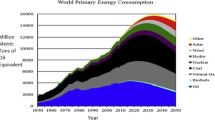
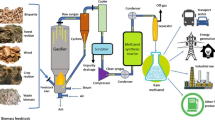
Abstract
The global energy system is characterized by a gradual de-carbonization and move to cleaner burning technologies: from wood to coal to oil and to natural gas. A final destination characterized by the term“hydrogen economy” is desired. Gas hydrate found in the earth’s crust is considered a source of natural gas that is essentially 100% methane (CH4) gas. Natural gas hydrate estimates worldwide range from 10,000 to 40,000 trillion cubic meters (TCM). Efforts are underway to exploit this resource. These methane hydrates in the earth’s crust also have the potential to be a significant factor in global climate change. Moreover, gas hydrates offer opportunities for the development of innovative technologies (separation of CO2 from CO2/N2 and CO2/H2 mixtures, CO2 sequestration, natural gas transportation and storage and H2 storage). In this work we assess the progress towards exploitation of gas hydrates as a resource for methane (cleaner energy) and summarize the state of the art with respect to the role of gas hydrates in the development of innovative technologies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacher, P.,“Meeting the Energy Challenges of the21 st Century,”Int. J. Energy Technology and Policy,1(1/2), 1 (2002).
Bains, S., Corfield, R. M. and Norris, R D.,“Mechanisms of Climate Warming at the End of the Paleocene,”Science,285, 724 (1999).
BeMent, W. O., Bil, K., Drenth, A. J. J., Klomp, U. C., Roodhart, L. P., Sambell, R. H., Swinkels, W. J. A., White, D. and Zoons, C. W.,Are There “Show Stoppers” to Commercial Gas Hydrate Production, Pro- ceedings of the Japan National Oil Corporation (JNOC), International Symposium on Methane Hydrates-Resources in the Near Future, Chiba City, Japan, October 20–22 (1998).
Berecz, E. and Balla-Achs, M.,Studies in Inorganic Chemistry 4: Gas Hydrates, Elsevier, Amsterdam (1983).
Brewer, P., Friederich, G., Peltzer, E. T. and Orr, F. M.,“Direct Experiments on the Ocean Disposal of Fossil Fuel CO2,”Science,284, 943 (1999).
Cale, J.,Geological Storage of CO2, Proceedings of 6th International Conference on Greenhouse Gas Control Technologies, October 1–4, Kyoto, Japan (2002).http://www.elsevier.com/wps/find/bookdescription.cws_home/672956/description#description
Chakravarti, S., Gupta, A. and Hunek, B.,Advanced Technology for the Capture of Carbon Dioxide from Flue Gases, Proceeding of 1st National Conference on Carbon Sequestration, May 14–17, Washington DC. (2001).http://www.netl.doe.gov/publications/proceedings/ 01/carbon_seq/carbon_seq01.html
Chun, M. K. and Lee, H.,“Kinetics of Formation of Carbon Dioxide Clathrate Hydrates,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,13, 620 (1996).
Dallimore, S. R., Uchida, T. and Collett, T. S.,“Scientific Results from JAPEX/JNOC/GSC Mallik 2L-38 Gas Hydrate Research well, Mackenzie Delta, Northwest Territories, Canada,” Geological Survey of Canada Bulletin 544, Ottawa (1999).
Dallimore, S. R., Collett, T. S., Uchida, T., Weber, M., Takahashi, H. and the Mallik Gas Hydrates Research Team,“Overview of the 2002 Mallik Gas Hydrate Production Research Well Program,” In Proceedings of 4th International Conference on Gas Hydrates, Yokohama, May 19–23, 36 (2002).
Davidson, D. W.,Gas Hydrates, In: Frank F., Eds., Water: A Comprehensive Treatise, Plenum Press, New York, Vol 2, Chapter 3, 115 (1973).
