine influences. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:2099–2103
Girdler SS, Straneva PA, Light KC, Pedersen CA, Morrow AL (2001) Allopregnanolone levels and reactivity to mental stress in premenstrual dysphoric disorder. Biol Psychiatry 49:788–797
Girdler SS, Lindgren M, Porcu P, Rubinow DR, Johnson JL, Morrow AL (2012) A history of depression in women is associated with an altered GABAergic neuroactive steroid profile. Psychoneuroendocrinology 37:543–553
Grobin AC, Morrow AL (2001) 3α-hydroxy-5α-pregnan-20-one levels and GABAA receptor-mediated 36Cl− flux across development in rat cerebral cortex. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 131:31–39
Gunn BG, Cunningham L, Mitchell SG, Swinny JD, Lambert JJ, Belelli D (2015) GABAA receptor-acting neurosteroids: a role in the development and regulation of the stress response. Front Neuroendocrinol 36:28–48
Klatzkin RR, Morrow AL, Light KC, Pedersen CA, Girdler SS (2006) Histories of depression, allopregnanolone responses to stress, and premenstrual symptoms in women. Biol Psychol 71:2–11
Korenbrot CC, Paup DC, Gorski RA (1975) Effects of testosterone propionate or dihydrotestosterone propionate on plasma FSH and LH levels in neonatal rats and on sexual differentiation of the brain. Endocrinology 97:709–717
Levine S, Mullins R (1967) Neonatal androgen or estrogen treatment and the adrenal cortica response to stress in adult rats. Endocrinology 80:1177–1179
Locci A, Porcu P, Talani G, Santoru F, Berretti R, Giunti E, Licheri V, Sanna E, Concas A (2017) Neonatal estradiol exposure to female rats changes GABAA receptor expression and function, and spatial learning during adulthood. Horm Behav 87:35–46
Maldonado-Devincci AM, Beattie MC, Morrow DH, McKinley RE, Cook JB, O’Buckley TK, Morrow AL (2014) Reduction of circulating and selective limbic brain levels of (3α,5α)-3-hydroxy-pregnan-20-one (3α,5α-THP) following forced swim stress in C57BL/6 J mice. Psychopharmacology 231:3281–3292
McCarthy MM (2008) Estradiol and the developing brain. Physiol Rev 88:91–124
McCarthy MM, Nugent BM (2013) Epigenetic contributions to hormonally-mediated sexual differentiation of the brain. J Neuroendocrinol 25:1133–1140
Motzo C, Porceddu ML, Maira G, Flore G, Concas A, Dazzi L, Biggio G (1996) Inhibition of basal and stress-induced dopamine release in the cerebral cortex and nucleus accumbens of freely moving rats by the neurosteroid allopregnanolone. J Psychopharmacol 10:266–272
Nugent BM, Wright CL, Shetty AC, Hodes GE, Lenz KM, Mahurkar A, Russo SJ, Devine SE, McCarthy MM (2015) Brain feminization requires active repression of masculinization via DNA methylation. Nat Neurosci 18:690–697
Patchev VK, Shoaib M, Holsboer F, Almeida OF (1994) The neurosteroid tetrahydroprogesterone counteracts corticotropin-releasing hormone-induced anxiety and alters the release and gene expression of corticotropin-releasing hormone in the rat hypothalamus. Neuroscience 62:265–271
Patchev VK, Hayashi S, Orikasa C, Almeida OF (1995) Implications of estrogen-dependent brain organization for gender differences in hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal regulation. FASEB J 9:419–423
Patchev VK, Hassan AH, Holsboer DF, Almeida OF (1996) The neurosteroid tetrahydroprogesterone attenuates the endocrine response to stress and exerts glucocorticoid-like effects on vasopressin gene transcription in the rat hypothalamus. Neuropsychopharmacology 15:533–540
Patchev VK, Hayashi S, Orikasa C, Almeida OF (1999) Ontogeny of gender-specific responsiveness to stress and glucocorticoids in the rat and its determination by the neonatal gonadal steroid environment. Stress 3:41–54
Paxinos G, Watson C (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates: Sixth Edition, Sixth Edition edn. Elsevier
Pisu MG, Garau A, Boero G, Biggio F, Pibiri V, Dore R, Locci V, Paci E, Porcu P, Serra M (2016) Sex differences in the outcome of juvenile social isolation on HPA axis function in rats. Neuroscience 320:172–182
