Abstract
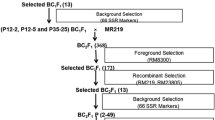
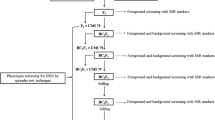
Flooding is one of the major hazards of rice production for the rainfed lowland rice ecosystem, and tolerant cultivars are urgently needed to help protect farmers from submergence damage. A quick and efficient strategy was implemented to introgress SUB1, a major QTL for submergence tolerance, into a rainfed lowland mega variety BR11 of Bangladesh by only two backcrosses and one selfing generation. In marker-assisted backcrossing (MABC), one tightly-linked simple sequence repeat (SSR) and two gene-based markers, four flanking SSR and 116 background SSR markers were used for foreground, recombinant and background selection, respectively, in backcrosses between a SUB1 donor IR40931-33-1-3-2 and BR11. BR11-Sub1, identified in a BC2F2 plant, possessed BR11 type SSR alleles on all fragments analyzed except the SUB1 QTL. The introgression size in BR11-Sub1 was 800 Kb indicating approximately 99.8% identity to BR11. BR11-Sub1 along with other introgression lines showed submergence tolerance similar to the tolerant parent. Yield, yield-component parameters and grain physico-chemical properties showed successful recovery of the BR11 traits in BR11-Sub1, with yield potential ranging from 5.2 to 5.6 t/ha, not significantly different from the recurrent parent mega variety BR11. Producing a large number (~1000) of backcross F1 plants was considered essential to achieve recombination on both sides of the gene, limiting linkage drag with only two backcrosses. A large number of background markers ensured proper recovery of the recurrent parent genome in the BC2F2 generation. The study demonstrates a rapid and highly precise strategy to introgress a major QTL by BC2F2 generation into a modern rice variety using an unadapted donor. The variety can replace BR11 on more than 2 million of ha in Bangladesh and provide major increases in rice production.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
BRRI (2007) BRRI annual internal review 2004–2005. Agricultural Economics Division, Bangladesh Rice Research Institute, Gazipur-1701, Bangladesh
Chen S, Lin XH, Xu CG, Zhang QF (2000) Improvement of bacterial blight resistance of ‘Minghui 63’, an elite restorer line of hybrid rice, by molecular marker-assisted selection. Crop Sci 40:239–244
Chen MS, Presting G, Barbazuk WB, Goicoechea JL, Blackmon B, Fang FC, Kim H, Frisch D, Yu YS, Sun SH, Higingbottom S, Phimphilai J, Phimphilai D, Thurmond S, Gaudette B, Li P, Liu JD, Hatfield J, Main D, Farrar K, Henderson C, Barnett L, Costa R, Williams B, Walser S, Atkins M, Hall C, Budiman MA, Tomkins JP, Luo MZ, Bancroft I, Salse J, Regad F, Mohapatra T, Singh NK, Tyagi AK, Soderlund C, Dean RA, Wing RA (2002) An integrated physical and genetic map of the rice genome. Plant Cell 14:537–545
Collard BCY, Mackill DJ (2008) Marker-assisted selection: an approach for precision plant breeding in the 21st century. Phil Trans Royal Soc B Rev 363:557–572
Collard BCY, Cruz CMV, McNally KL, Virk PS, Mackill DJ (2008a) Rice molecular breeding laboratories in the genomics era: current status and future considerations. Int J Plant Genomics 2008: Article ID 524847, 25 pp
Collard BCY, Iftekharuddaula KM, Thomson MJ, Pamplona AM, Mackill DJ (2008b) An electronic manual on marker assisted backcrossing in rice: theory and applications, 1st edn. GCP Wiki, International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philippines. http://mcclintock.generationcp.org/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=92&Itemid=114
HilleRisLambers D, Vergara BS (1982) Summary results of an international collaboration on screening methods for flood tolerance. In: Proceedings of the 1981 international deepwater rice workshop. Int. Rice Res. Inst., Los Baños, Philippines, pp 347–353
Hospital F (2001) Size of donor chromosome segments around introgressed loci and reduction of linkage drag in marker-assisted backcross programs. Genetics 158:1363–1379
Hospital F, Charcosset A (1997) Marker-assisted introgression of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 147:1469–1485
Hospital F, Chevalet C, Mulsant P (1992) Using markers in gene introgression breeding programs. Genetics 132:1199–1210