Dickens, G.R., Paull, C. K., Wallace, P. and the ODP Leg 164 Scientific Party,“Direct Measurement of insitu Methane Quantities in a Large Gas-hydrate Reservoir,”Nature,385, 426 (1997).
Dickens, G R., O’Neil, J. R., Rea, D. K. and Owen, R M.,“Dissociation of Oceanic Methane Hydrate as a Cause for the Carbon Isotope Excursion at the End of the Paleocene,”Paleoceanography,10, 965 (1995).
Englezos, P., “Nucleation and Growth of Gas Hydrate Crystals in Relation to Kinetic Inhibition,”Revue de l’Institut FranÇais du Pétrole,51(6), 789 (1996).
Englezos, P.,“Reviews: Clathrate Hydrates,”Ind. Eng. Chem. Res.,32(7), 1251 (1993).
Englezos, P. and Hall, S.,“Phase Equilibrium Data on Carbon Dioxide Hydrate in the Presence of Electrolytes, Water Soluble Polymers and Montmorillonite,”Can. J. Chem. Eng.,72, 887 (1994).
Englezos, P. and Ngan, Y T.,“Effect of Polyethylene Oxide on Gas Hydrate Phase Equilibria,”Fluid Phase Equilibria,92, 271 (1994).
Florusse, L. J., Peters, C. J., Schoonman, J., Hester, K. C., Koh, C. A., Dec, S. F., Marsh, K. N. and Sloan, E. D., “Stable Low-Pressure Hydrogen Clusters Stored in a Binary Clathrate Hydrate,”Science,306, 469 (2004).
Fukumoto, K., Tobe, T., Ohmura, R. and Mori, Y H., “Hydrate Formation using Water Spraying in a Hydrophobic Gas: A Preliminary Study,”AIChE J.,47, 1899 (2001).
Gaarder, C. and Englezos, P., “The Use of Clathrate Hydrates for the Concentration of Mechanical Pulp Mill Effluents,”Nordic Pulp and Paper Research Journal,2, 110 (1995).
Ginsburg, G D. and Soloviev, V. A.,Submarine Gas Hydrates (Russian), VNIIOkeangeologia, St. Petersburg (1998).
Gough, C., Shackley, S. and Cannell, M. G.R.,Evaluating the Options for Carbon Sequestration, Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research, Technical Report 2, UMIST, Manchester (2002).
Gudmundsson, J. S., Mork, M. and Graff, O. F.,Hydrate Non-pipeline Technology, In Proceedings of 4th International Conference on Gas Hydrates, Yokohama, May 19–23, pp. 997–1002 (2002).
Hall, C., Tharakan, P., Hallock, J., Cleveland, C. and Jefferson, M., “Hydrocarbons and the Evolution of Human Culture,”Nature,426(20), 318(2003).
Hatzikiriakos, S. G. and Englezos, P.,“The Relationship between Global Warming and Methane Gas Hydrates in the Earth,”Chem. Eng. Sci.,48(23), 3963 (1993).
Herzog, H. J. and Edmond, J.,Disposing of CO 2 in the Ocean, Carbon Dioxide Chemistry: Environmental Issues, Paul, J. and C.-M. Pradier (editors), The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, UK (1994).
Herzog, H., Drake, E. and Adams, E.,CO2 Capture, Reuse, and Storage Technologies for Mitigating Global Climate Change, DoE report (order No. DE-AF22-96PC01257), January (1997).
Hirohama, S., Shimoyama, Y. and Wakabayashi, A.,“Conversion of CH4-hydrate to CO2-hydrate in Liquid CO2,”J. Chem. Eng. Japan,29(6), 1014(1996).
Holbrook, W S., Hoskins, H., Wood, W. T., Stephen, R. A. and Lizarralde, D.,“Methane Hydrate and Free Gas on the Blake Ridge from Vertical Seismic Profiling,”Science,273(5283), 1840 (1996).
