Abstract
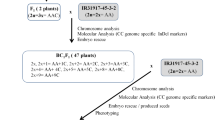
Recurrent parent genome (RPG) recovery is the most important step of marker assisted backcross breeding. This breeding approach is used to develop new varieties by inserting a particular gene of interest into the background of a modern variety, and removing undesirable segments linked with the target allele, which can survive after many generations of backcrossing. The marker assisted backcrossing technique is the most effective way to minimize the limitation of conventional breeding, and recover the parental genome within 2–3 generations. MR219, A modern rice variety of Malaysia (susceptible to submergence) was crossed with a high-yielding submergence tolerant variety Swarna-Sub1 (donor) to produce a new submergence tolerant rice variety. Foreground selection for the sub1 gene was done using tightly linked markers. Estimation of RPG recovery was conducted in earlier generations with previously screened polymorphic SSR markers. A total of 385 SSR markers were tested to identify the polymorphism between the parents and 88 of them found to be polymorphic. Background analysis revealed 65.55–77.8 and 78.79–95.5 % recovery in BC1F1 and BC2F1 generations, respectively. In the BC2F2 generation the average RPG recovery was 95.37 % and that for the selected plant was 96.3 %. This study revealed the usefulness of marker assisted backcrossing for the quick recovery of a parental genome in a backcrossing population.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed F, Rafii MY, Ismail MR, Juraimi AS, Rahim HA, Asfaliza R, Latif MA (2013) Waterlogging tolerance of crops: breeding, mechanism of tolerance, molecular approaches, and future prospects. Biomed Res Int 2013:963525. doi:10.1155/2013/963525
Allard RW (1999) Principles of plant breeding, 2nd edn. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Basavaraj SH, Singh VK, Singh A, Singh A, Singh A, Anand D, Yadav S, Ellur RK, Singh D, GopalaKrishnan S, Nagarajan M, Mohapatra T, Prabhu KV, Singh AK (2010) Marker-assisted improvement of bacterial blight resistance in parental lines of Pusa RH10, a superfine grain aromatic rice hybrid. Mol Breed 26:293–305
Bhatia D, Sharma R, Vikal Y, Mangat GS, Mahajan R, Sharma N, Lore JS, Singh N, Bharaj TS, Singh K (2011) Marker-assisted development of bacterial blight resistant, dwarf, and high yielding versions of two traditional basmati rice cultivars. Crop Sci 51:759–770
Chen S, Lin XH, Xu CG, Zhang Q (2000) Improvement of bacterial blight resistance of ‘Minghui 63’, an elite restorer line of hybrid rice, by molecular marker-assisted selection. Crop Sci 40:239–244. doi:10.2135/cropsci2000.401239x
Chen S, Xu CG, Lin XH, Zhang Q (2001) Improving bacterial blight resistance of ‘6078’, an elite restorer line of hybrid rice, by molecular marker-assisted selection. Plant Breed 120:133–137
Collard BC, Mackill DJ (2008) Marker-assisted selection: an approach for precision plant breeding in the twenty-first century. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 363:557–572
Collard BC, Vera Cruz CM, McNally KL, Virk PS, Mackill DJ (2008) Rice molecular breeding laboratories in the genomics era: current status and future considerations. Int J Plant Genomics 2008:524847. doi:10.1155/2008/524847
Cuc LM, Huyen LTN, Hien PTM, Hang VTT, Dam NQ, Mui PT, Quang VD, Ismail AM, Ham LH (2012) Application of marker assisted backcrossing to introgress the submergence tolerance QTL SUB1 into the Vietnam elite rice variety-AS996. Am J Plant Sci 3:528–536
Dey M, Upadhyaya H (1996) Yield loss due to drought, cold and submergence in Asia. In: Evenson RE, Herdt RW, Hossain M (eds) Rice research in Asia: progress and priorities. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 291–303
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Frisch M (2005) Breeding strategies: optimum design of marker-assisted backcross programs. In: Lörz H, Wenzel G (eds) Molecular marker systems in plant breeding and crop improvement. Springer, Berlin, pp 319–334
Frisch M, Melchinger AE (2005) Selection theory for marker-assisted backcrossing. Genetics 170:909–917
Frisch M, Bohn M, Melchinger AE (1999) Comparison of selection strategies for marker-assisted backcrossing of a gene. Crop Sci 39:1295–1301
Fukao T, Xu K, Ronald PC, Bailey-Serres J (2006) A variable cluster of ethylene response factor–like genes regulates metabolic and developmental acclimation responses to submergence in rice. Plant Cell 18:2021–2034