Hospital F, Moreau L, Lacoudre F, Charcosset A, Gallais A (1997) More on the efficiency of marker-assisted selection. Theor Appl Genet 95:1181–1189
IRGSP (2005) The map-based sequence of the rice genome. Nature 436:793–800
IRRI (2002) Standard evaluation system for rice. Int. Rice Res. Inst, Los Baños, Philippines
Kearsey MJ, Pooni HS (1996) The genetical analysis of quantitative traits. Stanley Thornes (Publishers) Ltd., Wiltshire
Mackill DJ (1986) Varietal improvement for rainfed lowland rice in South and Southeast Asia: results of a survey. Progress in rainfed lowland rice. Int. Rice Res. Inst, Los Baños, Philippines, pp 115–144
Mackill DJ (2006) Breeding for resistance to abiotic stresses in rice: the value of quantitative trait loci. In: Lamkey KR, Lee M (eds) Plant breeding: The Arnel R Hallauer international symposium. Blackwell Publishes, Ames, IA, pp 201–212
Mackill DJ, Amante MM, Vergara BS, Sarkarung S (1993) Improved semidwarf rice lines with tolerance to submergence of seedlings. Crop Sci 33:749–753
McCouch SR, Teytelman L, Xu Y, Lobos KB, Clare K, Walton M, Fu B, Maghirang R, Li Z, Zing Y, Zhang Q, Kono I, Yano M, Fjellstrom R, DeClerck G, Schneider D, Cartinhour S, Ware D, Stein L (2002) Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L.). DNA Res 9:199–207
Mohanty HK, Chaudhary RC (1986) Breeding for submergence tolerance in rice in India. Progress in rainfed lowland rice. Int. Rice Res. Inst, Los Baños, Philippines, pp 191–200
Neeraja CN, Maghirang-Rodriguez R, Pamplona A, Heuer S, Collard BCY, Septiningsih EM, Vergara G, Sanchez D, Xu K, Ismail AM, Mackill DJ (2007) A marker-assisted backcross approach for developing submergence-tolerant rice cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 115:767–776
Septiningsih EM, Pamplona AM, Sanchez DL, Neeraja CN, Vergara GV, Heuer S, Ismail AM, Mackill DJ (2009) Development of submergence tolerant rice cultivars: the Sub1 locus and beyond. Ann Bot 103:151–160
Takeuchi Y, Ebitani T, Yamamoto T, Sato H, Ohta H, Hirabayashi H, Kato H, Ando I, Nemoto H, Imbe T, Yano M (2006) Development of isogenic lines of rice cultivar Koshihikari with early and late heading by marker-assisted selection. Breed Sci 56:405–413
Temnykh S, DeClerck G, Lukashova A, Lipovich L, Cartinhour S, McCouch S (2001) Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza sativa L.): frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential. Genome Res 11:1441–1452
Van Berloo R (2008) GGT 2.0: versatile software for visualization and analysis of genetic data. J Hered 99:232–236
Visscher PM, Haley CS, Thompson R (1996) Marker-assisted introgression in backcross breeding programs. Genetics 144:1923–1932
Xu K, Mackill DJ (1996) A major locus for submergence tolerance mapped on rice chromosome 9. Mol Breed 2:219–224
Xu K, Xu X, Ronald PC, Mackill DJ (2000) A high-resolution linkage map in the vicinity of the rice submergence tolerance locus Sub1. Mol Gen Genet 263:681–689
Xu KN, Deb R, Mackill DJ (2004) A microsatellite marker and a codominant PCR-based marker for marker-assisted selection of submergence tolerance in rice. Crop Sci 44:248–253
Xu K, Xia X, Fukao T, Canlas P, Maghirang-Rodriguez R, Heuer S, Ismail AM, Bailey-Serres J, Ronald PC, Mackill DJ (2006) Sub1A is an ethylene response factor-like gene that confers submergence tolerance to rice. Nature 442:705–708
Young ND, Tanksley SD (1989) RFLP analysis of the size of chromosomal segments retained around the tm-2 locus of tomato during backcross breeding. Theor Appl Genet 77:353–359
Zheng K, Subudhi PK, Domingo J, Magpantay G, Huang N (1995) Rapid DNA isolation for marker assisted selection in rice breeding. Rice Genet Newsl 12:255–258
Zhou PH, Tan YF, He YQ, Xu CG, Zhang Q (2003) Simultaneous improvement for four quality traits of Zhenshan 97, an elite parent of hybrid rice, by molecular marker-assisted selection. Theor Appl Genet 106:326–331
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iftekharuddaula, K.M., Newaz, M.A., Salam, M.A. et al. Rapid and high-precision marker assisted backcrossing to introgress the SUB1 QTL into BR11, the rainfed lowland rice mega variety of Bangladesh. Euphytica 178, 83–97 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-010-0272-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-010-0272-2