Hong, H., Pooladi-Darvish, M. and Bishnoi, P. R.,“Analytical Modelling of Gas Production from Hydrates in Porous Media,”Journal of Canadian Petroleum Technology (JCPT),42(11), 45 (2003).
Hütz, U. and Englezos, P.,“Measurement of Structure H Hydrate Phase Equilibrium and the Effect of Electrolytes,”Fluid Phase Equilibria,117, 178 (1996).
Hyndman, R. D. and Dallimore, S. R.,“Natural Gas Hydrate Studies in Canada,” CSEG (Canadian Society of Exploration Geophysicists) Recorder, May, pp. 11–20 (2001).
Kang, S. P. and Lee, H., “Recovery of CO2 from Flue Gas Using Gas Hydrate: Thermodynamic Verification through Phase Equilibrium Measurements,”Environ Sci. Technol.,34, 4397 (2000).
Kang, S.-P., Lee, H. and Ryu, B.-J.,“Enthalpies of Dissociation of Clathrate Hydrates of Carbon Dioxide, Nitrogen, (Carbon Dioxide+Nitrogen), and (Carbon Dioxide+Nitrogen+Tetrahydrofuran),”J. Chem. Thermodynamics,53, 513 (2001a).
Kang, S.-P., Lee, H., Lee, C.-S. and Sung, W.-M.,“Hydrate Phase Equilibria of the Guest Mixtures Containing CO2, N2 and Tetrahydrofuran,”Fluid Phase Equilibria,185, 101 (2001b).
Katz, M. E., Pak, D. K., Dickens, G.R. and Miller, K. G.,“The Source and Fate of Massive Carbon Input during the Latest Paleocene Thermal Maximum,”Science,286, 1531 (1999).
Kerr, R.,“Did a Blast of Sea-floor Gas Hydrates Usher in a New Age?,”Nature,275, 1267 (1997).
Kerr, R.,“Gas Hydrate Resource: Smaller but Sooner,”Science,303, 946 (2004).
Klara, S. M. and Srivastava, R. D., “U.S. DOE Integrated Collaborative Technology Development Program for CO2 Separation and Capture”,Environmental Progress,21(4), 247 (2002).
Kleinberg, R. L. and Brewer, P., “Probing Gas Hydrate Deposits,”American Scientist,89, 244 (2001).
Khokhar, A. A., Gudmundson, J. S. and Sloan, E. D., “Gas Storage in Structure H Hydrate,”Fluid Phase Equilibria,150–151, 383 (1998).
Kuhs, W. F., Chazallon, B., Radaelli, P. G. and Pauer, F.,“Cage Occupancy and Compressibility of Deuterated N2-Clathrate Hydrate by Neutron Diffraction,”J. Inclusion Phenom. Mol. Recognit. Chem.,29, 65 (1997).
Kvenvolden, K. A.,“Gas Hydrates-geological Perspective and Global Change,”Reviews in Geophysics,31(2), 173 (1993).
Kvenvolden, K. A.,“Potential Effects of Gas Hydrate on Human Welfare,”Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences U.S.A.,96(7), 3420 (1999).
Kvenvolden, K. A.,“Gas Hydrate and Humans,”Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences,912, 17 (2000).
Lee, H., Seo, Y., Seo, Y.T., Moudrakovski, I. and Ripmeester, J. A.,“Recovering Methane from Solid Methane Hydrate with Carbon Dioxide,”Angewandte Chemie, International Edition,42(41), 5048 (2003).
Lee, J. W., Chun, M.-K., Lee, K. M., Kim, Y.J. and Lee, H.,“Phase Equilibria and Kinetic Behaviour of CO2 Hydrate in Electrolyte and Porous Media Solutions: Application to Ocean Sequestration of CO2”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,19, 673 (2002).
Lee, H., Lee, J., Kim, D. Y., Park, J., Seo, Y.-T., Zeng, H., Moudrakovski, I. L., Ratcliffe, C. I. and Ripmeester, J. A.,“Tuning Clathrate Hydrates for Hydrogen Storage,”Nature,434(7034), 743 (2005).