Gopalakrishnan S, Sharma RK, Anand Rajkumar K, Joseph M, Singh VP, Singh AK, Bhat KV, Singh NK, Mohapatra T (2008) Integrating marker assisted background analysis with foreground selection for identification of superior bacterial blight resistant recombinants in Basmati rice. Plant Breeding 127:131–139
Hasan MM, Rafii MY, Ismail MR, Mahmood M, Alam MA, Rahim HA, Malek MA, Latif MA (2015) Introgression of blast resistance genes into the elite rice variety MR263 through marker-assisted backcrossing. J Sci Food Agric. doi:10.1002/jsfa.7222
Herdt RW (1991) Research priorities for rice biotechnology. Rice Biotechnol 6:19–54
Hospital F (2001) Size of donor chromosome segments around introgressed loci and reduction of linkage drag in marker-assisted backcross programs. Genetics 158:1363–1379
Hospital F (2003) Marker-assisted breeding. In: Newbury HJ (ed) Plant molecular breeding. Blackwell Publishing, Oxford, pp 30–59
Hospital F, Charcosset A (1997) Marker-assisted introgression of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 147:1469–1485
Hospital F, Chevalet C, Mulsant P (1992) Using markers in gene introgression breeding programs. Genetics 132:1199
Huyen LTN, Cuc LM, Ismail AM, Ham LH (2012a) Introgression the salinity tolerance QTLs Saltol into AS996, the elite rice variety of Vietnam. Am J Plant Sci 3:981–987
Huyen LTN, Cuc LM, Ismail AM, Ham LH (2012b) Introgression the salinity tolerance QTLs Saltol into AS996, the elite rice variety of Vietnam. Am J Plant Sci 3. doi:10.4236/ajps.2012.37116
Iftekharuddaula KM, Newaz MA, Salam MA, Ahmed HU, Mahbub MAA, Septiningsih EM, Collard BCY, Sanchez DL, Pamplona AM, Mackill DJ (2011) Rapid and high-precision marker assisted backcrossing to introgress the SUB1 QTL into BR11, the rainfed lowland rice mega variety of Bangladesh. Euphytica 178:83–97
IRGSP, International Rice Genome sequencing Project (2005) The map-based sequence of the rice genome. Nature 436:793–800
Joseph M, Gopalakrishnan S, Sharma RK, Singh VP, Singh AK, Singh NK, Mohapatra T (2004) Combining bacterial blight resistance and Basmati quality characteristics by phenotypic and molecular marker-assisted selection in rice. Mol Breed 13:377–387
Kearsey MJ, Pooni HS (1996) The genetical analysis of quantitative traits. Chapman & Hall, London
Khanh TD, Linh TH, Xuan TD (2013) Rapid and high-precision marker assisted backcrossing to introgress the SUB1 QTL into the Vietnamese elite rice variety. J Plant Breed Crop Sci 5:26–33
Lewis RS, Kernodle S (2009) A method for accelerated trait conversion in plant breeding. Theor Appl Genet 118:1499–1508
Linh LH, Linh TH, Xuan TD, Ham LH, Ismail AM, Khanh TD (2012) Molecular breeding to improve salt tolerance of rice (Oryza sativa L.) in the Red River Delta of Vietnam. Int J Plant Genomics 2012:949038. doi:10.1155/2012/949038
Mackill DJ (2006) Breeding for resistance to abiotic stresses in rice: the value of quantitative trait loci. In: Lamkey KR, Lee M (eds) Plant breeding: the Arnel R. Hallauer International Symposium. Blackwell Publishing Ltd, Oxford, pp 201–212
Mackill DJ, Amante MM, Vergara BS, Sarkarung S (1993) Improved semidwarf rice lines with tolerance to submergence of seedlings. Crop Sci 33:749–753
Mackill DJ, Coffman WR, Garrity DP (1996) Rainfed lowland rice improvement. Int Rice Res Inst, Manila
Mackill DJ, Collard BCY, Neeraja CN, Rodriguez RM, Heuer S, Ismail AM (2007) QTLs in rice breeding: examples for abiotic stresses. In: Brar DS, Mackill DJ, Hardy B (eds) International rice genetics symposium, Manila (Philippines), 19–23 Nov 2005, 2007. International Rice Research Institute (IRRI), pp 155–167
Melchinger A (1990) Use of molecular markers in breeding for oligogenic disease resistance. Plant Breed 104:1–19
Miah G, Rafii MY, Ismail MR, Puteh AB, Rahim HA, Latif MA (2015) Recurrent parent genome recovery analysis in a marker-assisted backcrossing program of rice (Oryza sativa L.). C R Biol 338:83–94. doi:10.1016/j.crvi.2014.11.003
Nandi S, Subudhi P, Senadhira D, Manigbas N, Sen-Mandi S, Huang N (1997) Mapping QTLs for submergence tolerance in rice by AFLP analysis and selective genotyping. Mol Gen Genet 255:1–8