Porcu P, Morrow AL (2014) Divergent neuroactive steroid responses to stress and ethanol in rat and mouse strains: relevance for human studies. Psychopharmacology 231:3257–3272
Porcu P, Grant KA, Green HL, Rogers LS, Morrow AL (2006) Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and ethanol modulation of deoxycorticosterone levels in cynomolgus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 186:293–301
Porcu P, O’Buckley TK, Alward SE, Marx CE, Shampine LJ, Girdler SS, Morrow AL (2009) Simultaneous quantification of GABAergic 3α,5α/3α,5β neuroactive steroids in human and rat serum. Steroids 74:463–473
Porcu P, Mostallino MC, Sogliano C, Santoru F, Berretti R, Concas A (2012) Long-term administration with levonorgestrel decreases allopregnanolone levels and alters GABAA receptor subunit expression and anxiety-like behavior. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 102:366–372
Porcu P, Locci A, Santoru F, Berretti R, Morrow AL, Concas A (2014) Failure of acute ethanol administration to alter cerebrocortical and hippocampal allopregnanolone levels in C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 38:948–958
Porcu P, Barron AM, Frye CA, Walf AA, Yang SY, He XY, Morrow AL, Panzica GC, Melcangi RC (2016) Neurosteroidogenesis today: novel targets for neuroactive steroid synthesis and action and their relevance for translational research. J Neuroendocrinol 28
Purdy RH, Morrow AL, Blinn JR, Paul SM (1990) Synthesis, metabolism, and pharmacological activity of 3α-hydroxy steroids which potentiate GABA-receptor-mediated chloride ion uptake in rat cerebral cortical synaptoneurosomes. J Med Chem 33:1572–1581
Purdy RH, Morrow AL, Moore PH Jr, Paul SM (1991) Stress-induced elevations of gamma-aminobutyric acid type a receptor-active steroids in the rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:4553–4557
Santoru F, Berretti R, Locci A, Porcu P, Concas A (2014) Decreased allopregnanolone induced by hormonal contraceptives is associated with a reduction in social behavior and sexual motivation in female rats. Psychopharmacology 231:3351–3364
Sapolsky RM, Meaney MJ (1986) Maturation of the adrenocortical stress response: neuroendocrine control mechanisms and the stress hyporesponsive period. Brain Res 396:64–76
Serra M, Pisu MG, Floris I, Biggio G (2005) Social isolation-induced changes in the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in the rat. Stress 8:259–264
Sfikakis A, Galanopoulou P, Konstandi M, Tsakayannis D (1996) Stress through handling for vaginal screening, serotonin, and ACTH response to ether. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 53:965–970
Shen H, Gong QH, Aoki C, Yuan M, Ruderman Y, Dattilo M, Williams K, Smith SS (2007) Reversal of neurosteroid effects at α4β2δ GABAA receptors triggers anxiety at puberty. Nat Neurosci 10:469–477
Sotomayor-Zarate R, Tiszavari M, Cruz G, Lara HE (2011) Neonatal exposure to single doses of estradiol or testosterone programs ovarian follicular development-modified hypothalamic neurotransmitters and causes polycystic ovary during adulthood in the rat. Fertil Steril 96:1490–1496
Tzschentke TM (2001) Pharmacology and behavioral pharmacology of the mesocortical dopamine system. Prog Neurobiol 63:241–320
Ulrich-Lai YM, Herman JP (2009) Neural regulation of endocrine and autonomic stress responses. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:397–409
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Italian MIUR (Grant PRIN 2003057334), the Banco di Sardegna Foundation (Grant 2012.0255), and the University of Cagliari (Premialità 2009; Premialità 2012) to A.C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Porcu, P., Lallai, V., Locci, A. et al. Changes in stress-stimulated allopregnanolone levels induced by neonatal estradiol treatment are associated with enhanced dopamine release in adult female rats: reversal by progesterone administration. Psychopharmacology 234, 749–760 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4511-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4511-7