Link, D. D., Ladner, E. P., Elsen, H. A. and Taylor, C. E.,“Formation and Dissociation Studies for Optimizing the Uptake of Methane by Methane Hydrates,”Fluid Phase Equilibria,211, 1 (2003).
Loiseaux, J. M.,“Primary Energy Needs and Greenhouse Effect Increase: What can be Done?,”Int. J. Energy Technology and Policy,1(1/2), 27 (2002).
Lokshin, K. A., Zhao, Y., He, D., Mao, W.L., Mao, H.-K., Hemley, R. J., Lobanov, M. V. and Greenblatt, M., “Structure and Dynamics of Hydrogen Molecules in the Novel Clathrate Hydrate by High Pressure Neutron Diffraction,”Physical Review Letters,93(12), 125–503 (2004).
MacDonald, G J.,“The Many Origins of Natural Gas,”J. Petroleum Geology,5(4), 341 (1983).
Makogon, Y.F.,Hydrates of Natural Gas, Cieslewicz, W. J. Translation Penn Well Publishing Co., Tulsa, Oklahoma (1981).
Makogon, Y.F.,Hydrates of Hydrocarbons, PennWell Books, Tulsa, Oklahoma (1997).
Makogon, Y.F., Trebin, R A., Trofimuk, A. A., Tsarev, V. P. and Chersky, N. V.,“Detection of a Pool of Natural Gas in a Solid (Hydrate Gas) State,”Doklady of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR-Earth Science Sections,196, 197 (1972).
Mao, W L., Mao, H.-K., Goncharov, A. F., Struzhkin, V. V., Guo, Q., Hu, J., Shu, J., Hemley, R. J., Somayazulu, M. and Zhao, “Hydrogen Clusters in Clathrate Hydrate,”Science,297, 2247 (2002).
Mao, W L. and Mao, H.-K.,“Hydrogen Storage in Molecular Compounds,”PNAS-USA,101(3), 708 (2004).
Masuda, Y., Kurihara, M., Ohuchi, H. and Sato, T.,“A Field Scale Simulation Study on Gas Productivity of Formations Containing Gas Hydrates,” In Proceedings of 4th International Conference on Gas Hydrates, Yokohama, May 19–23, pp. 40–46 (2002).
McKee, B.,Zero Emissions Technologies-Technology Status Report, OECD/IEA, Paris (2002).
Mori, Y H.,“Recent Advances in Hydrate-based Technologies for Natural gas Storage-A Review,”J. Chem. Ind. & Eng. China,54, 1 (2003).
Moridis, G J.,“Numerical Studies of Gas Production from Methane Hydrates,” paper SPE 75691,SPE Journal,8(4), 359 (2003).
Moridis, G J.,“Numerical Studies of Gas Production from Class 2 and Class 3 Hydrate Accumulations at the Mallik Site, Mackenzie Delta, Canada,”SPE Reservoir Evaluation & Engineering,7(3), 175 (2004).
Nakajima, Y., Takaoki, T., Ohgaki, K. and Ota, S.,“Use of Hydrate Pellets for Transportation of Natural Gas-II-Proposition of Natural Gas Transportation in form of Hydrate Pellets,” In Proceedings of 4th International Conference on Gas Hydrates, Yokohama, May 19–23, pp. 987–990 (2002).
Ngan, Y T. and Englezos, P.,“Concentration of Mechanical Pulp Mill Effluents and NaCl Solutions through Propane Hydrate Formation,”Ind. Eng. Chem. Res.,35(6), 1894 (1996).
Nisbet, E. G.,“Sources of Atmospheric CH4 in Early Postglacial Time,”Journal of Geophysical Research,97(D12), 12859 (1992).