Neeraja CN, Maghirang-Rodriguez R, Pamplona A, Heuer S, Collard BCY, Septiningsih EM, Vergara G, Sanchez D, Xu K, Ismail AM, Mackill DJ (2007) A marker-assisted backcross approach for developing submergence-tolerant rice cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 115:767–776
Prigge V, Maurer HP, Mackill DJ, Melchinger AE, Frisch M (2008) Comparison of the observed with the simulated distributions of the parental genome contribution in two marker-assisted backcross programs in rice. Theor Appl Genet 116:739–744
Ribaut J-M, Jiang C, Hoisington D (2002) Simulation experiments on efficiencies of gene introgression by backcrossing. Crop Sci 42:557–565
Semagn K, Bjørnstad Å, Ndjiondjop M (2006) Progress and prospects of marker assisted backcrossing as a tool in crop breeding programs. Afr J Biotechnol 5:2588–2603
Septiningsih EM, Pamplona AM, Sanchez DL, Neeraja CN, Vergara GV, Heuer S, Ismail AM, Mackill DJ (2009) Development of submergence-tolerant rice cultivars: the Sub1 locus and beyond. Ann Bot 103:151–160
Singh VK, Singh A, Singh SP, Ellur RK, Choudhary V, Sarkel S, Singh D, Gopala Krishnan S, Vinod KK, Singh UD, Rathore R, Prashanthi SK, Agrawal PK, Bhatt JC, Mohapatra T, Prabhu KV, Singh AK (2012) Incorporation of blast resistance into “PRR78”, an elite Basmati rice restorer line, through marker assisted backcross breeding. Field Crops Res 128:8–16
Singh VK, Singh A, Singh SP, Ellur RK, Singh D, Gopala Krishnan S, Bhowmick PK, Nagarajan M, Vinod KK, Singh UD, Mohapatra T, Prabhu KV, Singh AK (2013) Marker-assisted simultaneous but stepwise backcross breeding for pyramiding blast resistance genes Piz5 and Pi54 into an elite Basmati rice restorer line ‘PRR78’. Plant Breed 132:486–495
Sundaram RM, Vishnupriya MR, Biradar SK, Laha GS, Reddy GA, Rani NS, Sarma NP, Sonti RV (2008) Marker assisted introgression of bacterial blight resistance in Samba Mahsuri, an elite indica rice variety. Euphytica 160:411–422
Sundaram RM, Vishnupriya MR, Laha GS, Rani NS, Rao PS, Balachandran SM, Reddy GA, Sarma NP, Sonti RV (2009) Introduction of bacterial blight resistance into Triguna, a high yielding, mid-early duration rice variety. Biotechnol J 4:400–407
Takeuchi Y, Ebitani T, Yamamoto T, Sato H, Ohta H, Hirabayashi H, Kato H, Ando I, Nemoto H, Imbe T (2006) Development of isogenic lines of rice cultivar Koshihikari with early and late heading by marker-assisted selection. Breed Sci 56:405–413
Tanksley SD (1983) Molecular markers in plant breeding. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1:3–8
Tanksley SD, Young ND, Patersonm AH, Bonierbale MW (1989) RFLP mapping in plant breeding: new tools for an old science. Nat Biotechnol 7:257–264
Visscher PM (1996) Proportion of the variation in genetic composition in backcrossing programs explained by genetic markers. J Hered 87:136–138
Visscher PM, Haley CS, Thompson R (1996) Marker-assisted introgression in backcross breeding programs. Genetics 144:1923–1932
Xu K, Mackill DJ (1996) A major locus for submergence tolerance mapped on rice chromosome 9. Mol Breed 2:219–224
Xu K, Xu X, Ronald P, Mackill D (2000) A high-resolution linkage map of the vicinity of the rice submergence tolerance locus Sub1. Mol Gen Genet 263:681–689
Xu K, Xu X, Fukao T, Canlas P, Maghirang-Rodriguez R, Heuer S, Ismail AM, Bailey-Serres J, Ronald PC, Mackill DJ (2006) Sub1A is an ethylene-response-factor-like gene that confers submergence tolerance to rice. Nature 442:705–708
Ye G, Smith KF (2008) Marker-assisted gene pyramiding for inbred line development: basic principles and practical guidelines. Int J Plant Breed 2:1–10
Young N, Tanksley S (1989) Restriction fragment length polymorphism maps and the concept of graphical genotypes. Theor Appl Genet 77:95–101
Zhou P, Tan Y, He Y, Xu C, Zhang Q (2003) Simultaneous improvement for four quality traits of Zhenshan 97, an elite parent of hybrid rice, by molecular marker-assisted selection. Theor Appl Genet 106:326–331
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Long-term Research Grant Scheme (LRGS), Food Security Project, Ministry of Higher Education, Malaysia, for the financial support on rice breeding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, F., Rafii, M.Y., Ismail, M.R. et al. Recurrent parent genome recovery in different populations with the introgression of Sub1 gene from a cross between MR219 and Swarna-Sub1 . Euphytica 207, 605–618 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1554-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1554-5