Ohmura, R., Kashiwazaki, S., Shiota, S., Tsuji, H. and Mori, Y M.,“Structure-I and Structure-H Hydrate Formation Using Water Spraying,”Energy & Fuels,16, 1141 (2002).
Ota, S., Uetani, H. and Kawano, H.,“Use of Hydrate Pellets for Transportation of Natural Gas-II-Safety Measures and Conceptual Design of Natural Gas Hydrate Pellet Carrier,” In Proceedings of 4th International Conference on Gas Hydrates, Yokohama, May 19–23, pp. 991–996 (2002).
Patchkovskii, S. and Tse, J. S.,“Thermodynamic Stability of Hydrogen Clathrates,”PNAS-USA,100(25), 14645 (2003).
Paull, C. K.,Sensing Marine Gas Reservoir, In: Holder, G D., Bishnoi, P. R. (Eds), Proceedings of 3rd International Conference on Gas Hydrates, Book of Abstracts, July 18–22, Salt Lake City, UT (1999).
Pooladi-Darvish, M.,“Gas Production from Hydrate Reservoirs and its Modelling,” Distinguished author series,Journal of Petroleum Tech- nology(JPT), 65 (2004).
Pooladi-Darvish, M. and Hong, H.,Effect of Conductive and Convective Heat Flow on Gas Production from Natural Hydrates by Depressurization, paper #4 in Advances in the Study of Gas Hydrates, Editors: Charles E. Taylor and Johnathan Kwan, November, Springer Publishing (2004).
Ripmeester, J. A., Tse, J. S., Ratcliffe, C. I. and Powell, B. M., “A New Clathrate Hydrate Structure,”Nature,325, 135 (1987).
Ripmeester, J. A. and Ratcliffe, C. I., “Xenon-129 NMR Studies of Clathrate Hydrates: New Guests for Structure II and Structure H,”Journal of Physical Chemistry,94(25), 8773 (1990).
Ripmeester, J. A., Ratcliffe, C. I., Klug, D. D. and Tse, J. S.,“Molecular Perspectives on Structure and Dynamics in Clathrate Hydrates,”Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences,715, 161 (1994).
Ripmeester, J. A.,“Hydrate Research-from Correlations to a Knowledge-based Discipline. The Importance of Structure,”Annals New York Academy of Sciences,912, 1 (2000).
Ripmeester, J. A.,Calculating Gas Storage Capacity in Hydrates, personal communication (2004).
Robinson, D. B. and Mehta, B. R.,“Hydrates in the Propane-Carbon Dioxide-Water System,”J. of Canadian Petroleum Technology,10(1), 33(1971).
Roo, J. L., Peters, C. J., Lichtenthaler, R. N. and Diepen, G A. M.,“Occurrence of Methane Hydrate in Saturated and Unsaturated Solutions of Sodium Chloride and Water in Dependence of Temperature and Pressure,”AIChE J.,29, 651 (1983).
Schneider, S. H.,“The Global Warming Debate: Science or Politics?,”Environ. Sci. Technol.,24, 432 (1990).
Schicks, J. M. and Ripmeester, J. A.,“The Coexistence of Two Different Methane Hydrate Phases under Moderate Pressure and Temperature Conditions: Kinetic Versus Thermodynamic Products,”Angewandte Chemie, International Edition,43(25), 3310 (2004).
Seo, Y.-T. and Lee, H.,“Multiple Phase Equilibria of the Ternary Carbon Dioxide, Methane, and Water Mixtures,”J. Phys. Chem. B,105, 10084 (2001a).
Seo, Y.-T. and Lee, H.,“A New Hydrate-based Recovery Process for Removing Chlorinated Hydrocarbons from Aqueous Solutions,”Environ. Sci. Technol.,35, 3386 (2001b).
Seo, Y.-T., Lee, H. and Uchida, T.,“Methane and Carbon Dioxide Hydrate Phase behavior in Small Porous Silica Gels: Three Phase Equilibrium Determination and Thermodynamic Modelling,”Langmuir,18, 9164 (2002).
Seo, Y.-T. and Lee, H.,“Hydrate Phase Equilibria of the Ternary CH4NaCl+Water, CO2+NaCl+Water and CH4+CO2+Water Mixtures in Silica Gel Pores,”J. Phys. Chem. B,107, 889 (2003a).
Seo, Y.-T. and Lee, H.,“13C NMR Analysis and Gas Uptake Measurements of Pure and Mixed Gas Hydrates: Development of Natural Gas Transport and Storage Method using Gas Hydrate,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,20, 1085 (2003b).
Seo, Y.-T., Lee, H., Moudrakovski, I. and Ripmeester, J.,“Phase Behavior and Structural Characterization of Coexisting Pure and Mixed Clathrate Hydrates,”ChemPhysChem,4(4), 379 (2003).
Seo, Y.-T. and Lee, H.,“Structure and Guest Distribution of the Mixed Carbon Dioxide and Nitrogen Hydrates As Revealed by X-ray Diffraction and13C NMR Spectroscopy,”J. Phys. Chem. B,108, 530 (2004).
Seo, Y.-T., Moudrakovski, I. L., Ripmeester, J. A., Lee, J.-W. and Lee, H., “Efficient Recovery of CO2 from Flue Gas by Clathrate Hydrate Formation in Porous Silica Gels,”Environmental Science and Technology,39(7), 2315 (2005).
Shindo, Y. and Komiyama, H. inThe Expanding World of Chemical Engineering, J. Garside (editor), Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, Langhorne, PA (1994).
Simpson, S.,“Methane Fever,”Scientific American,2, 24 (2000).
Sloan, E. D. Jr.,Clathrate Hydrates of Natural Gasses, 2nd edition, Marcel Dekker, New York (1998).
Sloan, E. D.,“Clathrate Hydrate Measurements: Microscopic, Mesoscopic, and Macroscopic,”J. Chem. Thermodynamics,35, 41 (2003a).
Sloan, E. D.,“Fundamental Principles and Applications of Natural Gas Hydrates,”Nature,426, 353 (2003b).
Sloan, E. D.,“Evaluation of CO2 Sequestration in Ocean Hydrates,” Proceedings of DEEP SEA & CO2 2000, International Symposium on Deep Sea Sequestration of CO2, February 1–2, Tokyo, Japan, pp. 2–5-1-2-5-10 (2000).
Stern, L. A., Circone, S., Kirby, S. H. and Durham, W B., “Temperature, Pressure, and Compositional Effects on Anomalous or“self” Preservation of Gas Hydrate,”Can. J. Phys.,81, 271 (2003).
Suess, E., Bohrmann, G., Greinert, J. and Lausch, E.,“Flammable Ice,”Scientific American,11, 76 (1999).
Sun, Z.-G., Wang, R., Ma, R., Guo, K. and Fan, S.,“Natural Gas Storage with the Presence of Promoters,”Energy Conversion and Management,44, 2733 (2003).
Sung, W., Lee, H. and Lee, C.,“Numerical Study for Production Performances of a Methane Hydrate Reservoir Stimulated by Inhibitor Injection,”Energy Sources,24, 499 (2002).
Takahashi, T., Goldberg, D. and Mutter, J. C.,“Secure, Long-Term Sequestration of CO2 in Deep Saline Aquifers Associated with Oceanic and Continental Basaltic Rocks,” Proceeding of DEEP SEA & CO2 2000, International Symposium on Deep Sea Sequestration of CO2, February 1–2, Tokyo, Japan, pp. 4-1-1–4-1-7 (2000).
Takahashi, M., Kawamura, T., Yamamoto, Y., Ohnari, H., Himuro, S. and Shakutsui, H., “Effect of Shrinking Microbubble on Gas Hydrate Formation,”The Journal of Physical Chemistry,107(10), 2171 (2003).
Takaoki, T., Iwasaki, T., Katoh, Y., Arai, T. and Horiguchi, K.,“Use of Hydrate Pellets for Transportation of Natural Gas-I-sadvantage of Pellet Form of Natural Gas Hydrate in Sea Transportation,” Proceedings of 4th International Conference on Gas Hydrates, Yokohama, May 19–23, pp. 982–986 (2002).
Taylor, F. W.,“The Greenhouse Effect and Climate Change,”Reports on Progress in Physics,54, 881 (1991).
Thambimuthu, K., Mercier, G., Wilson, M., Mitchell, B. and Ali, M.,“Canadian Initiatives on CO2 Capture and Storage: Towards Zero Emissions from Fossil Fules,” Proceedings of 6th International Conference on Greenhouse Gas Control Technologies, October 1–4, Kyoto, Japan (2002).
Thomas, S. and Dawe, R. A.,“Review of Ways to Transport Natural Gas Energy from Countries which do Not Need the Gas for Domestic Use,”Energy,28, 1461 (2003).
Tsuji, H., Ohmura, R. and Mori, Y H.,“Forming Structure-H Hydrates Using Water Spraying in Methane Gas: Effects of Chemical Species of Large-Molecule Guest Substances,”Energy & Fuels,18, 418 (2004).
Tulk, C. A., Ratcliffe, C. I. and Ripmeester, J. A.,“Chemical and Physical Analysis of Natural Gas Hydrate from the JAPEX/JNOC/GSC Mallik 2L–38 Gas Hydrate Research Well,” In: S. R. Dallimore, T. Uchida and T. S. Collett (Eds.), Geological Survey of Canada Bulletin 544, Ottawa, pp. 251–262 (1999).
Uchida, T.,“Physical Property Measurements on CO2-Clathrate Hydrates. Review of Crystallography, Hydration Number, and Mechanical Properties,”Waste Management,17(5/6), 343 (1997).
Udachin, K. A., Ratcliffe, C. I. and Ripmeester, J. A.,“Structure, Composition, and Thermal Expansion of CO2 Hydrate from Single Crystal X-ray Diffraction Measurements,”J. Phys. Chem. B,105, 4200 (2001).
van der Waals, J. H. and Platteeuw, J. C.,“Clathrate Solutions,”Advances in Chemical Physics,2, 1 (1959).
Vos, W L., Finger, L. W., Hemley, R. J. and Mao, H.-K., “Novel H2-H2O Clathrates at High Pressures,”Phys. Rev. Lett.,71(19), 3150 (1993).
West, O. R., Tsouris, C., Lee, S., McCallum, S. D. and Liang, L., “Negatively Buoyant CO2 -Hydrate Composite for Ocean Carbon Sequestration,”AIChEJ.,49(1), 283 (2003).
Wirth, T. E., Gray, C. B. and Podesta, J. D.,“The Future of Energy Policy,”Foreign Affairs, 132 (2003).
Yamamoto, Y., Komai, T., Yoon, J. H., Kang, S. P., Okita, S. and Kawamura, T.,“Removal of Hydrogen Sulfide from Gas Mixture by Hydrate Formation,”J. Chem. Eng. Japan,36(8), 971 (2003).
Yamasaki, A.,“A New CO2 Ocean Sequestration Scenario via a Crystallization Process of CO2 Hydrate Particles,” Proceedings of DEEP SEA & CO2 2000, International Symposium on Deep Sea Sequestration of CO2, February 1–2, Tokyo, Japan, pp. 2-2-1–2-1-7 (2000).
Zachos, J. C., Lohmann, K. C., Walker, J. C. G. and Wise, S. W.,“Abrupt Climate Change and Transient Climates during the Paleocene: A Marine Perspective,”Journal of Geology,101, 191 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Englezos, P., Lee, J.D. Gas hydrates: A cleaner source of energy and opportunity for innovative technologies. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 22, 671–681 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02705781
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02705781